RSA
How do Public/Private Keys Work?
Tyson Bhalla
Hello! You just learned about symmetric encryption. But doesn't that imply an asymmetric encryption? In this project, you will learn what that is and why it can be better than symmetric encryption. By going through these slides, you will understand the basics about the RSA cryptosystem and how public/private keys work to keep data secure.



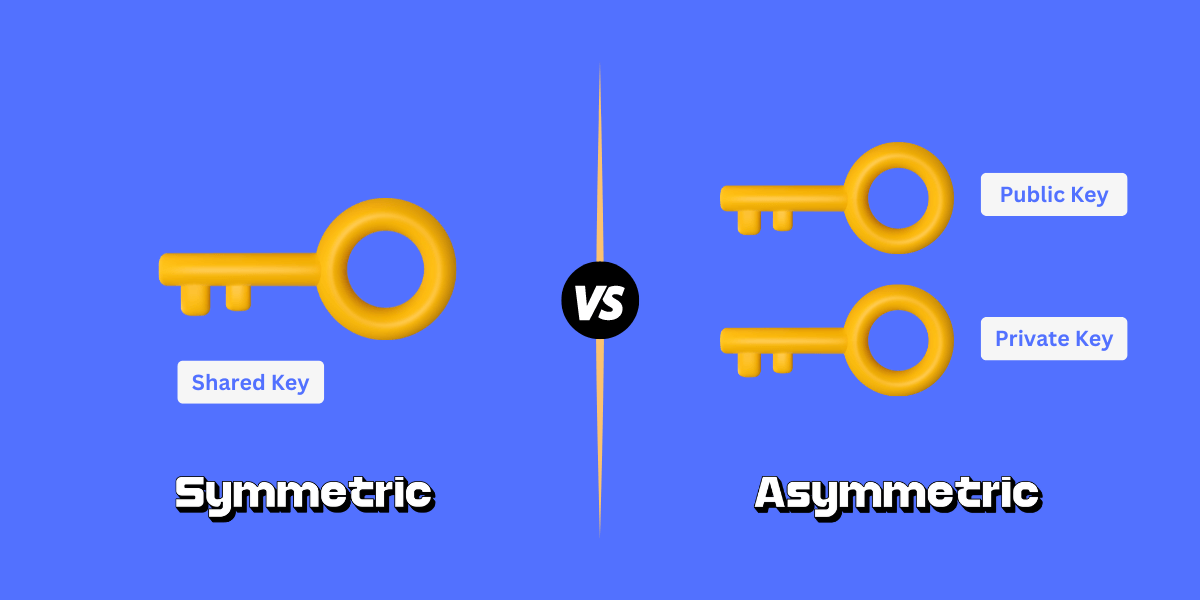
Symmetric
Asymmetric???
Imagine this Scenario
Alice want to send data to Bob. She tells the delivery man to walk the data to Bob.


Alice
Bob
Data
However, the delivery man wants to access this data and can easily do so.
Data
I now know all the secrets!!

Data
Symmetric Encryption


Alice
Bob

I locked this data using the
agreed-upon encryption.

I can unlock this data using
the agreed-upon decryption.
However, what if the delivery man was there when Alice and Bob exchanged the encryption/decryption methods?

I know the key to "unlock" this encryption since I overhead Alice and Bob!

Data

Symmetric Encryption
Data
Asymmetric Encryption


Alice
Bob

I can encrypt this using
asymmetric encryption.

I can decrypt this despite
never meeting Alice in person.
Is there a way for Alice and Bob to communicate securely without ever meeting?
Yes. This is possible using asymmetric encryption.

What? This is too secure for me!

Data
They realized that if people could never privately share encryption methods, they could share it publicly.
That's right. To keep data secure, the some information is open to the public. This encryption method is called the public key.
How to avoid meeting in person
Meet Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman
Diffie Hellman
However, to stop everyone from being able to decrypt private messages, Diffie and Hellman realized that there needs to be a decryption method that only the user knows. This is called the private key.
But how does that actually work?
Every user has a public key and a private key. And somehow, by sharing the public key, they can still keep their private key unknown. The user's private key will only decrypt messages encrypted with the user's public key.
Public and Private Keys
And that's what asymmetric encryption is. Instead of having a single key to encrypt and decrypt, there are two different keys: public and private!
Asymmetric Encryption
Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman created RSA to turn the concepts by Diffie and Hellman into an actual cryptosystem.
How RSA was created
Rivest Shamir Adleman
The RSA cryptosystem allows users to have a unique public and private key. But by sharing the public key, the private key remains hidden. RSA is not a concept. It has algorithms to actually create these public and private keys!
RSA Example
Data
Encrypted with
Bob's public key


Alice
Bob

I can encrypt this using
Bob's public key.

