Python
第二堂
Content
-
Review
-
List, Tuple, Set - Tuple
-
List, Tuple, Set - Set
-
List, Tuple, Set - Compare
-
Queue & Stack
-
String
-
Dictionary
Review
輸入&輸出
輸入:input( )
輸出:print( )
s = input("Type sth...")
#讀取整行直到換行print("Hello world")變數&型態
變數
資料型態
a = 1
a = 2
b = 3
c = a + b #5interger = 1
floatt = 1.1
string = "hello"
boolean = True
lst = [1, 2, 3]運算
| + | 加 |
| - | 減 |
| * | 乘 |
| / | 除 |
| // | 除 (向下取整) |
| % | 取餘數 |
| ** | 次方 |
List
lst = [1, 3, 4]
#索引
print(lst[0]) #1
print(lst[1:-1:1])
#新增
lst.append(5)
lst.insert(1, 2)
#刪除
lst.pop()
lst.remove(1)
del lst[2]
lst.clear()
#連接
lst1 = [1, 2]
lst2 = [3]
lst.extend(lst2)
lst1 += lst2
lst *= 2lst = [3, 2, 4]
#長度
print(len(lst)) #3
#順序
lst.sort()
lst.sort(reverse=True)
lst.reverse()
#最大/小值
print(max(lst)) #4
print(min(lst)) #2
#加總
print(sum(lst)) #9
#in or not in
print(1 in lst) #False
print(2 not in lst) #False
#位置/次數
print(lst.index(2)) #0
print(lst.count(1)) #0| append( ) | list 函式 | 無回傳值 |
| insert( ) | list 函式 | 無回傳值 |
| pop( ) | list 函式 | 回傳被移除值 |
| remove( ) | list 函式 | 無回傳值 |
| del | Python 內建 | 無回傳值 |
| clear( ) | list 函式 | 無回傳值 |
| extend( ) | list 函式 | 無回傳值 |
| len( ) | Python 內建 | 回傳長度 |
| sort( ) | list 函式 | 無回傳值 |
| reverse( ) | list 函式 | 無回傳值 |
| max( ) / min( ) | Python 內建 | 回傳最大 / 最小值 |
| sum( ) | Python 內建 | 回傳加總值 |
| in / not in | Python 內建 | 回傳 True / False |
| index( ) | list 函式 | 回傳 index |
| count( ) | list 函式 | 回傳出現次數 |
| int( ) / str( ) ... | Python 內建 | 回傳改變型態值 |
List, Tuple, Set
Tuple
Tuple
- 跟 list 很像,都是儲存資料的容器
- tuple 一旦建立,就不能更改裡面的內容
- tuple 使用小括號建立
- 若 tuple 裡只有一個元素,最後面需有逗號
lst = [3, "hello", 8, 1.1, 2]
tup = (1, 2, 3)
print(type(tup)) #<class 'tuple'>
print(tup[0]) #1
tup[0] = 2
#TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
tup2 = (1,)
tup3 = (1)
print(type(tup2), type(tup3)) #<class 'tuple'> <class 'int'>Methods
- 取值
- 負索引值
- len( )
- slice
- del
- + 號連結
- index( )
- count( )
- in / not in
- max( ), min( )
- sum( )
- * 重複
跟 List 一樣
tuple 函式
Methods
- 改變元素值
- append( )
- insert( )
- remove( )
- pop( )
- del t[ ]
- clear( )
- extend( )
- sort( )
- reverse( )
不能使用
排序:sorted( )
- 前面說過 tuple 是不能改變的,所以自然無法使用 sort( )
tup = (4, 2, 8, 1)
sortedTup = sorted(tup)
print(sortedTup, type(sortedTup))
#[1, 2, 4, 8] <class 'list'>sorted( ) 會回傳串列 (list)
- 要排序 tuple 的話要使用 sorted( )
Python 內建
sort ? sorted ?
前面說過 tuple 是不能改變的,所以自然無法使用 sort( )
那為什麼可以用 sorted( )?
