JavaScript

Basics
Front End Development



HTML
CSS
Javascript
HTML
- HyperText Markup Language
- Defines the structure of a webpage
- Place text here
- Place image here
- Place button here
- etc...
- Skeleton or "Nouns" of webpage

CSS
- Cascading Style Sheets
- Defines the style of HTML
- Make text purple
- Give this image a blue border
- Make all buttons be white with blue border
- etc...
- Skin or "Adjectives" of webpage

JavaScript
-
Defines the behavior of webpage
-
Add two numbers together
-
Change color when the user clicks
-
Load data from external source
-
-
Actions or "Verbs" of webpage

JavaScript - Part 1
-
Intro
-
Numbers
-
Strings
-
Booleans
-
Variables
-
JavaScript + HTML
Script
Series of Instructions that a computer can follow to achieve a specific goal
Like a Recipe
Follow Instructions one-by-one

Script
Series of Instructions that a computer can follow to achieve a specific goal
To write a script:
- Define Goal
- Break Goal down into series of tasks
- Figure out what steps are needed for each task
Statements
Each step in a script is formed as a JavaScript statement
var name = "Daniel Kelly";
var age = 21;
var item1_price = 49.99;
var item2_price = 19.99;
var subtotal = item1_price + item2_price;
var overall_total = subtotal + (subtotal * 0.125);
var message = name ": Your total bill is: " + overall_total;
alert(message);Each step is executed one after another in sequence
Types of Data
JavaScript has 5 basic categories of Data called Primitives
- Numbers
- Strings
- Booleans
- Null
- Undefined
JavaScript Console
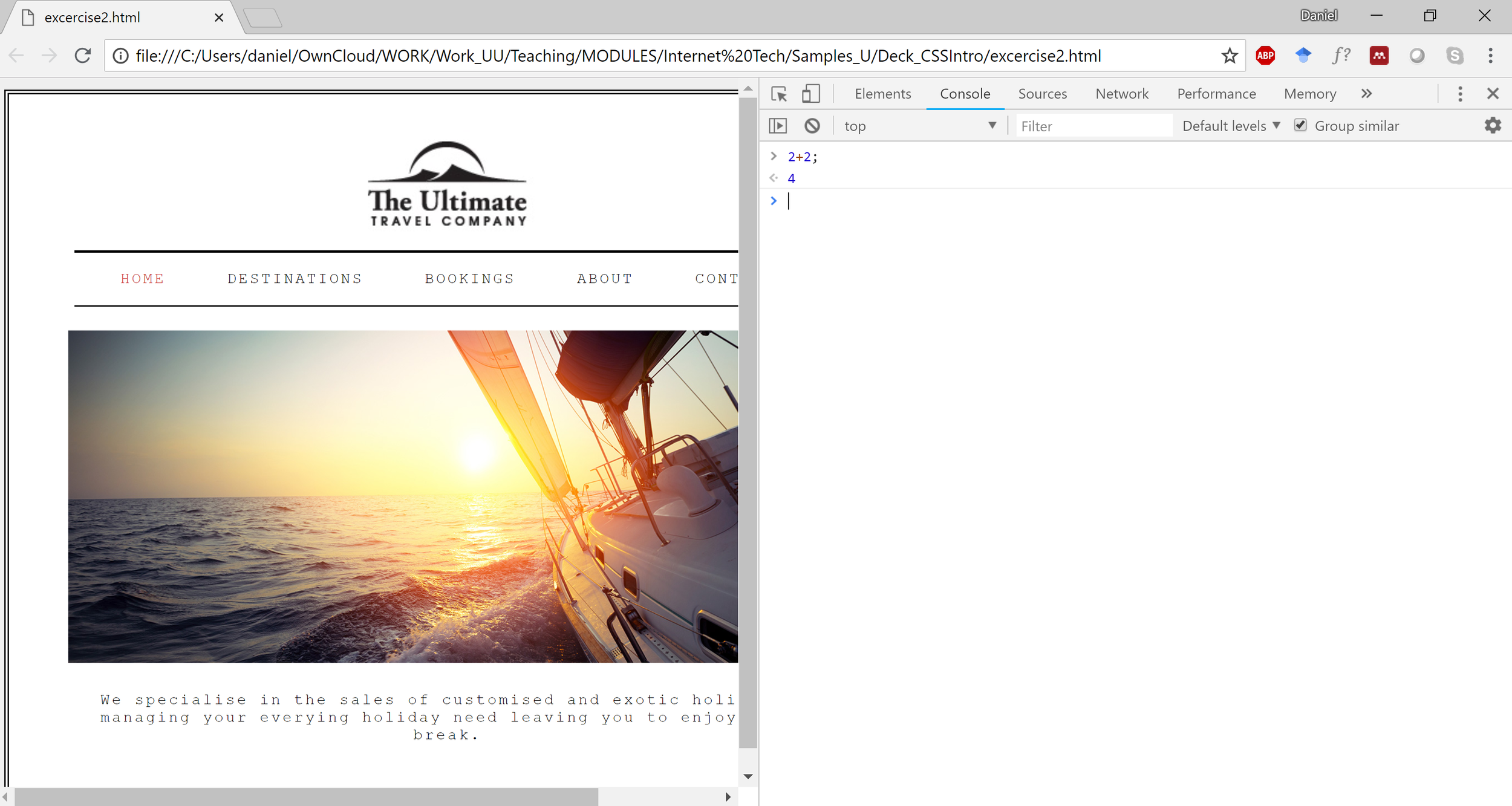
- Type Statement
- Press Enter
- Statement is executed and result is printed
If you want to enter multiple statements before executing, press Shift+Enter to go to new line without executing
