SOFTWARE TESTING
INTRODUCTION
SOME QUESTIONS FOR YOU:
-
What is testing?
-
Why do you think we should test software?
Bugs
Faults
Failures
Devs
Defect Prevention
Fault Tolerance
Defect Removal
REMEMBER OUR TARGET AS SOFTWARE ENGINEERS: REDUCE AND MINIMIZE IMPACT OF DEFECTS
Bugs
Faults
Failures
Devs
TESTING IS MOSTLY ABOUT DETECTING FAILURES SO WE CAN REMOVE DEFECTS
- Testing is using our software to observe deviations from the expected behaviour (a failure)
- If a failure is observed, we need to look for the reason for that failure (bug) and remove it so the failure doesn't happen again
- Testing helps to remove defects after they are already part of our code
BY REMOVING THE DEFECTS WE REMOVE THE FAILURES LINKED TO THEM
INPUT
OUTPUT
Look inside your code for the origin of the failures and when detected, remove it

Is the output different to the expected one? FAILURE
INPUT
OUTPUT
GOING BACK TO THE QUESTIONS
-
What is testing?
-
Why do we test?
-
Testing is the execution of software and the observation of its behavior or outcome
-
It's used to detect failures and fix the linked defects (sometimes it's also used to demonstrate quality or proper behaviour)
WHAT ARE THE LIMITATIONS OF TESTING?
TYPES OF TESTING
DEPENDING ON THE ITEM TO BE TESTED
UNIT TESTING
COMPONENT TESTING
INTEGRATION TESTING
SYSTEM TESTING
DEPENDING ON THE WAY TO DECIDE WHEN TO STOP TESTING
COVERAGE BASED
USAGE BASED
- Controlled Software Release to "Beta" Users
- The software is released iteratively checking after every iteration if the targets (e.g. number of bugs reported, etc.) have been met and we can ship the product to non-beta users
- PROS: It resembles the REAL environment
- CONS: It must be used with care, assessing which users and at which moment should we involve
- A set of test cases are pre-defined
- They are executed
- When the results of the execution, meets the targets, then we are ready to ship
- PROS: It's a very controlled way to execute tests
- CONS: It's far away to the users
DEPENDING ON THE PURPOSE
SMOKE TESTING
CERTIFICATION TESTING
REGRESSION TESTING
SMOKE TESTING: a non-exhaustive set of tests that aim at ensuring that the most important functions work. The result of this testing is used to decide if a build is stable enough to proceed with further testing.
REGRESSION TESTING: tests to determine that the system remains stable as it cycles through the integration of other subsystems and through maintenance tasks
CERTIFICATION TESTING: tests that if executed successfully guarantee that a product meets some certification requirements (e.g. regulation).
DEPENDING ON HOW TESTS ARE DEFINED
FUNCTIONAL TESTING
STRUCTURAL TESTING
DEPENDING ON WHO EXECUTES THE TEST
AUTOMATED
MANUAL
PERFORMANCE AND STRESS TESTING
Scalability tests determine the scaling limits of the system, in terms of user scaling, geographic scaling, and resource scaling
Stress tests put a system under stress in order to determine the limitations of a system and, when it fails, to determine the manner in which the failure occurs
High Availability tests verify that the system keeps working in situations where parts of the system fail (e.g. if the service is supported by multiple servers and of them is not available).
KEY CONCEPTS
Test Case
A test-case is the description of the procedure to test a specific functionality of the system, explaining clearly what the expected outcome of the execution
In software, a test-case is usually:
- Preconditions that should be established before the test is conducted.
- Clear sequence of actions and input data that constitutes the test sequence.
- Expected Result.
| Pre-conditions | Input 1 | Input 2 | Input 3 | Expected Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 2 | 2 | 6 | |
| 4 | 3 | 3 | 10 |
TEST CASES EXAMPLE
Test Cases for a function that calculates the addition of 3 numbers
-
Identification
-
Timing
-
Tester
-
Transactions
-
Results (and steps to reproduce)
-
Screenshots, logs, etc.
Test Execution is the act of performing the tasks related to execute a test case.
A Test Case can be executed as many times as needed and hence have multiple test executions.
