CMSC389L
Week 11
Databases + DynamoDB
Friday, April 13, 2018
Databases

Why Use a Database?
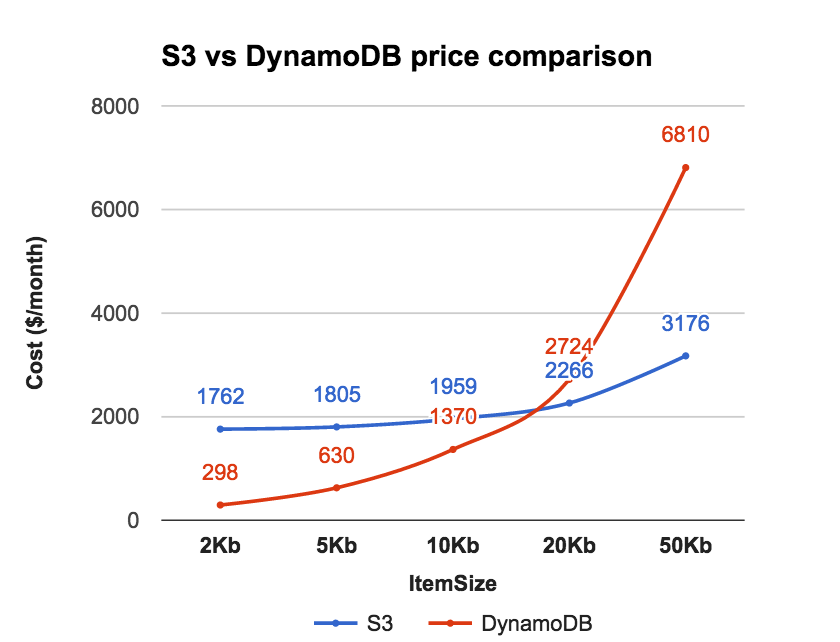
- For when you want to persist queryable data
- Usually small + frequently accessed data
- Game State
- Login Credentials
- A/B Test Configurations
- Product Catalogs
- Queryable File Metadata
- Messages
- ...
AWS Databases
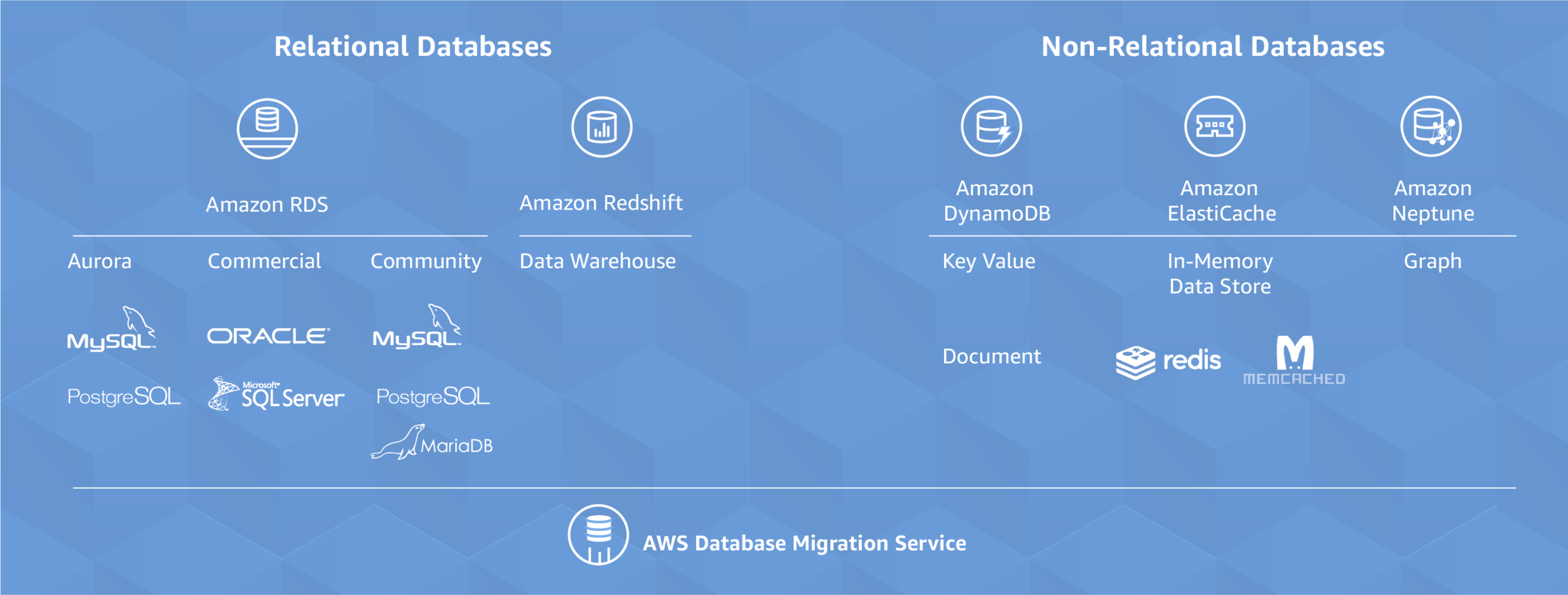
DynamoDB

DynamoDB Overview
"Amazon DynamoDB is a fast and flexible NoSQL database service for all applications that need consistent, single-digit millisecond latency at any scale. It is a fully managed cloud database and supports both document and key-value store models."