Ctrl+Shift+J
Numbers
//Different Types of Numbers
9
-10
//floating point numbers
3.14
//Math Operations
5 + 6
10.99 - 1.50
1 / 5
1.231 * 90Open Chrome JavaScript Console and Experiment (Ctrl+Shift+J)
Numbers
//Modulus...(remainder)
10 % 3
14 % 5
//Order of Operations
(10-5) * 2
(8+12) * (10-5)Open Chrome JavaScript Console and Experiment (Ctrl+Shift+J)
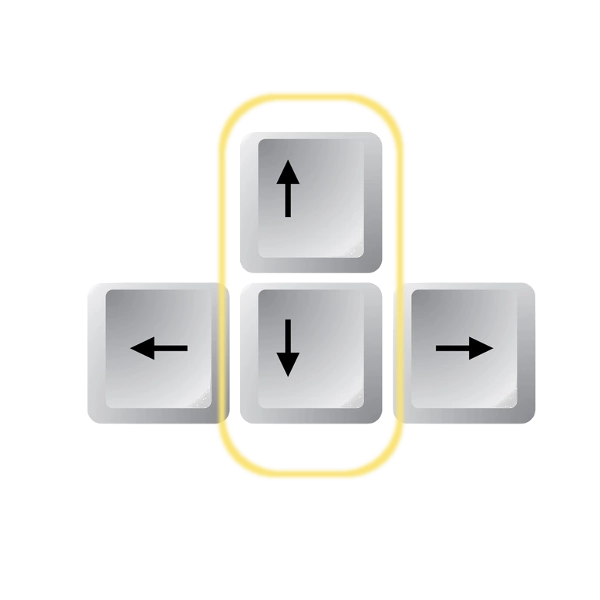
Up: Previous Statement
Down: Next Statement
Numbers
Open Chrome JavaScript Console and Experiment (Ctrl+Shift+J)
- Calculate area of a circle
- Radius is 2cm
- Calculate the service charge (@12.5%) for a table which has ordered the following
- 2 x Steak @ 12.95 each
- 1 x Pepsi @ 1.95
- 3 x Red Wine @ 5.95 each
- 2 x Cheesecakes @ 4.95 each
//Single or Double quotes can be used
"hello world"
'hello world'Sequence of characters
"string"//Combine Multiple Strings (Concatenation)
"Internet" + " Technologies"
"Daniel" + " " + "Kelly"Sequence of characters
"string"Strings
//Escape Characters start with a "\"
"This is a quote: \"Brevity is the soul of wit\" "
//Get the length of a string
"hello world".length
//Get individual characters using [] and index
"hello world"[0] //"h"
"hello world"[4] //"o"
Open Chrome JavaScript Console and Experiment (Ctrl+Shift+J)
Booleans
//can only be true or false
true
falseOpen Chrome JavaScript Console and Eperiment (Ctrl+Shift+J)
Null and Undefined
//null and undefined are values
//there is not multiple types of null or undefined
null
undefined
Open Chrome JavaScript Console and Eperiment (Ctrl+Shift+J)
Variables
-
Script will need to temporarily store pieces of information
-
Data is stored in Variables
- String Data
- Number Data
- Boolean Data
- Null/Undefined

