Postprocessing Neuroimaging methods in MRI and PET/MRI
with applications to Multiple Sclerosis and other Neurological diseases
Candidate: D. Poggiali
Tutor: Prof.ssa E. Pegoraro
Supervisor: Prof. P. Gallo
Cosupervisor: Prof. D. Cecchin
Summary:
- Introduction to Neuroimaging
- State of the art algorithms and pipelines
- Cortical Lesion Filling
- Glucose PET/MRI in MS
- Amyloid PET/MRI in AD
1. Introduction

One of the first brain measurement...
A modern neurological study aims to relate several biomarkers from different sources in order to explain the illness evolution improve prognostic accuracy and optimize the treatment.
A modern research group can have at disposal:
- clinical,
- imaging,
- neuropsychological,
- liquor biomarkers
Neuroimaging offers a fecund source of biomarkers
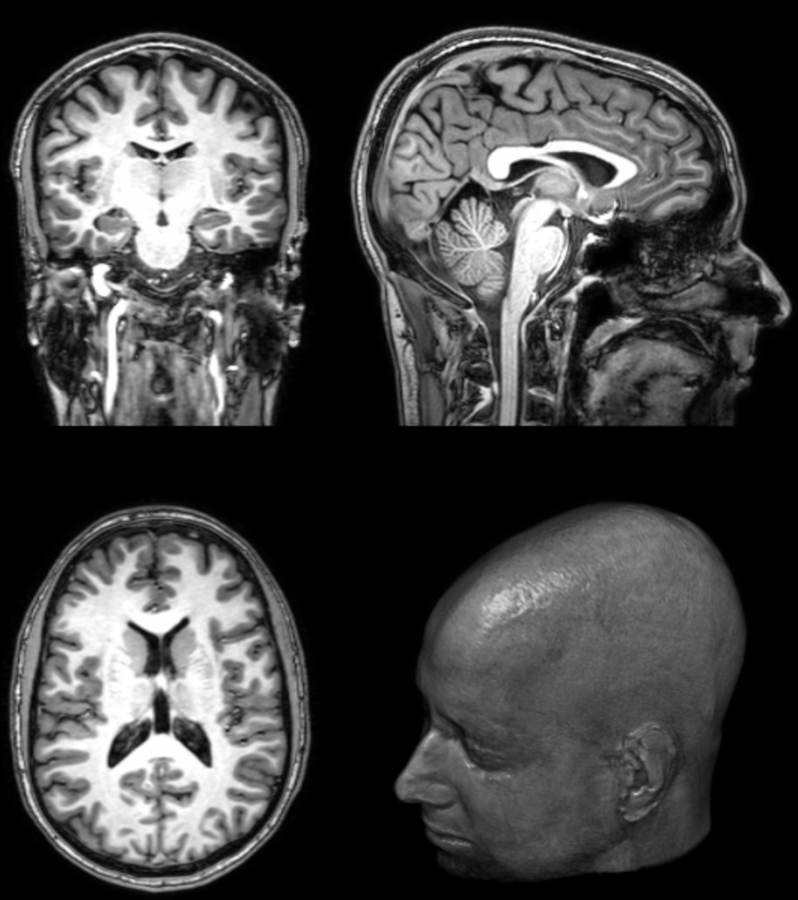
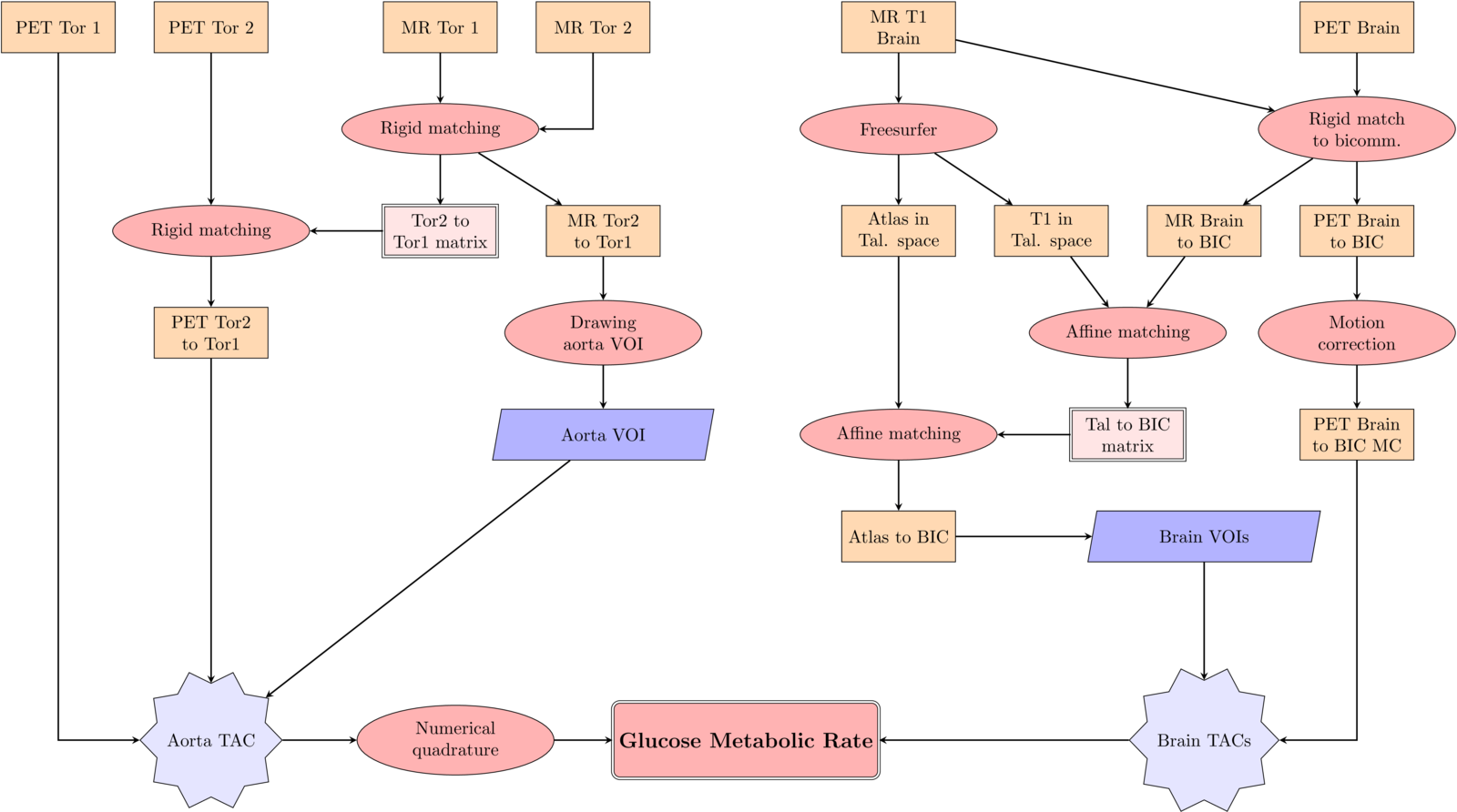
2. State of the art
1. Registration (rigid, affine, nonlinear)