DynamoDB Today
-
Basics
- Tables + Items
- Attributes
- Primary Keys
- Indexing
- Querying
- Secondary Indexes
- API
- Provisioning Capacity
- Auto Scaling
-
Advanced
- Partitioning
- Read Consistency
- DAX
- WIF
- Streams
- Lambda Triggers
- Best Practices
Basics
- Let's create a music database
- It should store a list of all songs
- w/ song metadata, ratings, etc.
- List of songs -> Table
- Song -> Item
- Song metadata -> Attributes

Attributes
- Attributes are the key:value pairs in an item.
-
Values: 3 Types
-
Scalar: Number, String, Binary, Boolean, Null
- Number: Inventory Quantity
- String: Name or Timestamp
- Binary: Encrypted Text Messages
- Boolean: Released album or not
-
Nested: JSON (lists, maps)
- Example: Address
-
Set: Number/String/Binary Sets
- Example: Set of artists in a band
-
Scalar: Number, String, Binary, Boolean, Null

Attributes (cont.)
- Schema-less!
- Easy to add/remove attributes
- No need to complex schema transitions
- One exception: primary keys
Primary Key
-
Primary Key: An attribute that uniquely identifies an item in a table.
- An identifier (f.e., Alexa device ID)
- Or date (daily sales metrics, etc.)
- etc.
- Two types of primary key:
- Partition Key: single attribute
- Composite Partition Key: two attributes (partition key, sort key)
- All attributes must be scalar!

Partition Key
- Partition Key: Used in an internal hash function to distribute keys across partitions.
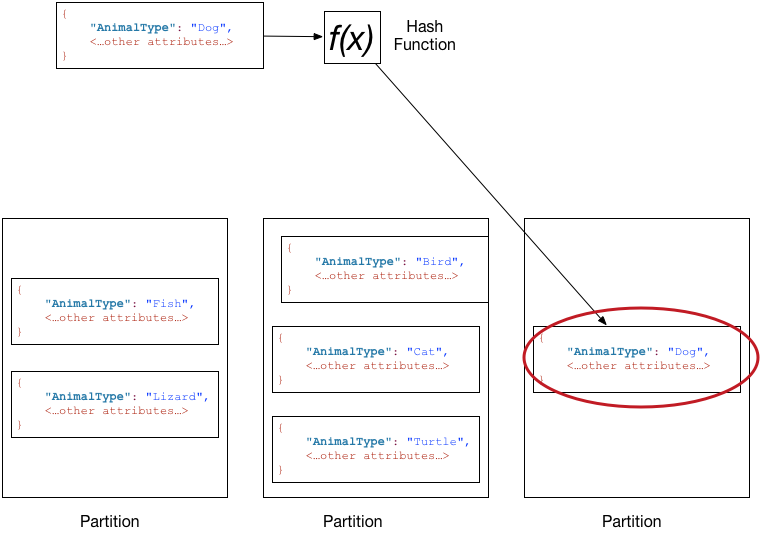
Composite Partition Key
-
Composite Partition Key: Adds a "sort key" which orders the items on a partition.
- Partition Key does not have to be unique.
- Important for range queries (where inventory_count > 0)

Querying
- What if you want all songs by an artist?
- Query by partition key
-
What if you want a specific song?
- Query by partition key, sort key
- What if you want all songs in an album?
- Can't do this!
- Need a secondary index.

Secondary Indexes
- Secondary Index: A copy of your DB with a different partition key and/or sort key.
- Queryable by the new partition/sort key
- Automatically maintained for you
- Two Types: Global and Local
-
Local: Different sort key,
same partition key- Shares resources with your base table
- Global: Different partition key [and optionally different sort key]
-
Local: Different sort key,
API
- Barebones CRUD API
-
PutItem: Create a new item in a table.
