Late Adulthood
(Age 60+)
Physical Changes
- Life expectancy v. Healthy life expectancy
- Functional age vs chronological age


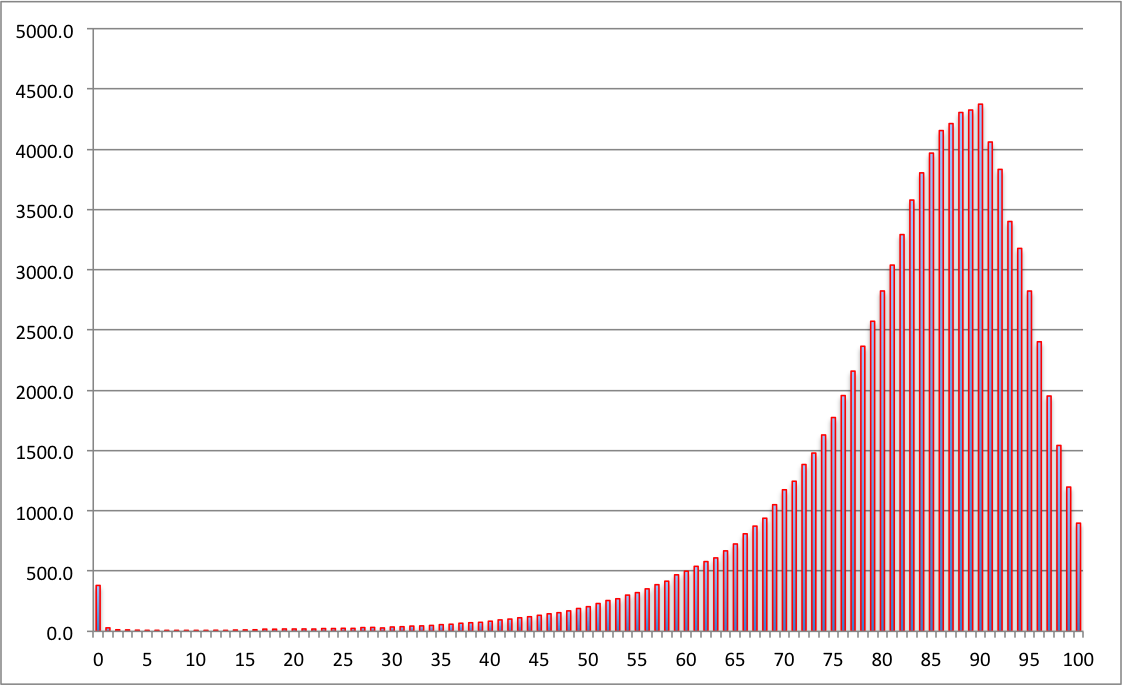
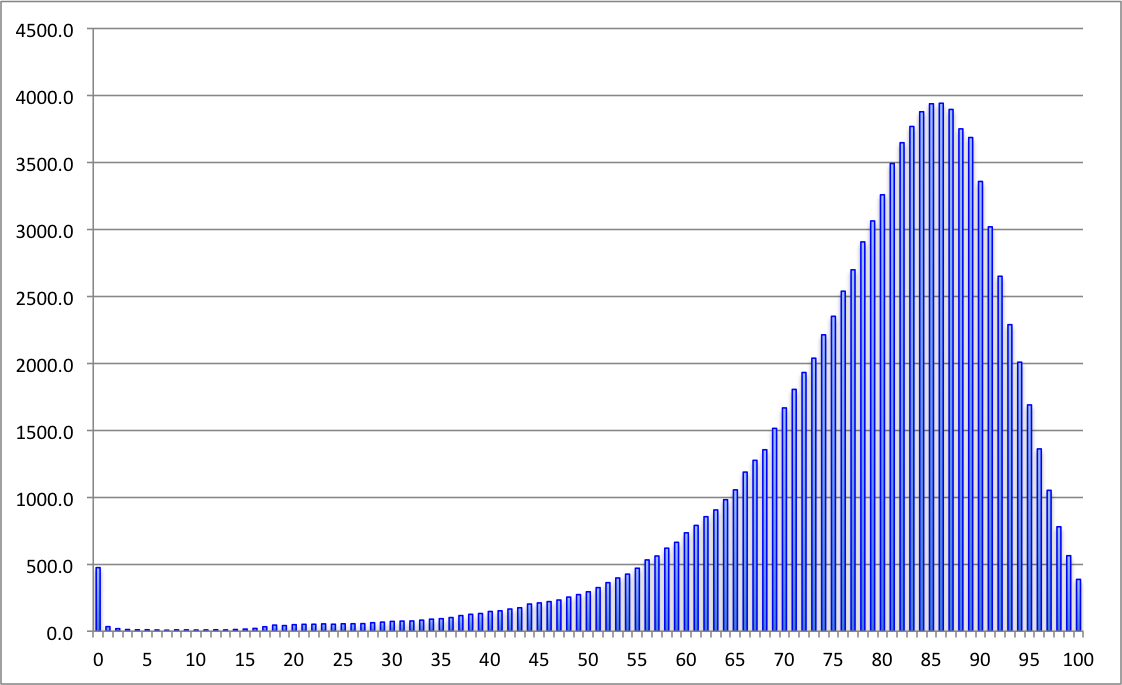
Healthy Life Expectancy