2. Correction (Bias Field, Lesion Filling,
Motion Correction, PVC)
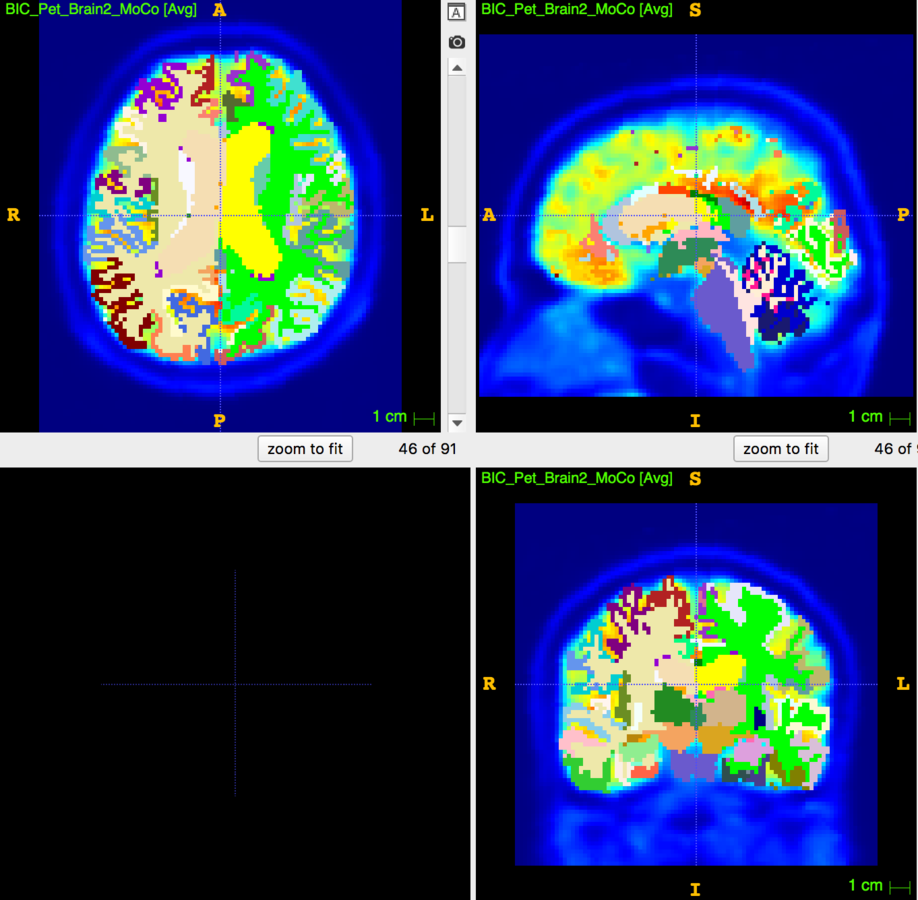
3. Segmentation (Manual, Template-based)
4. Measurement (mean, std over VOIs)
Registration
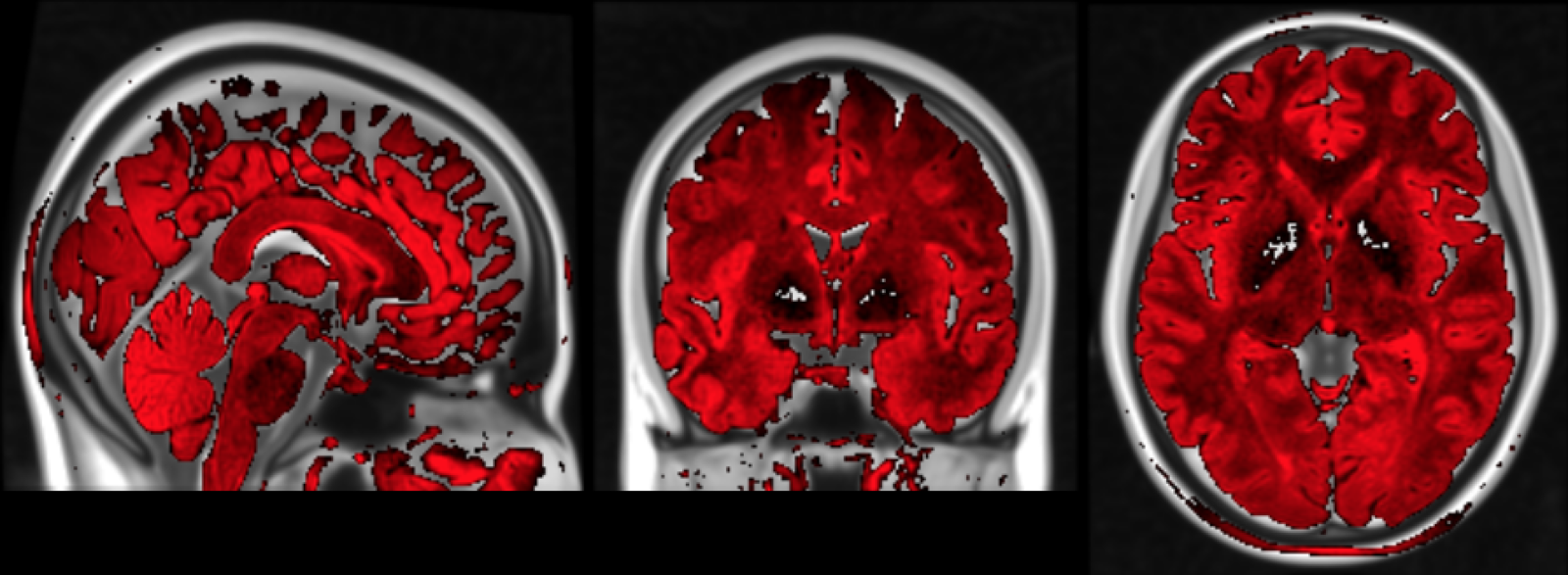
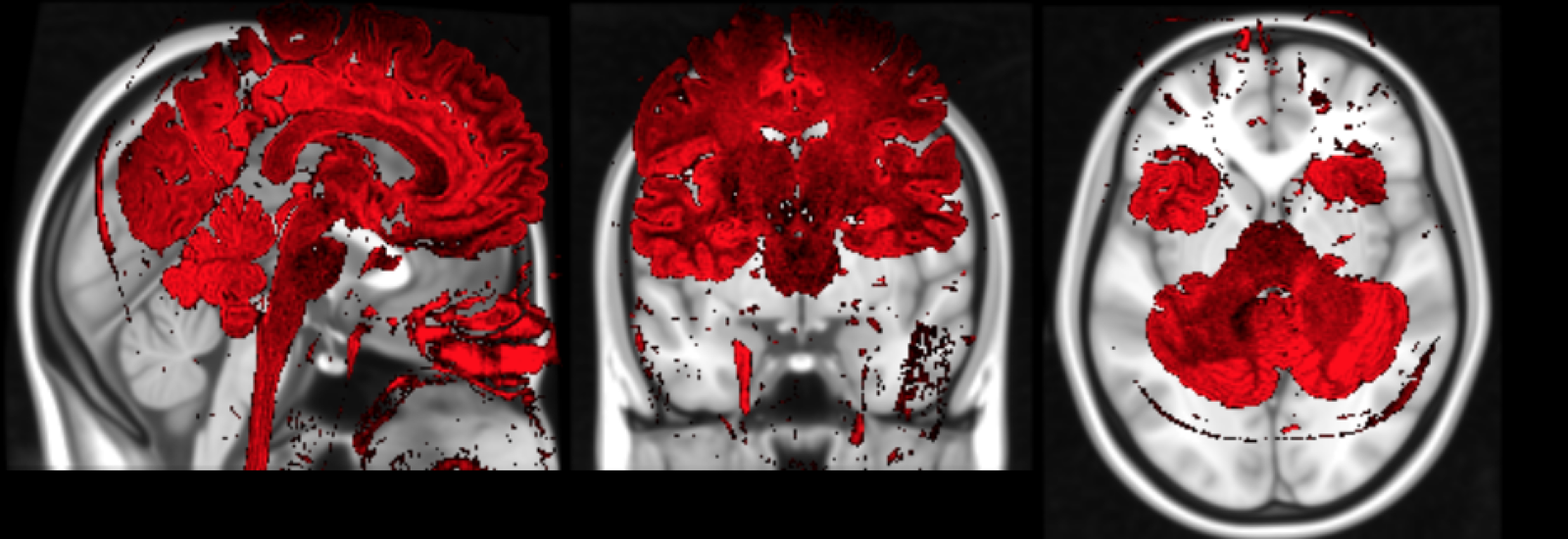
Correction
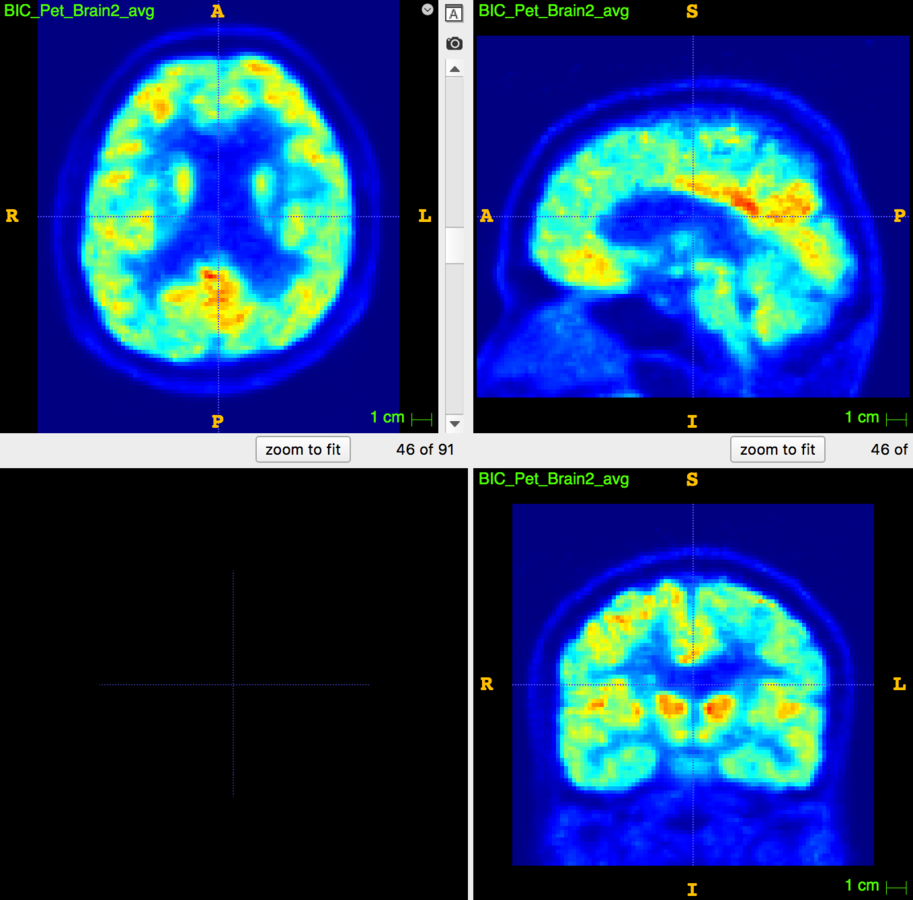
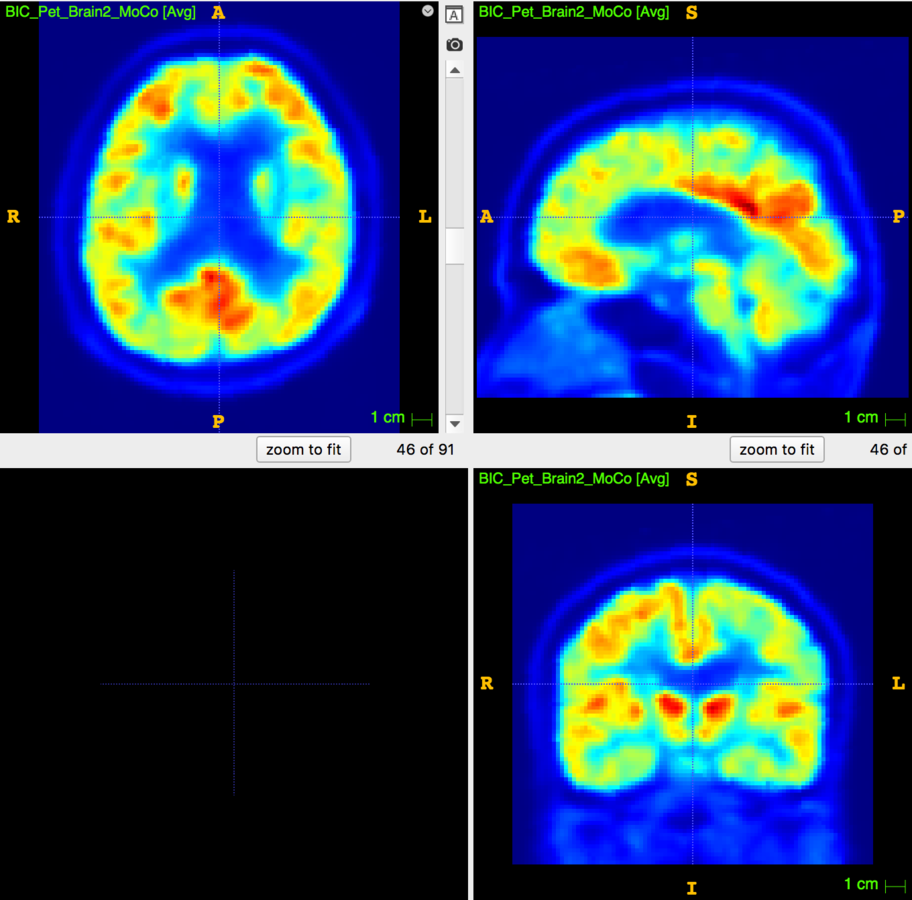
Motion Correction
Correction
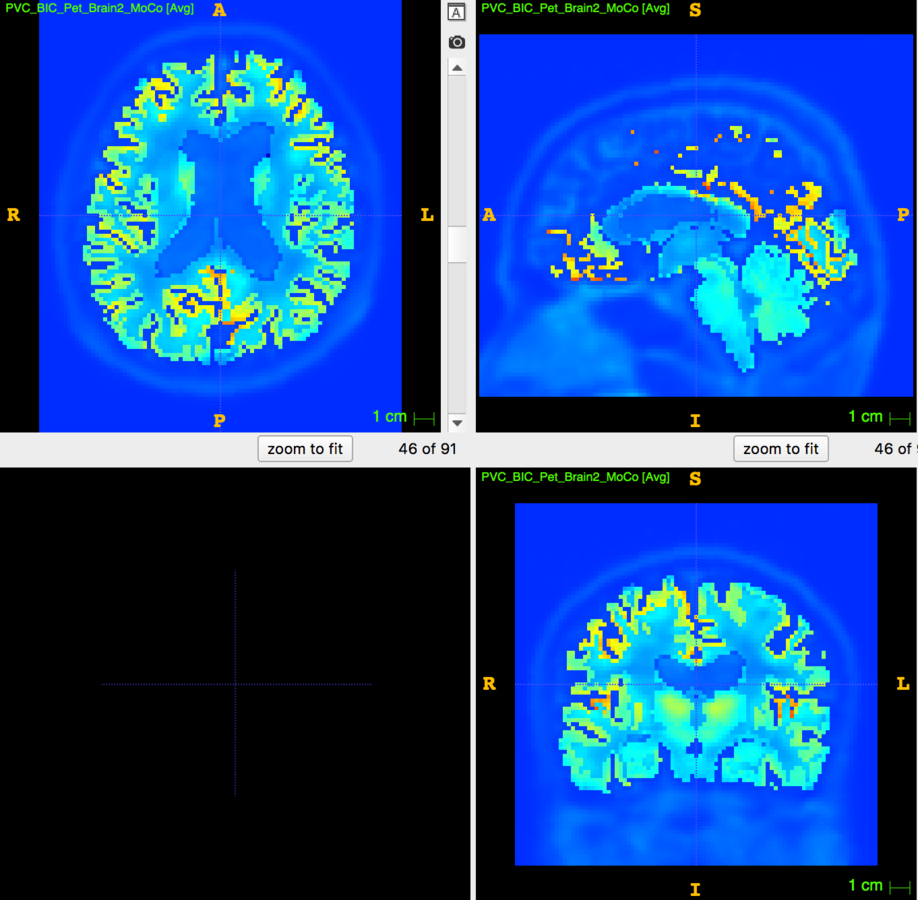
