CodeRational
Deep Code Generation with Rationales
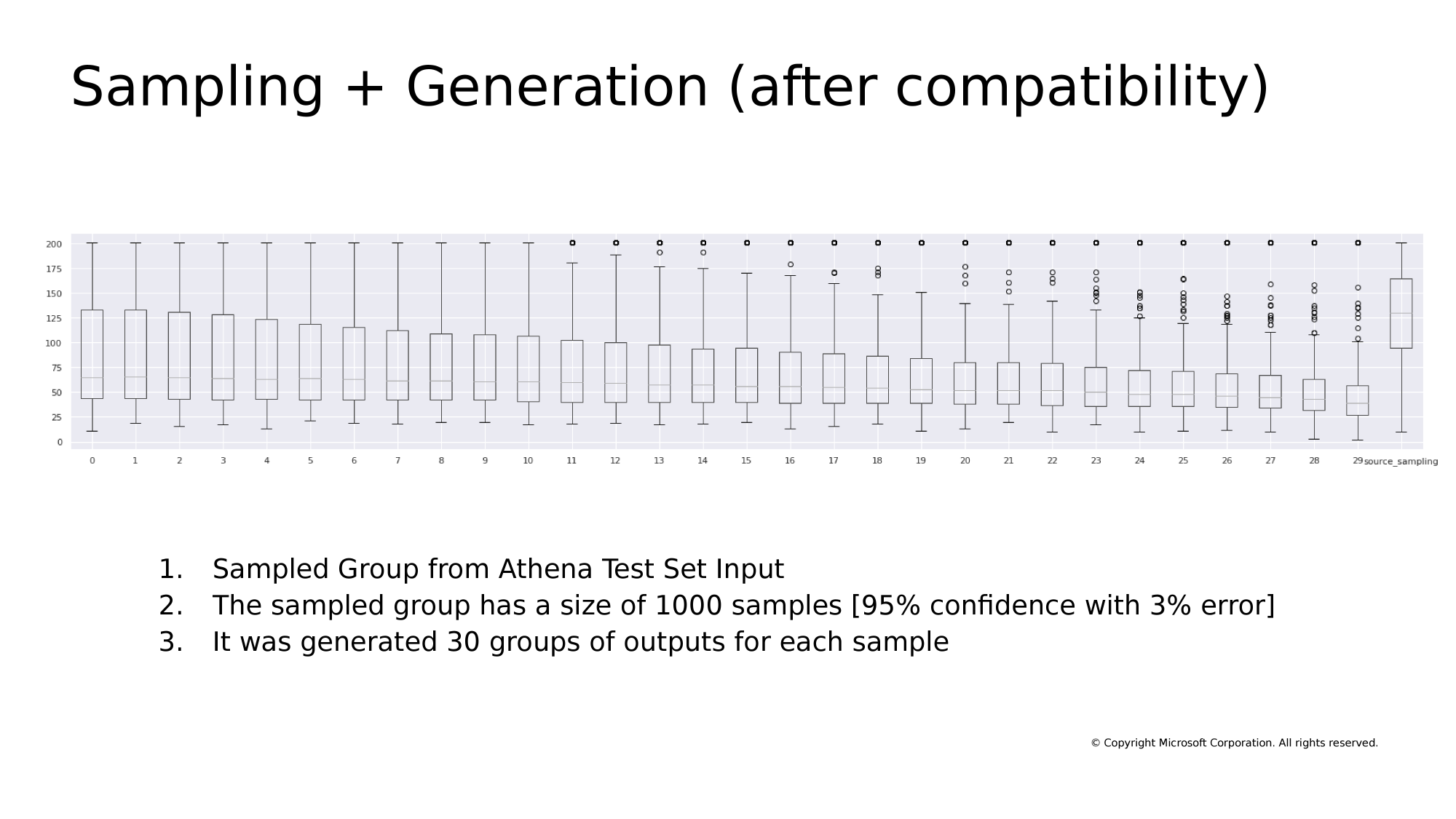
Sampling
Code Rational Process
Rationalization
Agregations
Exploration
Evaluation
Interpretability
Semantic
Non-Semantic
1
2
3
4
5
BLEU
Levenshtein
signature
docstring
sign + docs
Testbeds
fm_fc_ms_ff
fm_fc_co
fm_fc_ms
fm_fc
fm
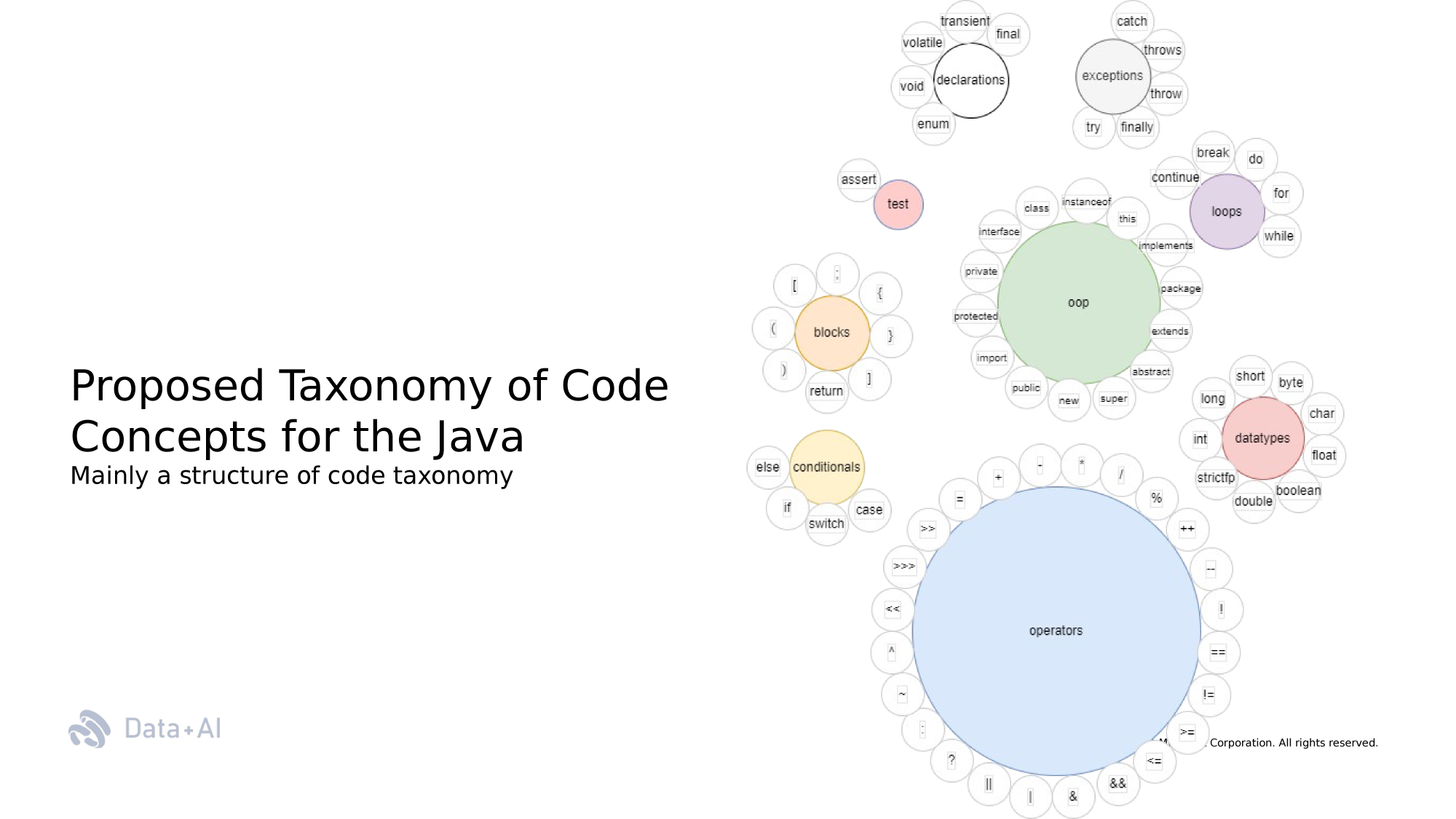
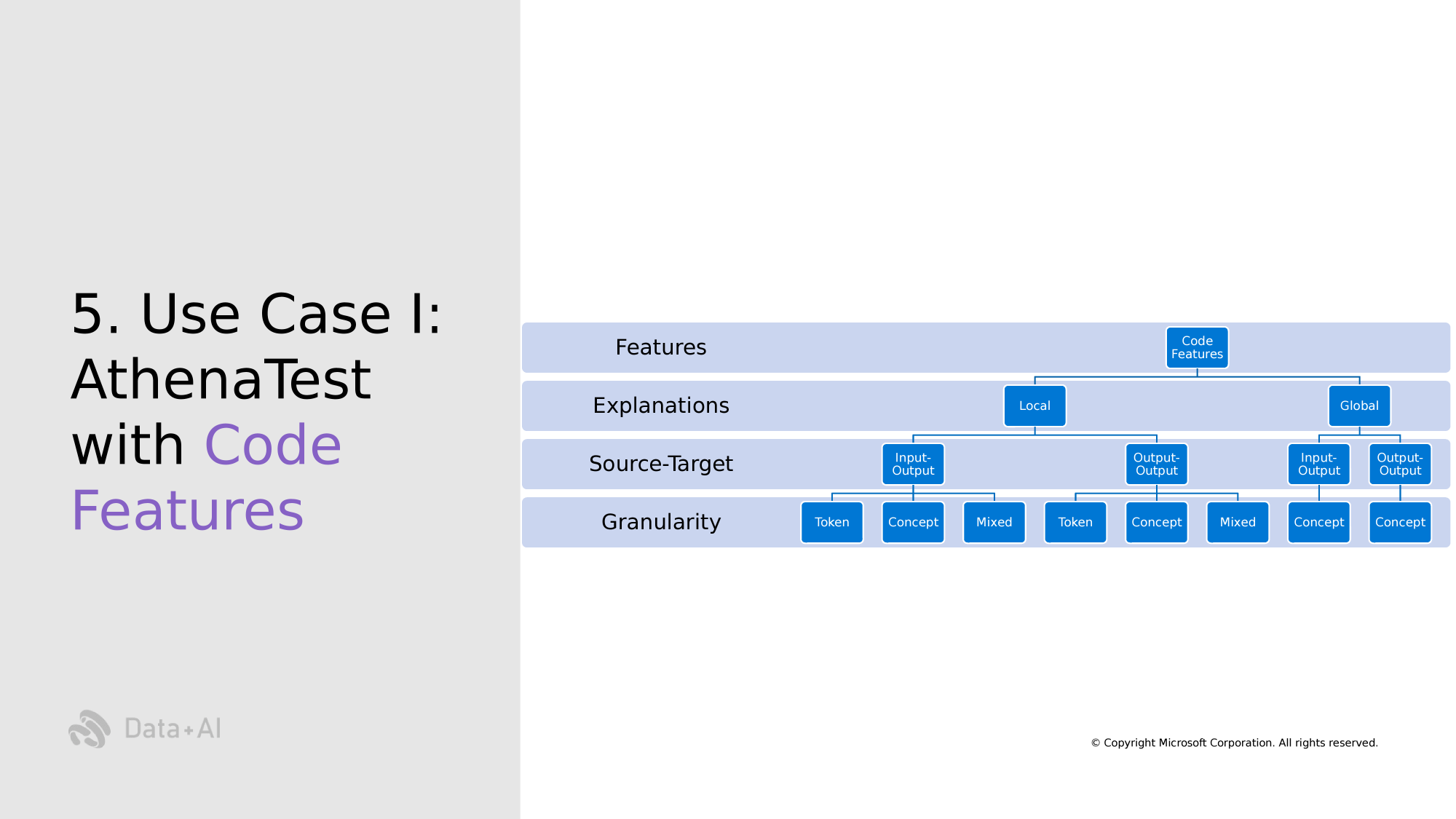
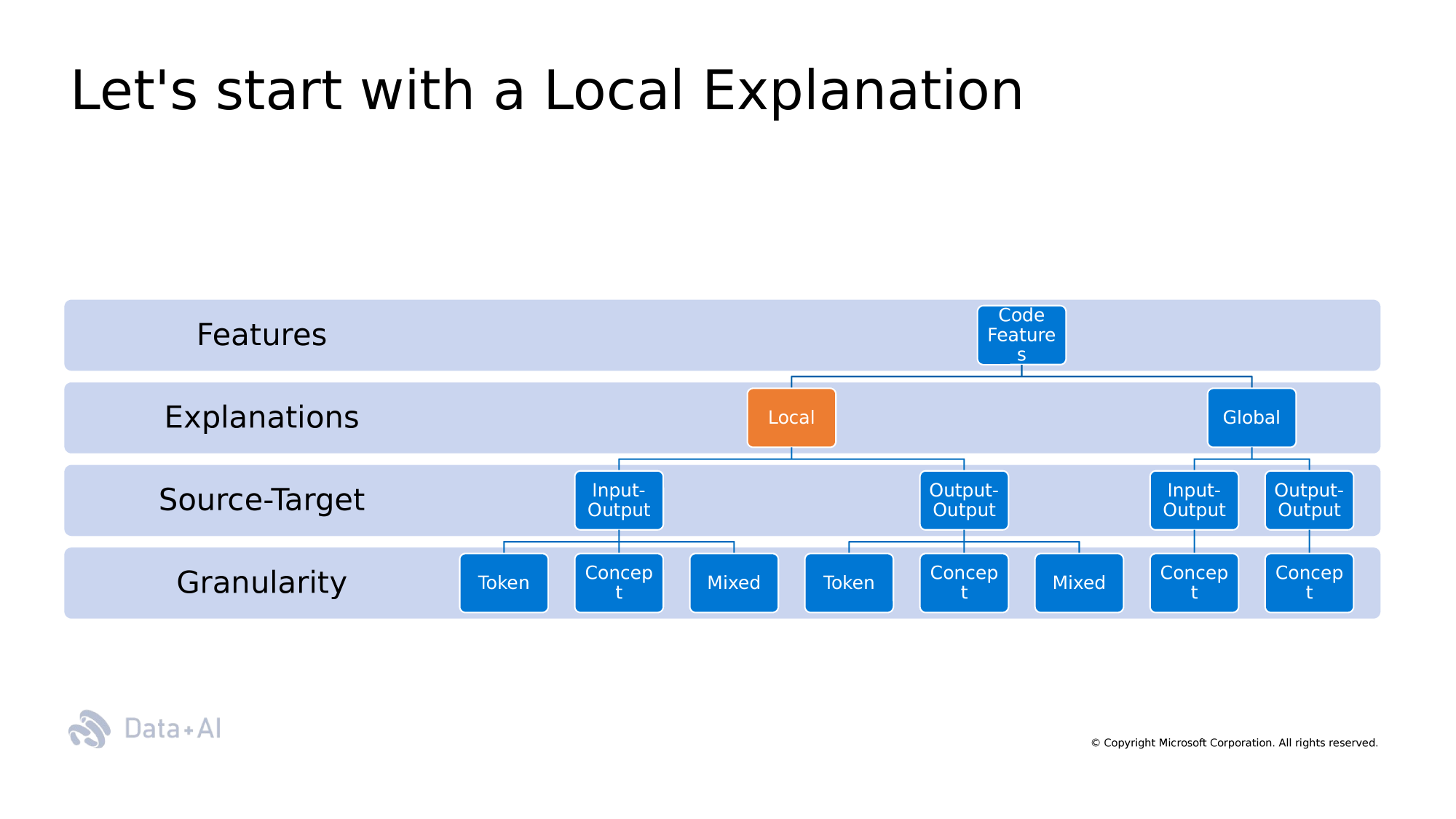
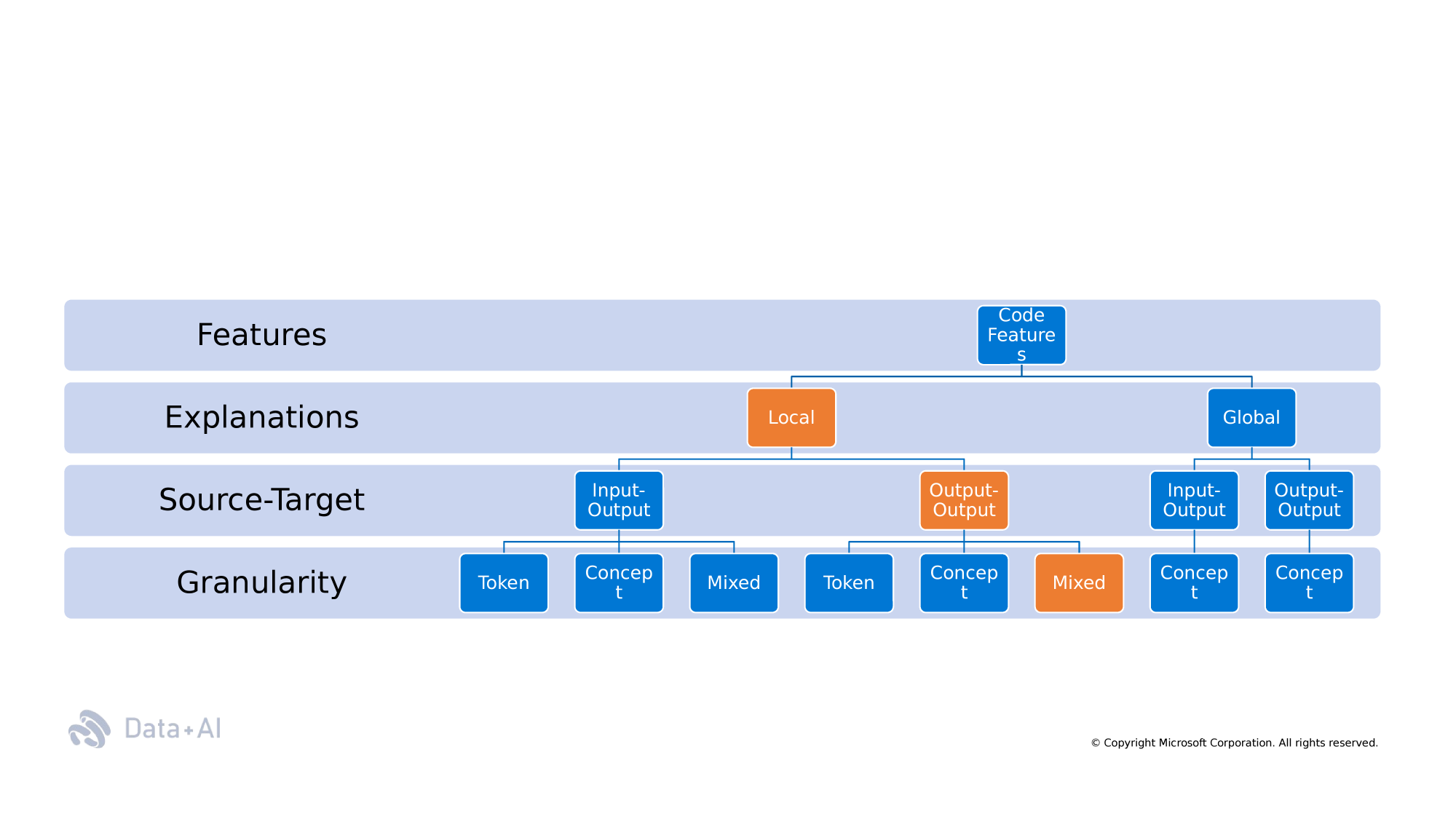
