Data Science
Deep Dive
-
What is data science
-
What data science can do
-
Pre-requisites & Skillset
-
Data science workflow
-
R Programming
-
Probability & Statistics
-
Data analysis & Visualization
-
Machine Learning
-
Course Curriculum
-
Q & A
What is data science?
"To gain insights into data through computations, statistics and visualization"
The ability to take data—to be able to understand it, to process it, to extract value from it, to visualize it, to communicate it—that’s going to be a hugely important skill in the next decades - Hal Varian
What data science can do?
- Predict whether a patient hospitalized due to a heart attach, will have a second heart attach. The prediction is to be based on demographic, diet & clinical measurement for that patient..
- Predict the price of a stock in 6 months from now, on the basis of company performance measures & economic data.
- Identify the risk factors for prostate cancer, based on clinical & demographic variables.
- It can also figure out whether a customer is pregnant or not by capturing their shopping habits from retail stores
- It also knows your age and gender, what brands you like even if you never told., including your list of interests(which you can edit) to decide what kind of ads to show you.
- It can also predict whether or not your relationship is going to last, based on activities and status updates on social networking sites. Police departments in some major cities also know you're going to commit a crime.
- It also tells you what videos you've been watching, what you like to read, & when you're going to quit your job.
- It also guess how intelligent you are how satisfied you are with your life, and whether you are emotionally stable or not -simply based on analysis of the 'likes' you have clicked
this is just the tip of the iceberg
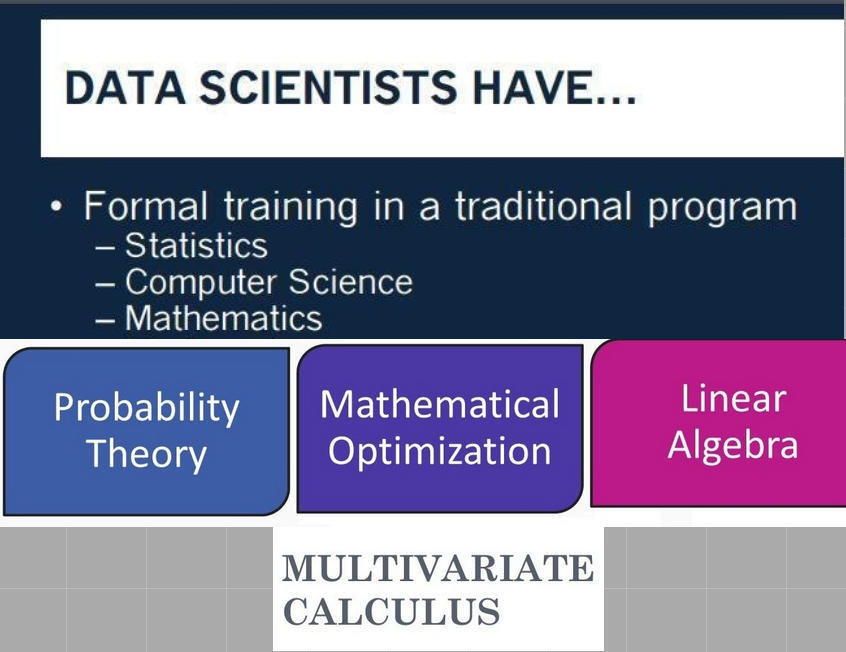
Pre-requisites & skillset
var vs. let / const
var snack = 'Meow Mix';
function getFood(food) {
var snack;
if (food) {
snack = 'Friskies';
return snack;
}
return snack;
}
getFood(false);
// undefined
var vs. let / const
let snack = 'Meow Mix';
function getFood(food) {
if (food) {
let snack = 'Friskies';
return snack;
}
return snack;
}
getFood(false);
// A
// B
// 'Meow Mix'

Credit: https://github.com/venegu
var vs. let / const
let snack = 'Meow Mix';
function getFood(food) {
if (food) {
let snack = 'Friskies';
return snack;
}
return snack;
}
getFood(false);
// A
// B
// 'Meow Mix'