Partial Volume Correction
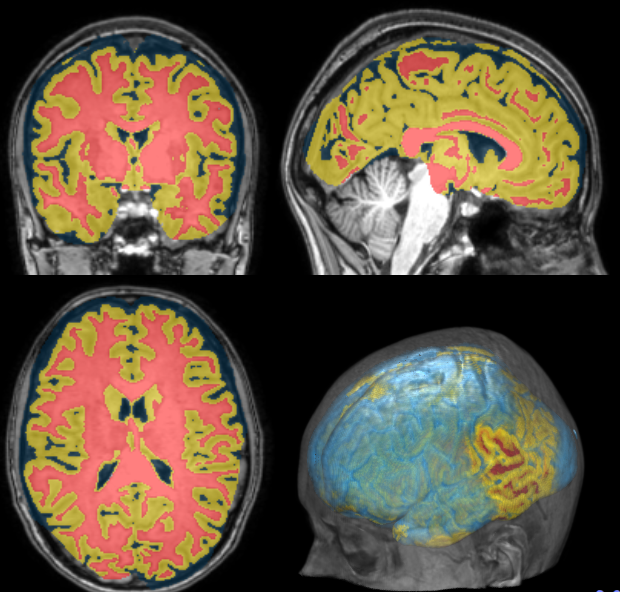
Segmentation
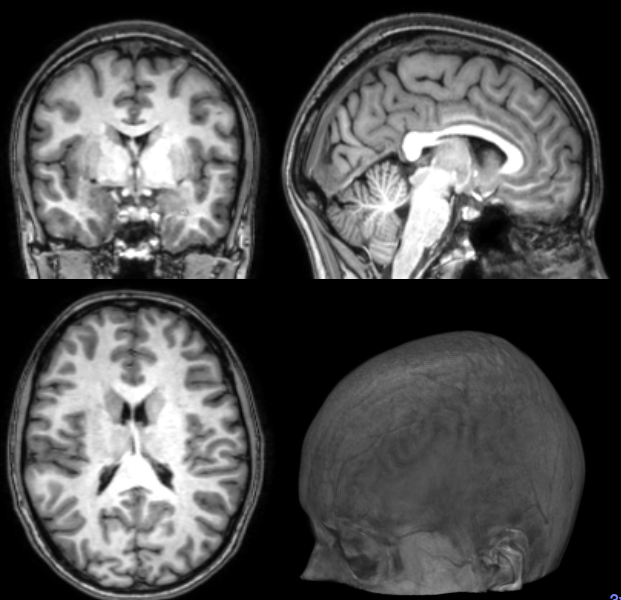
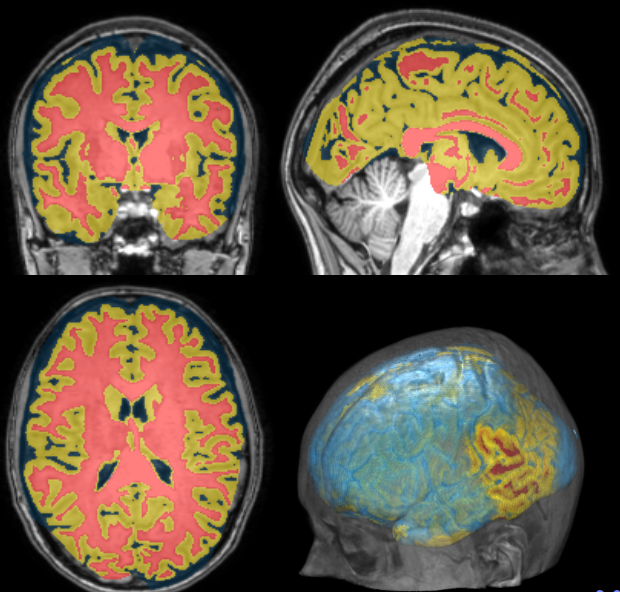
Measurements
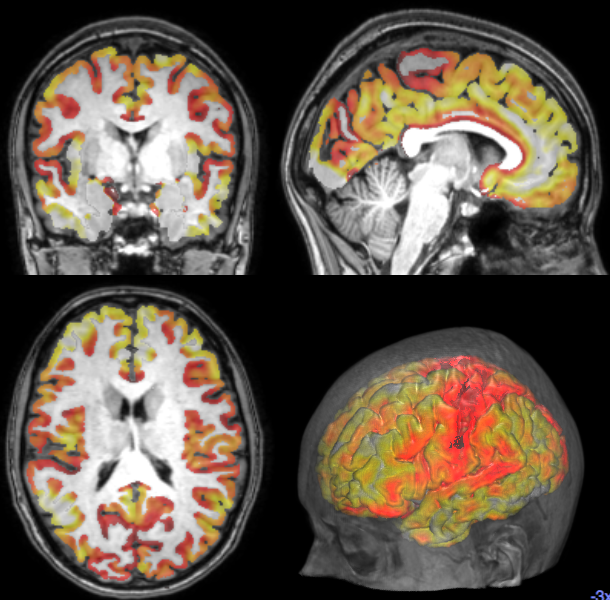
Cortical Thickness Estimation
Pipelining
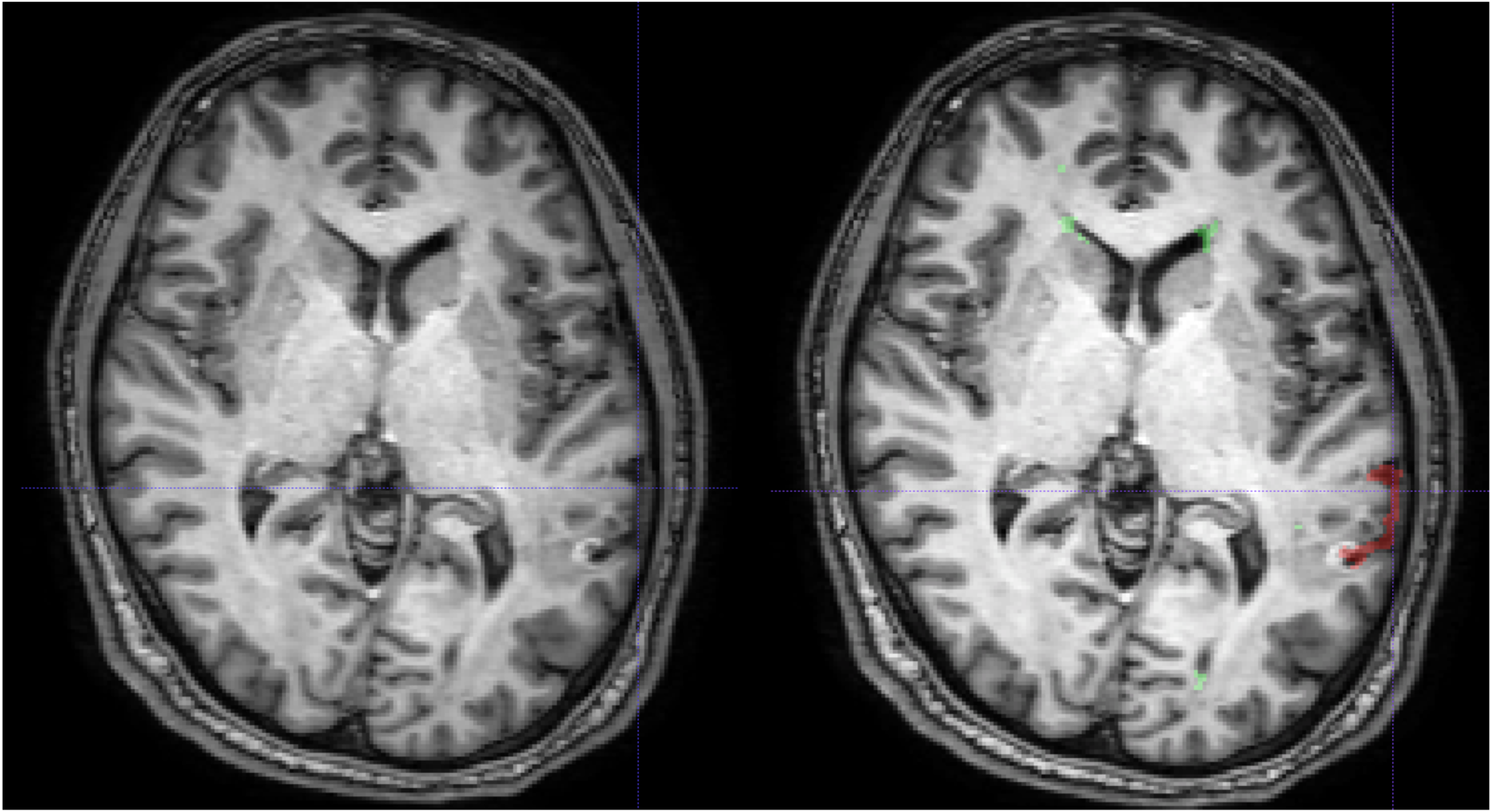
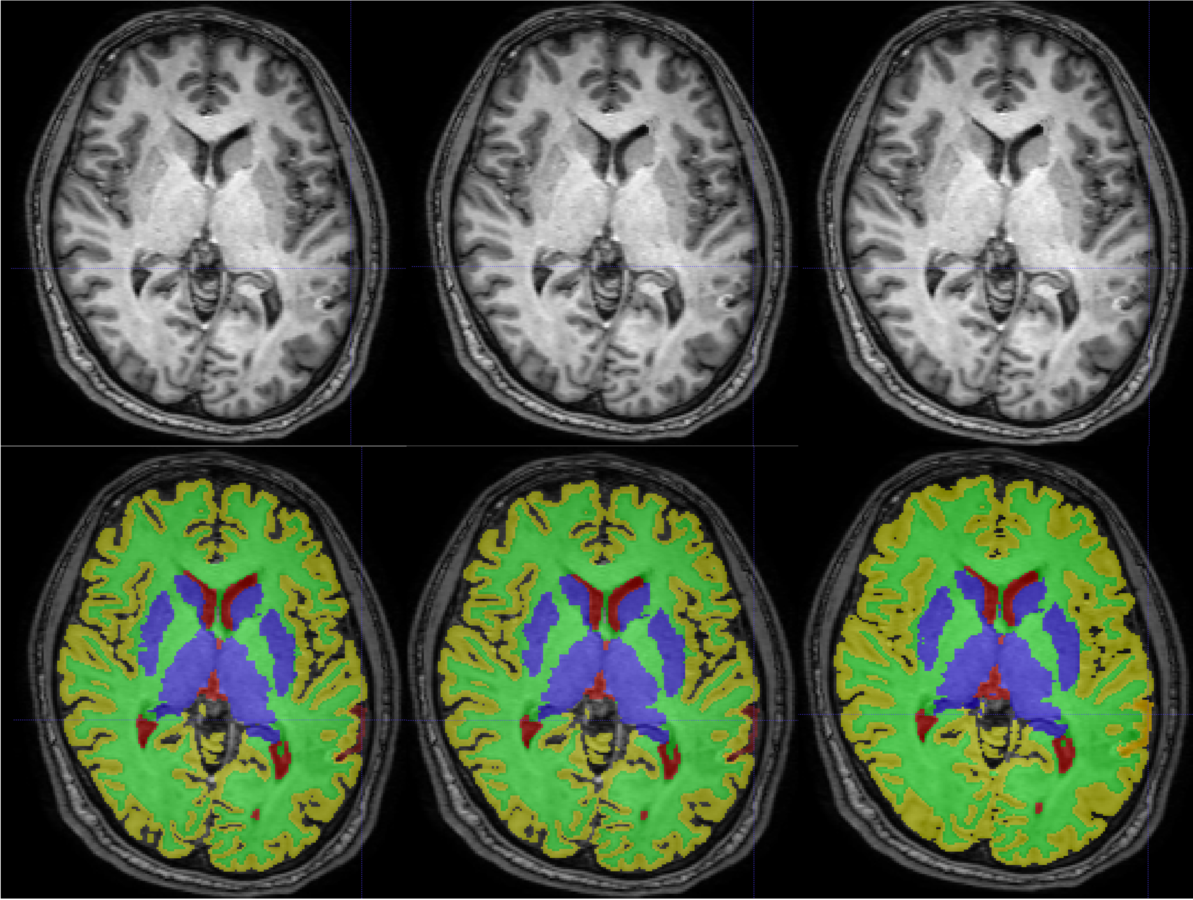
3. Cortical Lesion Filling
Lesion filling algorithms in MS try to inpaint T1 hypo-intense WM lesion (about 30% of FLAIR-appearing lesions) as Normal-Appearing White Matter (NAWM).