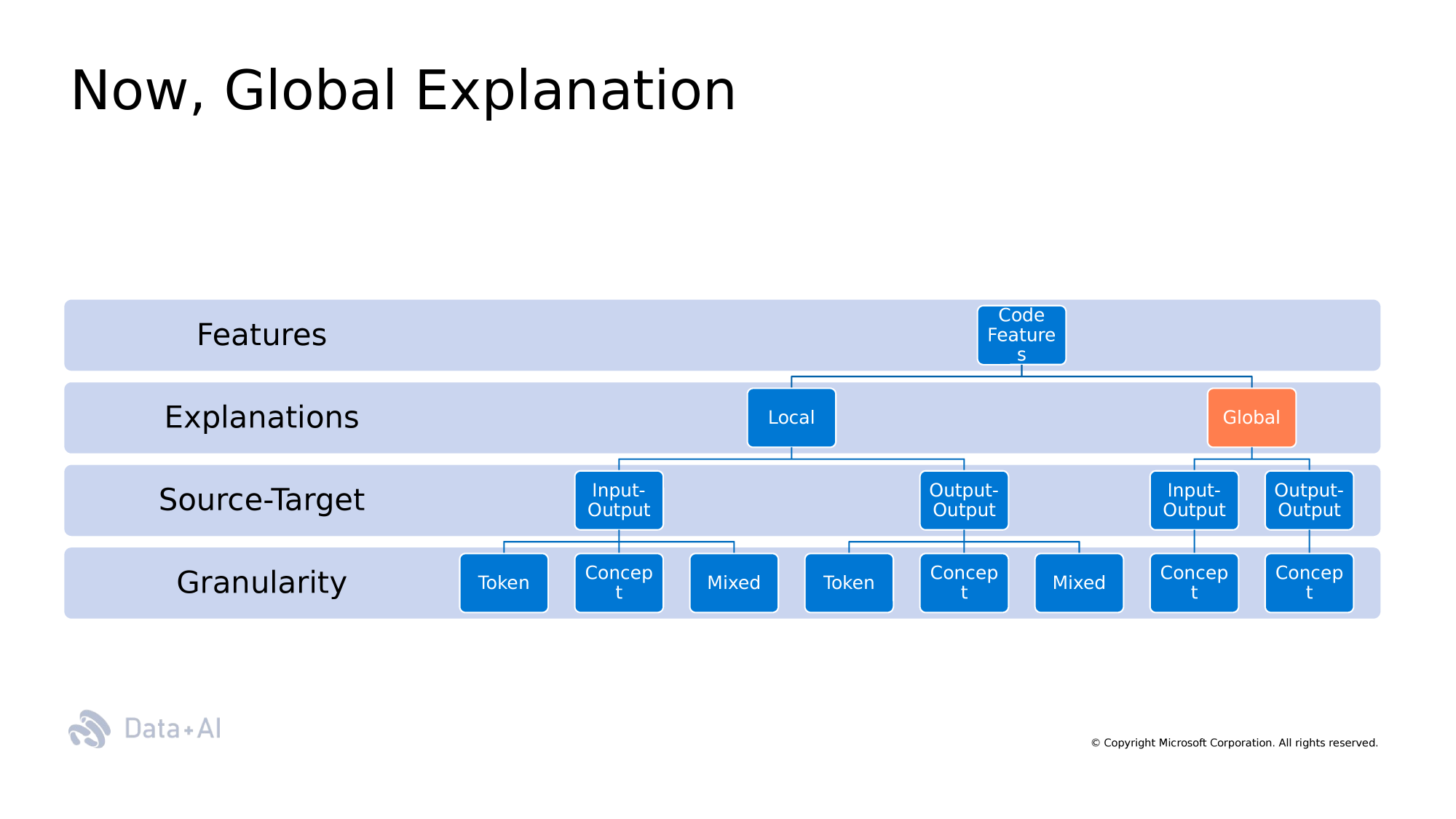
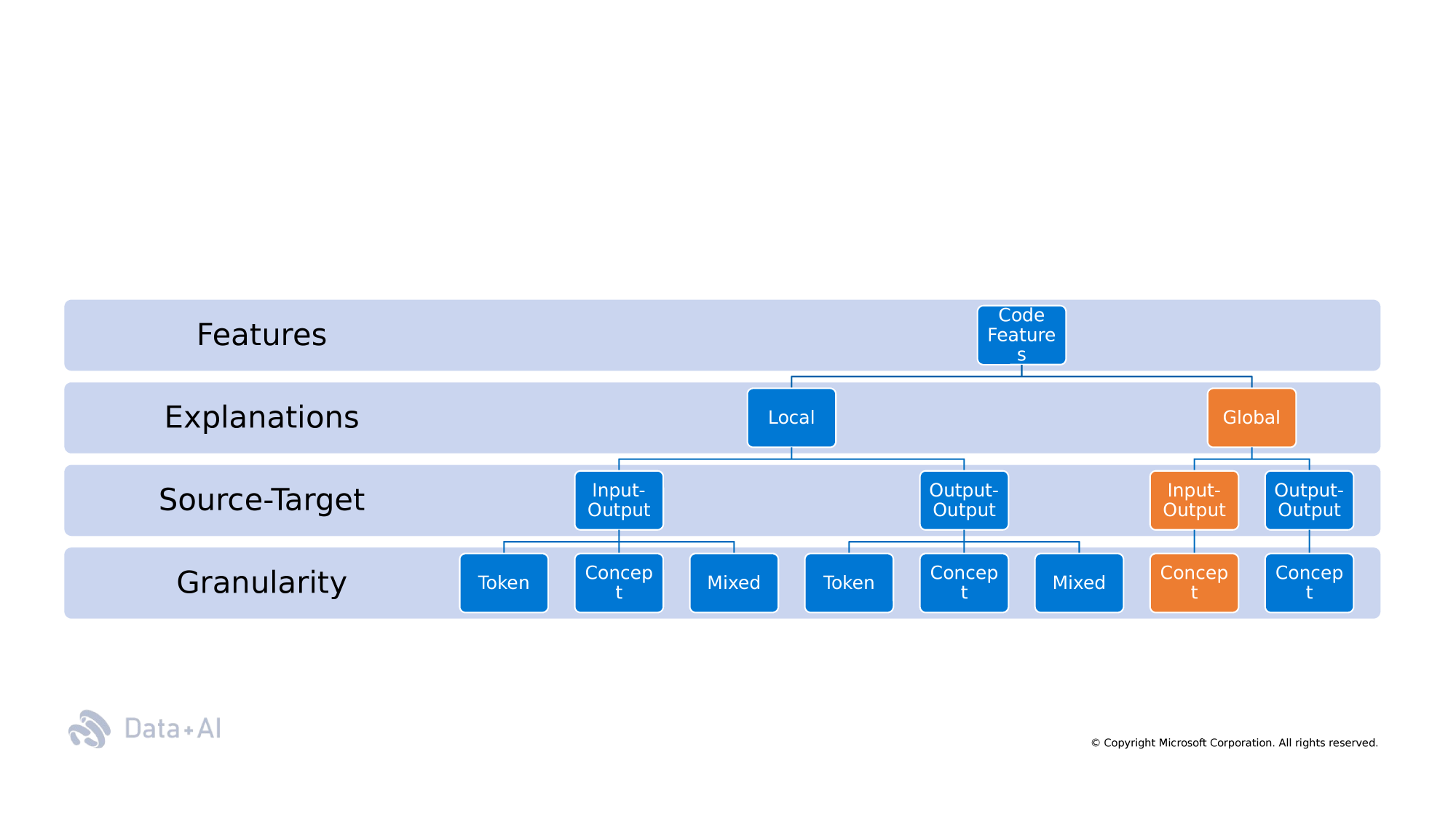
Taxonomy
completion
translation
random
Taxonomy
Semantic
Non-Semantic
types
exceptions
loops
conditionals
oop
parenthesis
semi_colon
operators
comma_dot
verbs
adjectives
nouns
asserts
<\n>
prepositions
determiners
conjunctions
identifiers
void
try
catch
throw
for
while
do
float
char
if
else
case
public
new
class
[
fair
uncountable
clever
large
countable
the
and
{
(
;
';
+
%
,
.
