HTML BASICS

HTML
HyperText Markup Language
HTML
- HTML - tagged markup language documents.
- HTML is a Markup Language. It is used to describe a structure of a webpage, so that your browser knows how to display the webpage.
- When you visit a webpage, you see your browser's rendering of the underlying HTML.
- Any document in the HTML language is a set of elements, with the beginning and end of each element is indicated by a special mark - Tags
- Tag - named label - the text contained between the start and end tag is displayed <small> text size smaller </ small>
HTML PAGE STRUCTURE
- html - root element that starts & ends a page
- head - instructions for browser ( not visible except <title>)
- body - all visible content goes here
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page title goes here</title>
</head>
<body>
Content goes here!
</body>
</html>BASIC STRUCTURE

What is <head>
HEAD AND BODY
- Auxiliary part, helps the browser to work with the data
- Describe the document - <title>
- Connect the system files to the document (css, favicon, etc.) - <link>
- Keywords, description meta tags, encoding, and others. - <meta>
What is <body>
- There is written the information to be displayed on the screen:
- lists
- titles
- menus
- paragraphs
- pictures
- etc.
Defining a description for your page
META
Defining keywords for your page
<meta name="description" content="Web tutorial"><meta name="keywords" content="HTML, JavaScript, VBScript">!DOCTYPE
- Tells the browser which version of (X) HTML you use on your page.
- Since the process of evolution has several versions of the HTML markup language to interpret the document browser must be reported, in what standard the document should be displayed.
Each type of tag affects the text inside of it in a different way
TAGS
- HTML markup tags are usually called HTML tags
- HTML tags are keywords (tag names) surrounded by angle brackets like <html>
- HTML tags normally come in pairs like <b> and </b>
- The first tag in a pair is the start tag, the second tag is the end tag
- The end tag is written like the start tag, with a forward slash before the tag name
- Start and end tags are also called opening tags and closing tags
HTML elements
tags vs. elements
HTML tags
An element in HTML represents some kind of structure or semantics and generally consists of a start tag, content, and an end tag. The following is a paragraph element:
<p>This is the content of the paragraph element.</p>Tags are used to mark up the start and end of an HTML element.
<p></p>ATTRIBUTES
- They are used to enhance the ability of individual tags, and to add more flexibility to manage the contents of the container.
- Tags can have attributes. Attributes can provide additional information about the HTML elements on your page.
- The <tag> tells the browser to do something, while the attribute tells the browser how to do it.