- Must specify primary key
- GetItem: Fetch a single item from a table by primary key.
- UpdateItem: Modify attributes in an item.
- DeleteItem: Remove a single item.
-
PutItem: Create a new item in a table.
- Batch methods:
- BatchGetItem, BatchWriteItem, ...
- Other:
- Query: Return multiple items based on a sort key query
-
Scan: Read all items in a table/index
- Can apply an attribute filter
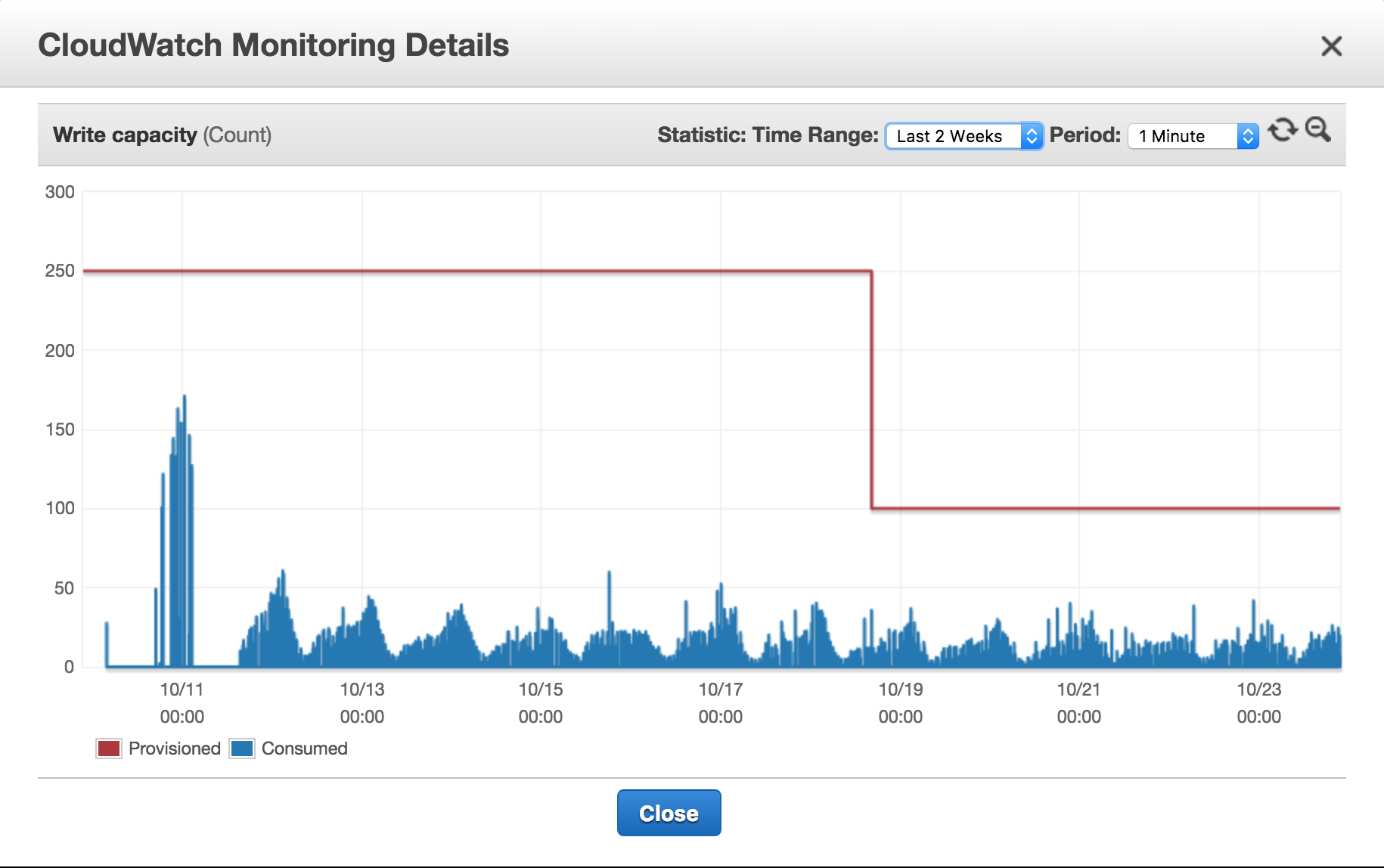
Provisioning Capacity
- DynamoDB requires that you provision capacity
-
Read Capacity Units
- 2 reads (<4KB) / second
-
Write Capacity Units
- 1 write (<1KB) / second
- Must provision for table AND indexes
-
Read Capacity Units
- DynamoDB applies throttling to requests
- SDKs built to handle this
-
Burst Capacity available
- Unused capacity from the previous 5m will be applied to bursty traffic
- Not reliable!