This procedure has shown to improve:
- Segmentation reliability
- Cortical Thickness estimation in longitudinal studies.
This procedure has NOT been studied before over Cortical Lesions: only ~15% appear as hypo-intense in T1.
4. Glucose PET/MRI in MS
29 patients, 14 CIS/eRRMS and 15 RRMS underwent a PET/MRI with:
- MRI sequences: 3D T1, 3D FLAIR, 3D DIR
- 18Fdg PET in list-mode
The aim is to study the relationship between:
- Cortical Thickness
- WM/GM lesion number/volume
- aMRGlu
Results are hard to put together!
No correlation was demonstrated between CTh and WM and GM lesion load
No correlation was found between global and regional aMRglu and CTh.
aMRglu correlated with lesion load
Inverse correlation was found between:
- the total number of focal lesions (WM+GM lesions) and the global cortical aMRglu (R=-0.36 e p=0.04)
- WM lesion volume and number and cortical global aMRglu (R=-0.4 and p=0.02 for both)
-
GM lesion number with global aMRglu (R=-0.36, p=0.046)
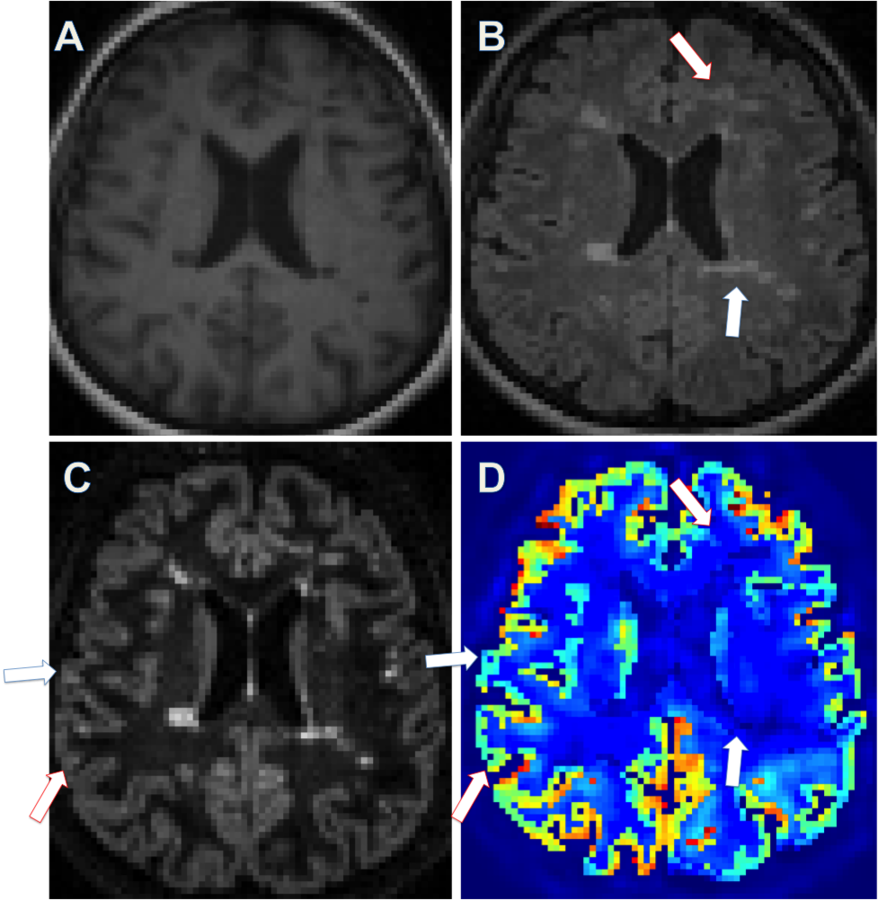
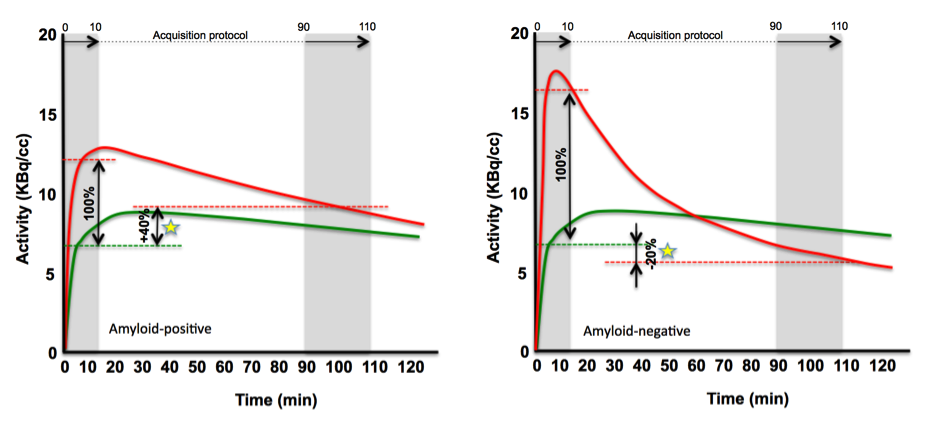
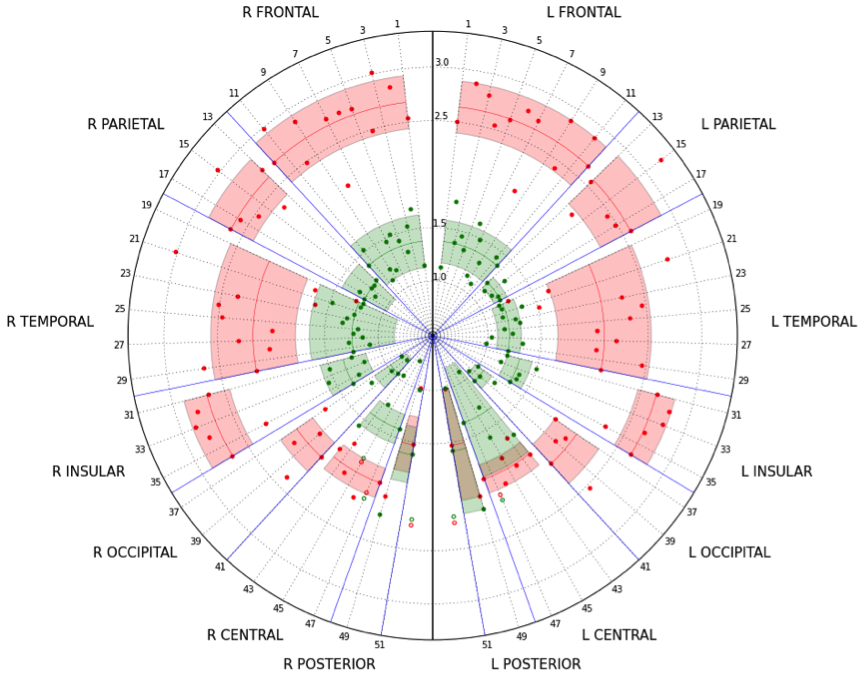
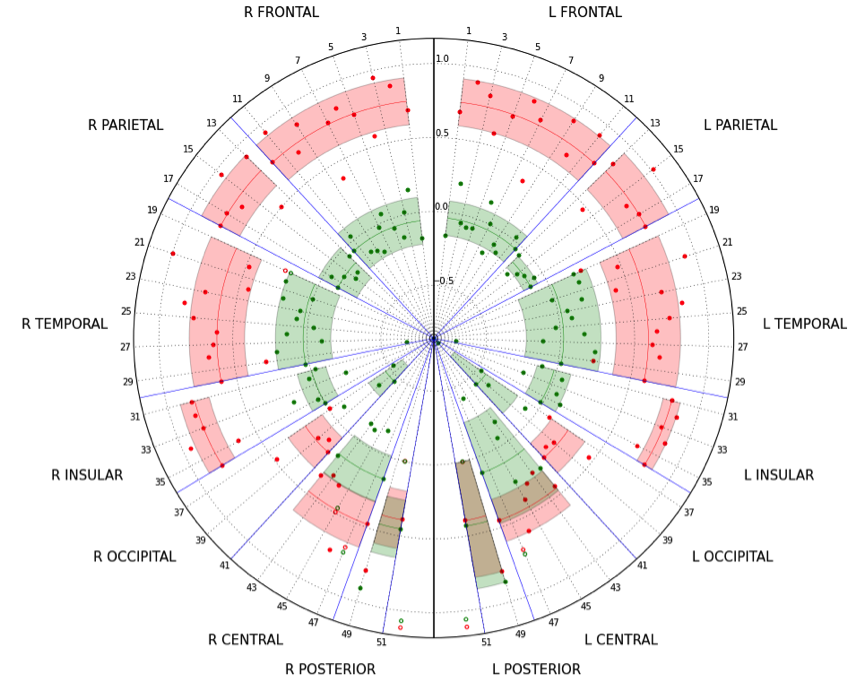
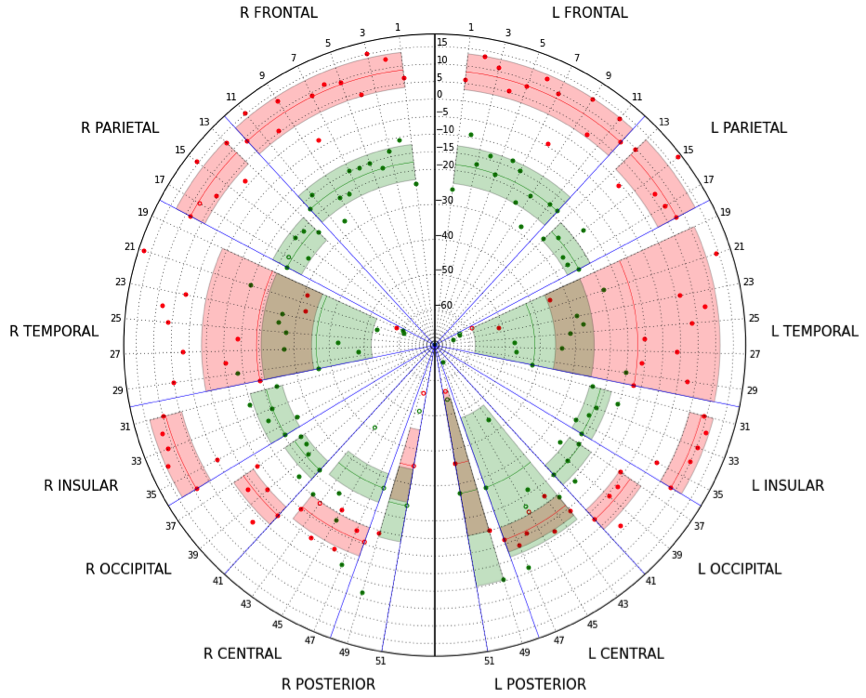
5. Amyloid PET/MRI in AD
86 cases (53 rated negatively and 33 positively by expert amyloid readers) of 18F-Fluorbetaben PET/MRI.