I can decrypt this using my
private key that no one else knows.

I know how this is encrypted, but I can't decprypt it since I don't know Bob's private key!

Data
What does the delivery man think of this?
RSA Example
Data
Encrypted with
Alice's public key


Alice
Bob

Thanks Bob! I can decrypt your
message using my own private key!

I can return a message encrypted
with Alice's public key since it is
publicly shared!

RSA is too secure for me. :(

Data
With RSA, Alice and Bob can communicate securly!
However, the delivery man has an idea:
Alice

What if I pretend to be Alice and send a message to Bob?
I can encrypt it with his public key since it is publicly shared!

Fake data
Encrypted with
Bob's public key

Bob

Alice sent me a message!
This is clearly not good.
Good thing RSA has a solution!
Signing your message
RSA has one more property that allows people to show messages came from them. Just like writing a signature on a letter, this is called signing.
We already know that RSA allows a private key to decrypt ciphertext encrypted with the matching public key.
Additionally, RSA allows the public and private keys to be swapped.
You can encrypt a message with your private key, and it can be decrypted using your public key!
Finding the Origin of Ciphertext


I found this ciphertext, but I don't know who it's from.
Data
Encrypted with
???'s private key
Decrypt with A's public key
Data
Data
Data
Decrypt with B's public key
Decrypt with C's public key


This ciphertext is from Person C since their public key decrypted it!


Alice
Bob

I signed my message.

I now know this came from Alice!
How Signing Works
What if the message is first encrypted with Alice's private key, and then encrypted once more with Bob's public key?
Data
Encryption #1 with Alice's private key
Encryption #2 with Bob's public key
Bob can then decrypt with his private key and then once more with Alice's public key. Since only Alice know's her private key, Bob can be sure that Alice sent the message if her public key decrypts it.
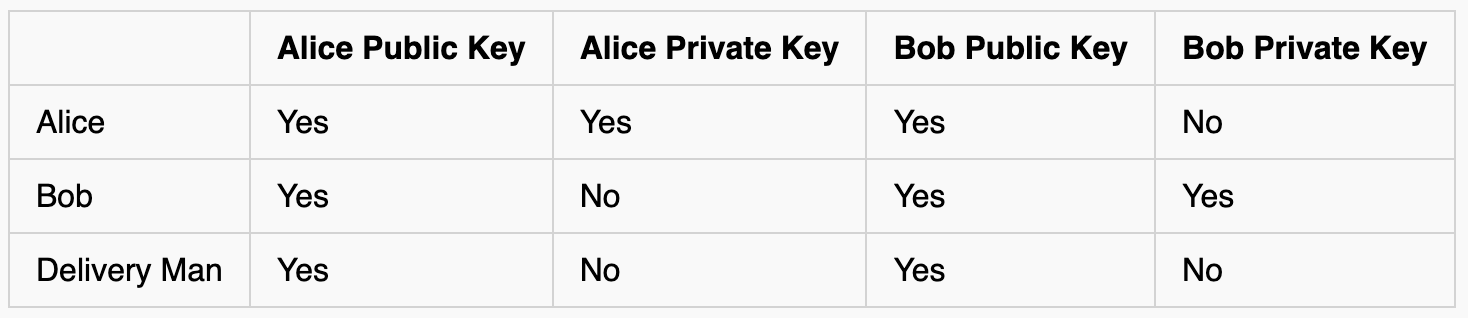
In this scenario, who knows what?


Alice
Bob

I signed my message.

I now know this came from Alice!
Data
Encryption #1 with Alice's private key
Encryption #2 with Bob's public key
Just like without signing, Bob can decrypt the message since he knows his own private key. However, this time, he can prove that Alice sent the message since only she knows her private key (and he decrypted it correctly with her public key)
If the delivery man tries to pretend to be Alice, then Bob will know since Alice's public key won't decrypt the ciphertext.

I'm pretending to be Alice, but I don't know her private key, so I used my own.


Bob

I got a message.
Data
Encryption #1 with Delivery
Man's private key
Encryption #2 with Bob's public key
When Bob tries to decrypt it...

Data
Encryption #1 with Delivery
Man's private key
Encryption #2 with Bob's public key

I can't "unlock" the red box with Alice's public key, so I know it isn't from her.
Bob
Using signing, Alice can prove when messages are from her and when others pretend to be her!

Foiled
Again!

