Python
第三堂
Content
-
Review
-
Dictionary
-
format
-
if - elif - else
-
for
-
while
Review
Tuple
tuple 是不可變的 ( immutable )
t = (1, 2, 3)
t[1] = 0 #TypeErrortuple methods
t = (1, 2, 3)
print(len(t)) #3
print(t.count(2)) #1
print(t.index(1)) #0
print(max(t)) #3
print(min(t)) #1
print(4 in t) #False
print(t * 2) #(1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3)
print(t + t) #(1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3)Set
set 裡的元素必須是不可變的
s = {1, 1.1, "string", (1, 2, 3)}
s1 = {[1, 2, 3]} #TypeErrorset methods
s = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
s.remove(2)
print(s) #{1, 3, 4, 5}
print(2 in s) #False
s.add(7)
print(s) #{1, 3, 4, 5, 7}
l = [1, 2, 3, 4, 4]
s1 = set(l)
print(s1) #{1, 2, 3, 4}Set
| 集合 | 方法 | 運算子 |
|---|---|---|
| 交集 | intersection( ) | & |
| 聯集 | union( ) | | |
| 差集 | difference( ) | - |
| 對稱差集 | symmetric_difference( ) | ^ |
Queue & Stack
- Queue: FIFO
- Stack: LIFO
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
1
2
3
3
1
2
3
1
2
Queue
from queue import Queue
q = Queue(maxsize = 3)
print(q.qsize()) #0
q.put('a')
q.put('b')
q.put('c')
print("Full :",q.full()) #Full : True
print(q.get()) #a
print(q.get()) #b
print(q.get()) #c
print("Empty :", q.empty()) #Empty : TrueStack
from queue import LifoQueue
st = LifoQueue(maxsize = 3)
print(st.qsize()) #0
st.put('a')
st.put('b')
st.put('c')
print("Full :", st.full()) #Full : True
print(st.get()) #c
print(st.get()) #b
print(st.get()) #a
print("Empty :", st.empty()) #Empty : TrueString
字串被宣告後無法改變字元
string methods
s = "string"
s[0] = 'd' #TypeErrors = "Hello World"
print(len(s)) #11
print(s.upper()) #HELLO WORLD
print(s.lower()) #hello world
l = s.split()
print(l) #['Hello', 'World']
print(', '.join(l)) #Hello, World
print(s.find('d')) #10
print(s.rfind('o')) #7
print(s.startswith('H')) #True
print(s.endswith('D')) #False
print(s.count('o')) #2Dictionary
字典
Dictionary
- 鍵 ( Key ) - 值 ( Value ) 對應的資料型態
- 用欄位的名稱索引
- 使用大括號 {} 創建
- value 可以是任何資料型態,但 key 必須是唯一且不可變
d = {'int':1, 'list':[1, 2], 'bool':True, 'str':'Hi'}
#key:value
print(type(d)) #<class 'dict'>
print(d['bool']) #True
print(d['int']) #1
print(d['float']) #KeyError: 'float'
d1 = {[1, 2]:1}
print(d1[[1, 2]]) #TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'新增值
字典可以新增值
dict[ key ] = value
EnToSpanish = {}
EnToSpanish['Hello'] = 'Hola'
EnToSpanish['Great'] = 'Excelente'
EnToSpanish['Wow'] = 'Guau'
print(EnToSpanish)
#{'Hello': 'Hola', 'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}len( )
回傳字典長度
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola', 'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}
print(len(EnToSpanish)) #3
d = {}
print(len(d)) #0keys( )
獲得字典所有的 key 值
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola', 'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}
print(EnToSpanish.keys()) #dict_keys(['Hello', 'Great', 'Wow'])
print(list(EnToSpanish.keys())) #['Hello', 'Great', 'Wow']dict 函式
回傳 dict_keys([...])
values( )
獲得字典所有的 value 值
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola', 'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}
print(EnToSpanish.values()) #dict_values(['Hola', 'Excelente', 'Guau']
print(list(EnToSpanish.values())) #['Hola', 'Excelente', 'Guau']dict 函式
回傳 dict_values([...])
items( )
將每一組 key-value 轉成一對 tuple
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
print(EnToSpanish.items())
#dict_items([('Hello', 'Hola'), ('Great', 'Excelente'), ('Wow', 'Guau')])
print(list(EnToSpanish.items()))
#[('Hello', 'Hola'), ('Great', 'Excelente'), ('Wow', 'Guau')]dict 函式
回傳 dict_items([...])