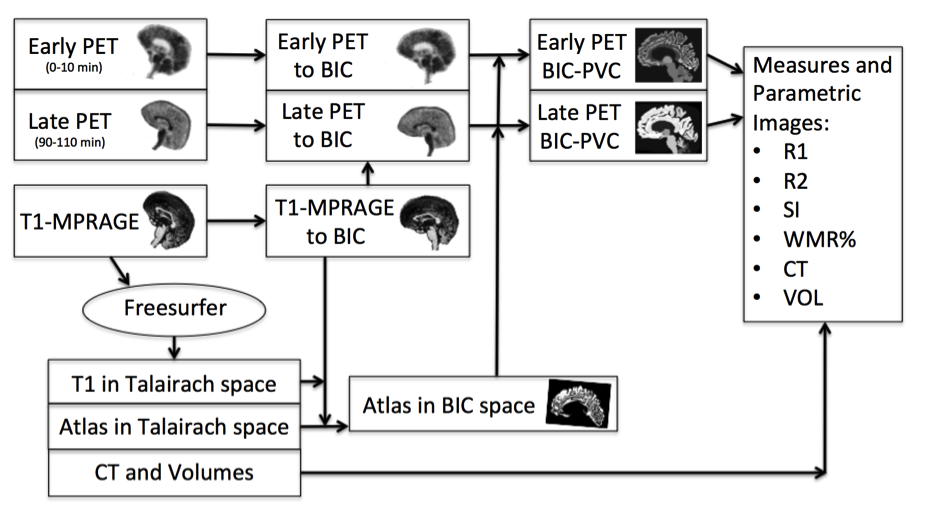
R2
SI
WMR
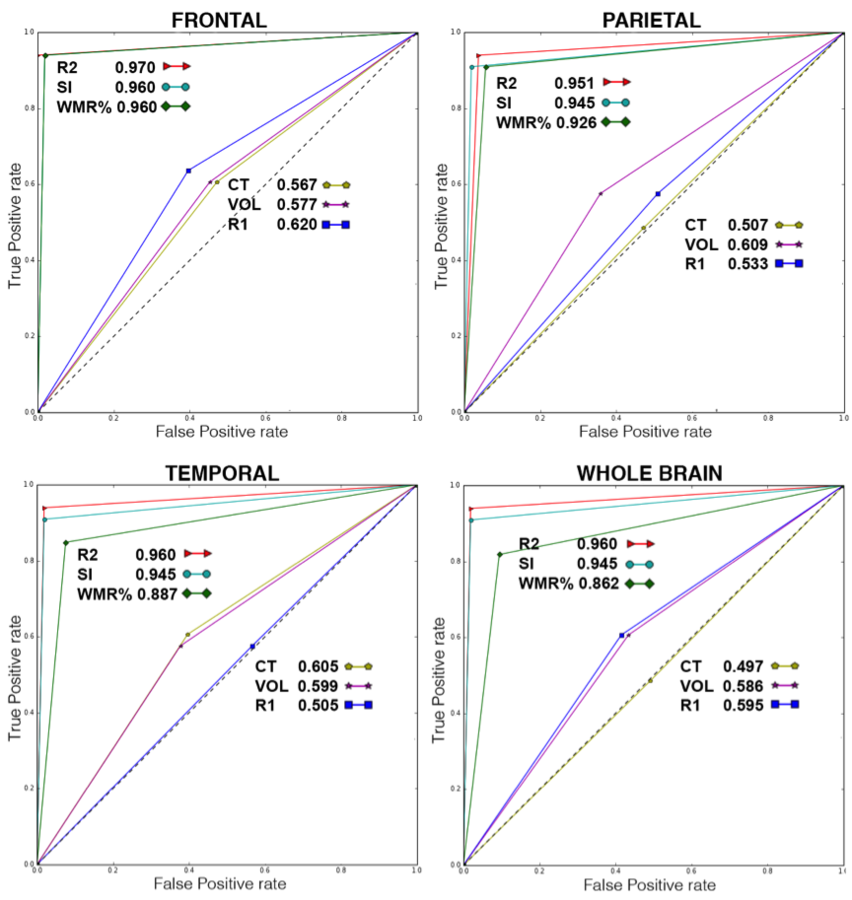
ROC (Receiver Operator Charateristic) curves
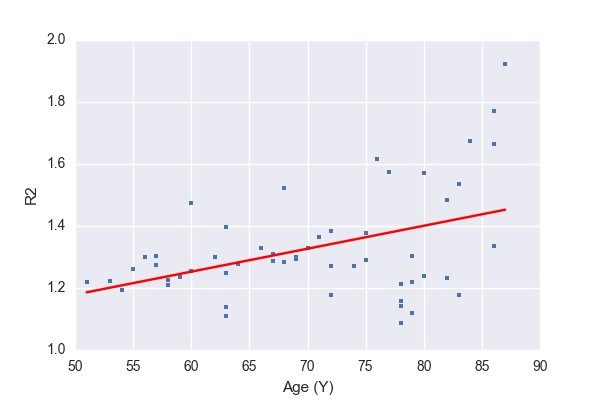
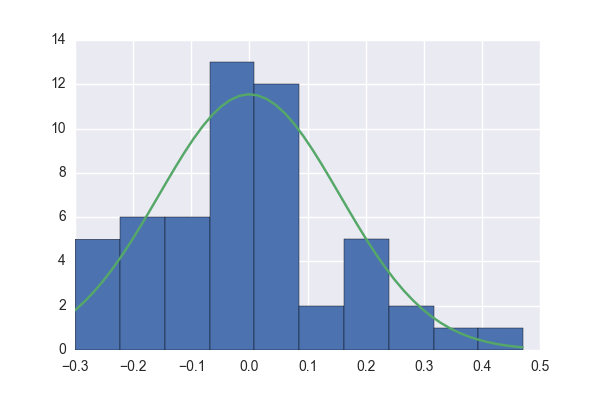
Normalization
z-score
Thanks to....
MS Centre Padova
Nuclear Medicine Padova
Neurology Padova
Neuroradiology Unit Padova
Nuclear Medicine Leipzig DE
all patients of course ...
... this audience for the attention!
Some References
- DT Chard, JS Jackson, DH Miller, CA Wheeler-Kingshott, Reducing the impact of white matter lesions on automated measures of brain gray and white matter volumes. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010
- SR Das, BB Avants, M Grossman, JC Gee, Registration based cortical thickness measurement, Neuroimage. 2009
- C Cobelli, D Foster, G Toffolo,Tracer kinetics in biomedical research, Springer, 2001.
- ME Juweid, OS Hoekstra, Positron Emission Tomography, Humana Press, 2011.
- CS Patlak, RG Blasberg, Graphical evaluation of blood-to-brain transfer constants from multiple-time uptake data. Generalizations, Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 1985.
- CL Epstein, ntroduction to the mathematics of Medical Imaging, Second Edition, Siam, 2008
-
TG Feeman, The mathematics of medical imaging: A beginners guide, Springer, 2010
relazione finale PhD
By davide poggiali
relazione finale PhD
- 743