Credit: https://github.com/venegu
IIFE > Blocks
(function () {
var food = 'Meow Mix';
}());
console.log(food);
// Reference Error
IIFE > Blocks
{
let food = 'Meow Mix';
}
console.log(food);
// Reference Error
Scoping
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
return arr.map(function (character) {
return this.name + character;
});
};
// Cannot read property 'name' of undefined
// A
// B
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
var that = this;
return arr.map(function (character) {
return that.name + character;
});
};
// Store this
Scoping
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
return arr.map(function (character) {
return this.name + character;
}, this);
}
Scoping
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
return arr.map(function (character) {
return this.name + character;
}.bind(this));
}Scoping
Arrow Functions
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.prefixName = function (arr) {
return arr.map((character) => this.name + character );
}
Arrow Functions
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
const squares = arr.map(x => x * x);
const squares = arr.map(function (x) { return x * x });
// Function Expression
// Terse
Strings
String.prototype.includes
var string = 'food';
var substring = 'foo';
console.log(string.indexOf(substring) > -1);
const string = 'food';
const substring = 'foo';
console.log(string.includes(substring));
// true
// true
String.prototype.repeat
function repeat(string, count) {
var strings = [];
while(strings.length < count) {
strings.push(string);
}
return strings.join('');
}
'meow'.repeat(3);
// meowmeowmow
Template Literals: Escaping Characters
var text = "This string contains \"double quotes\" which are escaped."
let text = `This string contains "double quotes" which are escaped.`
Template Literals: Interpolation
const name = 'Tiger';
const age = 13;
console.log(`My cat is named ${name} and is ${age} years old.`);
var name = 'Tiger';
var age = 13;
console.log('My cat is named ' + name + ' and is ' + age + ' years old.');

Credit: https://github.com/venegu
Template Literals: Multi-line Strings
var text = (
'cat\n' +
'dog\n' +
'nickelodeon'
)
var text = [
'cat',
'dog',
'nickelodeon'
].join('\n')
var text = (
`cat
dog
nickelodeon`
)
Template Literals: Expressions
let today = new Date()
let text = `The time and date is ${today.toLocaleString()}`
Template Literals: Multi-line Strings
let book = {
title: 'Harry Potter and The Sorcercers Stone',
summary: 'Much magic. Such depth.',
author: 'J.K. Rowling'
}
let html = `<header>
<h1>${book.title}</h1>
</header>
<section>
<div>${book.summary}</div>
<div>${book.author}</div>
</section>`
Destructuring
Destructuring
var luke = { occupation: 'jedi', father: 'anakin' }
var {occupation, father} = luke;
console.log(occupation); // 'jedi'
console.log(father); // 'anakin'
var [a, b] = [10, 20]
console.log(a); // 10
console.log(b); // 20
Destructuring
function getCoords () {
return {
x: 10,
y: 22
}
}
var {x, y} = getCoords()
console.log(x); // 10
console.log(y); // 22
Modules

