Replication & Synchronization

Replication
The act of propagating changes across a system of nodes, such that all the participating nodes in the have the full set, or subset, of changes their individual configurations require.
Synchronization
The method nodes in a system use to process change sets to achieve the same state for the objects those changes affect.
Replication Walkthrough
- A change occurs, or a new replicant node is added.
-
Metadata about the changes a node holds are communicated to other nodes.
-
Nodes use the metadata to isolate the changes they need.
-
The missing changes are sent between nodes until they arrive at the set/subset they need.
Has changes 1 and 3,
wants all changes
Has changes 2 and 4,
wants all changes
Has no changes,
wants changes 1 and 4
Synchronization Walkthrough
- A change is received that represents the creation of a new object or a modification (including deletion) of an existing object.
-
The change is inspected and discarded if it is a duplicate or doesn't comply with permission requirements.
-
If the change is valid, it is grouped for processing with the object it represents
-
Changes are compiled together using a merge strategy, which, if deterministic, should yield the same state for a given object across all nodes
{ Modify ABC }
{ Create XYZ }
{ Create ABC }
{ Create XYZ }
Changes
Time
- Conflict-Free Replicated Datatypes, or CRDTs, are a deterministic data convergence mechanism.
- CRDTs deterministically merge changes to objects without a centralized database, trusted coordinator, etc. Typically, ordering of operations in a CRDT is based on vector clocks (Lamport timestamps).
- There are many different flavors of CRDTs , but regardless of which is selected, the outcome is the ability to merge objects together in a way that does not generate conflicts in the way you see in other data merging protocols, like Git.
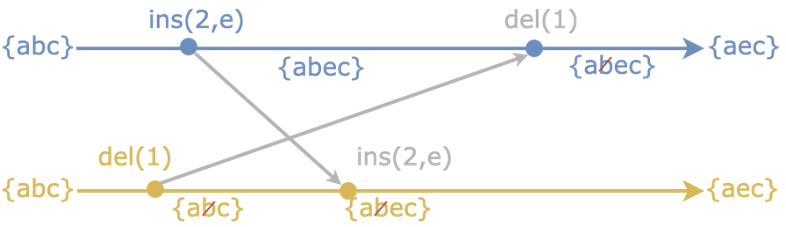
CRDTs for Merging Data
Replication & Synchronization
By Daniel Buchner
Replication & Synchronization
- 1,174