先來看 Python 官方文件
list.sort( ) 方法只有定義在串列上,而
sorted( ) 函式可以接受任何可疊代物件
list.sort( ):原地排序串列並回傳 None
sorted( ):回傳一個新的串列
轉型:tuple( )
sorted( ):回傳一個新的串列
要怎麼把 list 轉為 tuple?
⭢ 使用 tuple( )
tup = (4, 2, 8, 1)
sortedTup = sorted(tup)
listToTuple = tuple(sortedTup)
print(listToTuple, type(listToTuple))
#(1, 2, 4, 8) <class 'tuple'>packing / unpacking
Python 允許元組出現在賦值運算子的左側,在這種情況下,元組中的變數會從賦值運算子右側的元組接收對應的值
#packing
t = 1, 2, 4
print(type(t)) #<class 'tuple'>
print(t) #(1, 2, 4)
#unpacking
a, b, c = t
print(a, b, c) #1 2 4序列拆解 (sequence unpacking),可運用在任何位在等號右邊的序列。
序列拆解要求等號左邊的變數數量必須與等號右邊的序列中的元素數量相同。
tuple 講完了
好水
So why choose tuple?
Why choose tuple?
跟之前這頁說過的原因一樣
tuple is immutable
因此運行速度會比 list 來的快
Practice
給定一個 tuple: (5, 8, 3),讓使用者輸入 3 個數字插入該 tuple 中,並將其排序,用 tuple 印出
tup = (5, 8, 3)
# 輸入數字並插入 tup
# 排序
# 印出tup = (5, 8, 3)
lst = list(tup)
a = int(input())
b = int(input())
c = int(input())
lst[3:6] = [a, b, c]
lst.sort()
print(tuple(lst))Practice
List, Tuple, Set
Set
Set
- 跟 list, tuple 很像,都是儲存資料的容器
- set 不會包含重複的資料,由字串、數字、布林值組成
- set 使用大括號建立
- set 裡的元素需要是不可變的 ( immutable )
- 建立空集合的方法是 set( )
set1 = set()
n_set1 = {}
set2 = {1, 2, 3, 3}
set3 = set((1, 2, 4, 5, 2))
print(type(set1), type(n_set1)) #<class 'set'> <class 'dict'>
print(set2) #{1, 2, 3}
print(set3) #{1, 2, 4, 5}
print(set2[0]) #TypeError: 'set' object is not subscriptableremove( )
刪除元素
a = {1, 2, 3, 4}
a.remove(2)
print(a) #{1, 3, 4}
a.remove(8) #KeyErrorset 函式
無回傳值
discard( )
刪除元素
若刪除不存在的元素不會報錯
a = {1, 2, 3, 4}
a.discard(2)
print(a) #{1, 3, 4}
a.discard(8)
print(a) #{1, 3, 4}set 函式
無回傳值
add( )
可以添加元素至 set 中
a = {1, 2, 3, 4}
a.add(2)
a.add(0)
print(a) #{0, 1, 2, 3, 4}set 函式
無回傳值
set( )
轉型成 set
lst = [1, 5, 2, 4, 5]
s = set(lst)
print(s) #{1, 2, 4, 5}
s = set()
s.add(2)
print(s) #{2}Python 內建
回傳一個 set
運算型態
交集、聯集、差集、對稱差集
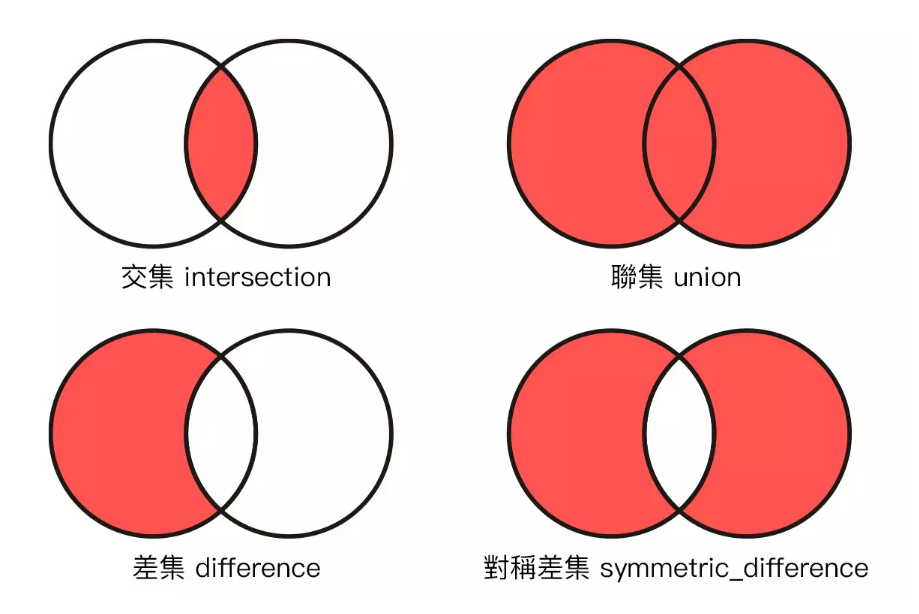
運算型態
| 集合 | 方法 | 運算子 |
|---|---|---|