as
by
a
but
==
on
ask
rise
<@>
Programming Language
Natural Language
<\t>
bool
Semantic
Non-Semantic
types
exceptions
loops
conditionals
oop
operators
verb
nouns
asserts
indentation
try
catch
for
while
float
char
if
else
public
new
[
NN
VB
NNP
;
in
%
VBN
Programming Language
Natural Language
bool
\n
\t
functional
punctuation
assert
true
false
lambda
with
w_item
w_clause
return
return
structural
attribute
module
statements
assignment
expression
call
async
identifier
comment
string
errors
pronouns
WP
PRP
adverb
RB
RBR
determiner
DT
WDT
preposition
IN
TO
particle
RP
modal
MD
conjunction
CC
cardinal
CD
list
LS
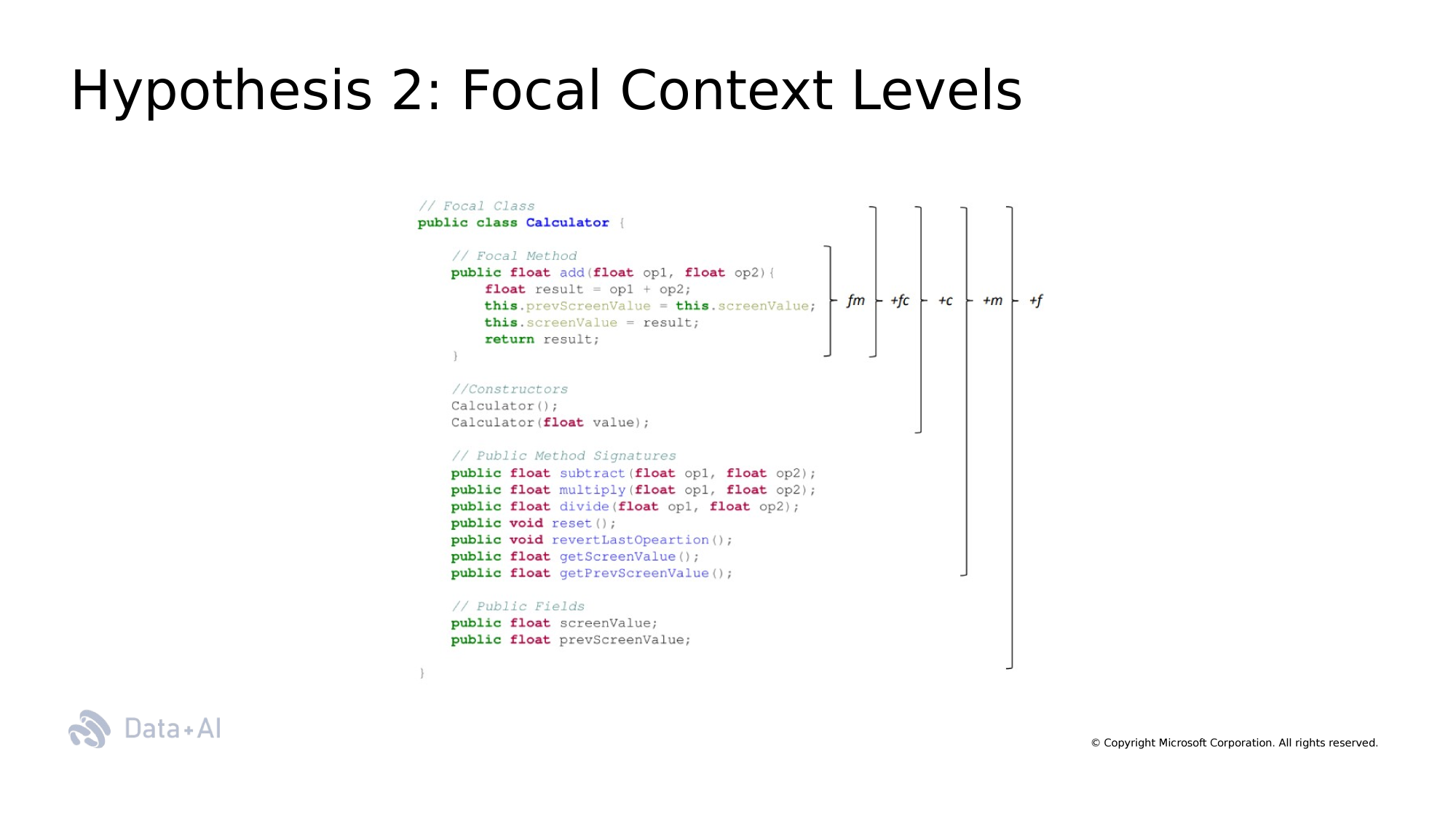
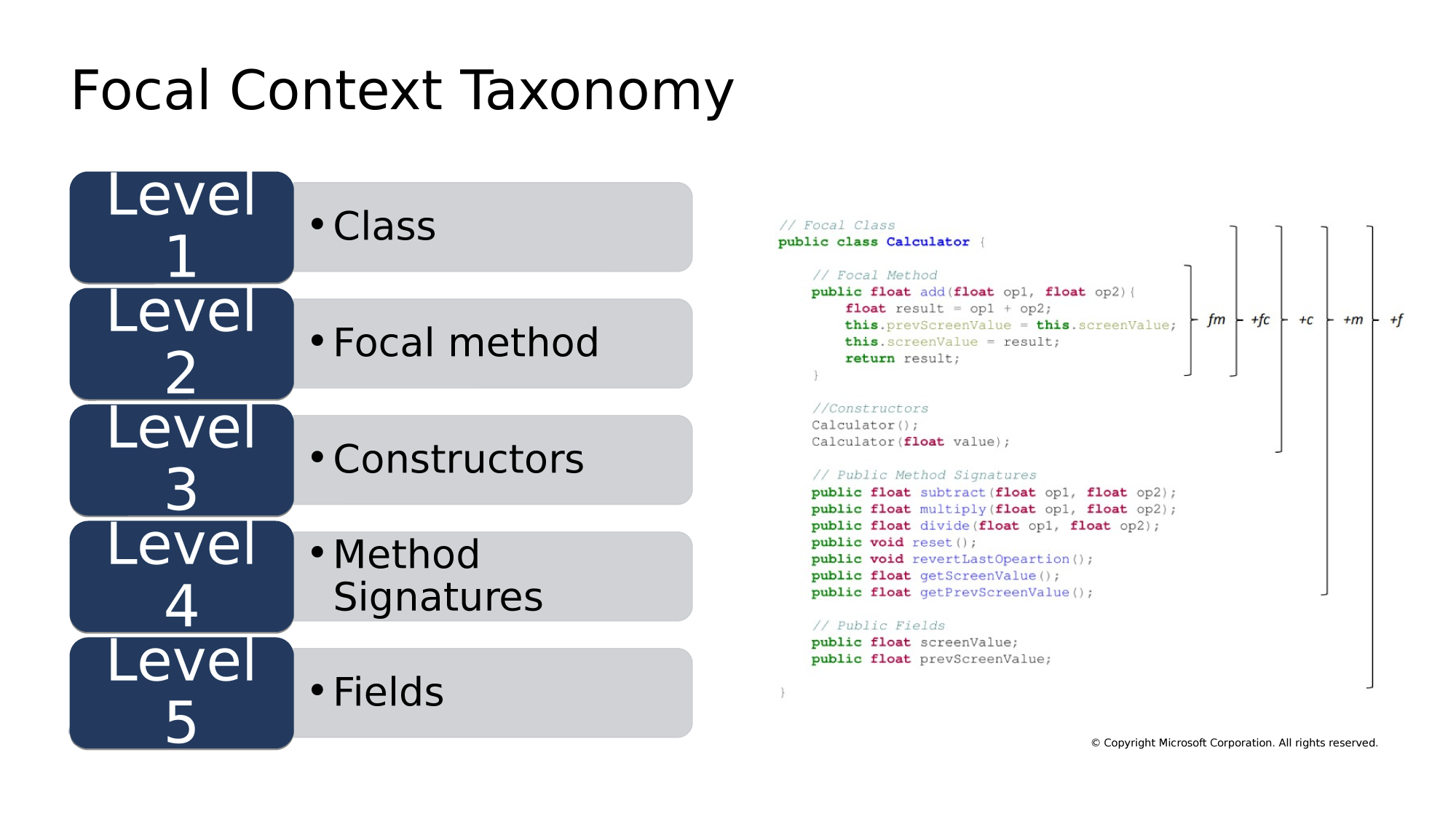
class
focal method
constructor
signature
field
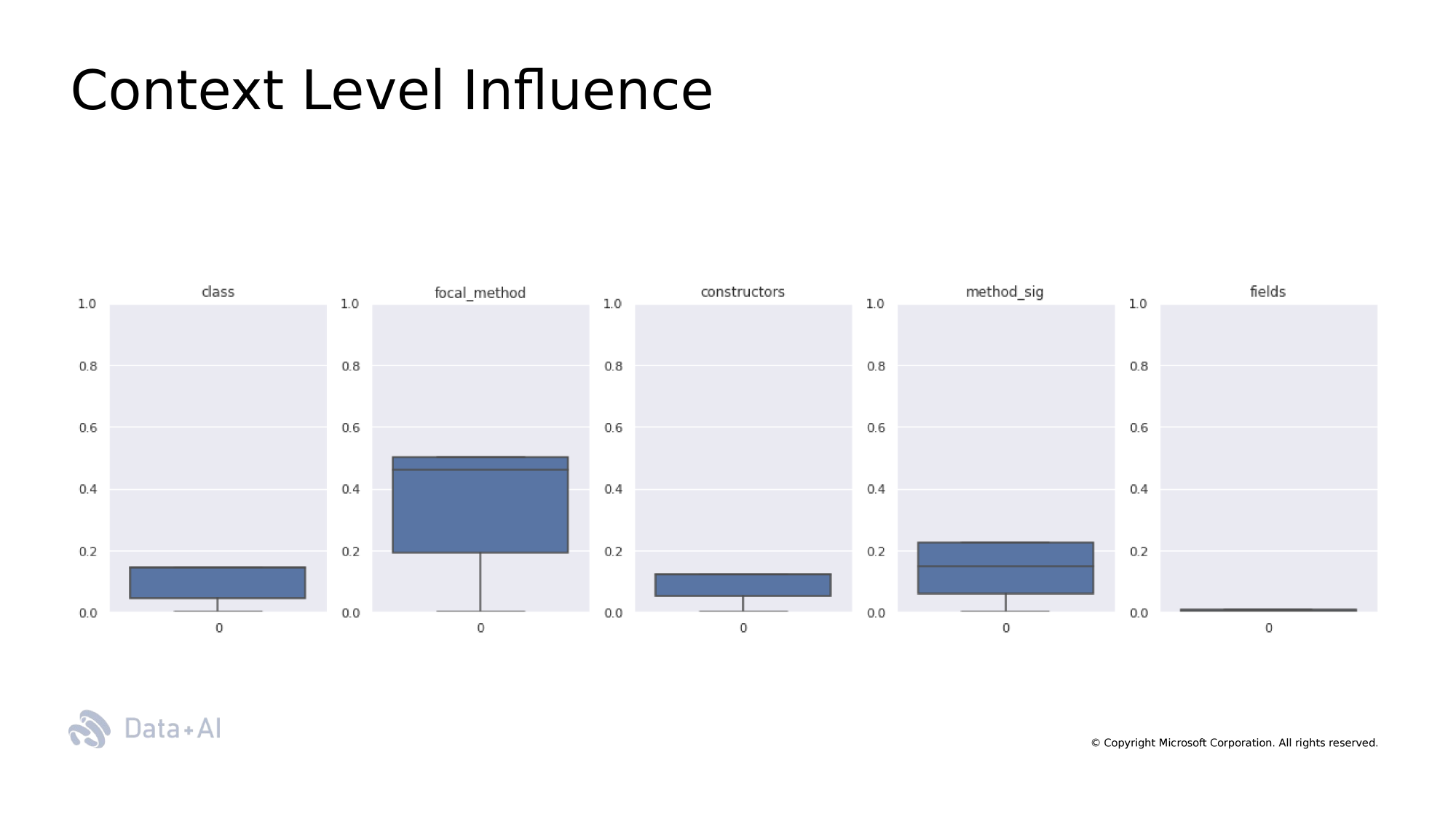
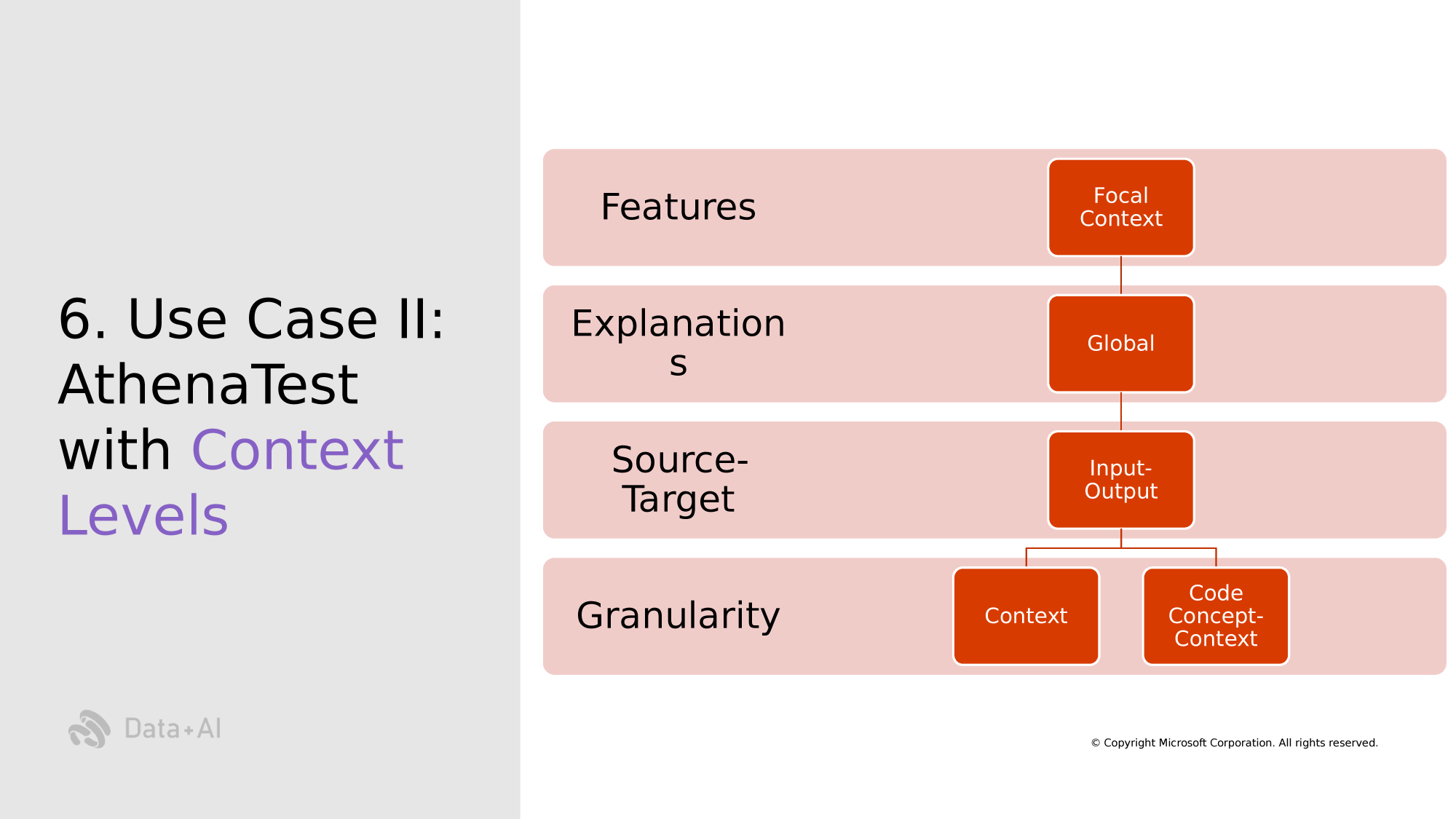
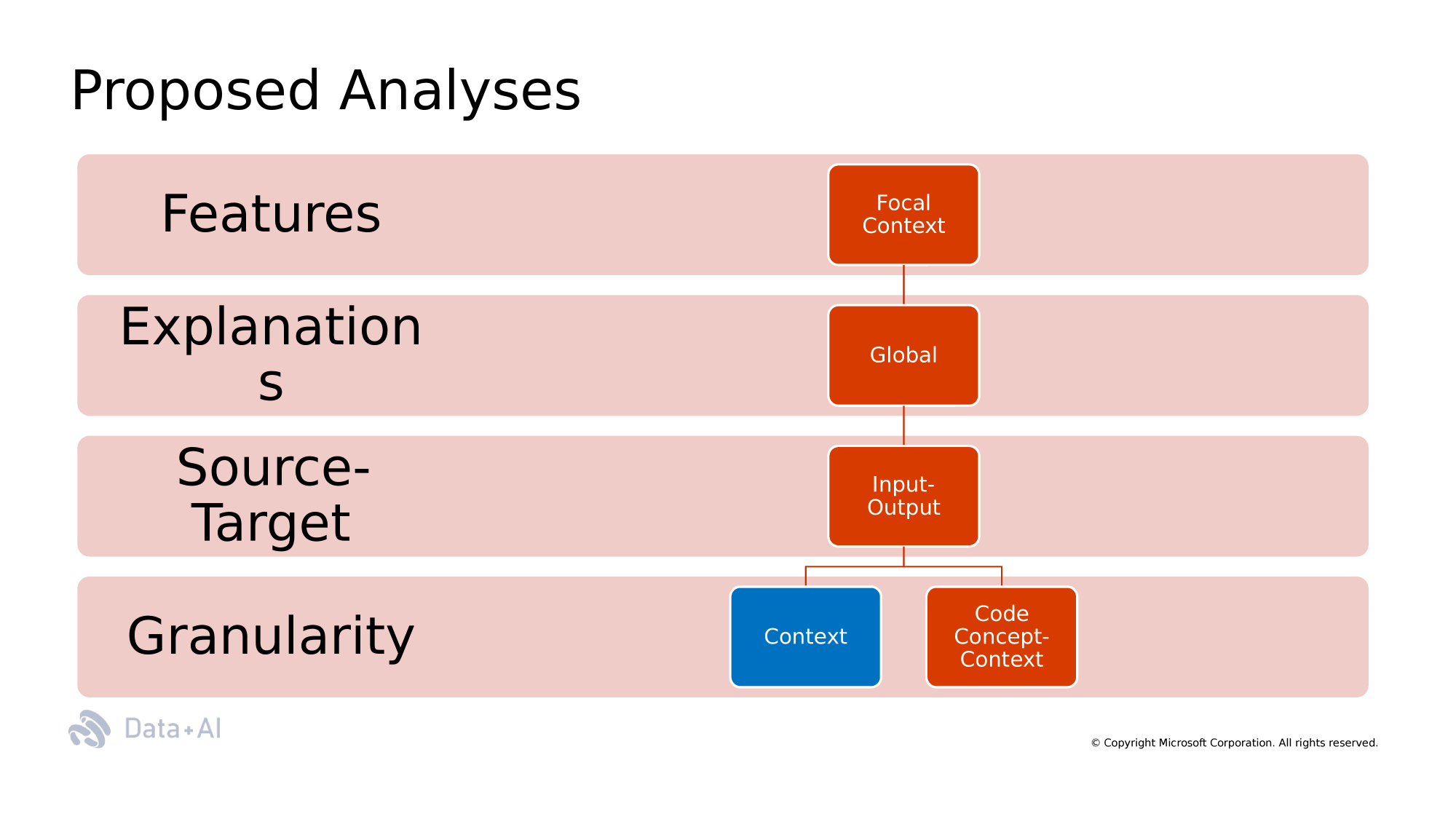
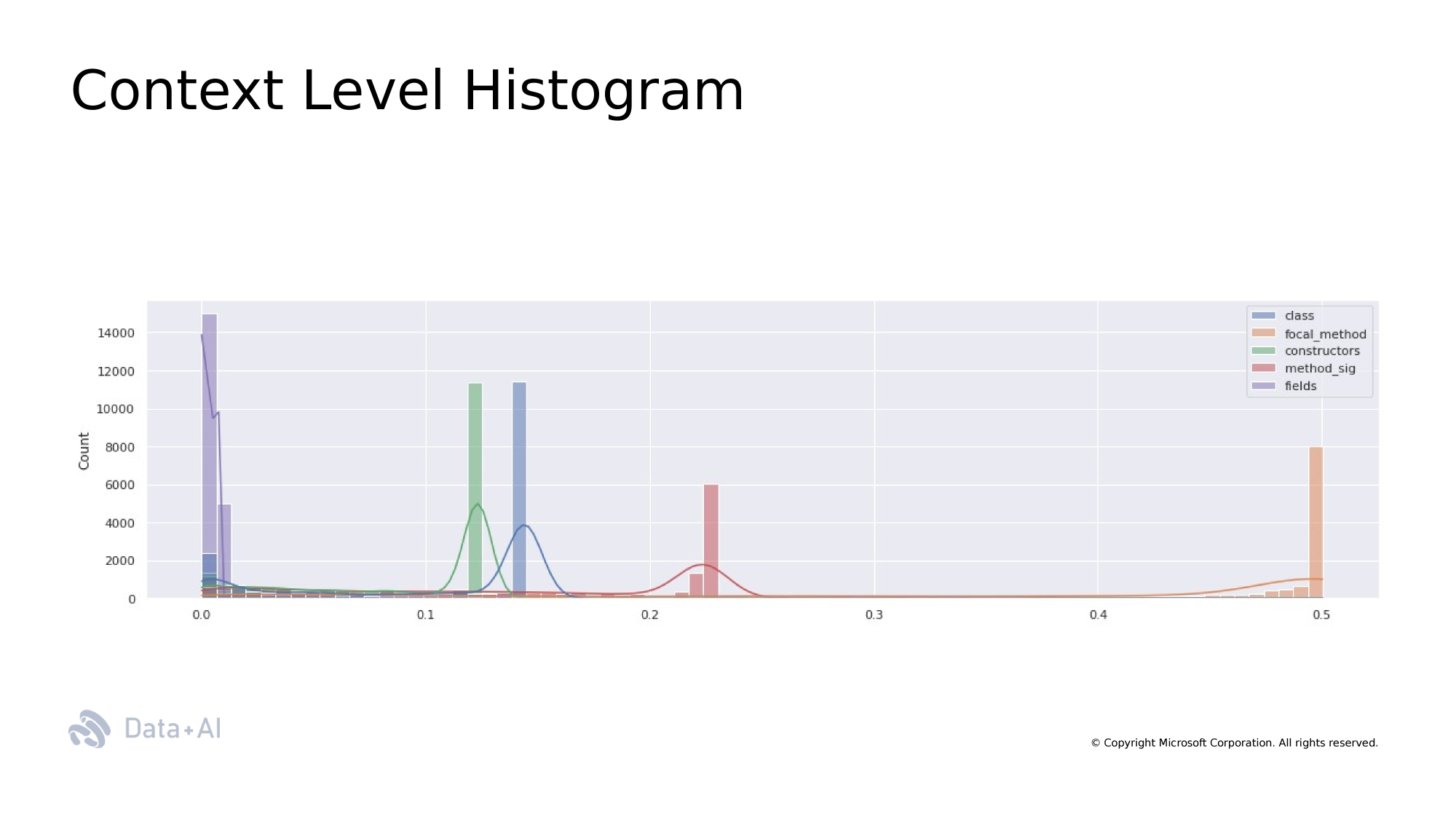
Context Windows
Semantic
Non-Semantic
types
exceptions
loops
conditionals
oop
operators
verb
nouns
asserts
indentation
try
catch
for
while
float
char
if
else
public
new
[
NN
VB
NNP
;
in
%
VBN
Programming Language
Natural Language
bool
\n
\t
functional
punctuation
assert
true
false
with
w_item
w_clause
return
structural
attribute
module
statements
assignment
expression
call
async
identifier
comment
string
errors
pronouns
WP
PRP
adverb
determiner
preposition
particle
modal
conjunction
cardinal
list
class
focal method
constructor
signature
field
Context Window
Semantic
Non-Semantic
Natural Language in Code
Syntax Error
Whole Taxonomy
def data(self)->TensorImage:
"Return this images pixels as a tensor."
return self.pxdef data(self)->TensorImage:
"Return this images pixels as a tensor."
return self.px
def __contains__(self, key, params):
...."""Generate Python code that True if this Entry has references from any AppSession.
If not, it can be removed from the cache.and signature is """
def has_refs(self) -> bool:
return len(self._session_report_run_counts) > 0"""Generate Python code that True if this Entry has references from any AppSession.
If not, it can be removed from the cache.and signature is"""
def has_refs(self) -> bool:
self.ref, self.context = None
else:def readlines(self):
#remember to close after open
f = open(self.filename, 'r')
...def readlines(self):
#remember to close after open
f = close(self.filename, 'r')
...Failure Type
Prompt (shadowed: Expected Generation)
Erroneous Generation
Case A: Code Completion
Case B: Test Case Generation
Multiple Functions
Keyword Misuse (Syntax error)
Misaligned Algorithm (Semantic error)
BalanceBooks implements Closeable {
public BalanceBooks(int totalClients, int iterations) {
this(totalClients, iterations, new ConfigurationFactory().get());
}
BalanceBooks(int totalClients, int iterations);
BalanceBooks(int totalClients, int iterations, Configuration conf);
void init();
void run();
boolean verify();
void close();
static void main(String[] args);
}@Test
public void testBalanceBooks() throws Exception {
BalanceBooks bb = new BalanceBooks(5, 100, testUtil.getConfiguration());
try {
bb.init();
bb.run();
assertTrue(bb.verify());
} finally {
bb.close();
}
}@Test