get( )
指定 key 取字典中的某個 value
若字典中沒有該 key,則回傳指定文字
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
print(EnToSpanish.get('Great', "Doesn't exist")) #Excelente
print(EnToSpanish.get('Hey', "Doesn't exist")) #Doesn't existdict 函式
回傳 value 或指定文字
copy( )
複製。
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
y = EnToSpanish.copy()
print(y) #{'Hello': 'Hola', 'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}dict 函式
回傳字典
update( )
將指定字典更新成另一字典的值
沒有重複的部分會保留
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
y = {'Great': 'Excelente', 'Hey':'ey'}
y.update(EnToSpanish)
print(y)
#{'Great': 'Excelente', 'Hey': 'ey', 'Hello': 'Hola', 'Wow': 'Guau'}dict 函式
無回傳值
del
刪除一個指定 key,連同 value 一起刪除
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
del EnToSpanish['Hello']
print(EnToSpanish)
#{'Great': 'Excelente', 'Wow': 'Guau'}Python 內建
無回傳值
in / not in
回傳布林值,表示 key 是否在該字典中
EnToSpanish = {'Hello': 'Hola',
'Great': 'Excelente',
'Wow': 'Guau'}
print('Wow' in EnToSpanish) #True
print('Guau' in EnToSpanish) #False
print('Hello' not in EnToSpanish) #FalsePython 內建
回傳 True / False
Question
請問執行以下程式後輸出的結果:
x = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3, 'd':4}
y = {'a':3, 'b':4, 'e':0}
del x['d']
z = y.copy()
x.update(z)
print(x){'a': 3, 'b': 4, 'c': 3, 'e': 0}Format
格式化
Format Method
可以將輸出內容格式化
a = "Hi, I am %s."
print(a % "pomelo") #Hi, I am pomelo.
b = "I have %d dollars."
print(b % 3.333) #I have 3 dollars.
c = "Now I have %f dollars."
print(c % 3.333) #Now I have 3.333000 dollars.
a = "Hello, I am {}, and I like to eat {}."
print(a.format("pomelo", "apple"))
#Hello, I am pomelo, and I like to eat apple.
b = "Hello, {:-^10s}."
print(b.format("world")) #Hello, --world---.
name = "pomelo"
age = 15.187
print(f"My name is {name}, I am {age} years old.")
#My name is pomelo, I am 15.187 years old.
print(f"Hello {name.upper()}, I am {age:-^.1f} years old.")
#Hello POMELO, I am 15.2 years old.%
用法:格式化字串 % 資料
a = "Hi, I am %s."
print(a % "pomelo") #Hi, I am pomelo.輸出結果會將資料插入格式化的位置
要格式化的字串
格式化位置要放入的資料
要格式化的位置
%
| 格式化字串 | 轉換型態 |
|---|---|
| %s | 字串 |
| %d | 十進位整數 |
| %x | 十六進位整數 |
| %o | 八進位整數 |
| %f | 十進位浮點數 |
| %e | 指數浮點數 |
| %g | 十進位或指數浮點數 |
| %% | 常值 % |
%
a = "Hello, %s."
print(a % "pomelo") #Hello, pomelo.
print("Hello, %s, %s, %s.", ("A", "B", "C"))
#Hello, A, B, C.
age = 18
print("%d years old." % age) #18 years old.
print("16: %x years old." % age) #16: 12 years old.
print("8: %o years old." % age) #8: 22 years old.
age = 180.804
print("float: %f years old." % age)
#float: 180.804000 years old.
print("e: %e years old." % age)
#e: 1.808040e+02 years old.
print("g: %g years old." % age)
#g: 180.804 years old.
print("%%: %d%% years old." % age)
# %: 180% years old.程式碼較不易讀
format( )
用法:格式化字串.format(資料)
a = "Hi, I am {}."
print(a.format("pomelo")) #Hi, I am pomelo.輸出結果會將資料插入{}
要格式化的字串
格式化位置要放入的資料
要格式化的位置
format( )
a = "Hello, {}, {}."
print(a.format("pomelo", "python"))
#Hi, I am pomelo, python.可以在字串裡填入多個{}
a = "Hello, {1}, {0}."
print(a.format("pomelo", "python"))
#Hi, I am python, pomelo.也可以在{}填入數字,表示填入資料的順序
format( )
a = "My name is {name}, I am {age} years old."
print(a.format(name="pomelo", age=18))
#My name is pomelo, I am 18 years old.{}裡可以填入具名引數
p = {'name': 'pomelo', 'age': 18}
a = "Hello, {name}, I am {age} years old."
print(a.format(**p))
#Hello, pomelo, I am 18 years old.
