Vue Bulgaria
DOBROMIR HRISTOV
WORKSHOP

BEGINNERS
Who am I ?
Dobromir Hristov
- Lead FE Developer @Hypefactors
- Over 3 years of Vue experience
- Article author
- Open Source author
- Vue Ecosystem Contributor
- Vue Community Leader
Preparation for the Workshop
0
0
Preparation for the Workshop
What are we building?
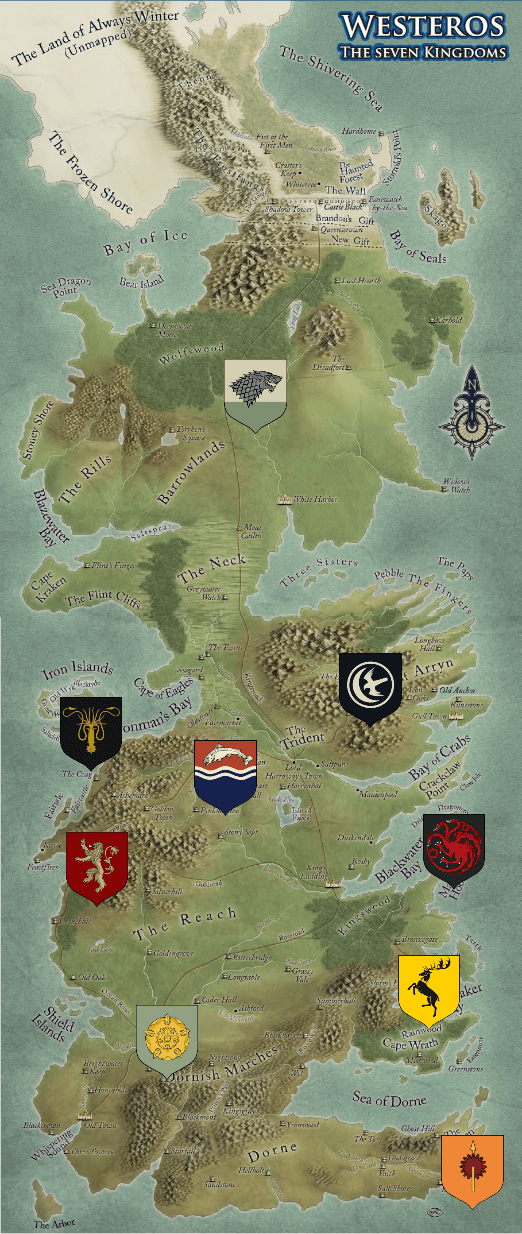
We will build a simple multi page Vue SPA in the form of a dynamic map of Westeros from Game of Thrones.
The map will be populated by the 9 great houses, each in its respective place.
Each house will have a drop down menu with a few of its main members.
Each member will have their own personal page.
0
Preparation for the Workshop
- The minimum requirements needed to build a Vue.js powered SPA.
- We will dive into the basics like directives, methods and computed properties.
- We will look into more interesting topics, like Vue Components, Multi page routing with Vue Router.
- The final chapter will introduce Vue CLI and Single File Vue Components
What will we learn?
0
Preparation for the Workshop
- Have Node and NPM installed - only for last chapter
- Have a recent version of Firefox or Chrome
- Install the Vue Devtools on your browser
- Favorite Code Editor - Webstorm, Sublime, VSCode, Atom
- Download the Vue Cheat Sheet
- Visit repository - https://github.com/dobromir-hristov/vue-beginner-workshop
-
git clone https://github.com/dobromir-hristov/vue-beginner-workshop.git
Before we start
0
Preparation for the Workshop
- Describe Vue features and show usage examples.
- Explain chapter challenges.
- Live code first part of challenges.
- Participants solve the second part of the challenges.
- Lecturer live codes second part of the challenges with participants explaining good practices.
- Debrief.
Workflow
Introduction to
Vue
I
I
Introduction to Vue
- Modern
- Progressive
- Composable
- Core - View Only
- Declarative
- Reactive
What is Vue?
I
Introduction to Vue
- Small - 21kb
- Performant - Virtual Dom
- Approachable - little JS knowledge
- Versatile - incrementally adaptable with libs
Key Features
- Documented
- Flexible - SASS, TS, Pug
- Official libraries- Vuex, VueRouter
- Transition System
I
Introduction to Vue
The Vue Instance
....
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue/dist/vue.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ vueText }}
</div>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
vueText: 'Hello Vue'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html><div id="app">
Hello Vue
</div>I
Introduction to Vue
Basic Example
<div id="app">
<div>
{{ vueText }}
</div>
<input type="text" v-model="vueText">
</div>I
Introduction to Vue
Challenges
- Use the 1-introduction/base/index as a base.
- Define a dynamic data property inside the new Vue instance's data object.
- Display the newly defined data property in the template using moustache syntax - {{ dataProperty }}
- Test in the Browser