| 交集 | intersection( ) | & |
| 聯集 | union( ) | | |
| 差集 | difference( ) | - |
| 對稱差集 | symmetric_difference( ) | ^ |
回傳一個 set
運算型態
a = {1, 3, 4, 8}
b = {2, 4, 5, 8}
#交集
print(a.intersection(b))
print(a & b) #{8, 4}
#聯集
print(a.union(b))
print(a | b) #{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 8}
#差集
print(a.difference(b))
print(a - b) #{1, 3}
#對稱差集
print(a.symmetric_difference(b))
print(a ^ b) #{1, 2, 3, 5}子集 & 超集
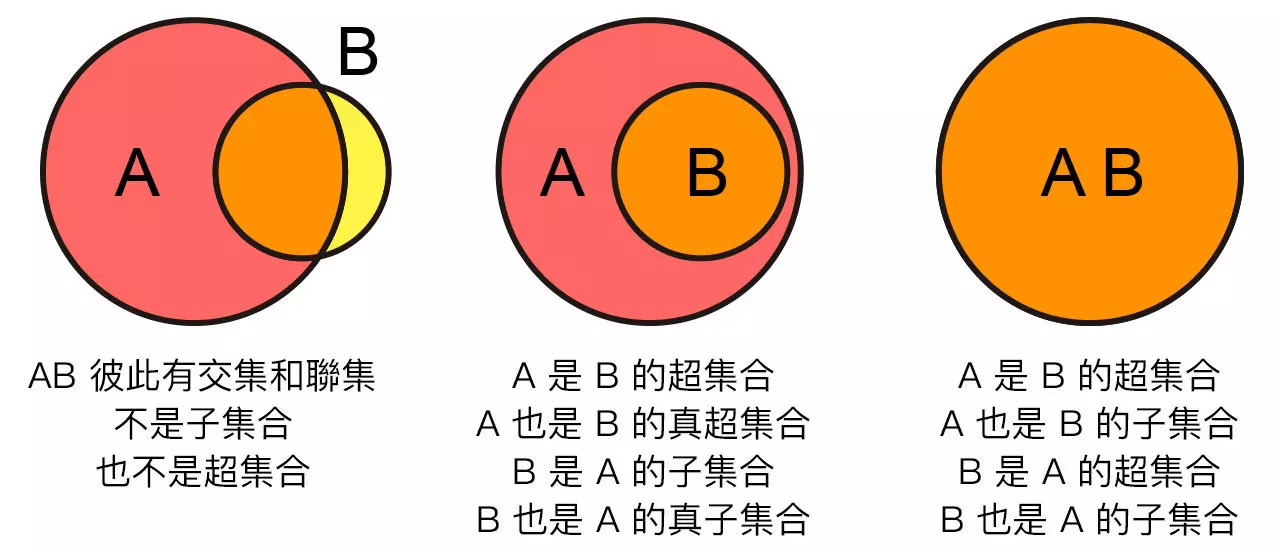
子集 & 超集
a = {1, 2, 3, 4}
b = {1, 4}
c = {1, 5, 6}
print(a <= a) #True a 是自己的子集合
print(a < a) #False a 不是自己的真子集
print(a >= b) #True b 是 a 的子集合
print(a > b) #True b 是 a 的真子集
print(a < c) #False a 跟 c 沒有集合關係a
b
c
子集 & 超集
a = {1, 2, 3, 4}
b = {1, 4}
c = {1, 5, 6}
print(b.issubset(a)) #True b 是 a 的子集合
print(a.issuperset(b)) #True a 是 b 的超集
print(c.issubset(a)) #False a 跟 c 沒有集合關係a
b
c
issubset( ) / issuperset( )
判斷是否為子集合或超集合
Practice
讓使用者輸入三個數字,放入一個集合中,並依序輸出此集合與 {1, 2, 5} 取交集、聯集、差集後的集合
輸入:
輸出:
Practice
set1 = set() #不能用 {}
set2 = {1, 2, 5}
a = int(input())
set1.add(a)
a = int(input())
set1.add(a)
a = int(input())
set1.add(a)
print("Intersection:", set1.intersection(set2))
print("Union:", set1.union(set2))
print("Difference:", set1.difference(set2))List, Tuple, Set
Compare
List, Tuple, Set
| list | 串列 |
| tuple | 元組 (數組) |
| set | 集合 |
| 可變 | 排序 | 索引 / 切片 | 相同元素 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| list | v | v | v | v |
| tuple | x | v | v | v |
| set | v | x | x | x |
Queue & Stack
Queue
- 一種資料結構
- First-In, First-Out ( FIFO ) 的輸入輸出順序
queue = []
#入隊 ( Enqueue )
queue.append('a')
queue.append('b')
queue.append('c')
print("Queue:", queue)
#出隊 ( Dequeue )
print(queue.pop(0))
print(queue.pop(0))
print(queue.pop(0))
print("Queue:", queue)隊列
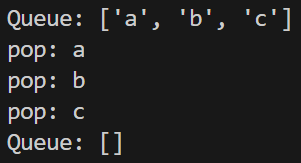
用 list 模擬 Queue
Queue Methods
| qsize( ) | 返回 Queue 大小 |
| empty( ) | 返回 Queue 是否為空 |