public void testBalanceBooks() throws Exception {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
BalanceBooks book = new BalanceBooks(i);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
book.add(new BalanceBooks(i, i));
}
book.add(new BalanceBooks(i, i));
book.add(new BalanceBooks(i, i));Prompt
Expected Test
Erroneous Generation
Repetitive Generation
"""Generate Python code that True if this Entry has references from any AppSession.
If not, it can be removed from the cache.and signature is """
def has_refs(self) -> bool:
return len(self._session_report_run_counts) > 0"""Generate Python code that True if this Entry has references from any AppSession.
If not, it can be removed from the cache.and signature is"""
def has_refs(self) -> bool:
self.ref, self.context = None
else:def readlines(self):
#remember to close after open
f = open(self.filename, 'r')
...def readlines(self):
#remember to close after open
f = close(self.filename, 'r')
...Failure Type
Prompt 1 (Highlighted: Lines 1-3)
(Expected Generation: Line 4)
Erroneous Generation: Line 3
Case A: Code Completion
Case B: Test Case Generation
Keyword Misuse (Syntax error)
Misaligned Algorithm (Semantic error)
FindLongestConsecutiveSequence {
public int findRecursive(int[] array) {
validateInput(array);
return findRecursiveInner(array, 1, 0, 0);
}
int findIterative(int[] numbers);
int findRecursive(int[] array);
}@Test
public void shouldFindLongestConsecutiveSequenceRecursive() {
int[] array = {1, 3, 4, 5, 64, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 98, -1, -2};
int sequenceLength = lcs.findRecursive(array);
assertEquals(7, sequenceLength);
}@Test
public void shouldFindLongestConsecutiveSequenceRecursive() {
int[] array = {1, 3, 4, 5, 64, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 98, -1, -2};
int sequenceLength = lcs.findIterative(array);
assertEquals(7, sequenceLength);
}Input
Expected Test
Erroneous Generation
Repetitive Generation
Erroneous Generation: Line 5
Prompt 2 (Highlighted: Lines 1-2)
(Expected Generation: Line 3)
Semantic
Non-Semantic
types
exceptions
loops
conditionals
oop
operators
verb
nouns
asserts
indentation
try
catch
for
while
float
char
if
else
public
new
[
NN
VB
NNP
;
in
%
VBN
Programming Language
Natural Language
bool
\n
\t
functional
punctuation
assert
true
false
with
w_item
w_clause
return
structural
attribute
module
statements
assignment
expression
call
async
identifier
comment
string
errors
pronouns
WP
PRP
adverb
determiner
preposition
particle
modal
conjunction
cardinal
list
class
focal method
constructor
signature
field
Context Window
Semantic
Non-Semantic
Natural Language in Code
Syntax Error
Deep Code Generation Case Studies
Code-Based Rationalization
1
2
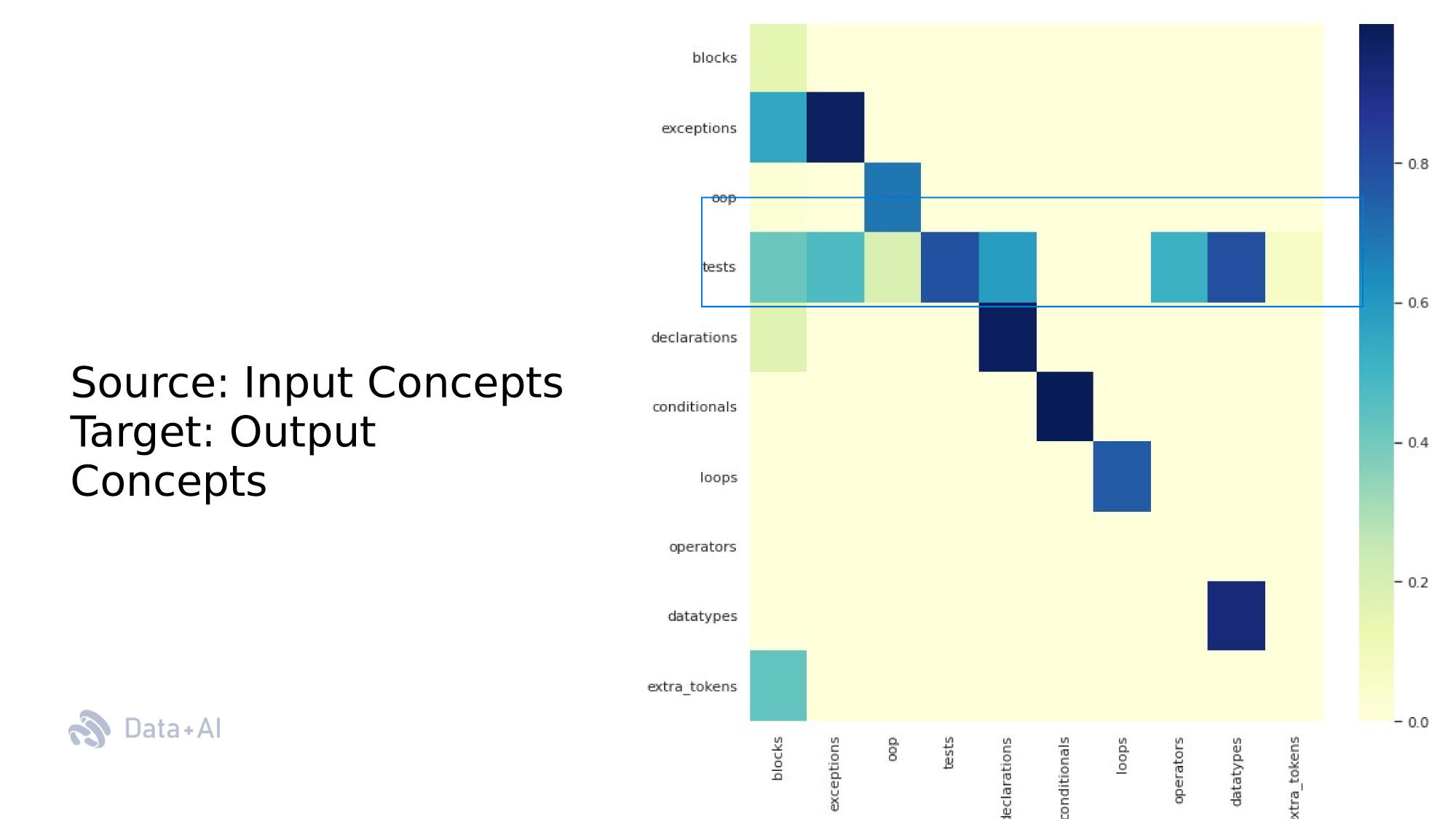
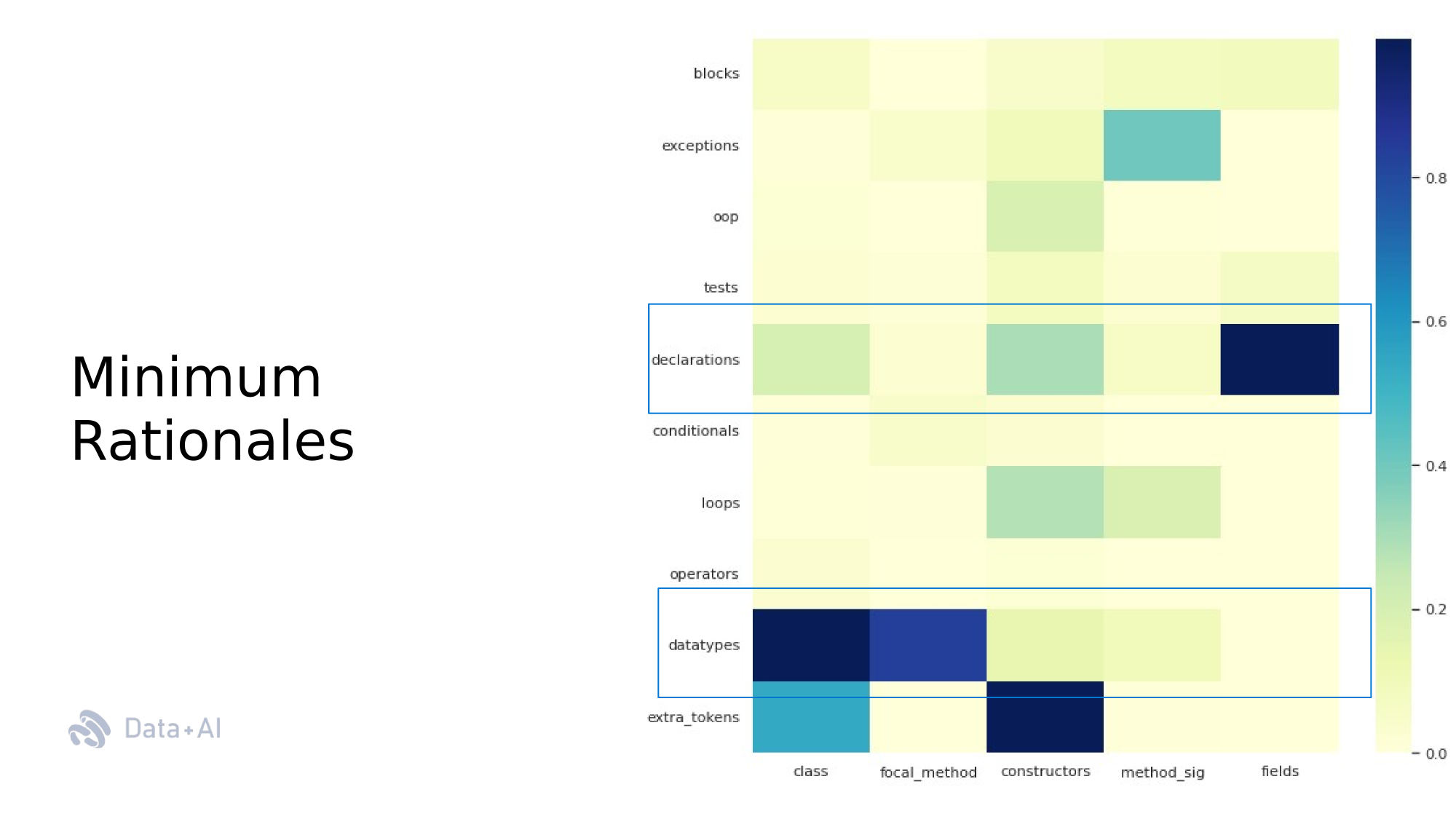
Dependency Map of Rationales
structural
Statements
Semantic
[ else ]
Concept View
Rationales
Generated Token
self
context
\n
context
self
Natural Language in Code
identifier
Non-Semantic
operator
=
Programming Language
Natural Language
Python
noun
Semantic
Non-Semantic
preposition
If
if
Code Completion
""" Generate Python code that True if this Entry has references from any AppSession.