HTML defines the elements on a webpage, and CSS defines the design of those elements.
STRUCTURE AND DESIGN
Let's break that concept apart:
- Structure: Telling the web page that there's a block of text that should go underneath another block of text. Oh, and that we want a series of links beneath all of that text.
- Design: Telling the web page exactly how those pieces of text (and those links) should actually look: what color they are, how they're relatively positioned, how big they are, and much more.
ENCODING
To tell the browser the encoding of symbols on web pages, you must set the special meta tag.
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=encoding name">For the Windows operating system and Cyrillic charset usually takes the value of utf-8 or windows-1251
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Encoding</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=windows-1251">
</head>
<body>
<p>
Cyrillic
</p>
</body>
</html>HTML COMMENTS
- Comment tags <!-- and --> are used to insert comments in HTML
- Comments are not displayed by the browser
- Comments can help document HTML
- Comments can help in debugging HTML and help finding errors in the document
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Encoding</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>
<!-- Comment -->
</p>
</body>
</html>Tags
TAGS BY PURPOSE
- Headers <h1> - <h6>
- Lists <ul> <ol> <dl>
- Blocks <div>
- Tables <table>
- Forms <form>
- Images <img>
- Links <a>
- ...
ALLOW DIVIDE TEXTS INTO SECTIONS
HEADERS
<Ul> tag sets a bulleted list. Each entry must start with the tag <li> (list item)
UNOREDERED LIST
<ol> tag sets a numbered list. Each entry must begin with a <li> tag
ORDERED LIST
One list can be nested into another list
NESTED LISTS
Tag <dl> (definition list) creates a list of definitions. It includes the tag <dt> - is what we want to describe and tag <dd> is where we write the definition of the term.
DEFENITION LIST
DIVISION
- <div> element is a block element and is intended to highlight the fragment to change the type of content.
- Typically, the form block is controlled via styles.
- By itself (without attributes and styles css), <div> tag does not affect the elements of html pages
PARAGRAPH
- The HTML <p> element defines a paragraph.
- Generally, the units share the text paragraphs (paragraphs).
- By default between paragraphs there is a small vertical indentation called margin.
HORIZONTAL RULE
- Tag <hr> adds a horizontal rule
- It is a block element
- It doesn't have a closed tag
TABLES
Any table consists of rows and cells that are set using the tag <tr> (table row) and <td> (table data)
IMAGES
- src - the image url
- alt - alternative text. It is shown when the image is not available
LINK
- href - url to a resource
- name - it sets the name of the anchor
TEXT FORMAT
Most of these elements are not used anymore. Text formatting is usually done using CSS
PREFORMATTED TAGS
BREAK LINE
Breaks the line where this tag is placed
SPAN
Span is universal inline element. It does not do anything
TAG TYPES
Tag types
BLOCK
Inline
These elements are shown as rectangles extending each other downwards.
This element takes up the entire available width, the height of the element is determined by its contents, and it always begins on a new line.
These are the elements of the document that are just part of a string.
These elements are arranged one behind the other in the same row, if they don't fit in their parent, it is transferred to another line.
BLOCK TAGS
- <div> - section of the document
- <h1> - <h6> - headlines
- <li> - list item
- <p> - paragraph
- <ul> - bulleted list
- <ol> - numbered list
- <dl> - a list of definitions
- <table> - table
- <tr> - creates a row in the table
- ...
INLINE TAGS
- <a> - creating links
- <b> - bold font sets
- <br> - newline
- <i> - sets the italic font
- <span> - a versatile line element
- <th> - creates a header cell in a table
- <td> - creates a table cell
- <sup> - displays the font as a superscript
- ...
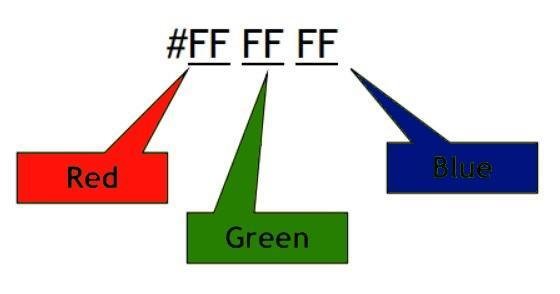
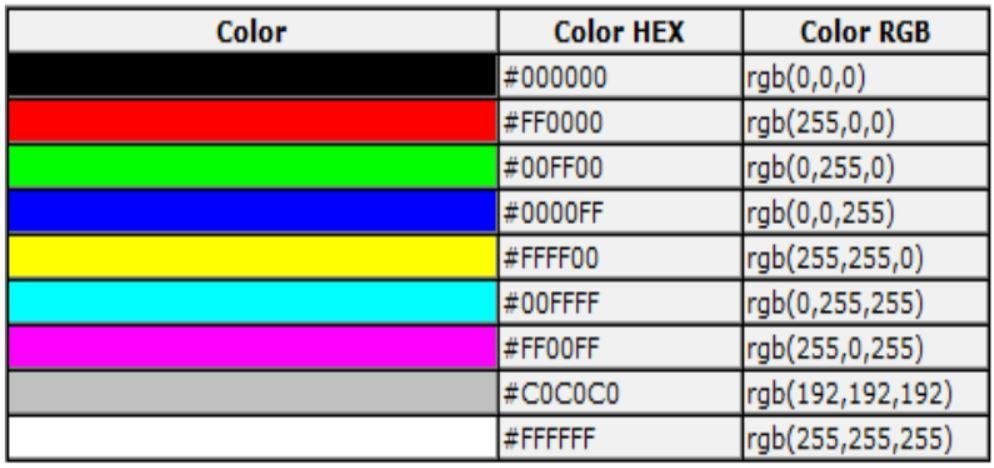
COLORS
Color
- Colors are displayed combining RED, GREEN, and BLUE
- Values vary from 00 to FF (hexadecimal)
HTML COLOR CODES
SETing BACKGROUND
To set background to the element use style attribute
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Encoding</title>
</head>
<body style="background-color: #cccccc;">
<p style="background-color: rgb(0,255,0);">
Text
</p>
</body>
</html>DOM
DOCUMENT OBJECT MODEL
DOM
- When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page
- The HTML DOM model is constructed as a tree of Objects
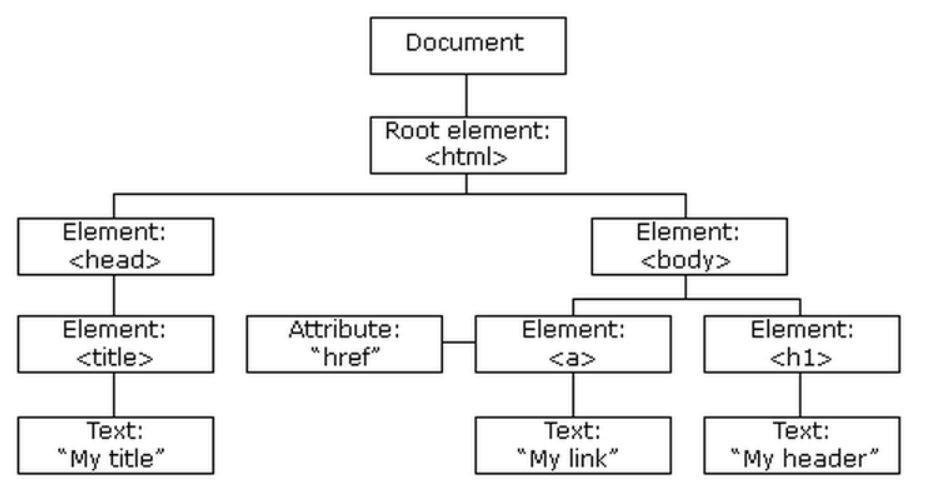
HIERARCHY

