
Little History and Introduction
Ruby is an interpreted, object-oriented, dynamically typed language created by Yukihiro Matsumoto in 1993.
In Ruby everything is an expression even the statements, it is a pure object orientation allows you to treat objects in a uniform and consistent way.
Ruby has features that are similar to those of Smalltalk, Perl, and Python. and these are scripting languages.
The Programming Model
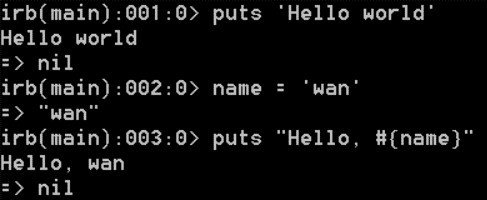
Everything returned a value. In fact, Every line of code in Ruby
returns something.
The Programming Model
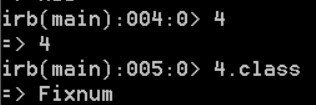
Ruby is a pure object-oriented language, everything in Ruby is an object even the number that in many other languages designate as primitives
Variables always hold references to objects. Every function is a method and methods are always called on an object.
Variable
Ruby has four types of variable scope, local, global, instance and class.
In addition, Ruby has one constant type.
Each variable type is declared by using a special character at the start of the variable name
| Name Begins With | Variable Scope |
|---|---|
| $ | A global variable |
| @ | An instance variable |
| [a-z] or _ | A local variable |
| [A-Z] | A constant |
| @@ | A class variable |
Decisions
Ruby offers conditional structures that are very common to many others modern languages
if conditional [then]
code...
[elsif conditional [then]
code...]...
[else
code...]
endDecisions
Ruby also provide unless Statement. It will execute the code if conditional is false. If the conditional is true, code specified in the else clause is executed.
unless conditional [then]
code
[else
code ]
endDecisions
you can use both block forms or one-line.
Example :
# one-line code
puts 'It is number 4' if x==4
puts 'It is not number 4' unless x==4
# block form
unless x==4
puts 'it is not number 4'
else
puts 'it is number 4'
endDecisions
In the condition, the values can be others than true and false as expressions
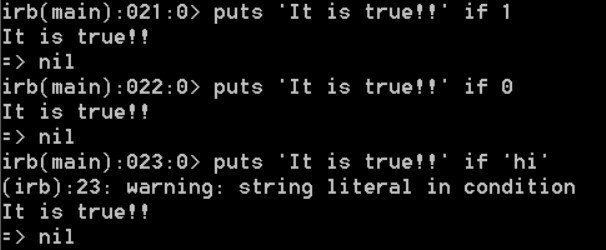
Even 0 is return true. Only false and nil that will return false.
Decisions
Logical operators:
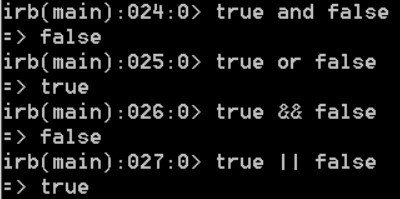
and (&&) is a logical and. or (||) is a logical or.
Arrays
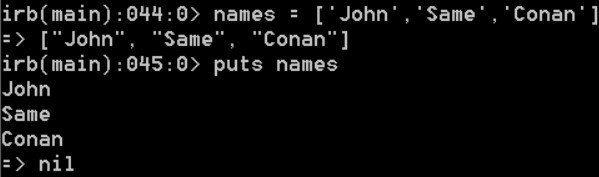
Ruby arrays are created similarly to those found in other dynamic
languages
Arrays
It is also a heterogeneous data type. Which mean it can store
elements of different types.
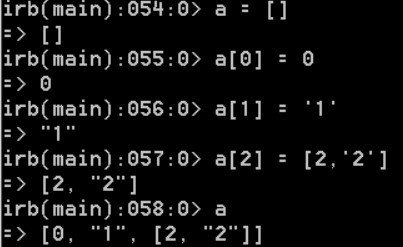
[] is a method on Array. This, [] and []= are just syntactic sugar that allow to access an array.
As you can see, names[-1] returned the first element from the end and names[-3] returned the third element from the end. These features called syntactic sugar.
Arrays
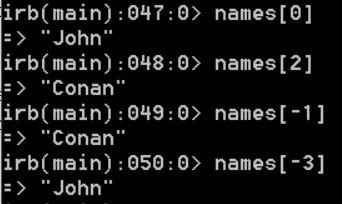
Ruby give you a lot of freedom to access the data in the array
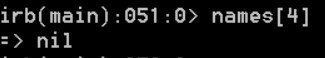
Most languages will get error if you attempt to access an array index that does not exist. But Ruby simply returns nil.
Arrays

Hashes
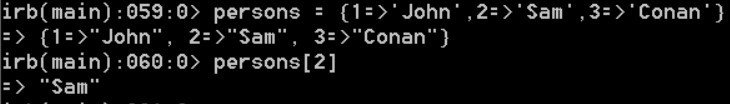
The label is the key, and the object is the value.
The keys are not limited to integer, the hash can have any arbitrary key. It is similar to Python’s dictionaries.
The collections are buckets for objects. In the hash bucket, every object has a label.
Code Blocks and Yield
Basically, a code block is a function without a name.
The code between braces {..} is called a code block
It able to do this because the number is an object.
