Emotional & Social Development in Infancy and Toddlerhood
Ch6 of textbook
Attatchment Theory
- Attachment - A long-term affectionate relationship
- Harlow (1959) - Rhesus monkey attachment study
- Preference of comfort over food

Ethics Q:
Paradox of
animal research
Theory of Attatchment
-
John Bowlby (1969)- theory rooted in psychoanalysis
- Infant attatchment is basis of future relationships
- Form "Internal working model" of expectations
- Preattachment Phase - 0 to 6wks
- Attatchment in the making - 6wk to ~7mo
- Clear-cut attachment- ~7mo to ~21 mo
- Formation of reciprocal relationship- onward

- Attachment - A long-term affectionate relationship
- Harlow (1959) - Rhesus monkey attachment study
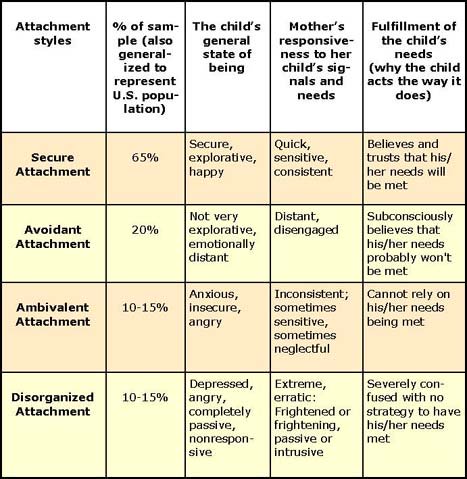
The Strange Situation
- Ainsworth (1978)- measurement of infant attachment
Initially, yield 4 types of Attachment:
• Secure
• Anxious/Avoidant
• Ambivalent/Resistant
• Disorganized/Disoriented




Attatchment Theory
- Focus on mothers, but Bowlby's theory allows more.
- Impact of SES
- Poverty and life stressors promote insecure attatchment
- Impact o Culture
- Individualistic (eg US) vs Collectivist (eg Japanese)
- Interactional synchrony- When a caregiver responds to infant signals in appropriate fashion ("a dance")


Big Moods
- Self-conscious emotions- around 1.5 - 3yrs old
- Shame
- Embarrassment
- Guilt
- Pride
- Envy
- Need to understand adult instructions on when/how to feel emotions
- Need a sense of "self"

Development of "Self"
- What is the "self" again? Is there such a thing as an individual?
-
self-recognition & self-awareness
- Mirror/rouge study (Lewis & Brooks-Gunn, 1979)
-
Empathy
- Understanding of "self" in others
- "What is it like to be a bat?" Thomas Nagel
- Categorical self


Self-regulation
- Self-control; self-regulation
- Delay of gratification – Marshmallow Test
-
Effortful control Rothbart (2003):
- capacity to voluntarily suppress a dominant response in order to execute a more adaptive response (executive functioning, inhibition of impulsivity)
- Role of prefrontal cortex (PFC)?

Structure of Temperament
- Thomas and Chess (1991) study
- Easy: 40%
- Good mood and quick to adapt. More social.
- Difficult: 10%
- Irregular routines and frequent crying
- Slow-to-warm-up: 15%
- low activity, somewhat negative
- Unclassified: 35%
- Easy: 40%
- Mix of Emotionality, Socialibility, and Activity level
- Stability is low in infancy and toddlerhood



deck
By cypurr
deck
- 143