#**: unpacking p to name = 'pomelo', age = 18也可以在{}填入字典引數
format( )
| 格式化數值 | 說明 |
|---|---|
| : | 開頭需要加上冒號 |
| 不加東西、> | 靠右對齊 |
| < | 靠左對齊 |
| ^ | 至中對齊 |
| 填補字元 | 將不足最小寬度的空白以字元填齊 |
| 數字.數字 | 最小寬度.最大字元數 |
format( )
| 格式化字串 | 轉換型態 |
|---|---|
| :s | 字串 |
| :d | 十進位整數 |
| :x | 十六進位整數 |
| :o | 八進位整數 |
| :f | 十進位浮點數 |
| :e | 指數浮點數 |
| :g | 十進位或指數浮點數 |
format( )
print("Hello, {:10s}.".format('world'))
#Hello, world .
print("Hello, {:>10s}.".format('world'))
#Hello, world.
print("Hello, {:+<10s}.".format('world'))
#Hello, world+++++.
print("Hello, {:-^10s}.".format('world'))
#Hello, --world---.
print("Hello, {:-^6.3s}.".format('world'))
#Hello, -wor--.
print("I have {:.2f} dollars.".format(123.456))
#I have 123.46 dollars.
#.2f: 四捨五入至小數點後第 2 位程式碼較冗長
f-string
用法:f'{變數或運算式}'
name = 'pomelo'
print(f"Hi, I am {name}") #Hi, I am pomelo.輸出結果會將資料插入{}
以小寫 f 開頭
要格式化的位置
{}裡放入變數名稱
f-string
s = "world"
print(f"Hello, {'world':10s}.")
#Hello, world .
print(f"Hello, {s:>10s}.")
#Hello, world.
print(f"Hello, {s:+<10s}.")
#Hello, world+++++.
print(f"Hello, {s:-^10s}.")
#Hello, --world---.
print(f"Hello, {s:-^6.3s}.")
#Hello, -wor--.
dollar = 123.456
print(f"I have {dollar:.2f} dollars.")
#I have 123.46 dollars.與 format 類似
practice
讓使用者輸入名字及資產,印出
My name is 名字, I have 資產 dollars.
名字:長度 <= 3
資產:取到小數點後第三位
practice
name = input()
dollar = float(input())
print(f"My name is {name:.3s}, I have {dollar:.3f} dollars.")if - elif - else
條件判斷
if
- 如果...就...
- 用法:
if 條件: - 使用縮排
- 如果條件為
True 就執行程式 若為 False 則跳過判斷式
a = 1
b = 2
if a < b:
print("a is smaller than b")
if a > b:
print("a is bigger than b")
#a is smaller than bTrue, 因此執行 print
False, 不執行
if - else
- 如果條件為
True 就執行 if 程式 若為 False 則執行 else 程式
a = 1
b = 2
if a > b:
print("a is bigger than b")
else:
print("a is smaller than b")
#a is smaller than bFalse, 不執行
執行 else
if - elif - else
- 用法:
elif 條件: -
if&elif 針對各自對應的 True 結果執行 - 若前面的 if 或 elif 不成立且自己成立才執行
若為 False 則執行 else 程式
a = 1
b = 2
if a > b:
print("a is bigger than b")
elif a == b:
print("a is equal to b")
elif a < b:
print("a is smaller than b")
else:
print("Nothing happen")
#a is smaller than bFalse, 不執行
False, 不執行
True, 執行
結束條件判斷,不會跳到 else
pass
如果遇到「不想執行任何動作」的狀況,可以使用「pass」作為空式子,藉以保持語法的正確性
a = 1
b = 2
if a > b:
pass
else:
print("a < b")
#a < b巢狀判斷
一個判斷式裡,還有另外 n 個判斷式
a = 1
b = 0
if a > b:
print("a > b")
if a and b:
print("a and b == 1")
elif a or b:
print("a or b == 1")
else:
pass
else:
print("a < b")
#a > b
#a or b == 1第一層
第二層
and & or
| a = 0, b = 0 | a = 1, b = 0 | a = 1, b = 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a and b | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| a or b | 0 | 1 | 1 |
a = 1
b = 0
if a and b: #0 (False)
print("and")
elif a or b: #1 (True)
print("or")
#orand & or
a = 1
b = 0
c = 0