TEST EXECUTION INFO
TESTING ACTIVITIES
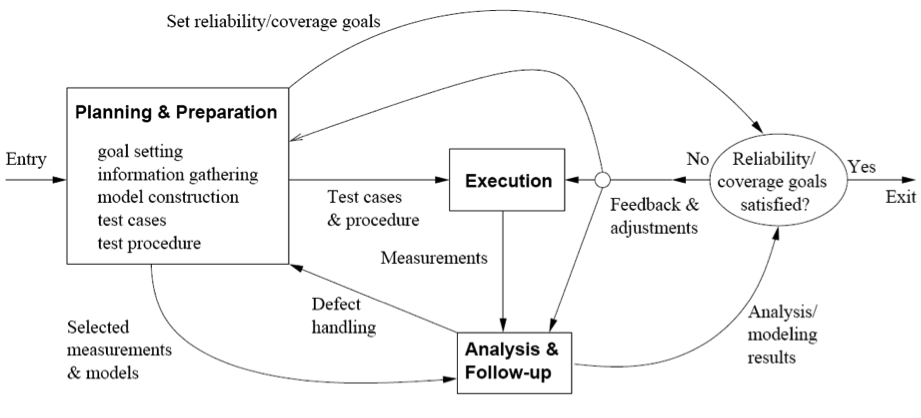
TEST PLANNING
-
Types of testing
-
How to define test cases
-
When to execute tests
-
Resources
TEST EXECUTION
-
Ensure resources assignment
-
Execute Test
-
Record Test Execution Results
TEST ANALYSIS & FOLLOW-UP
-
Defect Fixing: For test-executions that led to a failure, look for the linked defects and fix them
-
Management Decisions: Study how testing worked for this product, how are defect distributed, etc. and take remedial actions
EXAMPLE
- Define Test Cases for every User Story in every sprint
- QA Engineers are going to define the Test Cases
- Rate of Test Cases per User Story should be at least 5
- Developers are responsible of executing tests but after a user story is completed, QA engineers will also verify
- After every 3 sprints, the QA team will run a regression test. The regression test is a selection of the User Stories tests.