| full( ) | 返回 Queue 是否滿了 |
| get( ) | 移除並返回 Queue 元素 |
| put( item ) | 將 item 放入 Queue |
| maxsize | 設定 Queue 的上限 |
Queue
from queue import Queue
q = Queue(maxsize = 3)
print(q.qsize()) #0
q.put('a')
q.put('b')
q.put('c')
print("Full :",q.full()) #Full : True
print(q.get()) #a
print(q.get()) #b
print(q.get()) #c
print("Empty :", q.empty()) #Empty : True使用 Python 函式庫裡的 queue
來輕鬆達成 queue 的操作
Stack
- 一種資料結構
- Last-In, First-Out ( LIFO ) 的輸入輸出順序
堆疊
A
B
C
D
In
A
B
C
D
A
B
C
D
Out
Stack
堆疊
stack = []
#push
stack.append('a')
stack.append('b')
stack.append('c')
print("Stack", stack)
#pop
print(stack.pop())
print(stack.pop())
print(stack.pop())
print("Stack", stack)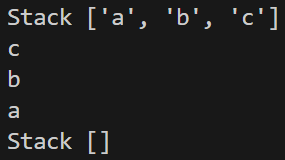
用 list 模擬 Stack
Stack Methods
| qsize( ) | 返回 Queue 大小 |
| empty( ) | 返回 Queue 是否為空 |
| full( ) | 返回 Queue 是否滿了 |
| get( ) | 移除並返回 Queue 元素 |
| put( item ) | 將 item 放入 Queue |
| maxsize | 設定 Queue 的上限 |
Stack
from queue import LifoQueue
st = LifoQueue(maxsize = 3)
print(st.qsize()) #0
st.put('a')
st.put('b')
st.put('c')
print("Full :", st.full()) #Full : True
print(st.get()) #c
print(st.get()) #b
print(st.get()) #a
print("Empty :", st.empty()) #Empty : True使用 Python 函式庫裡的 LifoQueue
來達成 stack 的操作
String
字串
String
- string ( 字串 ), 一種資料型態
- 用引號 " " 包住
- 可以用 list 的方式取得字元 ( char )
- 當字串被宣告後,無法更改裡面的字元
s = "Python"
print(type(s)) #<class 'str'>
print(s[1]) #y
print(s[-1]) #n
print(s[0:-1:2]) #Pto
s[0] = 'a'
#TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignmentlen( )
取得字串長度
s = "Python"
print(len(s)) #6
s = "Good morning"
print(len(s)) #12upper( )
將字串所有字元轉為大寫
s = "Hello"
print(s.upper()) #HELLO
s = "abcdefg1234"
print(s.upper()) #ABCDEFG1234string 函式
回傳字串
lower( )
將字串所有字元轉為小寫
s = "Hello"
print(s.lower()) #hello
s = "ABCDEFG1234"
print(s.lower()) #abcdefg1234string 函式
回傳字串
join( )
" " . join( lst )
lst = ["Python", "is", "great", "!"]