If not, it can be removed from the cache.and signature is """
def has_refs(self) -> bool: \n
self.ref, self.context = NoneRational Positions
"""Generate Python code that True if this Entry has references from any AppSession.
If not, it can be removed from the cache.and signature is"""
def has_refs(self) -> bool:
self.ref, self.context = None
else:Rationales Dependency Map
structural
statements
Semantic
else
self
context
\n
Natural Language in Code
identifier
Non-Semantic
operator
=
Programming Language
Natural Language
Python
noun
Semantic
Non-Semantic
preposition
If
if
"""Generate Python code that True if this Entry has references from any AppSession.
If not, it can be removed from the cache.and signature is"""
def has_refs(self) -> bool: [\n]
self.ref, self.context = None
else:Prompt 1
module
statements
function
string
identifier
parameters
identifier
type
identifier
block
statements
assignments
pattern_list
identifier
Concept View
Syntax Code Concepts
Generated Token
FindLongestConsecutiveSequence {
public int findRecursive(int[] array) {
validateInput(array);
return findRecursiveInner(array, 1, 0, 0);
}
FindLongestConsecutiveSequence();
int findIterative(int[] numbers);
int findRecursive(int[] array);
public float sequence;
}Focal Method
Class
Constructor
Method Signatures
Fields
Rationales
AST-Based
Context Window
Dependency Map of Rationales
Method Signature
[ findIterative ]
Context View
Generated Token
Source Rationales
Target Rationals
.
Test Case Generation
Source Rational
find
Target Rational and Position
Iterative
Source Rational and Position
@Test
public void shouldFindLongestConsecutiveSequenceRecursive() {
int[] array = {1, 3, 4, 5, 64, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 98, -1, -2};
int sequenceLength = lcs.FindLongestConsecutiveSequence {
public int findRecursive(int[] array) {
validateInput(array);
return findRecursiveInner(array, 1, 0, 0);
}
int findIterative(int[] numbers);
int findRecursive(int[] array);
}Dependency Map of Rationales
types
exceptions
asserts
conditionals
oop
else
if
default
Semantic
[ if ]
Concept View
Rationales
Generated Token
float
char
int
class
private
instanceof
try
catch
assert
Natural Language in Code
identifier
string
var_1
'sql comment'
Non-Semantic
indentation
\t
punctuation
,
Programming Language
Natural Language
run
test
verb
Semantic
Non-Semantic
determiner
the
a
Artificial Code Generation is the automatic construction of code by means of Large Language Models; we hypothesize that LLMs might be substantially better at "statistically learning" SE tasks
Neural Network
Program
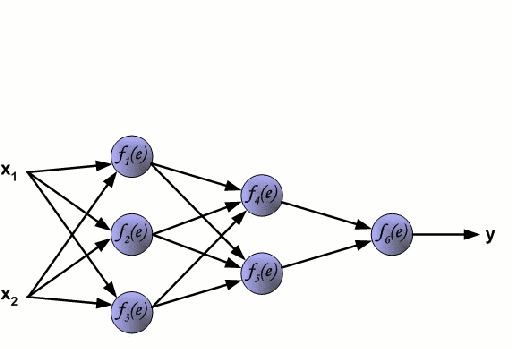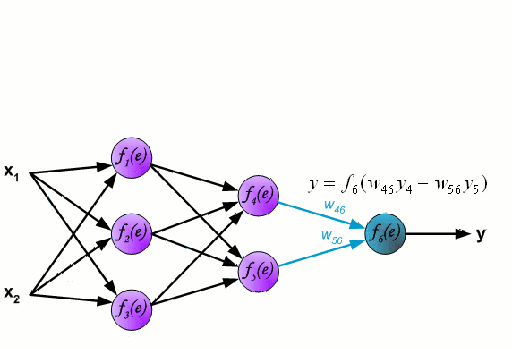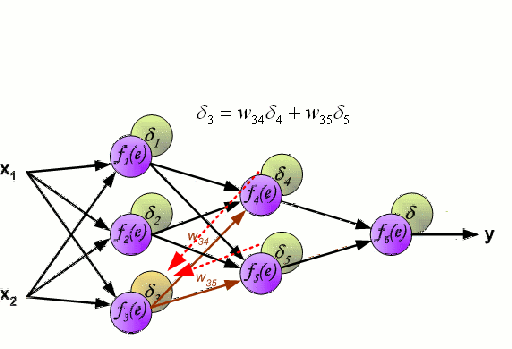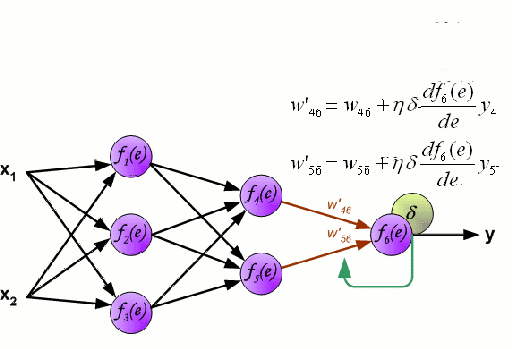

Artificial Code Generation subtasks:
- Code Completion
- Code Summarization
- Commit Message Generation
- Test Case Generation
- Bug Fixing
- Injection Code Mutant
- Assert Generation
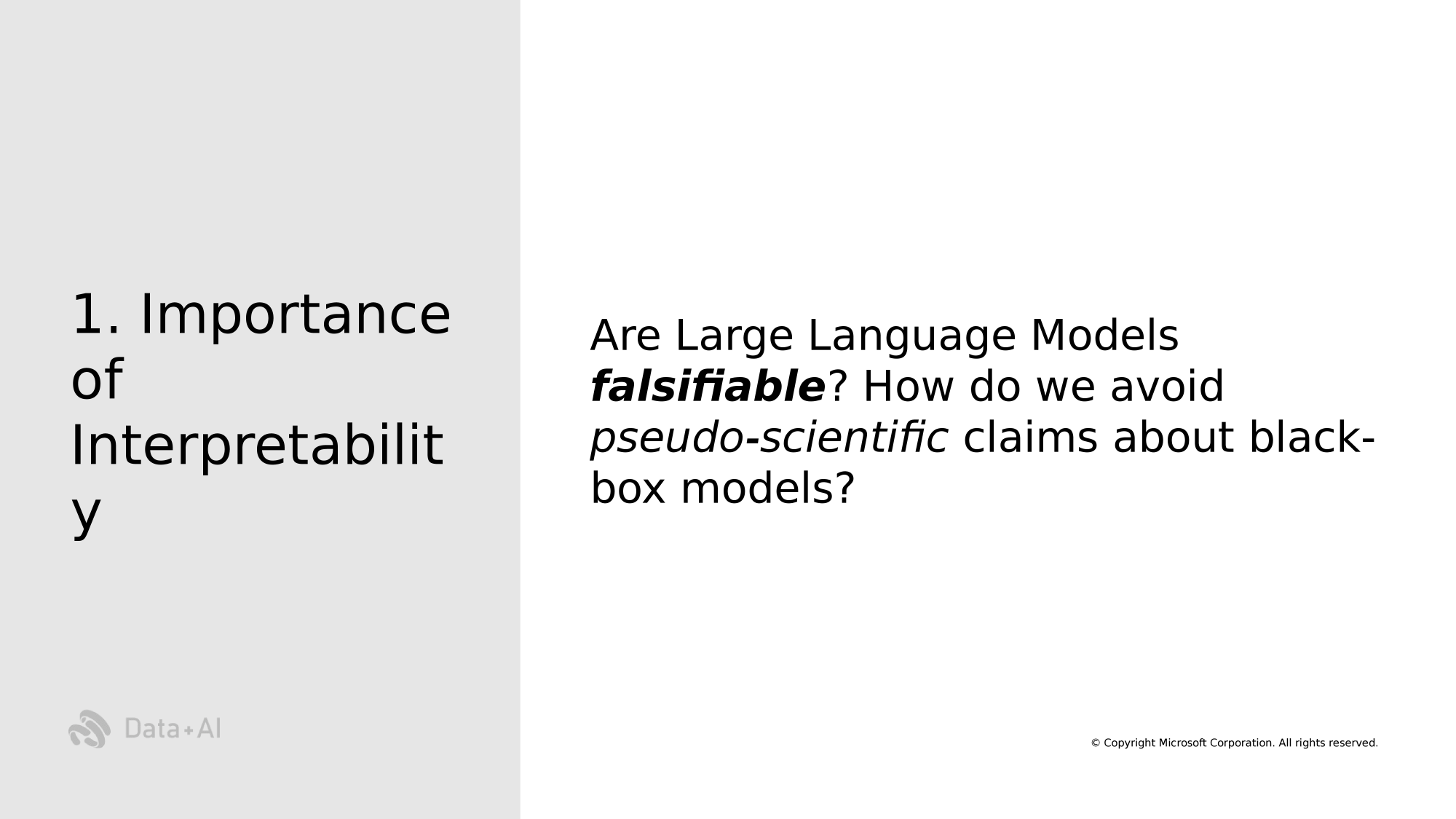
Importance of Interpretability in Artificial Code Generation
How can we make Large Language Models for Code (LLMc) falsifiable?