- Before releasing the software a regression test will be executed, no major failure should be detected.
PLANNING
EXECUTION
- The Scrum Master ensures that test are executed as planned
- Results of every test execution are registered
FOLLOW-UP
- Team fixes defects detected
- Based on Test Execution Results, Product Owner decides when User Stories are completed
- User Stories with high % of defects detected are assessed for further understanding the reasons
STEPS TO FIX A DEFECT
WHICH STEPS YOU THINK SHOULD BE FOLLOWED TO FIX A DEFECT?
TEST CASES VS. TEST COVERAGE
Exhaustive Testing is impossible...
1) Which test cases to select
2) How many tests cases are enough
An Example
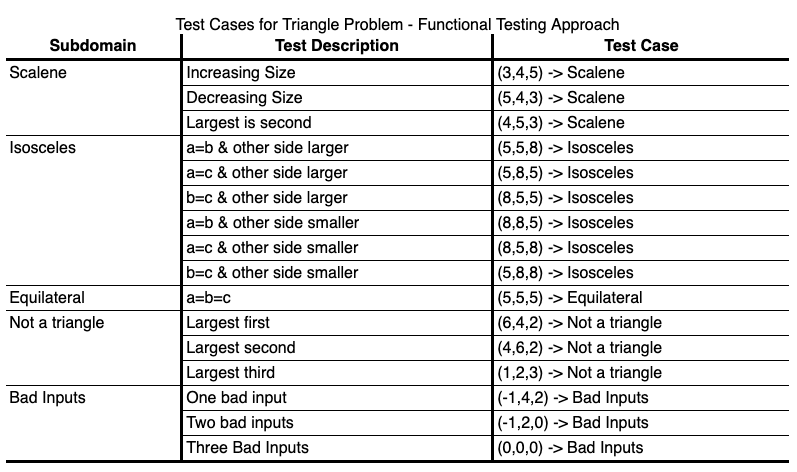
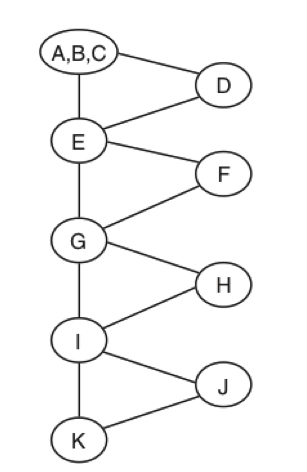
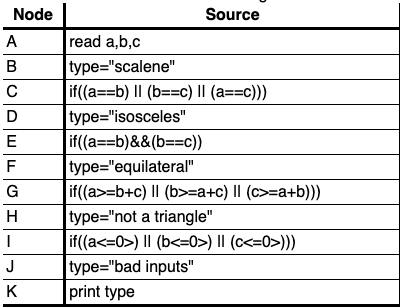
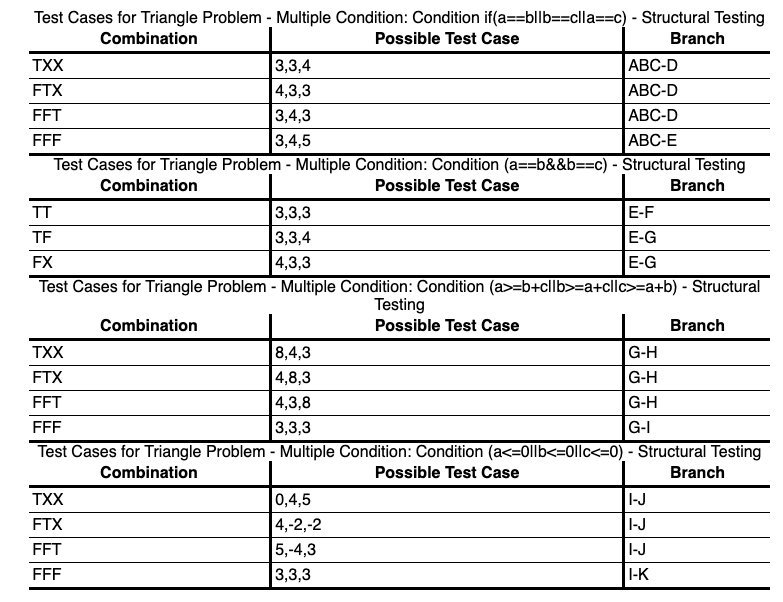
In the book "The Art of Software Testing", Glenford Myers poses the following functional testing problem: Develop a good set of test cases for a program that accepts three numbers, a, b, c, interprets