Credit: https://www.flickr.com/photos/lucaohman/3473867313
Exporting in CommonJS
module.exports = 1
module.exports = { foo: 'bar' }
module.exports = ['foo', 'bar']
module.exports = function bar () {}
export default 1
export default { foo: 'bar' }
export default ['foo', 'bar']
export default function bar () {}
Named Exports
module.exports.name = 'David';
module.exports.age = 25;
export var name = 'David';
export var age = 25;
Exporting in ES6
// math/addition.js
function sumTwo(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function sumThree(a, b) {
return a + b + c;
}
export { sumTwo, sumThree };
Exporting in ES6
export function sumTwo(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
export function sumThree(a, b) {
return a + b + c;
}
Exporting default bindings
function sumTwo(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function sumThree(a, b) {
return a + b + c;
}
var api = {
sumTwo : sumTwo,
sumThree: sumThree
}
export default api
Importing Modules
var _ = require('underscore');
import _ from 'underscore';
import { sumTwo, sumThree } from 'math/addition'
import {
sumTwo as addTwoNumbers,
sumThree as sumThreeNumbers} from
} from 'math/addition'
import * as util from 'math/addition'
Parameters
Default Parameters
function addTwoNumbers(x, y) {
x = x || 0;
y = y || 0;
return x + y;
}
function addTwoNumbers(x=0, y=0) {
return x + y;
}
addTwoNumbers(2, 4); // 6
addTwoNumbers(2); // 2
addTwoNumbers(); // 0
Rest Parameters
function logArguments() {
for (var i=0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
console.log(arguments[i]);
}
}
function logArguments(...args) {
for (let arg of args) {
console.log(arg);
}
}
Named Parameters
function initializeCanvas(options) {
var height = options.height || 600;
var width = options.width || 400;
var lineStroke = options.lineStroke || 'black';
}
function initializeCanvas(
{ height=600, width=400, lineStroke='black'}) {
...
}
function initializeCanvas(
{ height=600, width=400, lineStroke='black'} = {}) {
...
}
Spread Operator
Math.max(...[-1, 100, 9001, -32]) // 9001
var arr = [1, ...[2,3], 4];
console.log(arr); // [1, 2, 3, 4]
var arr1 = [0, 1, 2];
var arr2 = [3, 4, 5];
arr1.push(...arr2);
Classes
Base Classes
function Person(name, age, gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
}
Person.prototype.incrementAge = function () {
return this.age += 1;
};
Extended Classes
function Personal(name, age, gender, occupation, hobby) {
Person.call(this, name, age, gender);
this.occupation = occupation;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
Personal.prototype = Object.create(Person.prototype);
Personal.prototype.constructor = Personal;
Personal.prototype.incrementAge = function () {
return Person.prototype.incrementAge.call(this) += 1;
}
Base Classes in ES6
class Person {
constructor(name, age, gender) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.gender = gender;
}
incrementAge() {
this.age += 1;
}
}
Extended Classes in ES6
class Personal extends Person {
constructor(name, age, gender, occupation, hobby) {
super(name, age, gender);
this.occupation = occupation;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
incrementAge() {
super.incrementAge();
this.age += 20;
console.log(this.age);
}
}
// Calls parent incrementAge()
Symbols
Unique Property Keys
const key = Symbol();
const keyTwo = Symbol();
const object = {};
>> key === keyTwo
>> false
object.key = 'Such magic.';
object.keyTwo = 'Much Uniqueness'
Symbols as Concepts
const anakin = 'jedi';
const yoda = 'jedi master';
const luke = 'jedi';
const anakin = Symbol();
const yoda = Symbol();
const luke = Symbol();
Maps
(Hash) Maps in ES5
var map = new Object();
map[key1] = 'value1';
map[key2] = 'value2';
Seems functional, right...?
Get Own Properties
function getOwnProperty(object, propertyKey) {
return (object.hasOwnProperty(propertyKey) ? object[propertyKey]: undefined);
}
We should be safe...right?
> getOwnProperty({ hasOwnProperty: 'Hah, overwritten'}, 'Pwned');
> TypeError: Propery 'hasOwnProperty' is not a function

Credit: http://memesvault.com/nooo-meme-darth-vader/
Second time is the charm.
function getOwnProperty(object, propertyKey) {
return (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty(object, propertyKey) ? object[propertyKey]: undefined);
}

credit: http://deloiz.blogspot.com/2014/01/Pusheen.html
Maps in ES6
let map = new Map();
> map.set('name', 'david');
> map.get('name'); // david
> map.has('name'); // true
// key
// value
Keys can be more than strings!
Arbitrary values as keys
let map = new Map([
['name', 'david'],
[true, 'false'],
[1, 'one'],
[{}, 'object'],
[function () {}, 'function']
]);
for (let key of map.keys()) {
console.log(typeof key);
// > string, boolean, number, object, function
};
.entries( )
for (let entry of map.entries()) {
console.log(entry[0], entry[1]);
}
for (let [key, value] of map.entries()) {
console.log(key, value);
}
WeakMaps
Classes 101
class Person {
constructor(age) {
this.age = age;
}
incrementAge() {
this.age += 1;
}
}
Private data?
Naming Conventions
class Person {
constructor(age) {
this._age = age;
}
_incrementAge() {
this._age += 1;
}
}
WeakMaps to the rescue!
(Maybe they're not so weak)
WeakMaps for Privacy
let _age = new WeakMap();
class Person {
constructor(age) {
_age.set(this, age);
}
incrementAge() {
let age = _age.get(this);
if(age > 90) {
console.log('Midlife crisis');
}
}
}
> const person = new Person(90);
> person.incrementAge(); // 'Midlife crisis'
> Reflect.ownKeys(person); // []