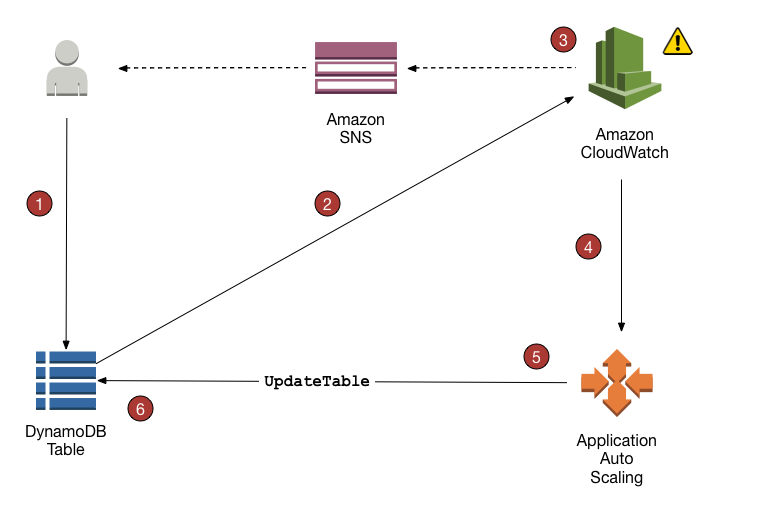
Scaling Capacity
- Manually
- Increase as many times as you need
- Decrease up to 9 times / day
- 4 / day + 1 per 4 hours
- Often inefficient!
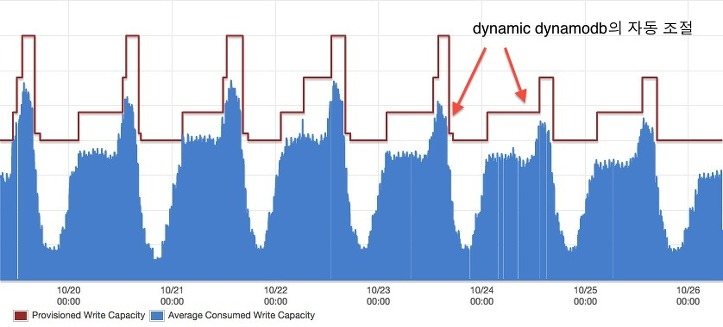
Scaling Capacity
- Automatically
- Just set auto-scaling range + target utilization
- Good for non-bursty traffic -- because of limits
DynamoDB Today
-
Basics
- Tables + Items
- Attributes
- Primary Keys
- Indexing
- Querying
- Secondary Indexes
- API
- Provisioning Capacity
- Auto Scaling
-
Advanced
- Partitioning
- Read Consistency
- DAX
- WIF
- Streams
- Lambda Triggers
- Best Practices
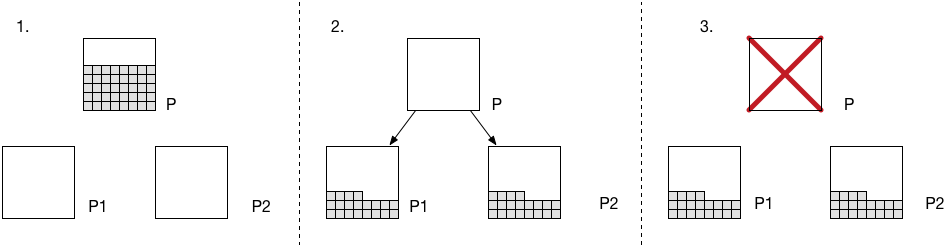
Partitioning
- Data is stored in partitions
- Each partition consists of multiple physical servers
- Effectively replicates across AZs
- Each server has a 10GB SSD
-
Occasionally requires partition splitting
- Done in the background -- with no downtime!
Consistency
-
Eventual Consistency
- Reads may not reflect most up-to-date result
- Recent write operations may not have fully propagated
- Asks a random server in the correct partition
- Usually consistent within <1s
- Reads may not reflect most up-to-date result
-
Strong Consistency
- Reads reflect all prior successful write operations
- Checks the majority of servers in the correct partition
- Uses 2x the RCUs
DAX
-
Latency
- DynamoDB: single-digit milliseconds
- DynamoDB Accelerator (DAX): microseconds
- 10x latency improvement
- DAX: in-memory cache
- Good for:
- Real-time bidding
- Multiplayer Gaming
- Stock Trading
- ...