VALIDATION
VALIDATION
Validation is a checking of a document by the special program - validator to compliance with the web standards and detection of existing errors. These standards are called specification (developed by the World Wide Web Consortium or abbreviated W3C).
Work validator is as follows: first, determine the type of document (specified with the <! DOCTYPE>), and then for the correctness and error-checked HTML-code. At the same time as checks for proper use of the name tags of their nesting.
CHECK list
- Validation syntax
- Check the nesting of tags
- Validation DTD
- Check for foreign elements
If at least one of the tests is not successful, then HTML is considered as invalid
PROS AND CONS
For
The main argument for the validation of HTML is the provision of cross-browser compatibility
Against
Validation is too strict, and does not correspond to specified requirements for websites
SHOULD I USE VALIDATTION?
It will help you to:
- Identify existing weaknesses
- Write correct code
definitely yes
HOW TO USE VALIDATION?
- Visit http://validator.w3.org/
- Choose validation source or use direct input
- Click check
- There are should be no errors in the responce
WHAT WE'VE LEARNT
- What is HTML
- HTML Page structure
- What is HEAD and BODY
- What is META, Doctype
- What is Tag
- What is Attribute
- Encodding
- Headers
- Lists
- Div
- Paragraph
- Horizontal line
- Table Basics
- Image
- Link
- Pre tags
- Break line
- Span
- Tag types
- Colors
- DOM
- Validation
Tasks
Task 1
- Create HTML Page with basic markup
- Add Meta information
- Add Headers from 1 to 6 and after each header add a horizontal line
- Add list
- Add div and change its background using HEX format
- Att simple table with 3 columns and 2 rows
- Add image
- Add link to your favorite site
- Add pre tag with white space
- Add paragraph with four lines which are broken by <br> tag
Task 2

Layout this page. For text generation you can use http://ru.lipsum.com/
Home work
Task 1
http://htmlbook.ru/samhtml - Except "Frame" topics
THANKS FOR YOUR ATTENTION
Html basics
HTML BASICS
By Dima Pikulin
HTML BASICS
- 1,234