print(' '.join(lst)) #Python is great !
print('.'.join(lst)) #Python.is.great.!
print(' haha '.join(lst)) #Python haha is haha great haha !string 函式
回傳字串
將 list 裡的元素接在一起,變成一個字串,元素間以 " " 裡的內容隔開
split( )
s = "Python\t is\n great !"
print(s.split()) #['Python', 'is', 'great', '!']
s = "pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis"
print(s.split('n'))
#['p', 'eumo', 'oultramicroscopicsilicovolca', 'oco', 'iosis']
s = "a b c d"
print(s.split(' ', 1)) #['a', 'b c d']
print(s.split(' ', 2)) #['a', 'b', 'c d']
print(s.split(' ', 9)) #['a', 'b', 'c', 'd']string 函式
回傳串列
將一個字串以空格 ( 預設 ) 分開
split( " " ) :將字串以 " " 裡的內容分開
split( ,num ) :將字串分成 n+1 個段落
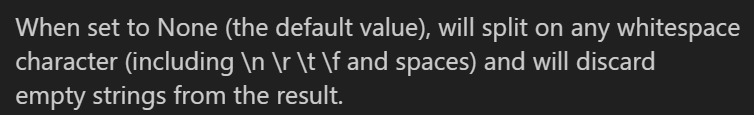
Practice
請將 "Python is really really good !" 更改成 "PYTHON+IS+REALLY+REALLY+GOOD"
Practice
s = "Python is really really good !"
s = s.upper()
lst = s.split()
a = '+'.join(lst[0:5])
print(a)有沒有更好的寫法?
find( )
s = "pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis"
print(s.find('n')) #1
print(s.find('co')) #19
print(s.find('abcd')) #-1string 函式
回傳第一個找到的字元位置
從字串中找尋特定字串
並回傳第一個找到的字元位置
rfind( )
s = "pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis"
print(s.rfind('n')) #39
print(s.rfind('co')) #37
print(s.rfind('abcd')) #-1string 函式
回傳第一個找到的字元位置
從字串的最後往前找尋特定字串
並回傳第一個找到的字元位置
count( )
s = "pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis"
print(s.count('n')) #4
print(s.count('co')) #3
print(s.count('abcd')) #0string 函式
回傳字串出現次數
計算一個字串中該字串出現過幾次
startswith( )
s = "abcdefg1234"
print(s.startswith('abc')) #True
print(s.startswith('123')) #False
print(s.startswith(('1', 'ab', 's'))) #Truestring 函式
回傳 True / False
回傳字串是否為該字串開頭
( "string", "string" ... ) 中只要有一個成立,就會回傳 True
endswith( )
s = "abcdefg1234"
print(s.endswith('abc')) #False
print(s.endswith('1234')) #True
print(s.endswith(('1', 'ab', '4'))) #Truestring 函式
回傳 True / False
回傳字串是否為該字串結尾
( "string", "string" ... ) 中只要有一個成立,就會回傳 True
Advanced
使用者輸入一個句子及分隔單字的一個字元,請將句子全部轉為小寫,並用指定分隔單字的字元連接單字
飯粒:
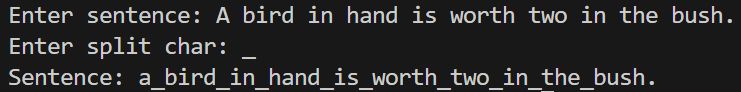
s = input("Enter sentence: ")
ch = input("Enter split char: ")
s = s.lower()
lst = s.split()
s = ch.join(lst[0:len(lst)])
print("Sentence:", s)Dictionary
字典
Dictionary
- 鍵 ( Key ) - 值 ( Value ) 對應的資料型態
- 用欄位的名稱索引
- 使用大括號 {} 創建
- value 可以是任何資料型態,但 key 必須是唯一且不可變
d = {'int':1, 'list':[1, 2], 'bool':True, 'str':'Hi'}
#key:value
print(type(d)) #<class 'dict'>
print(d['bool']) #True
print(d['int']) #1
print(d['float']) #KeyError: 'float'
d1 = {[1, 2]:1}
print(d1[[1, 2]]) #TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'新增值
字典可以新增值
dict[ key ] = value
EnToSpanish = {}