- Good for:
WIF
-
Authentication
- Want to allow a client to directly access your database?
- Dangerous!
- Instead, restrict access via IAM roles
- Want to allow a client to directly access your database?
-
Web Identity Federation (WIF):
- Social login (Amazon, Facebook, Google)
- Provides temporary Amazon credentials to access DB from client
Streams
-
DynamoDB Stream: Chronologically ordered log of stream records.
-
Stream record: Defines a modification to an item
- New items, removed items, modified items, ...
-
Stream record: Defines a modification to an item
- Used for:
- Cross region replication
- Real-time metrics
- Notifications/Emails
- Important: 24 hour TTL
- Can configure a Lambda trigger on a DynamoDB stream
Streams (Example)
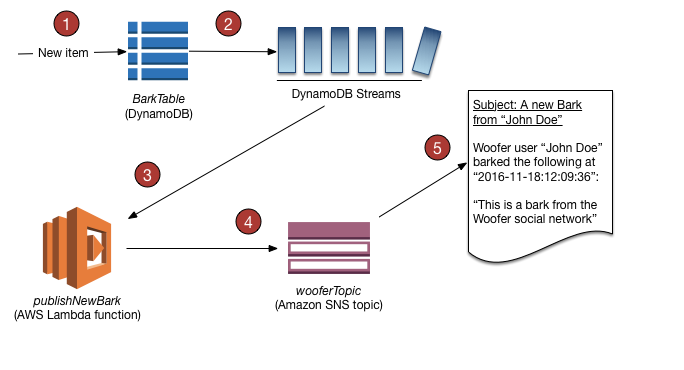
Best Practices
- Choose a good primary key!
- |Partition Key| >> |items|
- Use a cache (like ElasticCache)
-
Compress large values, such as messages or logs
- Store as binary
- Or use S3!
- Avoid indexes where possible
Best Practices
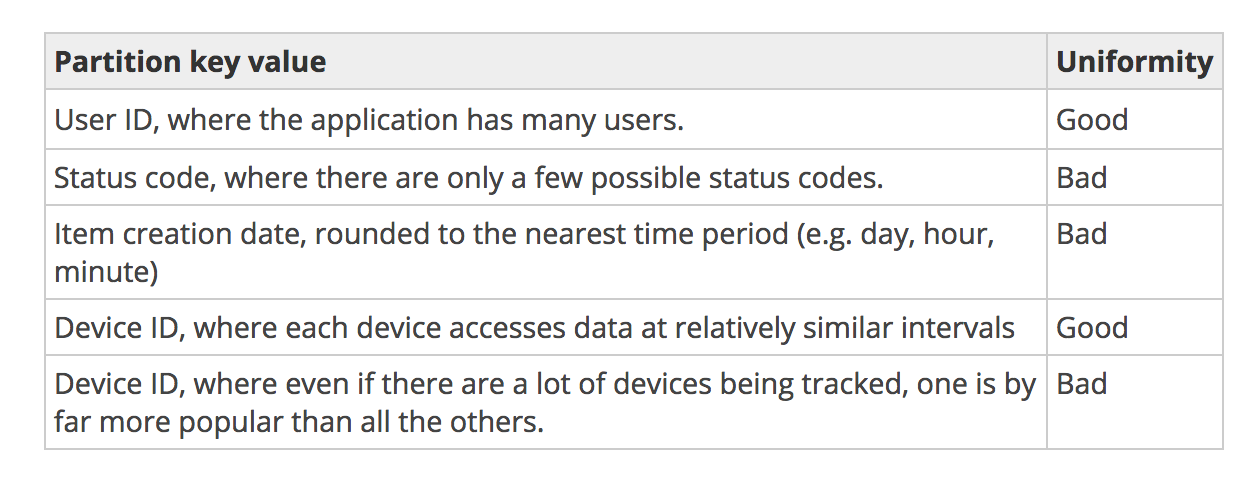
Pricing
- RCUs: $0.47 / WCU / month
- WCUs: $0.09 / RCU / month
- Data Transfer Out: $0.09 / GB
- Storage: $0.25 / GB-month
-
Stream Reads: $0.02 / 100k reads
- Lambda triggered reads are free!
Free Tier: 25 WCU, 25 RCU, 1GB out, 25GB storage, 2.5M stream reads
Wrapping Up
CMSC389L S18: DynamoDB
By Colin King
CMSC389L S18: DynamoDB
- 1,240