print(a or b and c) #1 => a or (b and c)
print(a and b or c) #0 => (a and b) or cand 比 or 優先判斷
and & or
print(1 and 2 and 3) #3 全部為 True, 回傳最右邊的值
print(0 and 1 and 2) #0 有 False, 回傳 0
print(1 or 2 or 3) #1 沒有 False, 回傳最左邊的值
print(0 or 1 or 2) #1 遇到 False, 所以回傳 1
print(1 and 2 or 0) #2
#-> (1 and 2) or 0
#-> 2 or 0
print(1 or 2 and 3) #1
#-> 1 or (2 and 3)
#-> 1 or 3
print(1 and 2 or 3 and 4 or 5) #2
#-> (1 and 2) or (3 and 4) or 5
#-> 2 or 4 or 5and & or 不同回傳值
三元運算式
變數 = 值1 if 條件 else 值2
a = 1
b = 2
bigger = 'a' if a > b else 'b'
print(bigger) #ba = 1
b = 2
if a > b:
bigger = 'a'
else:
bigger = 'b'
print(bigger) #b等同於
Practice
讓使用者輸入一個數字,判斷此數字除以三的餘數
若餘數為 0,輸出「大吉」
若餘數為 1,輸出「吉」
若餘數為 2,輸出「大凶」
Practice
n = int(input())
mod = n % 3
if mod == 0:
print("大吉")
elif mod == 1:
print("吉")
else:
print("大凶")for
迴圈
for
- 使用縮排
- 用法:
for 變數 in 可迭代物件: - for 迴圈會將可迭代的物件取出,賦值給變數
for i in 'abc':
print(i, end=" ") #a b c
for i in ['a', 'b', 'c']:
print(i,end=" ") #a b c
for i in {'a', 'b', 'c'}:
print(i, end=" ") #c b a
for i in {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3}:
print(i, end=" ") #a b cfor
range( )
range(初始值,結束值,間隔)
for i in range(0, 2):
print(i, end=" ") #0 1
for i in range(0, 10, 2):
print(i, end=" ") #0 2 4 6 8
for i in range(5, 2, -1):
print(i, end=" ") #5 4 3break, continue
break:跳出迴圈
continue:跳過此迴圈
for i in range(1, 10):
if i % 5 == 0:
continue
elif i == 7:
break
else:
print(i, end=" ")
#1 2 3 4 6enumerate( )
將可遍歷的物件組合為一個索引序列
回傳 ( index, value )
print(list(enumerate(['a', 'b', 'c'])))
#[(0, 'a'), (1, 'b'), (2, 'c')]可以用於 for 迴圈
lst = [1, -4, 2, 5, -1]
for i, v in enumerate(lst):
if v > 0:
print(i, end=" ")
#0 2 3巢狀迴圈
for 裡有 for,從最內圈開始執行
for x in range(1, 10):
for y in range(1, 5):
print(x * y, end=" ")
print()
# 1 2 3 4
# 2 4 6 8
# 3 6 9 12
# 4 8 12 16
# 5 10 15 20
# 6 12 18 24
# 7 14 21 28
# 8 16 24 32
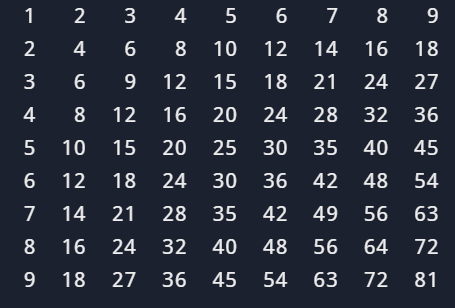
# 9 18 27 36 practice
印出九九乘法表
practice
for x in range(1, 10):
for y in range(1, 10):
a = x * y
print(f"{a:3d}", end=" ")
print()practice
讓使用者輸入數字 n,印出 n 層三角形

practice
n = int(input("Layer: "))
num = n * 2 - 1
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for y in range(0, (num // 2) - i + 1):
print(" ", end="")
for y in range(0, i * 2 - 1):
print("*", end="")
print()while
迴圈
while
- 使用縮排
- 用法:while 條件:
- 若
條件為 True 就不斷執行迴圈 若條件為 False 則終止迴圈
n = 5
while n > 0:
print(n, end=" ")
n -= 1
#5 4 3 2 1practice
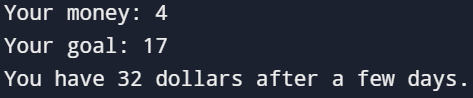
兩津發明了一種倍倍儲蓄法,只要每天讓自己的存款倍增,很快就能達到目標的存款
輸入一開始的金額 money,以及目標的金額 goal
輸出將 money 一直倍增直到超過 goal 時的金額
practice
money = int(input("Your money: "))
goal = int(input("Your goal: "))
while money < goal:
money *= 2
print(f"You have {money} dollars after a few days.")結束啦 :D
報秋遊 ! ! !

Python - 3
By d11231621莊智甯
Python - 3
- 180