those numbers as the lengths of the sides of a triangle, and outputs the type of the triangle. Myers reports that in his experience most software developers will not respond with a good test set.
APPROACHES TO DEFINE TEST CASES
FUNCTIONAL TESTING
DOMAIN TESTING
Idea: Partition of the input domain into a relatively small number of groups (domains) and then select some representative tests from each group
Domains can be also divided into subdomains and the range of possible output values can be also considered (output domains)
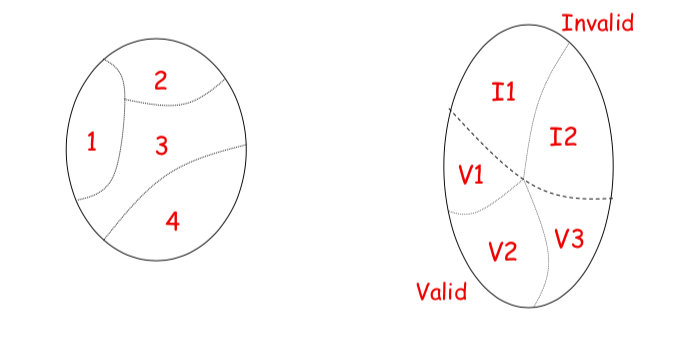
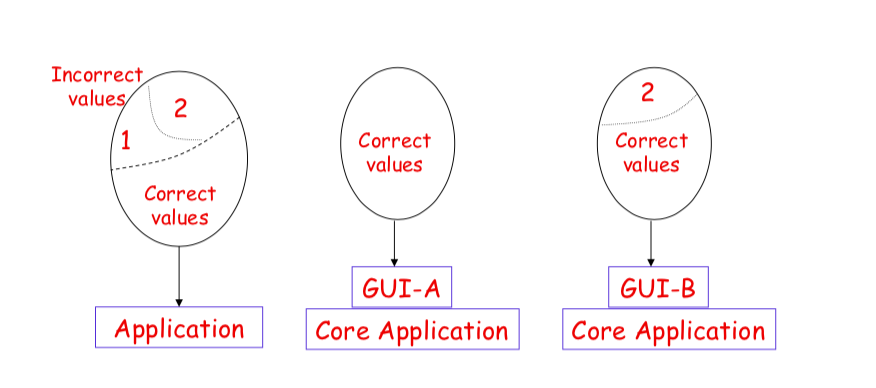
The Importance of Domain Boundaries

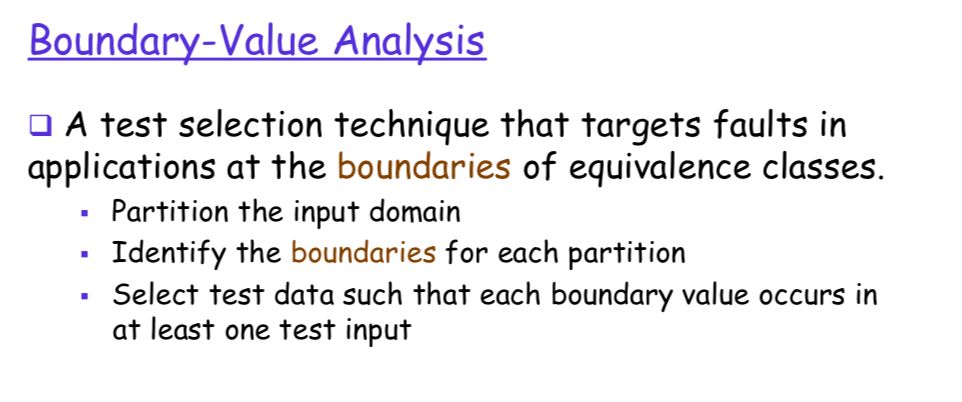

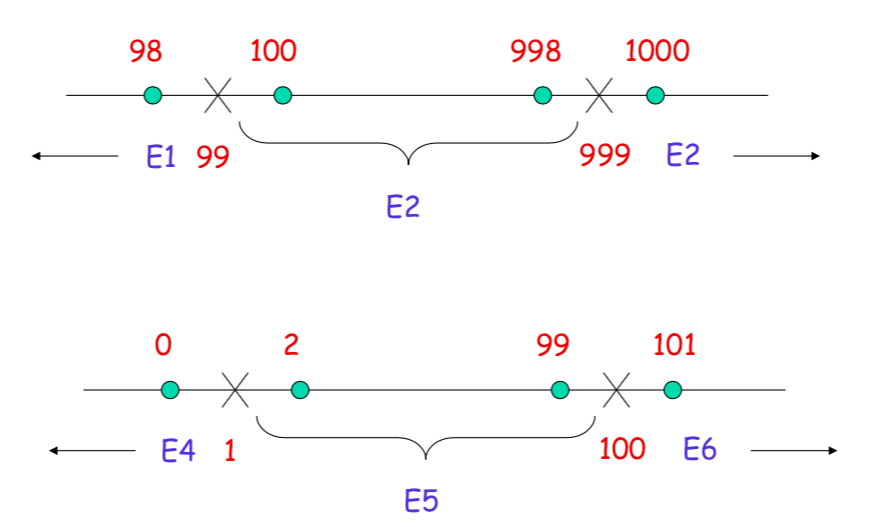

TEST MATRICES
A way to formalize the identification of subdomains
Build a matrix using the conditions that we can identify from the specification and then systematically identify all combinations of these conditions as being true or false.
