
Dana Janoskova
Senior Software Engineer at

Vue.js, React, Node.js, CSS, Flutter
What we'll do today
- Learn vuex basics
- See common vuex store structure
- Explore Vue CLI options
- See a "blog app" code example
- Live code the blog app!
What is vuex?
- a centralized store for all the components in an application
- the state can only be mutated in a predictable fashion
Generate an app with vuex built-in
Vue CLI has support for vuex out of the box.
npm install -g @vue/cli
# OR
yarn global add @vue/cli


What does a vuex store structure look like?
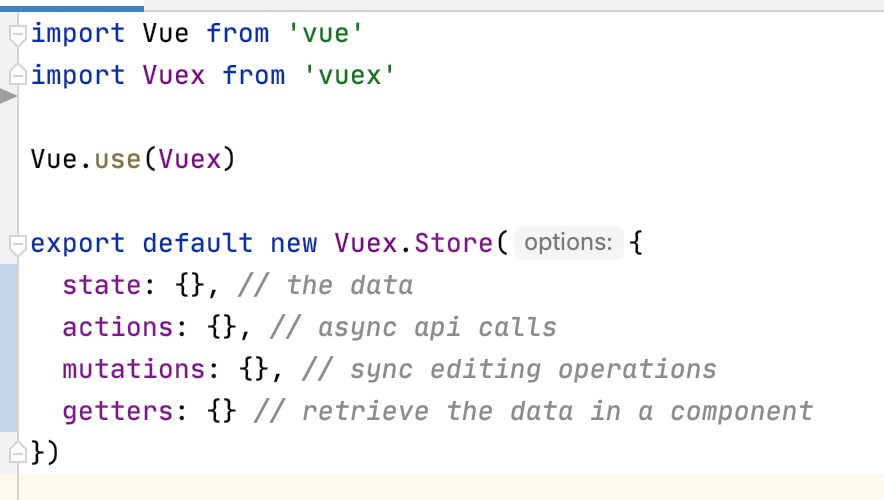
Vuex "state"
- State is a single state tree
- it's a single object that contains all your application level state and serves as the "single source of truth"

Vuex "mutations"
- Mutations are the place where we where we modify state
- The handler function will receive the state as the first argument
- Those functions are synchronous only

Vuex "actions"
- Actions can contain asynchronous operations
- The handler function accepts the context parameter
- From the context you can commit mutations or dispatch actions

This is how you call a mutation in an action. The first argument is the mutation name and the second is the data you wish to pass in.
Vuex "getters"
- Use getters to retrieve the variables from state
- You can use them for computed, reactive logic

Use actions, mutations and getters in a component

Import mapActions, mapGetters and mapMutations from 'vuex' to use them in your components.
In this example, the mounted() method calls POSTS_FETCH(), which after being executed and having received data, updates the vuex state.
Then our computed variable from getter will trigger a re-render of the component.

PostsContainer.vue ← connected to vuex
You'd then access and render the posts the same way as you access your internal state.
Post.vue ← an independent presentational component,
not connected to vuex

Code examples
Blog state
Let's start simple 😁
state: {
posts: []
}Blog mutations
mutations: {
POSTS_SET(state, data) {
state.posts = data
},
POST_ADD(state, data) {
state.posts.unshift(data)
},
POST_MODIFY(state, data) {
const postIndex = state.posts.findIndex(p => p.id === data.id)
state.posts[postIndex] = data
},
POST_REMOVE(state, id) {
state.posts = state.posts.filter(p => p.id !== id)
}
}Blog actions
actions: {
async POSTS_FETCH(context) {
const response = await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts')
const posts = response.data.slice(0, 20)
context.commit('POSTS_SET', posts)
return posts
},
async POST_CREATE(context, data) {
const response = await axios.post('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts', data)
const post = response.data
context.commit('POST_ADD', post)
return post
},
async POST_UPDATE(context, data) {
const response = await axios.put('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/' + data.id, data)
const post = response.data
context.commit('POST_MODIFY', post)
return post
},
async POST_DELETE(context, id) {
await axios.delete('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/posts/' + id)
context.commit('POST_REMOVE', id)
}
}Blog getters
getters: {
posts(state) {
return state.posts
},
postById: (state) => (id) => {
return state.posts.find(post => post.id === id)
}
}Posts.vue
<template>
<div>
<Post v-for="post in posts" :key="post.id" :post="post" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
import Post from '../components/Post'
export default {
mounted() {
if (!this.posts.length) this.POSTS_FETCH()
},
methods: {
...mapActions(['POSTS_FETCH'])
},
computed: {
...mapGetters(['posts'])
},
components: { Post }
}
</script>
Post.vue
<template>
<div class="post-container">
<h3>{{ post.title }}</h3>
<div class="post-body">
{{ post.body }}
</div>
<div class="post-actions">
<router-link :to="{ name: 'edit', params: { id: post.id } }">Edit</router-link>
|
<a @click="handleDelete">Delete</a>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
props: {
post: Object
},
methods: {
...mapActions(['POST_DELETE']),
handleDelete () {
this.POST_DELETE(this.post.id)
}
}
}
</script>CreatePost.vue
<template>
<form @submit.prevent="handleSubmit">
<input type="text" placeholder="Post title" v-model="model.title" />
<br />
<textarea placeholder="Post body" v-model="model.body" rows="5" />
<button type="submit">
<template v-if="isEdit">Save</template>
<template v-else>Create</template>
</button>
</form>
</template>
<script>
import { mapActions, mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
data() {
return {
model: {
title: '',
body: ''
}
}
},
methods: {
...mapActions([
'POSTS_FETCH',
'POST_CREATE',
'POST_UPDATE'
]),
async handleInputsFill() {
let posts = this.posts
if (!posts.length) {
posts = await this.POSTS_FETCH()
}
const { id } = this.$route.params
if (!id) {
this.model = {
title: '',
body: ''
}
return
}
const result = posts.find(post => post.id === Number(id))
this.model = { ...result }
},
async handleSubmit () {
const promise = this.isEdit ? this.POST_UPDATE : this.POST_CREATE
await promise(this.model)
this.$router.push({ name: 'posts' })
}
},
computed: {
...mapGetters([
'posts'
]),
isEdit () {
return !!this.$route.params.id
}
},
mounted() {
this.handleInputsFill()
},
watch: {
'$route'() {
this.handleInputsFill()
}
}
}
</script>
Get started with Vuex
By Dana Janoskova
Get started with Vuex
- 2,274