"Capacity to be proven wrong" ~K. Popper
What is interpretability?
Interpretability is the extent to which a cause and effect can be observed within a system. It is the extent to which you are able to predict what is going to happen, given a change in input or algorithmic parameter (Molnar, 2021)
What is interpretability?
Interpretability is the extent to which a cause and effect can be observed within a system. It is the extent to which you are able to predict what is going to happen, given a change in input or algorithmic parameter (Molnar, 2021)
Interpretability is a measure of the causal effect between the input of a model (i.e., prompt) and the observable output (i.e., autocompleted code)
Reasons for Interpretability
- [goal of science] Interpretability makes it possible to extract knowledge captured by ML models.
- [bias] Interpretability is a useful debugging tool for detecting bias.
- [reliability] Interpretability increases social acceptance of ML models.
- [debugging] Interpretability allows ML models to be debugged and audited.
A single metric, such as classification accuracy, is an incomplete description of most real-world (Software Engineering) tasks
~Doshi-Velez and Kim, 2017
Problem Statement
For certain Software Engineering Tasks, such as Artificial Code Generation, it is not enough to get the prediction (the what). The LLM must also explain how it came to the prediction (the why) because a correct prediction only partially solves the original problem.
Our Approach
CodeRational

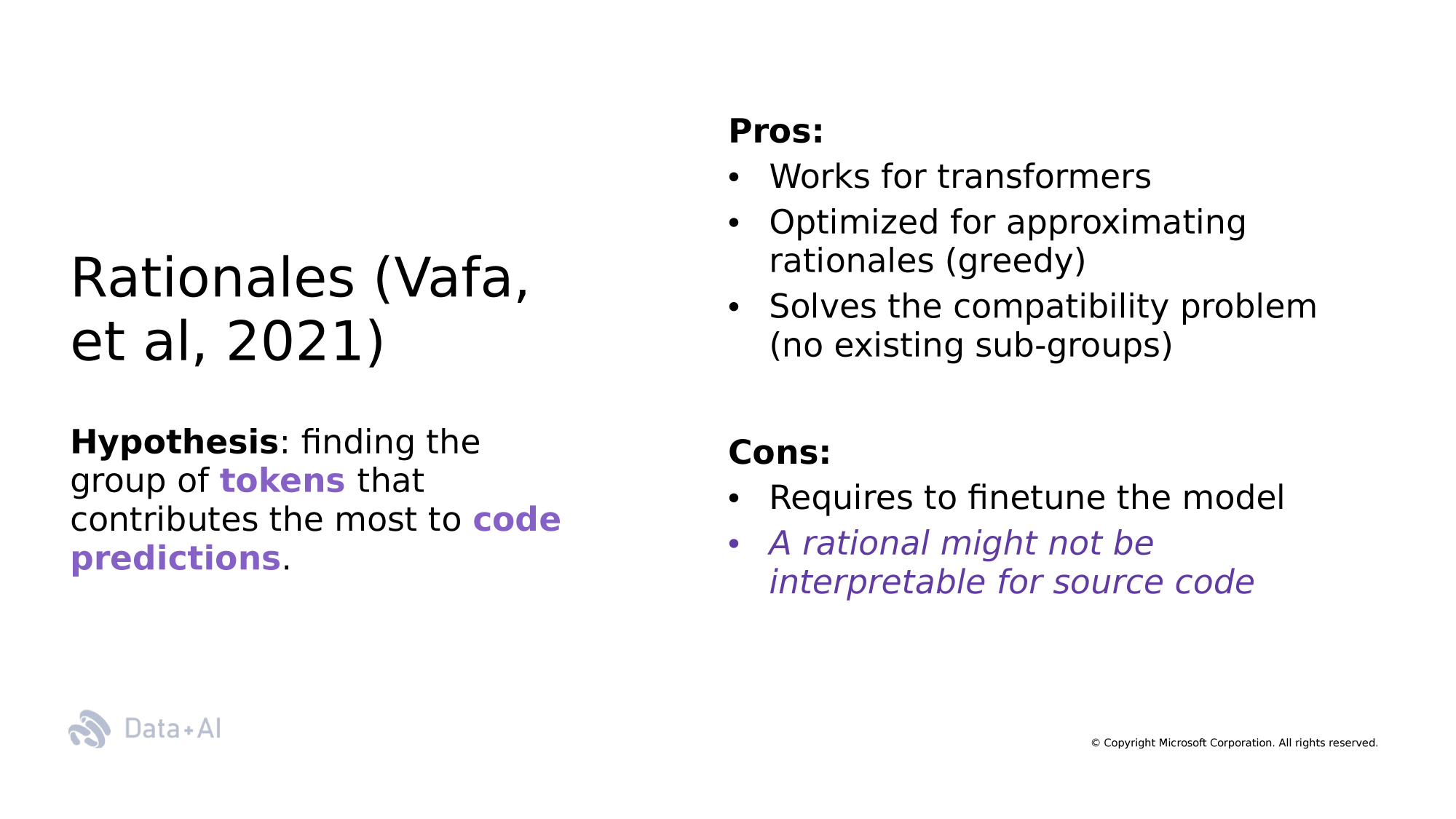
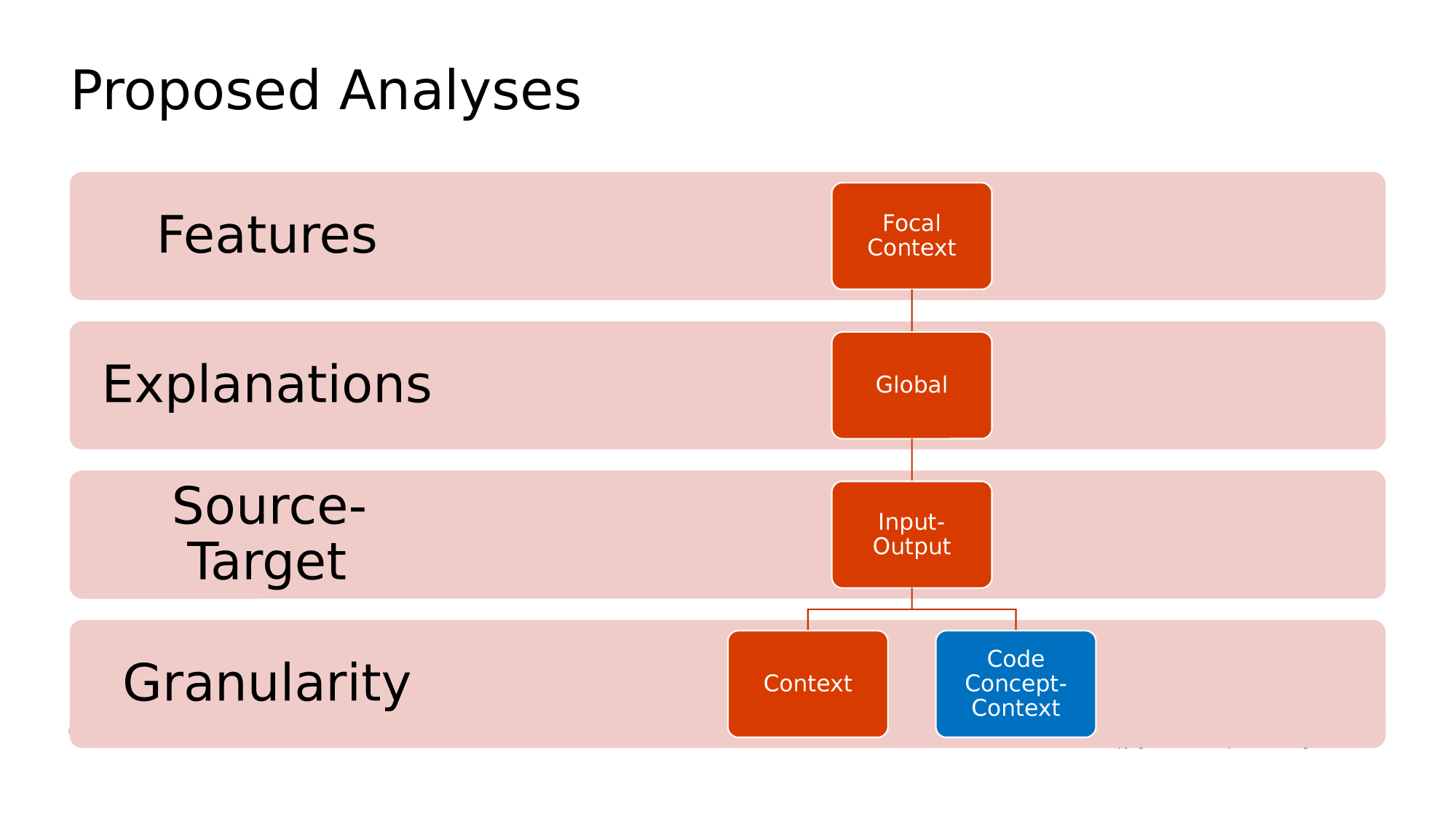
[RQ1] Which group of tokens (rationales) explain the Next Token Predictions?
[RQ1] Which group of tokens (rationales) explain the Next Token Predictions?
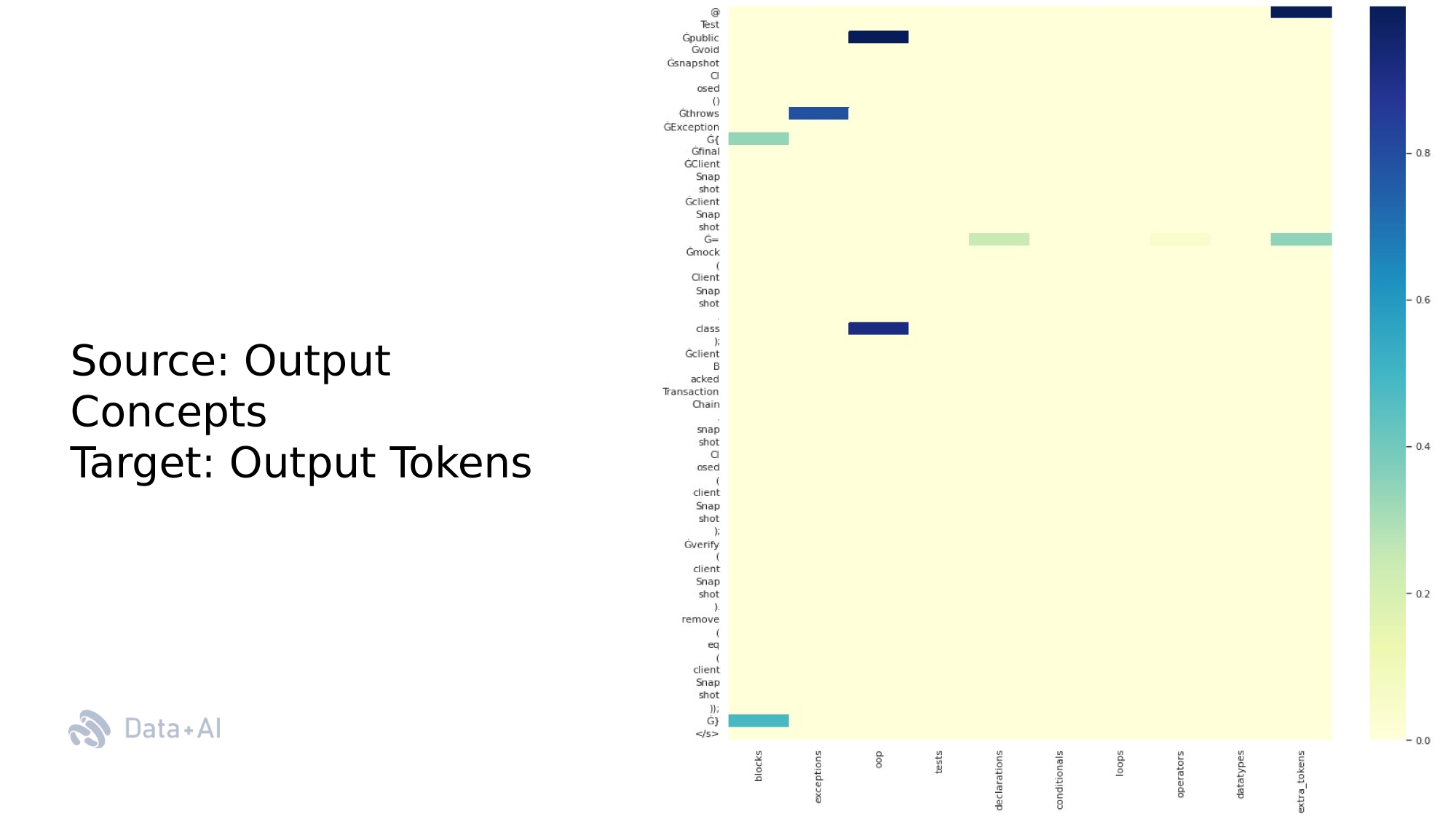
Which features in the prompt explain artificial test cases?