USA
Healthy Concerns

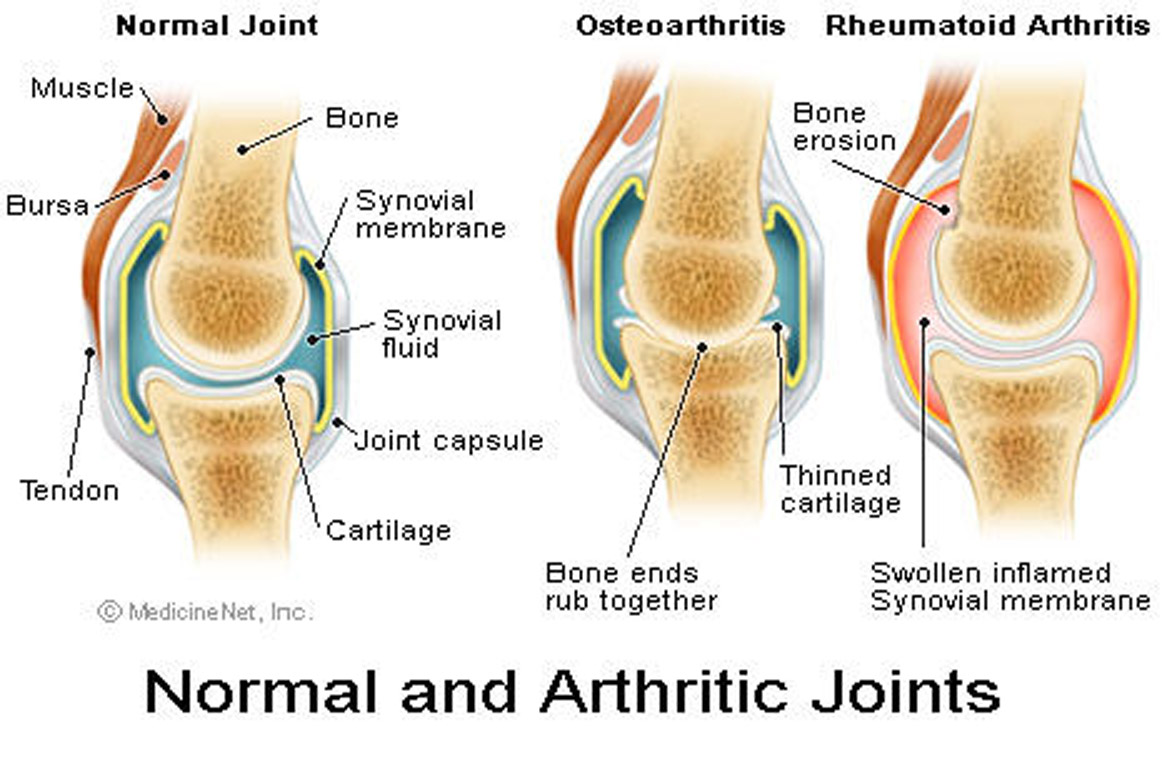
Physical Aging
- HLE associated with diet, exercise, lifestyle, genetics & healthcare
- Primary v Secondary aging
- Increase in autoimmune responses
- Decline in cardiovascular and respiratory systems
- Vision: Rise in cataracts
- Hearing: Continued decline
- Smell: Decreased number of receptors after 60yr
- Taste: reduced sensitivity to 5 basic tastes
- Touch: Declines after age 70

Implicite v. Explicite Memory
-
Implicit Memory (& bias)
- Evidence from research on priming
- Fragment Completion Task
- P S_ _ H O _ O G Y
- (Motsly raed enitre wrods)
-
Explicit (Declarative) Memory
- Episodic memory
- Semantic memory
- Associative memory
- Remote memory
- Prospective memory


Memory in Late Adulthood
- Implicit memory continues to strengthen in old age
- Steady decline in explicite memory-- mitigated by practice
- Prospective: event-based better than time-based
-
Dementia
- Alzheimer's Disease (AD): early-onset (5%; 40s/50s) , late-onset and familial (<1%, strong genetic component)
- Proteins known as Prions implicated?

Social Development
Erikson: Integrity v. Despair
- Ego Integrity: See life in larger context, sense of serenity and contentment
- Despair: Feel they have made many wrong decisions , wasted their life
-
Peck (1968): Three steps of ego integrity
- Ego differentiation—focus on finding ways outside of the career to find self-worth
- Body transcendence—focus on psychological strengths
- Ego transcendence—focus on a larger, more distant future
- Joan Erikson (1998): Gerotranscendence or "positive aging"
Social Development
- Emotional Expertise (Labouvie-Vief)
- more in touch with emotions and use them to reflect on life experiences
- display affect optimization
- retain a high level of cognitive-affective complexity
- Social Isolation and dependency
- Loss of spouses, family, friends etc
- increasing health issues and reduced mobility
- Health is strong predictor of well-being
- Retirement
- Nursing homes -- controversial
Social Development
- Disengagement theory
- mutual withdrawal
- Activity theory
- social barriers to engagement
- Continuity theory
- striving to maintain a consistent personal system
- Socioemotional selectivity theory
- selective interactions and social networks
Late Adulthood
By cypurr
Late Adulthood
- 208