The Math Behind RSA
Now, let's learn about the math behind RSA. How does this ingenious system work?
Public and Private keys with RSA are actually two numbers.
Public keys have the format (n, e)
and private keys look like (n, d).
That means that by sharing your public key, you tell everyone to use the numbers n and e in a specific algorithm.
About The Modulo Operator
If you've never heard of modulo before, I'll quickly explain it to you now.
It means to take the remainder when dividing by a number.
a (mod b) = Remainder of a/b
For example 10 (mod 4) = 2 since 10/4 has a remainder of 2
Here are more examples:
5 (mod 6) = 5
3 (mod 1) = 0
-2 (mod 5) = 3
8 (mod 8) = 0
Now that we know the modulo operator, we can see how RSA works!
Let's say you already know your public and private keys -- that is you know the numbers n, e, and d.
To encrypt your message (m) to ciphertext (c),
c = m^e (mod n)
And to decrypt the ciphertext:
m = c^d (mod n)
Reminder:
Public key = (n, e)
Private key = (n, d)
That's it!
For example, let's say n=14, e=5, and d=11.
We want to encrypt the letter b.
We can code it as m=2.
Encryption:
c = m^e (mod n)
c = 2^5 (mod 14)
c = 32 (mod 14)
c = 4
Decryption:
m = c^d (mod n)
m = 4^11 (mod 14)
m = 4194304 (mod 14)
m = 2 (b)
We just encrypted b as the number 4, then back to b! This method works as long as you can convert letters into numbers. One way you can do this is:
a=1, b=2, c=3...
How do we find what n, e, and d should be?
Step 1: Find two prime number P and Q
Step 2: n = P*Q
Step 3: M = (P-1)*(Q-1)
Step 4: Find number e that shares no factors with M and e < M
Step 5: Find d such that e*d (mod M) = 1
Note: This math might be a little confusing, but it's fine if you understand the bigger concepts of why this works.
Try it with me
Step 1: Find two prime number P and Q
Step 2: n = P*Q
Step 3: M = (P-1)*(Q-1)
Step 4: Find number e that shares no factors with M and 1 < e < M
Step 5: Find d such that e*d (mod M) = 1
P = 2, Q = 7
n = 2*7 = 14
M = 1*6=6
e = 5 (process of elimation)
since 5*11 (mod 6) = 1, d = 11
Steps:
Example:
We can now say the public key is (14, 5)
and the private key is (14, 11)!
Reminder:
Public key = (n, e)
Private key = (n, d)
Follow these steps to find different keys!
Why does this work?
RSA uses properties of modulo to insure e and d can reverse each other.
c = m^e (mod n)
m = c^d (mod n)
Therefore c^d = m^(e*d) (mod n)
Euler's theorem states that anything^M (mod n) = 1
so m^(e*d) (mod n) = m.
Therefore c^d = m.
This shows why RSA encryption and decryption works.
Note: This math might be a little confusing, but it's fine if you understand the bigger concepts of why this works.
Key Point: How is RSA secure?
Remember that the public key (n, e) is known by everyone and the private key is protected.
RSA protects the private key by using prime numbers.
RSA uses primes P and Q to create the keys. Since n = P*Q, P and Q can be found be factoring n. However, factoring can be hard -- especially if P and Q are HUGE.
Imagine if P and Q are hundreds of digits long. There is no easy way to factor n other than checking lots and lots of numbers. This may take thousands of years to do.
Therefore, P and Q are kept protected even though n is known, which keeps the private key private.
RSA is Used Everywhere!
Ever heard of HTTPS? The S stands for secure.
HTTPS uses RSA to keep your data safe.
RSA is also used in email encryption.
RSA can be used in VPNs.
RSA is used to help keep healthcare data private.
RSA protects customer data online.
RSA is used in online banking transactions.
RSA is used to store data files securely.
RSA is used in many more places!


Recap: What did we Learn?
- Asymmetric encryption uses public and private keys
- You never need to meet people in real life. Just share your public key to the world!
- You can send a secure message to someone by encrypting it with their public key
- You can sign messages by also encrypting them with your public key to ensure proof of origin
- RSA keeps private keys private by making it near-impossible to factor the product of two primes
Data
Encrypted with
Bob's public key


Alice
Bob

I can encrypt this using
Bob's public key.

I can decrypt this using my
private key that no one else knows.
Thanks for Reading!
I encourage you to read these sources if you want to learn more about RSA:

What two primes multiply to

Data
56187372842383416492172167181889100636307067166076286008843970481235731100942922297595030852453020296036869940064092759748039251286184807652334046251610198605292116388985787351792835674445561257199757
Asymmetric Encryption
Tyson Bhalla - RSA and Public/Private Keys
By Dan Ryan
Tyson Bhalla - RSA and Public/Private Keys
Tyson Bhalla - FYS Project
- 68