SE Task: Test Case Generation
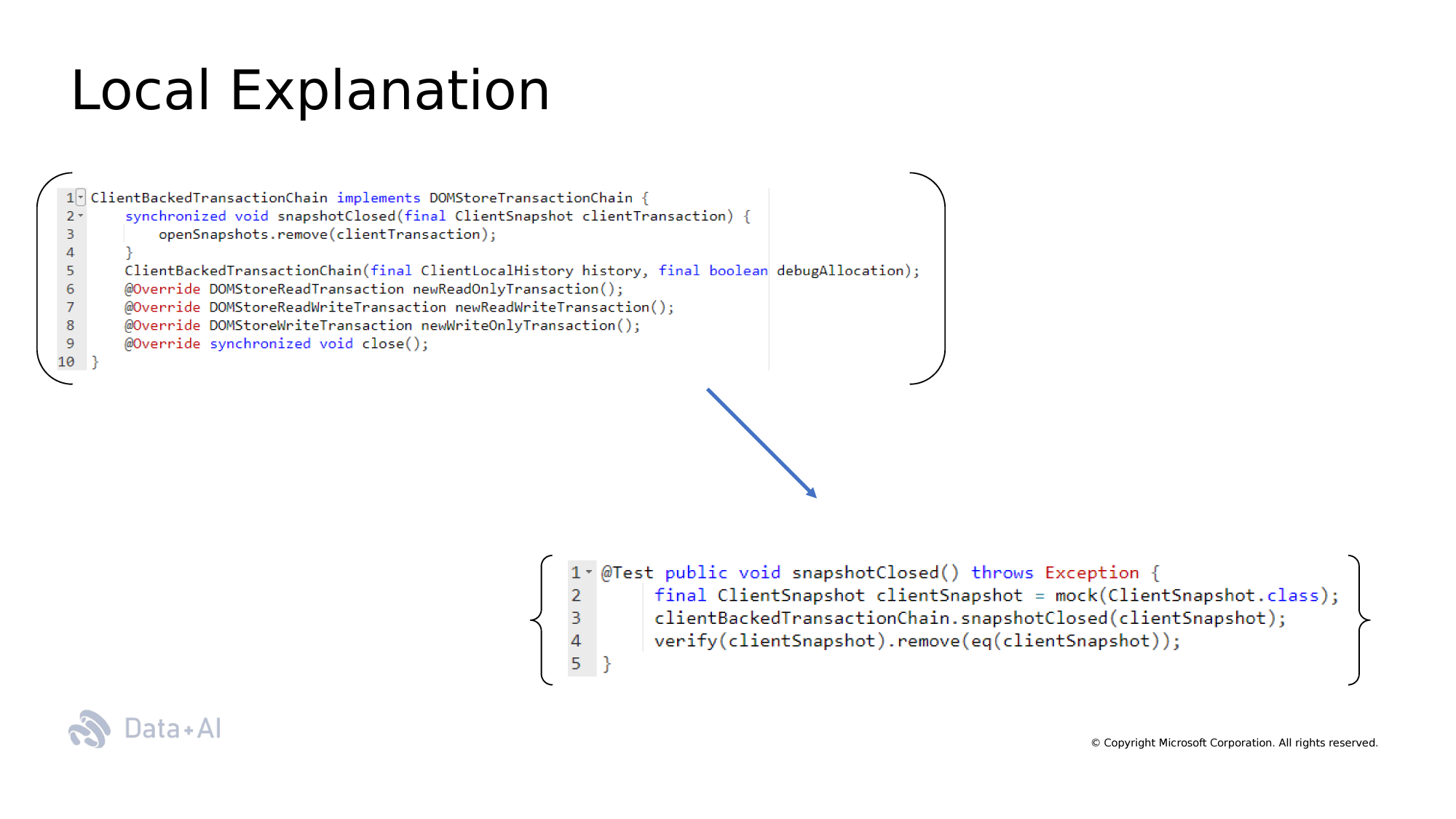
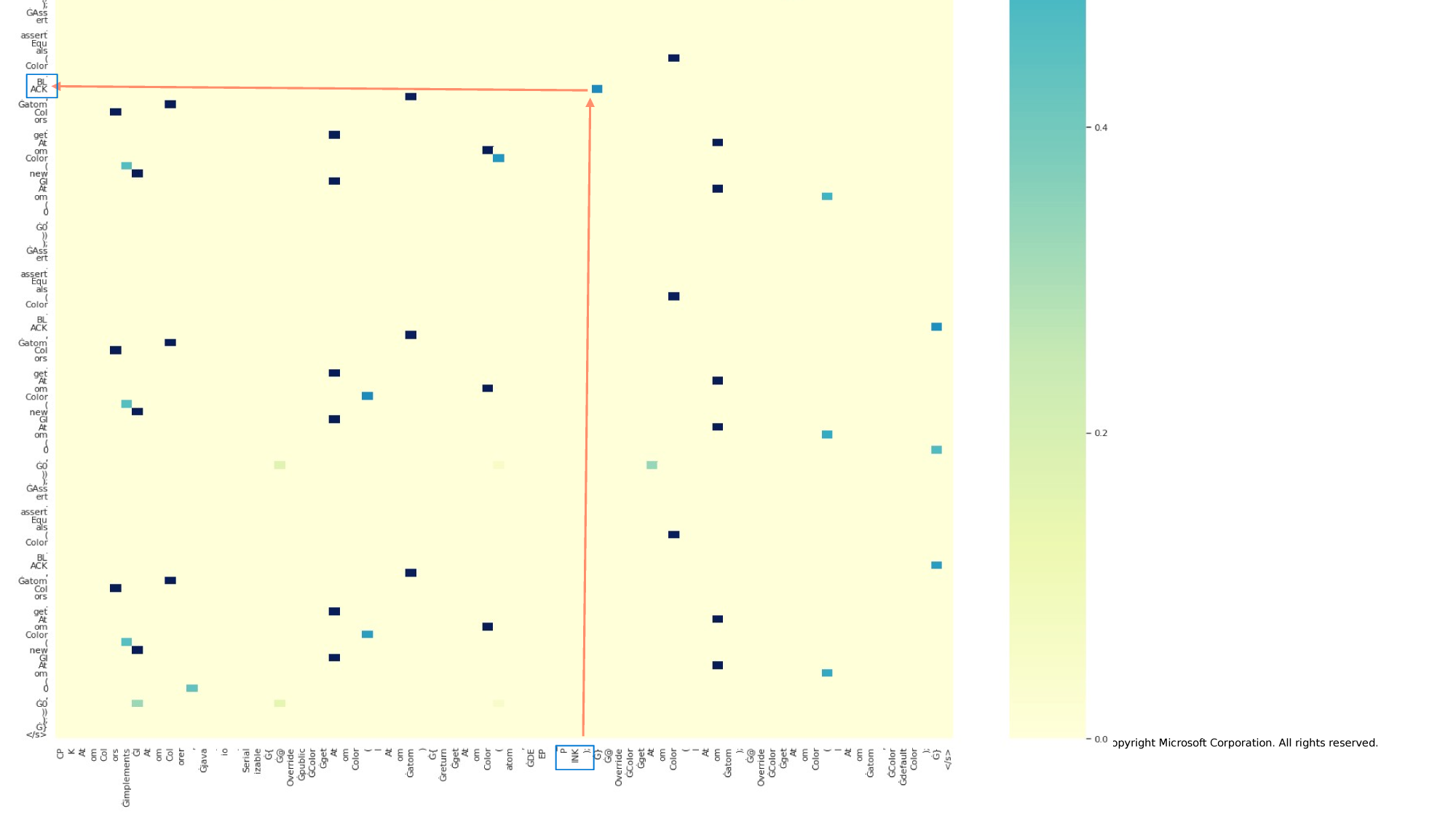
Rationales of code following the original approach
Rationales of Code is an impractical approach. Our solution is introducing aggregation functions that correspond to SE-tasks needs
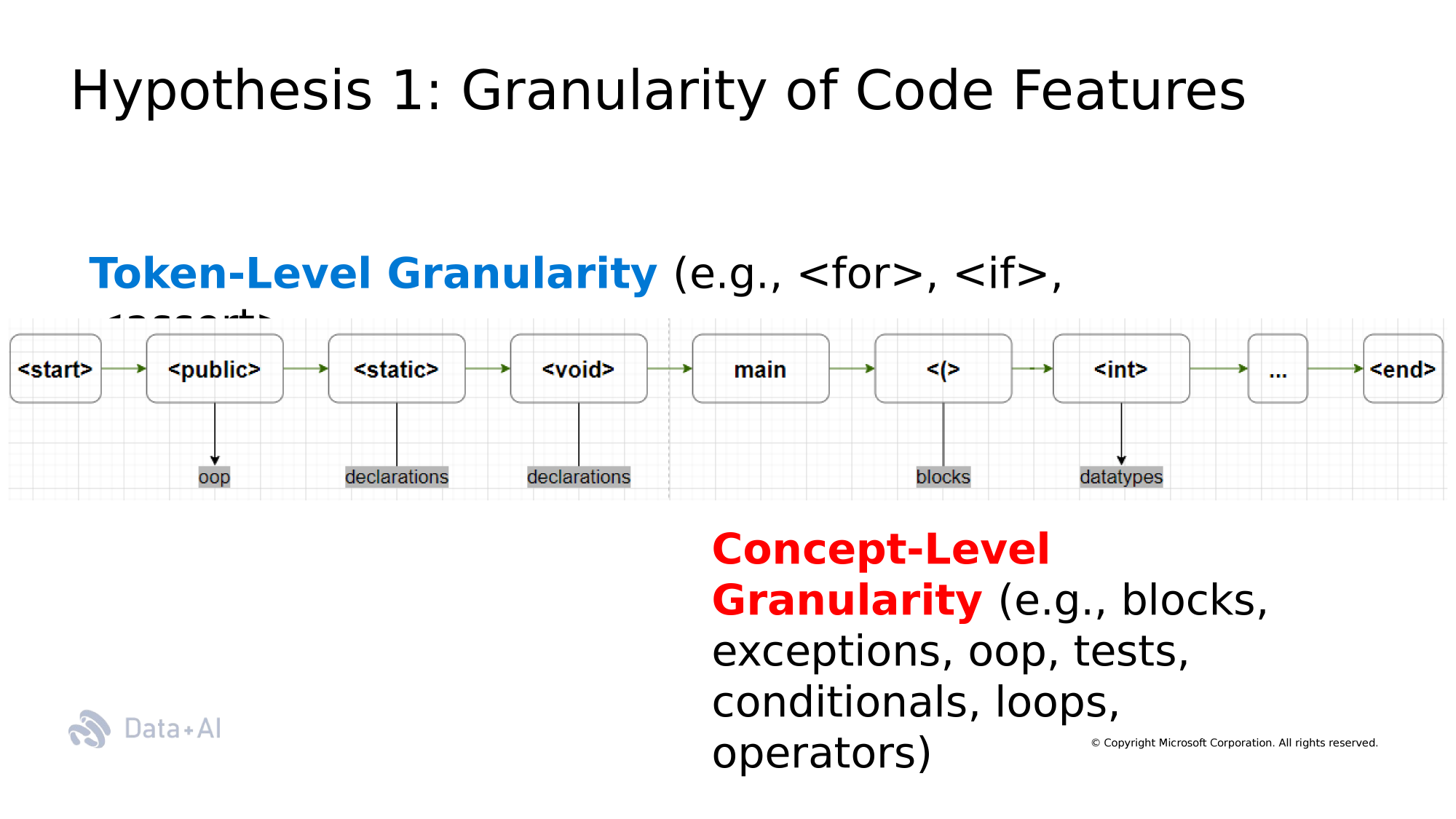
In summary,
- AST Rationales for code completion tasks
- Context Level Rationales for test case generation
- What about commit message generation?
- or Bug Fixing or Code Refinement or Assert generation?
Empirical Evaluation & User Study
Artificial Code Generation subtasks by LLM:
Encoder-Decoder (BART)
- Code Summarization
- Test Case Generation
- Bug Fixing
- Injection Code Mutant
- Assert Generation
Decoder-Only (GPT)
- Code Summarization
- Commit Message Generation
- Test Case Generation
- Code completion
Proposed Research Questions
- RQ1. Which group of tokens (rationales) explain the Next Token Predictions by artificial code generation subtask?
- Which features in the prompt explain SE subtasks?
- Which features in the input explain SE subtasks?
- RQ2. To what extent do code rationales affect LLMs' accuracy?
User Study
- RQ3. How useful and reliable are CodeRational to explain artificial code generation subtasks?
Holistic View

Source Code Generative Agent

Real Source Code
Synthetic Source Code







A (deep) NN model is able to learn the abstract features of source code to generate the same structure
Source Code Generative Agent
SE Discriminative Agent


A generative agent can be converted into a discriminative one to solve a supervised task (e.g., Code Reviews, Refactorings, Bug Classification)
Transfer Learning
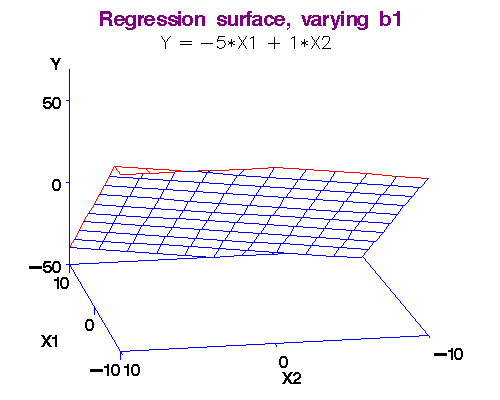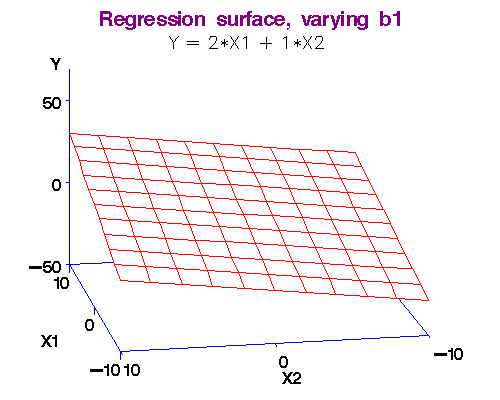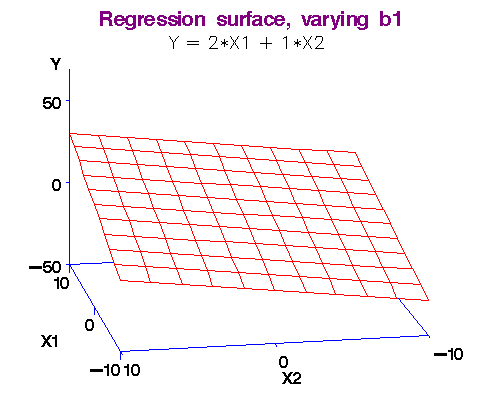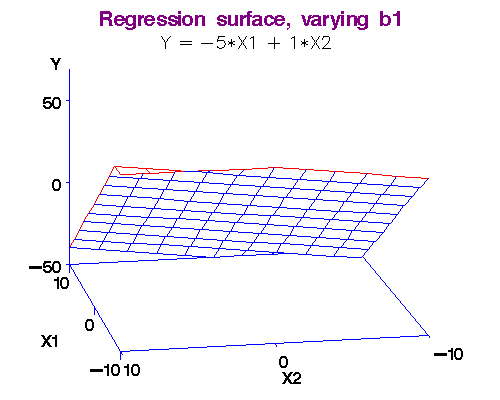
Are machines able to learn how to generate "unique" source code?