credit: http://wildermuth.com/images/pinky-promise_2.jpg
Promises
Callback Hell
func1(function (value1) {
func2(value1, function(value2) {
func3(value2, function(value3) {
func4(value3, function(value4) {
func5(value4, function(value5) {
// Do something with value 5
});
});
});
});
});
D
O
O
M
Promises
func1(value1)
.then(func2(value1) { })
.then(func3(value2) { })
.then(func4(value3) { })
.then(func5(value4) {
// Do something with value 5
});
Promises


Promises
new Promise(resolve => resolve(data))
.then(result => console.log(data));
new Promise((resolve, reject) =>
reject(new Error('Failed to fufill Promise')))
.catch(reason => console.log(reason));
Promises

Promises
var fetchJSON = function(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
$.getJSON(url)
.done((json) => resolve(json))
.fail((xhr, status, err) => reject(status + err.message));
});
}
Parallelizing using Promises
var urls = [
'http://www.api.com/items/1234',
'http://www.api.com/items/4567'
];
var urlPromises = urls.map(fetchJSON);
Promise.all(urlPromises)
.then(function(results) {
results.forEach(function(data) {
});
})
.catch(function(err) {
console.log("Failed: ", err);
});
Generators
Syntax
function* sillyGenerator() {
yield 1;
yield 2;
yield 3;
yield 4;
}
var generator = sillyGenerator();
var value = generator.next();
> console.log(value); // { value: 1, done: false }
> console.log(value); // { value: 2, done: false }
> console.log(value); // { value: 3, done: false }
> console.log(value); // { value: 4, done: false }
What about using return?
Return in a Generator
function* sillyGenerator() {
yield 1;
yield 2;
yield 3;
yield 4;
return 5;
}
for(let val of sillyGenerator()) {
console.log(val); // 1, 2, 3, 4
}
Real Generator Function
function* factorial(){
let [current, total] = [0, 1];
while (true){
yield total;
current++;
total = total * current;
}
}
for (let n of factorial()) {
console.log(n);
if(n >= 100000) {
break;
}
}
Writing Sync-Async
function request(url) {
getJSON(url, function(response) {
generator.next(response);
});
}
function* getData() {
var entry1 = yield request('http://some_api/item1');
var data1 = JSON.parse(entry1);
var entry2 = yield request('http://some_api/item2');
var data2 = JSON.parse(entry2);
}
Not without problems though...
-
How do we handle errors?
-
getJSON not in control
-
Parallelize?

Generators & Promises
function request(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
getJSON(url, resolve);
});
}
Generators & Promises
function iterateGenerator(gen) {
var generator = gen();
var ret;
(function iterate(val) {
ret = generator.next();
if(!ret.done) {
ret.value.then(iterate);
} else {
setTimeout(function() {
iterate(ret.value);
});
}
})();
}
Generators & Promises
iterateGenerator(function* getData() {
var entry1 = yield request('http://some_api/item1');
var data1 = JSON.parse(entry1);
var entry2 = yield request('http://some_api/item2');
var data2 = JSON.parse(entry2);
});
Alternate Solution?
Beyond ES6
Async / Await (ES7)
var request = require('request');
function getJSON(url) {
request(url, function(error, response, body) {
return body;
});
}
function main() {
var data = getJSON('http://some_api/item1');
console.log(data); // Undefined
}
main();
Async / Await (ES7)
var request = require('request');
function getJSON(url) {
return new Promise(function(resolve, reject) {
request(url, function(error, response, body) {
resolve(body);
});
});
}
async function main() {
var data = await getJSON();
console.log(data); // NOT undefined!
}
main();
console.log('The data is: ');


Thank you everyone!
Github: https://github.com/DrkSephy
LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/drksephy
Twitter: https://twitter.com/DrkSephy
ES6 Cheatsheet: https://github.com/DrkSephy/es6-cheatsheetCopy of ECMAScript 2015
By Data Science Portal
Copy of ECMAScript 2015
An overview of ES6 features.
- 65