Code Blocks and Yield
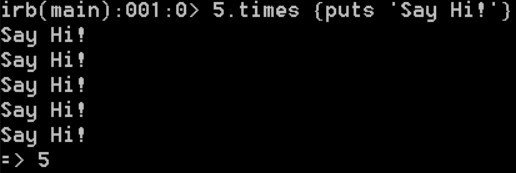
you can use code blocks with {/}
5.times do
puts 'Say Hi!'
end
5.times {
puts 'Say Hi'
}OR do/end
Duck Typing
Ruby is strongly typed and case sensitive. You will get error when the type did not match. Ruby makes these type checks at run time, not compile time.
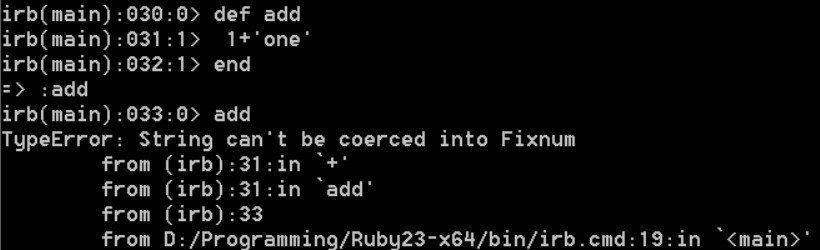
Ruby does not do type checking until you actually try to execute code. This concept is called dynamic typing.
Duck Typing
Duck typing:
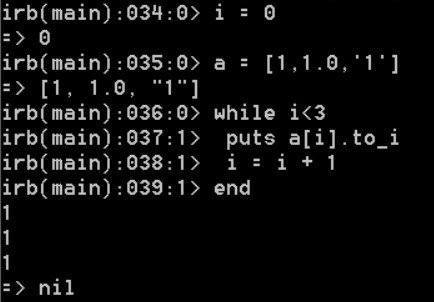
This is example of Duck typing, the first element of the array is an Integer, second is a Float and third is a String. The same code converts each to an integer via to_i. it doesn’t care what the type might be.
“If it walks like a duck and quacks like a duck, then it must be a duck.”
Functions
In ruby, you do not have to build a whole class to define a function
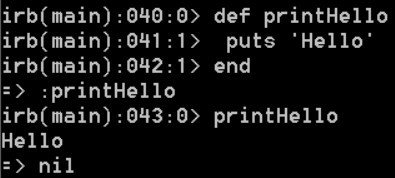
Every function returns something. If you do not specify an explicit return, the function will return the value of the last expression that’s processed before exiting.
Classes
Ruby supports inheritance. Ruby class can inherit from only one parent called a superclass
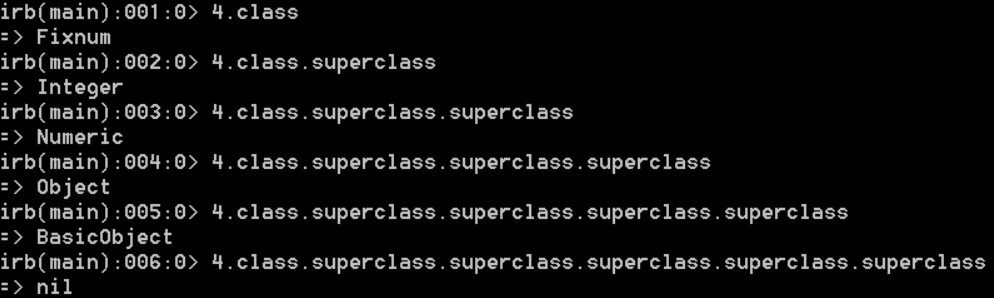
As you can see, the 4’s class is Fixnum, which inherits from Integer, Numeric, Object and BasicObject.
Classes
Ruby meta-model :
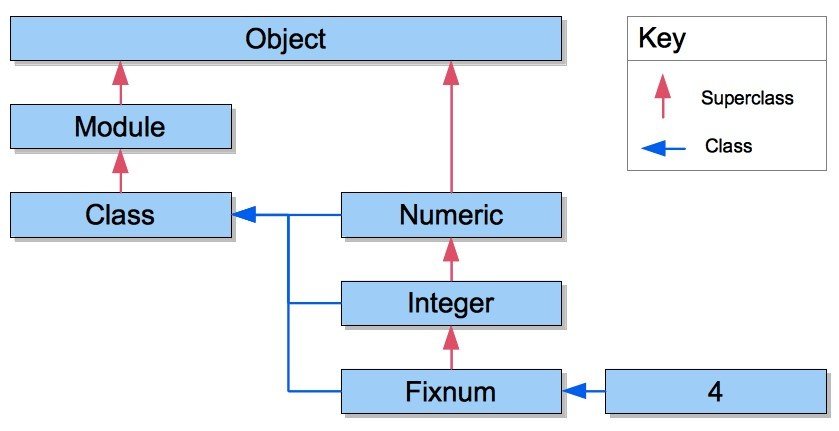
Everything in Ruby has a common ancestor “Object”
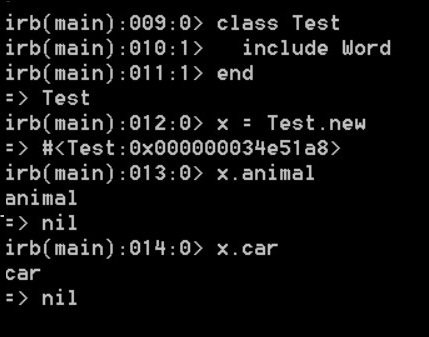
Mixin
Ruby use a module as a collection of functions and constants
module Word
def animal
puts 'animal'
end
def car
puts 'car'
end
end
When you include a module as part of a class, those behaviors and constants become part of the class
Ruby
By Cwan Yo
Ruby
- 238