name
"This is my sentence data"
String Data:
Variables

sent1
"This is my sentence data"
String Data:

price
299
Number Data:

over18
True
Boolean Data:
1. Declare Variable
var myVariable;Declare you are using a variable and what is name is
2. Assign Value
myVariable = 3;Assign a value to be stored in the variable

myVariable
3
Variables

sent1
"This is my sentence data"
String Data:

price
299
Number Data:

over18
True
Boolean Data:
var sent1;
sent1 = "This is my sentence data";var price;
price = 299;var over18;
over18 = true;//you can declare and assign in the same statement also
var myVariable = myValue;
//Variables can store numbers, string, booleans
var myStringVariable = "Hello";
var myNumberVariable = 414;
var myBooleanVariable = true;
Variables
//declare variable and assign value
var myName = "Daniel";
//call the variable to get its value
myname
Variables
Access stored values by calling the variable

myName
"Daniel"
//use the values of variables along with other values
"hello there " + myName; //"hello there Daniel"
Variables
Variables
Access stored values by calling the variable
- Create 3 variables: firstName, surname and age
- Assign values to these
- Recall the values in the variables.
- Create 4th variable called "combined" which is a combination of your firstName and surname
//create variable and then use it in calculation
var price = 34.50;
5 + 17 + price; //56.5
//Change value of existing variable
price = 41.99;
Variables
Variables
Null
Undefined

