Infancy and Toddlerhood
Physical Growth
- Growth spurts
- up to 1/2 inch in a day
- Height doubles in 1 yr
- "Baby fat" for temperature regulation
-
Cephalocaudal trend
- head growth
-
Proximodistal trend
- center-out growth

Neurons
- 100-200 billion neurons in the brain, many with thousands of connections
- Connections called a synapse
- Communicate with neurotransmitters, e.g. dopamine.
- Glial cells responsible for fatty sheath known as myelin


Synaptic pruning
- Prenatal development creates more neurons than needed
- Overabundance of synapses
- Unused neurons dies to make space
- Unused synapses are pruned to be used later
- Improves connections --sensitive periods
- ~86 billion neurons as an adult




Molding a living sculpture
"Mature" brains
To keep in mind all semester:
- Debated, when is a brain "fully developed" (if ever?)
- End of motor development? (~16 yrs old)
- End of synaptic pruning? (mid-20s)
- End of myelination (~ age 32)
- End of plasticity?

Cerebral Cortex Regions

Text

Breast v. Bottle
Breastfeeding
- Correct balance of macro/micro nutrients
- protects against disease
- short-term health benefits
- Digestable
- Easier transition to solid food
- Less reliant on economic/political factors (e.g. more accessible, no contaminants)
- Not everyone can do it
Bottle feeding
- Can supplement breast milk with formula
- Same attachment and emotional adjustment
- little long-term impact (esp after 1st year)
- More freedom for parents
- More & less social stigma

Motor Development
Gross-motor Development
- Using large muscles, allows movement
- Crawling, standing, walking jumping, running
- Assessed by Physical Therapists (PT)
Fine-motor Development
- Small precise movements
- Milestones
- Ulnar Grasp (3-4mo)- whole hand
- Hand-to-hand Transfer (4-5mo)
- Pincer Grasp (8-11mo) - finger & thumb
- Assess with Occupational Therapists (OT)

Culture and Motor Development
Kipsigis of Kenya
- Children are almost always kept upright
- Children skip crawling, much faster gross motor development
In the west
- Move from tummy-time to laying on back (SIDS)
- Slower gross-motor development
Central Asia
- Gahvora craddle (Karasik, 2016)


Early Perception
Hearing
- Music (4-7mo)
- Speech (~5mo)
Statistical learning- listen for patterns, will learn meaning later
Vision
- 3 days: basic face perception
- 2-3 wks: Movement
- 2 mos: focus and color perception. complex face perception
- 3 mo: facial recognition
- 5 mo onward: facial expressions
- 7 mo: full depth perception
differentiation theory-- Infants look for stable reference points

Classical Conditioning
Remember Pavlov's Dogs?
- UCS +NS = UCR
- NS becomes CS
- CS = CR
Infants are receptive to classical conditioning
- Little Albert Experiment - John B. Watson (1920)



Operant Conditioning
Reinforcer
- Increases probability that behavior will occur again by
- presenting desirable stimulus
- removing unpleasant stimulus
Punishment
- Reduces probability that behavior will occur again by
- presenting unpleasant stimulus
- removing desirable stimulus


Theory of Attatchment
-
John Bowlby (1969)- theory rooted in psychoanalysis
- Infant attatchment is basis of future relationships
- Form "Internal working model" of expectations
- Preattachment Phase - 0 to 6wks
- Attatchment in the making - 6wk to ~7mo
- Clear-cut attachment- ~7mo to ~21 mo
- Formation of reciprocal relationship- onward

- Attachment - A long-term affectionate relationship
- Harlow (1959) - Rhesus monkey attachment study

The Strange Situation
- Ainsworth (1978)- measurement of infant attachment
Initially, yield 4 types of Attachment:
• Secure
• Anxious/Avoidant
• Ambivalent/Resistant
• Disorganized/Disoriented




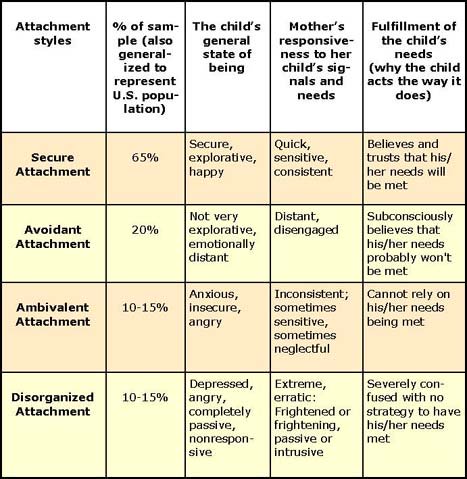
Attatchment Theory
- Impact of SES
- Poverty and life stressors promote insecure attatchment
- Impact o Culture
- Individualistic (eg US) vs Collectivist (eg Japanese)

Big Moods
- Self-conscious emotions- around 1.5 - 3yrs old
- Shame
- Embarrassment
- Guilt
- Pride
- Envy
- Need to understand adult instructions on when/how to feel emotions
- Need a sense of "self"
- "Categorical Self"

Development of "Self"
- What is the "self" again? Is there such a thing as an individual?
-
self-recognition & self-awareness
- Mirror/rouge study (Lewis & Brooks-Gunn, 1979)
- Self-control; self-regulation
- Delay of gratification – Stanford Marshmallow Experiment (Mischel 1970)


Structure of Temperament
- Thomas and Chess (1991) study
- Easy: 40%
- Good mood and quick to adapt. More social.
- Difficult: 10%
- Irregular routines and frequent crying
- Slow-to-warm-up: 15%
- low activity, somewhat negative
- Unclassified: 35%
- Easy: 40%
- Mix of Emotionality, Socialibility, and Activity level
- Stability is low in infancy and toddlerhood



Facial Expressions
- Still face Experiment (Tronick et al 1975)
- Infants connect facial expressions /w emotions, social building block
- Newborn babies imitate some expressions? Inconsistent findings
- A study by Meltzoff & Moore (1977)
- Mirror neurons- in primates


Physical Development in Infancy and Toddlerhood
By cypurr
Physical Development in Infancy and Toddlerhood
Textbook Ch 4
- 149