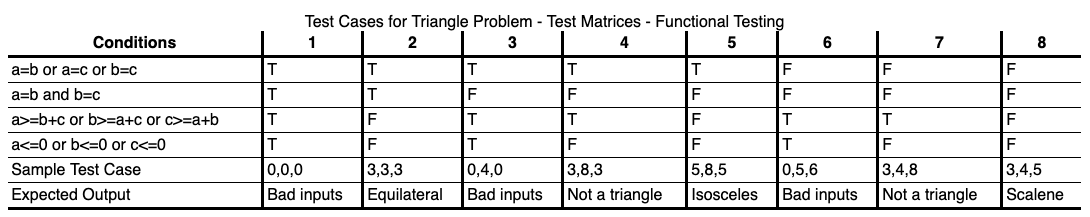
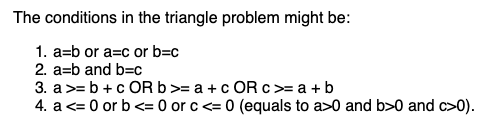
RANDOM TESTING
Select the test cases randomly in the possible values of the input domains
STRUCTURAL TESTING
In order to define the test cases, the knowledge about the structure of the software it's used
EVERY STATEMENT
Execute at least once every sentence of the software
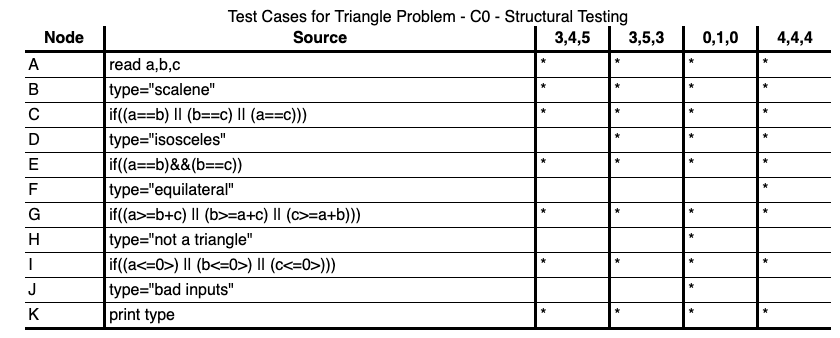
EVERY BRANCH
Go at least once for every decision branch of the code
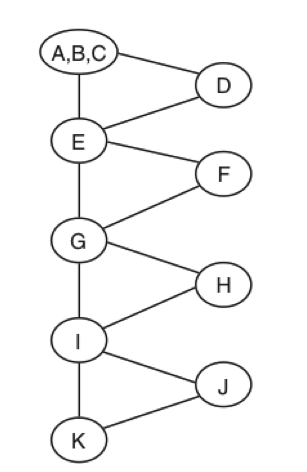
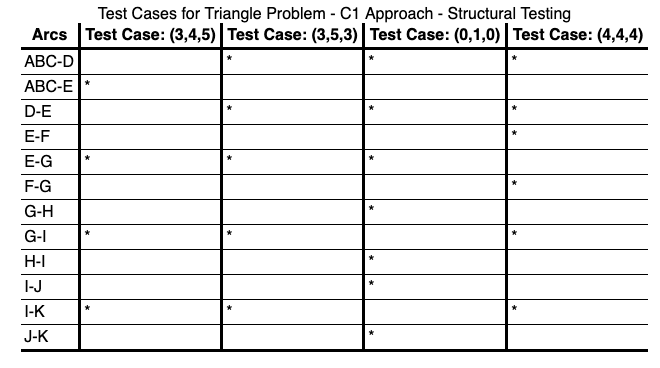
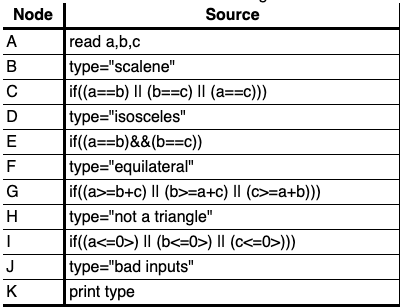
EVERY PATH
Test all the feasible paths in the software.