=
//these variable have been declared
//...but NOT assigned a value
var firstName;
var surname;
Variables
Undefined:
When a variable has been declared but not give any value
Variables
//this variable is declared
//...it is also assigned a value
var voucherNo = "Voucher101"
//later if we want to set
//the voucher to "nothing"
//we assign it a null value
voucherNo = null; //expired
Null:
When you want to explicitly state the variable has no value
Functions
Organize Code in manageable chunks
Series of Statements that are grouped together because they perform a specific task.
{
}
Open Browser
Click on address bar
Type "learning.ulster.ac.uk"
Enter Username
Enter Password
Click "COM414"
Open COM414 Blackboard
Functions
Organize Code in manageable chunks
Series of Statements that are grouped together because they perform a specific task.
//1. Declare Function
function myFunction()
{
//code goes here
//do some stuff: step 1
//do some stuff: step 2
//do some stuff: step 3
}Functions
Organize Code in manageable chunks
Series of Statements that are grouped together because they perform a specific task.
//1. Declare Function
function myFunction()
{
//code goes here
var myVar = "Hello!!!"
var myVar2 = " World"
var combine = myVar + myVar2
}Functions
Organize Code in manageable chunks
Series of Statements that are grouped together because they perform a specific task.
//1. Declare Function
function myFunction()
{
//code goes here
var myVar = "Hello!!!"
var myVar2 = " World"
var combine = myVar + myVar2
return combine
}Functions
Organize Code in manageable chunks
Series of Statements that are grouped together because they perform a specific task.
//1. Declare Function
function myFunction()
{
//code goes here
var myVar = "Hello!!!"
return myVar;
}Functions
Organize Code in manageable chunks
- After a function is declared, you can call it
- Calling of function means code inside the function will be executed
- Return statements sends value back to where function was called
//Declared Function
function myFunction()
{
var myVar = "Hello!!!"
return myVar;
}//Call Function
var myReturnedVar = myFunction();1->
2->
myReturnedVar
//"Hello!!!""Hello!!!"
Functions
Functions with Paramaters
//1. Declare Function
function calcSquared(value)
{
var squared = value * value;
return squared;
}Functions
Organize Code in manageable chunks
- After a function is declared, you can call it
- Calling of function means code inside the function will be executed
- Return statements sends value back to where function was called
//Declared Function
function calcSquared(value)
{
var squared = value * value;
return squared;
}//Call Function
var mySqauredVal = calcSquared(5);1->
2->
mySquaredVal
//2525
25
5
5
Functions
Functions with multiple paramaters
//1. Declare Function
function calcPrice(cost,quantity)
{
var total = cost * quantity;
return total;
}Functions
Organize Code in manageable chunks
- After a function is declared, you can call it
- Calling of function means code inside the function will be executed
- Return statements sends value back to where function was called
//Declared Function
function calcPrice(cost,quantity)
{
var total = cost * quantity;
return total;
}//Call Function
var price = calcPrice(2.99,10);1->
2->
price
//29.9029.90
29.90
2.99
10
Functions
Functions with Paramaters
//1. Declare Function
function calcPrice(cost,quantity)
{
var total = cost * quantity;
return total;
}//2. Call Function
var cost = 9.50;
var quantity = 2;
var myPrice = calcPrice(cost,quantity); //19.00
Function Challenges:
//1. Declared Function
function calcPrice(cost,quantity)
{
var total = cost * quantity;
return total;
}//2. Call Function
var price = calcPrice(2.99,10);Open Blank Replit
In the "script.js" file, edit it to create two functions:
Use the "console" on bottom right to enter commands to call your functions
- Service Charge:
- Declare a function which takes one parameter (the cost of a restaurant bill) and returns the service charge amount(calculated as 12.5% of the bill)
- Call the service charge function with a number of different bill amounts to test that it works correctly.
- Split the bill
- Declare a function which takes two paramaters (the total bill price and the number of people) and returns the amount required to pay by each person (assuming the bill is being evenly split)
- Call the split the bill function with a number of different total bill prices and numbers of people to test that it works correctly
Sample Code to Help:
Built in Functions
Functions that someone else wrote...that we can use
//Alert Function
alert("Hello World!");
//Console Log function
console.log("Hello World!");
//Prompt function
prompt("What is you name?");var myName = prompt("What is you name?");Linking HTML with Javascript
<script src="myJavascriptFile.js"></script>Linking HTML with Javascript
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Linking HTML and JS</h1>
<script src="myScript.js"></script>
</body>
</html>index.html
var name = prompt("Please Enter your Name");
alert("Welcome " + name);
console.log("Printing Name to Log: " + name);script.js
- Edit the HTML file
- Link the html with the "script.js"
- Edit JavaScript File
- Enter the following Code
- Run
Linking HTML with Javascript
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Linking HTML and JS</h1>
<script src="myScript.js"></script>
</body>
</html>myHTMLFile.html
var name = prompt("Please Enter your Name");
alert("Welcome " + name);
console.log("Printing Name to Log: " + name);myScript.js
Note: By Default, JavaScript code runs when you load (or refresh) the page
-
Edit the HTML file with some basic content (e.g. a h1 tag with basic heading)
-
Create JavaScript to do the following
-
Prompt user for first name
-
Prompt user for last name
-
Prompt user for age
-
In an alert, print out the users full name in a sentence
-
In the console, print out the users age in a sentence
-
-
Link the HTML with the Javascript File
-
Test the script
javascript1
By D.Kelly
javascript1
- 975