EnToSpanish['Hello'] = 'Hola'
EnToSpanish['Great'] = 'Excelente'
EnToSpanish['Wow'] = 'Guau'
print(EnToSpanish)
#{'Hello': 'Hola', 'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}len( )
回傳字典長度
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola', 'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}
print(len(EnToSpanish)) #3
d = {}
print(len(d)) #0keys( )
獲得字典所有的 key 值
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola', 'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}
print(EnToSpanish.keys()) #dict_keys(['Hello', 'Great', 'Wow'])
print(list(EnToSpanish.keys())) #['Hello', 'Great', 'Wow']dict 函式
回傳 dict_keys([...])
values( )
獲得字典所有的 value 值
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola', 'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}
print(EnToSpanish.values()) #dict_values(['Hola', 'Excelente', 'Guau']
print(list(EnToSpanish.values())) #['Hola', 'Excelente', 'Guau']dict 函式
回傳 dict_values([...])
items( )
將每一組 key-value 轉成一對 tuple
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
print(EnToSpanish.items())
#dict_items([('Hello', 'Hola'), ('Great', 'Excelente'), ('Wow', 'Guau')])
print(list(EnToSpanish.items()))
#[('Hello', 'Hola'), ('Great', 'Excelente'), ('Wow', 'Guau')]dict 函式
回傳 dict_items([...])
get( )
指定 key 取字典中的某個 value
若字典中沒有該 key,則回傳指定文字
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
print(EnToSpanish.get('Great', "Doesn't exist")) #Excelente
print(EnToSpanish.get('Hey', "Doesn't exist")) #Doesn't existdict 函式
回傳 value 或指定文字
copy( )
複製。
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
y = EnToSpanish.copy()
print(y) #{'Hello': 'Hola', 'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}dict 函式
回傳字典
update( )
將指定字典更新成另一字典的值
沒有重複的部分會保留
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
y = {'Great': 'Excelente', 'Hey':'ey'}
y.update(EnToSpanish)
print(y)
#{'Great': 'Excelente', 'Hey': 'ey', 'Hello': 'Hola', 'Wow': 'Guau'}dict 函式
無回傳值
del
刪除一個指定 key,連同 value 一起刪除
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
del EnToSpanish['Hello']
print(EnToSpanish)
#{'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}Python 內建
無回傳值
in / not in
回傳布林值,表示 key 是否在該字典中
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
print('Wow' in EnToSpanish) #True
print('Guau' in EnToSpanish) #False
print('Hello' not in EnToSpanish) #FalsePython 內建
回傳 True / False
Question
請問執行以下程式後輸出的結果:
x = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3, 'd':4}
y = {'a':3, 'b':4, 'e':0}
del x['d']
z = y.copy()
x.update(z)
print(x){'a': 3, 'b': 4, 'c': 3, 'e': 0}結束啦 :D
Python - 2
By d11231621莊智甯
Python - 2
- 321