Open Research Question
Large scale agent interactions might produce "emergent" (human-level) source code
Close-ended Evolution
Open-Ended Evolution





Evolutionary Computation to communicate SC agents



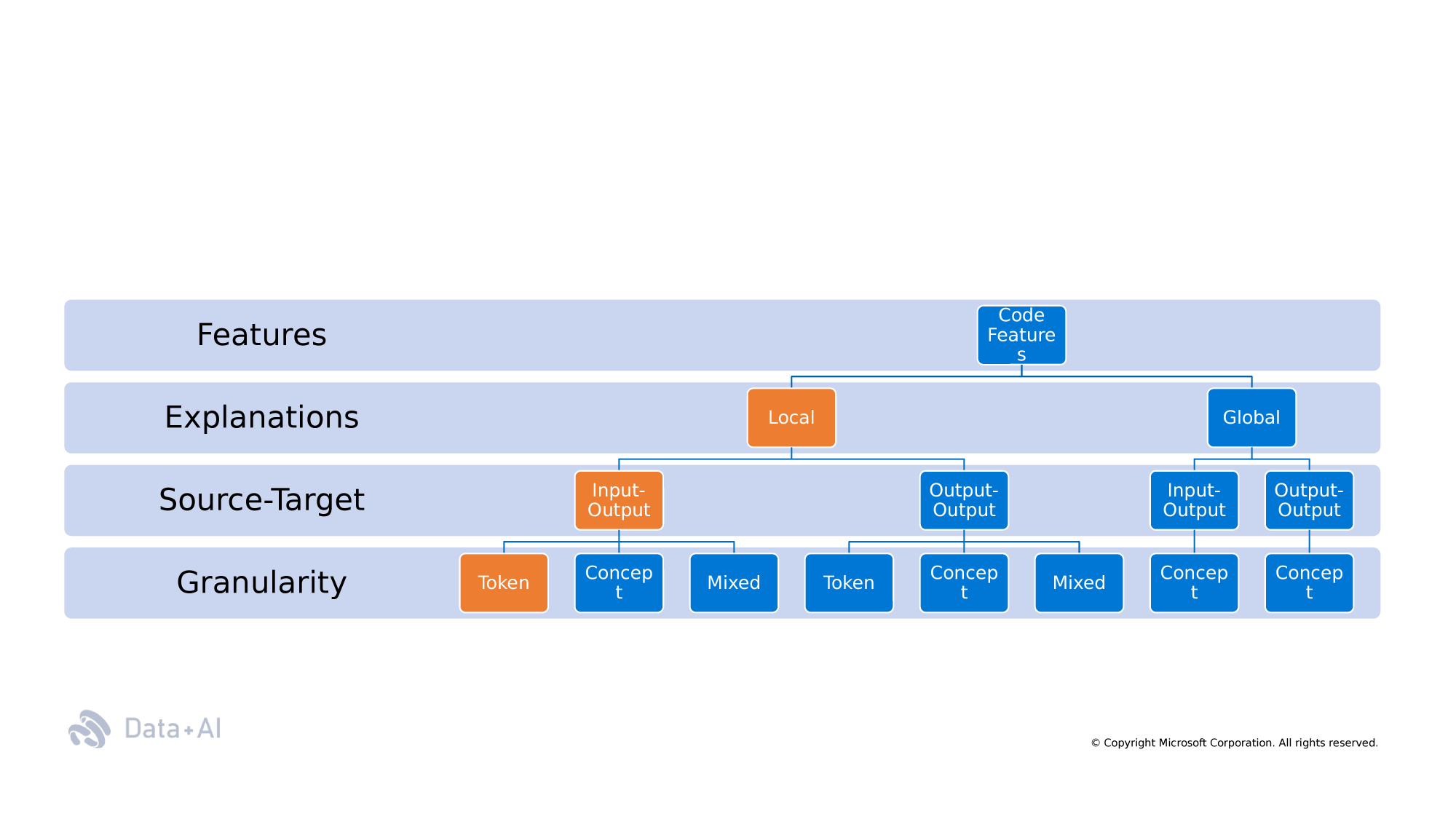
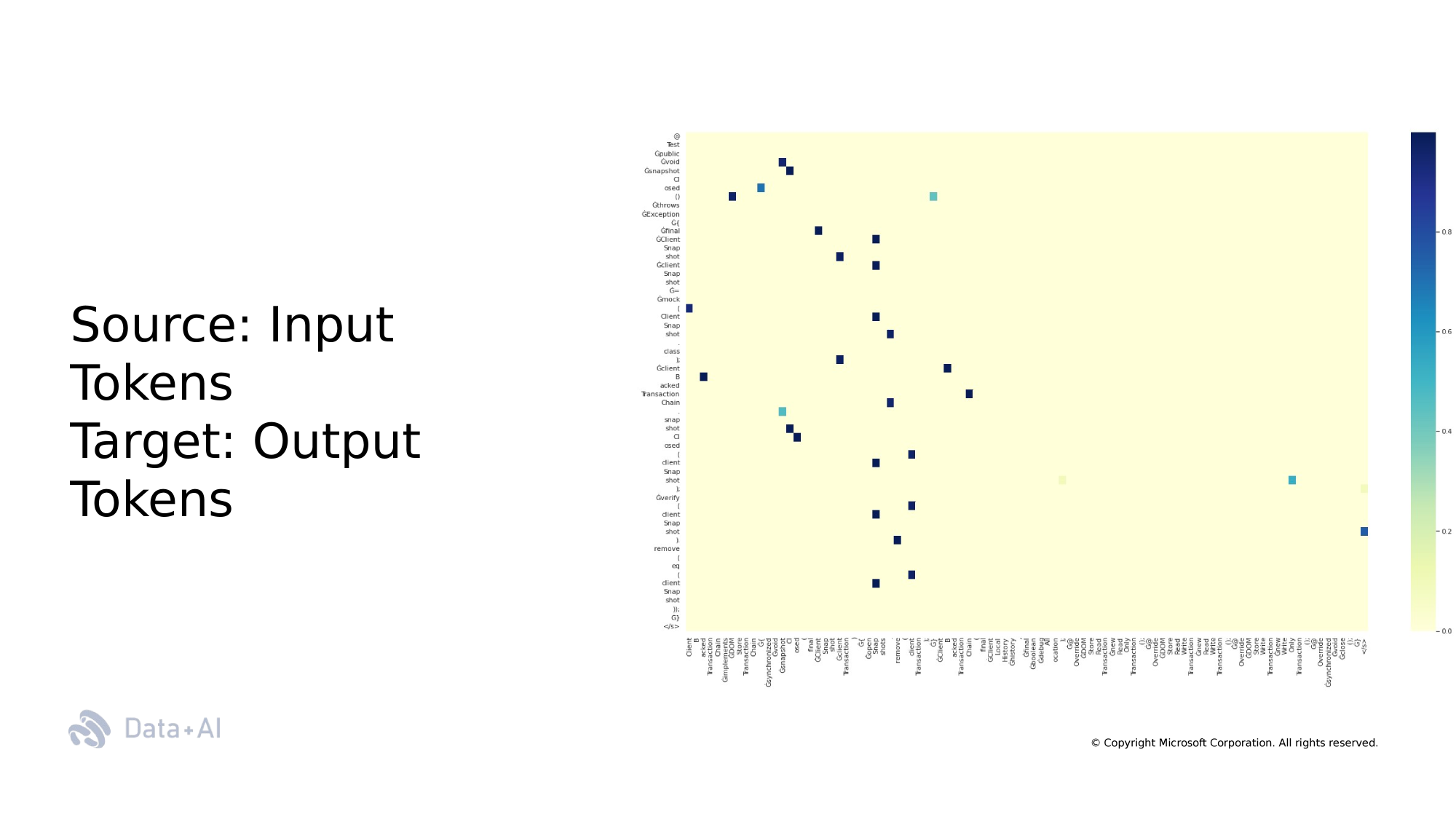
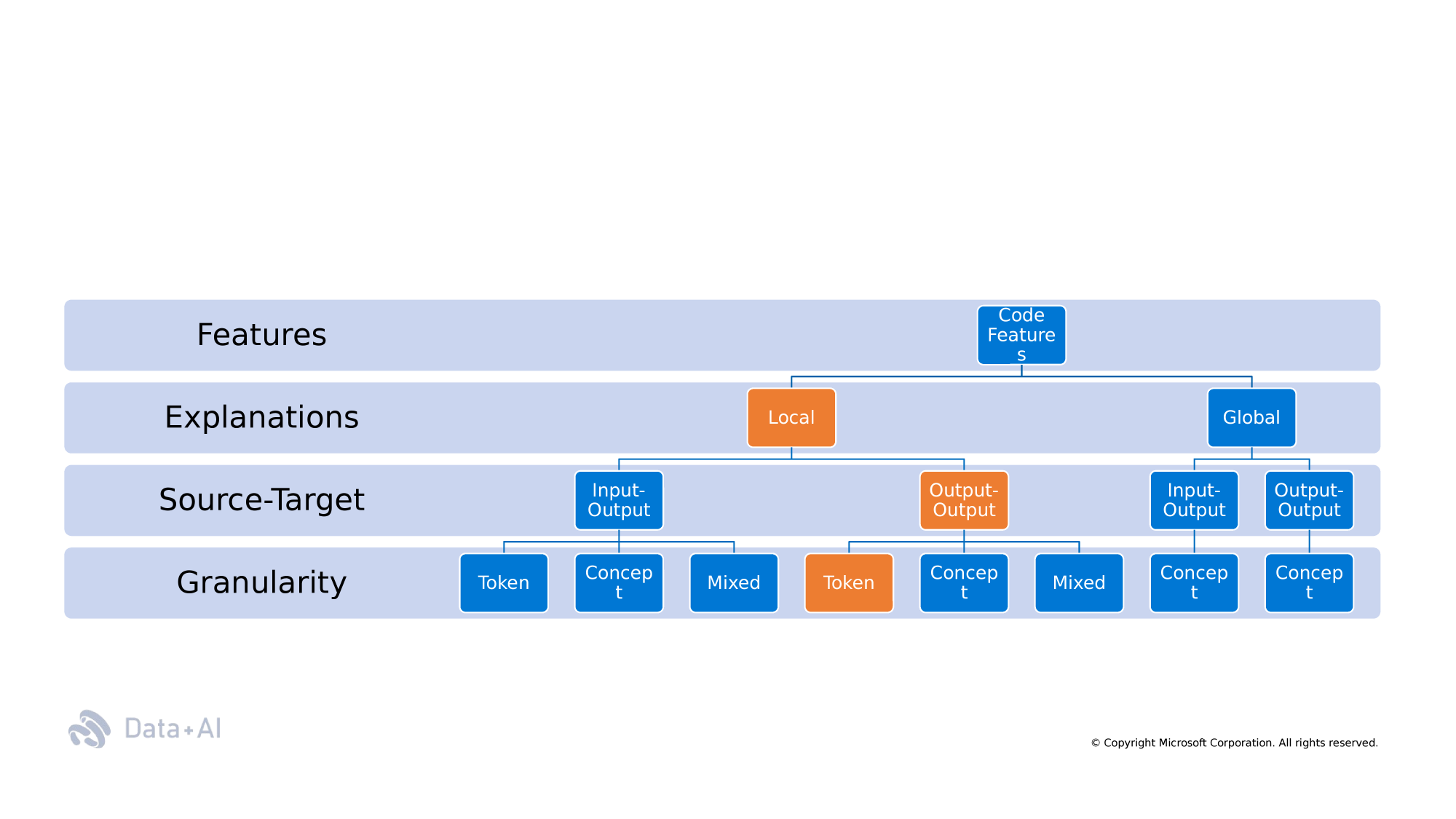
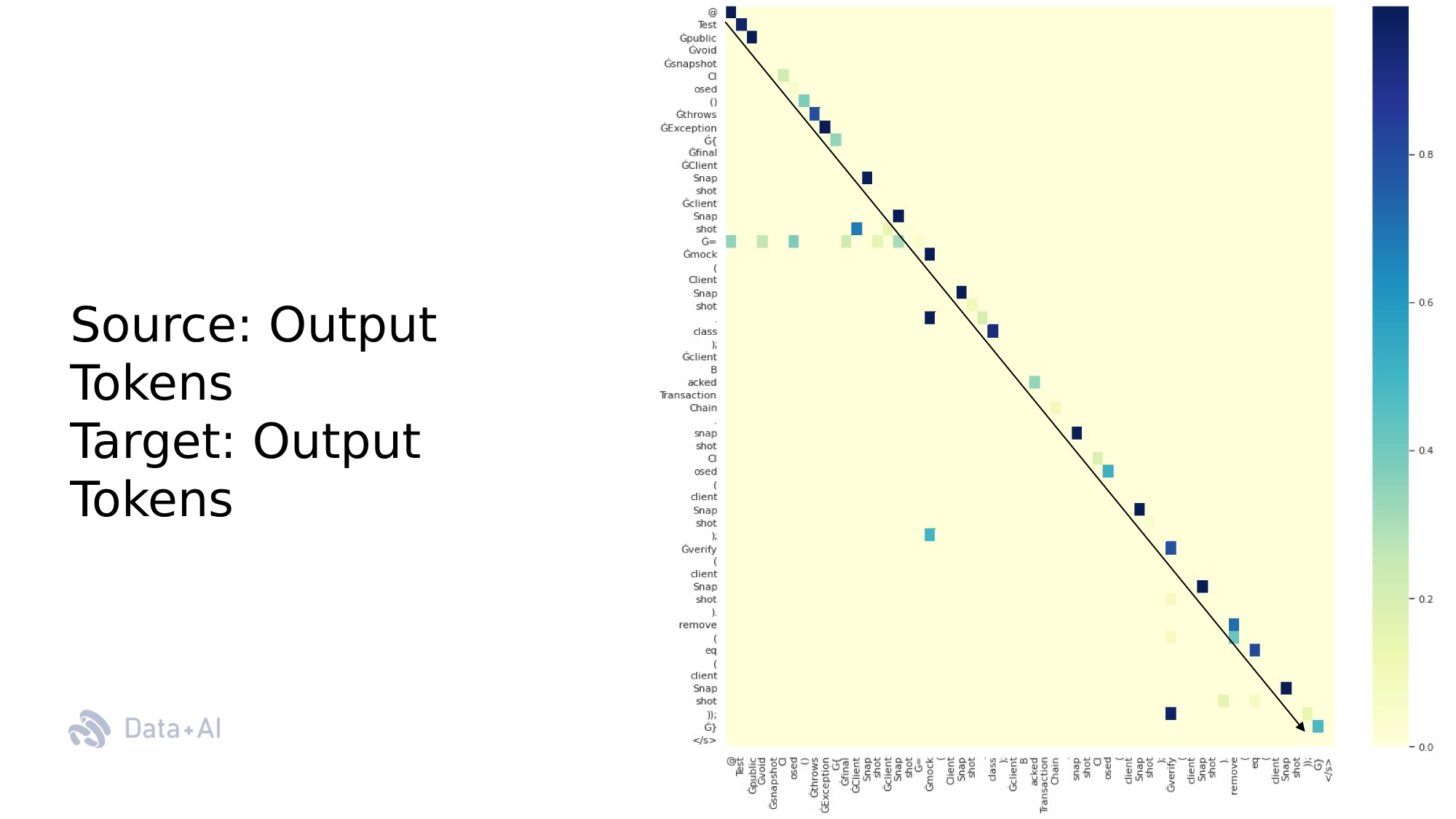



Code Rationales
By David Nader Palacio
Code Rationales
- 286