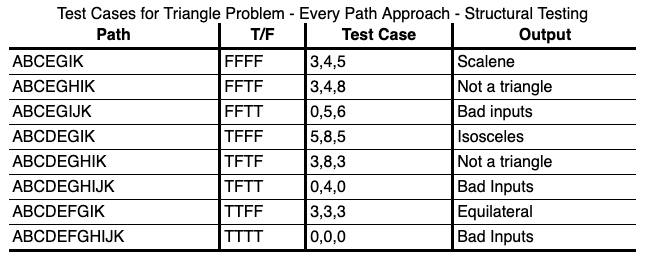
MULTIPLE CONDITION COVERAGE
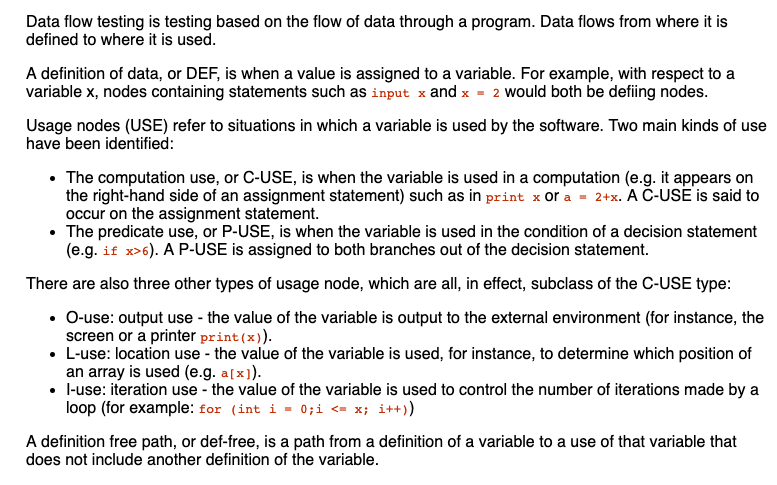
DATA FLOW TESTING
TEST AUTOMATION
What part of testing can be automated?
Planning, Definition, Execution, Analysis...
What types of testing can be automated?
Unit Testing, End-to-End testing, etc.
The flow of an automated test:
1. Preparation (initializations)
2. Execution
3. Assessment (check result of test)
Frameworks for any programming language
1. JUnit
2. QUnit
3. NUnit
...
Principles of Automation
-
Fully Automated
-
Self-Checking
-
Repeatable
-
Simplicity
-
Maintainability
TEST DRIVEN DEVELOPMENT
TFD: Test First Design
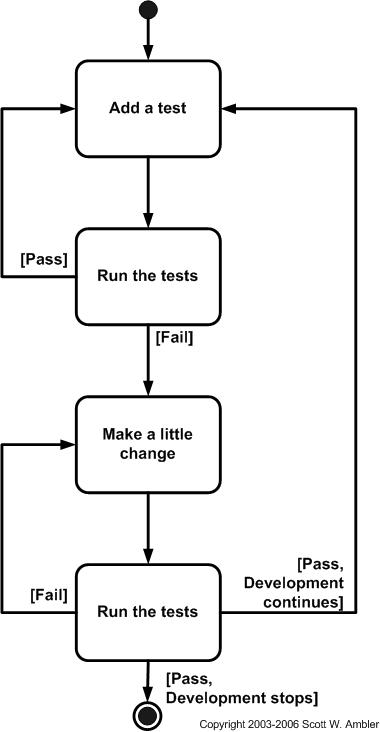
First Step: Add a test, just enough code to fail
Second Step: Run the test, it should fail
Third Step: Update the functional code to pass the test
Fourth Step: Run the tests. If fails, fix it, if not, start over the process
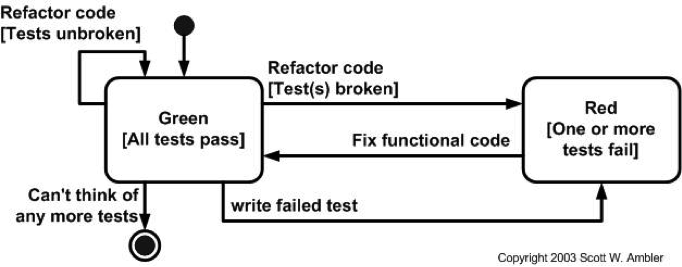
TEST DRIVEN DEVELOPMENT consists in combining the idea of automating tests in advance (TFD) with a continuous refactor
- Everything starts with tests
- New Functionality is not added unless there is a test failing (like in TFD)
- Re-factor is encouraged at any time (as part of adding new functionality) or by making the structure of the code better
- Any time a new feature is added, the first question is whether the existing design is the best design possible and if not, refactor it!
TDD Benefits
You are thinking since beginning about the specification, verification, completeness...
Good balance between external quality (test cases) and internal quality (refactor)
TDD improves documentation
Tests themselves are documentation and examples about how to use the software
(they don't replace documentation but complement them)
Testing - Slides
By Daniel Coloma
Testing - Slides
Software Testing
- 1,402



