cRIME PREVENTION MODEL
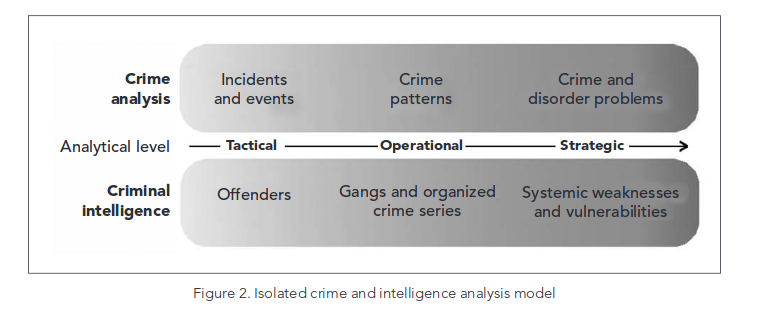
CRIME ANALYSIS
The qualitative and quantitative study of crime and law enforcement information in combination with socio-demographic and spatial factors to apprehend criminals, prevent crime, reduce disorder, and evaluate organizational procedures.
TYPES : Intelligence Analysis, Investigative Analysis, Tactical Analysis, Administrative Analysis
CRIME ANALYSIS
Strategic Analysis
The
study of crime and law enforcement information integrated with
socio-demographic and spatial factors to determine long term “patterns”
of activity, to assist in problem solving, as well as to research and
evaluate responses and procedures.
1) Assist in the identification and analysis of long-term problems such as drug activity or auto theft
2) Conduct studies to investigate or evaluate relevant responses and procedures
SARA problem solving approach
CRIME ANALYSIS
GEOGRAPHIC Space & CrIME
Ecologist theories : 19th century French sociologists and 20th century Chicago School
Placed-based theories : Cohen and Felson 1979, Cornish and Clarke (1986)
Behavioral : Becker (1968), Ehrlich (1973), Osorio (2013)
Urbanization theories: Glaezer and Sacerdote (1996)
Atheoretical models Marselli and Vannini (1997), Ehtorf and Spengler (2000), Luiz (2001)
Social Bio-Physics Bastin, Rollason, Hilton et. al (2007), Berestycki, Rodriguez, Ryzhik (2013)
sPATIAL eCONOMETRICS
Spatial effects
spatial heterogeneity
aspects of socioeconomic structure over space
and spatial dependence
socioeconomic interaction among agents
Classical Linear Regression Heteroskedasticity ass'n is violated
ESDA
Exploratory Spatial Data Analysis
- existence of spatial regimes
- preliminary spatial autocorrelation
- potential regressors
- spatial trends
- the influence of local outliers
- spatial clusters (“hot spots” and “cool spots”)
Precedes a good spatial econometric model
It is intended to discover spatial patterns in data and suggest hypotheses
ESDA
Distribution Mapping (choropleth map)
Summary Statistics (min, max, mean, sd, skew, kurt, q's)
Global spatial autocorrelation Tests --- Weight Matrix
Statistics: Z-statistic, Moran (1948) I and Geary (1954) C
Moran Scatterplot, each location's : value vs spatial lag
ESDA
Spatial Clustering Analysis : Local Indicator of Spatial Association
Further evidence of spatial regimes: Spatial ANOVA Regression, Include Spatial Lag
Outliers Analysis, Spatial Trends (Trend Surface Model)
LISA & ANOVA
Relevant identification of significant spatial clusters via pattern decomposition
Diagnostic of local instability (spatial outliers) in measures of global spatial association.
Via statistical tests
Multicollinearity k,
Normality J-B,
Heteroskedasticity K-B,
Spatial Dependence I, LM
"econo" BAckGRound
many many variables....
real consumption per
capita, unemployment rate, the share of employed in the service sector, social security
benefits, average monthly salary, the share of young male on the total population, the share of students that achieved the secondary and high school degree, the share of foreign residents, share of location firms, government expenditure, more proxies, etc
+
Causality Test : Granger and Newbold (1977)
Game Theory, Political, Development & Dynamic Economics
Crime Prediction & TIME DYNAMICS
UniMethods: Leading Indicators, Point Process Model, Polygon Grid/Raster GIS Methods,
Point Pattern Analysis: quadrat count and kernel estimation and Bayesian Networks
Areal Analysis
CROSS SECTION ----> PANEL ANALYSIS
Multivariate Methods --> VAR Models
overcome collinearity ---> BVAR Litterman (1980, 1986)
MAth MEat
Adaptative Machine Learning, Link Analysis, Genetic Programming
+
Biology: Epidemiological models
+
Physics: Reaction-Diffusion models
Biblio
Crime Mapping Laboratory, Police Foundation
Community Oriented Policing Services, US Dept of JNucleo de Economia Reg. y Urb U. Sao Paulo (NEREUS)
División de Desarrollo Social, CEPAL
Centre d’analyse et de mathématique sociales (CAMS)
FONDAZIONE ENI ENRICO MATTEI
& MANY MORE
EXTREME PROGRAMMING

Prevention Model
By csampez
Prevention Model
- 743