Directives and
Rendering Data
II
II
Directives and Rendering Data
- v-if
- v-else
- v-for
- v-model
- v-show
- v-bind
- v-on
- v-html
What is a Directive?
<div v-if="isVisible === true"> That's hot! </div>- Special attributes that begin with "v-" prefix
- Attribute value is a single JavaScript expression
- Automatically apply side effects to the DOM when the value of its expression changes
Expression Body
Directive Name
II
Directives and Rendering Data
V-IF vs V-SHOW
<div v-if="false">
Invisible div?
</div><div v-show="false">
Invisible div?
</div><!----><div style="display: none">
Invisible div?
</div>Conditionally display elements in the DOM
Hides the element
Removes the element
II
Directives and Rendering Data
V-FOR
- Renders the DOM element that it is attached to, for each property in the data collection that is looped
- Works with Arrays, Objects and Numbers
<div class="pepper" v-for="chilli in chillies">
{{ chilli }}
</div>// the Vue Instance
data: {
chillies: [
'Cayenne',
'Habanero',
'Jalapeno',
'Ghost Pepper',
'Trinidad Moruga Scorpion',
'Carolina Reaper'
]
}


We love extremely hot food!

II
Directives and Rendering Data
V-BIND
Dynamically binds DOM element attributes to data on the Vue instance
<button :disabled="isSaving === true">
Save Form
</button><button disabled="disabled">
Save Form
</button>v-bind:property has a shorthand as just :property
data: {
isSaving: true
}II
Directives and Rendering Data
V-BIND Examples
<button :disabled="isActive" :class="userEnergyLevel">
Get in Shape
</button>
<div :class="{ active: isActive }"> Sports! </div>
<div :class="[ favoriteSport, isActive ? 'active': 'passive' ]">
Activity
</div>
<!-- assign multiple at once -->
<div v-bind="{ class: { active: isActive }, title: 'Healthy' }">
Running is fun.
</div><button disabled="disabled" class="low">
Get in Shape
</button>
<div class="active"> Sports! </div>
<div class="rugby active">
Activity
</div>
<!-- assign multiple at once -->
<div class="active" title="Healthy">
Running is fun.
</div>data: {
isActive: true,
userEnergyLevel: 'low',
favoriteSport: 'rugby'
}II
Directives and Rendering Data
V-MODEL
Creates a two way bond between a form element and data property on the instance
<form>
<label>Recipe Name</label>
<input v-model="form.name" type="text">
<label>Portions</label>
<input
v-model="form.portions"
type="number">
<label>Vegan
<input
v-model="form.isVegan"
type="checkbox">
</label>
<label>Difficulity</label>
<input
v-model="form.difficulity"
type="range">
</form>II
Directives and Rendering Data
Things to watch for
- V-model - always predefine your data properties.
- V-bind shorthand - always add semicolon to short syntax.
- V-for - Define :key binding with an unique value.
- V-else can only after v-if.
II
Directives and Rendering Data
Challenges
- Use the 2-directives-rendering/base/index as base.
- Аdd a .map div and inside it a .house div to #app.
- On the .house add a dynamic class to houses.stark.name. Transform it to toLowerCase. Check in Browser
- Add an img tag inside the .house div and bind it's src attribute to the houses.stark.sigil property. Check in Browser - should see Stark sigil.
- Loop over the houses by using v-for on the .house element.
- On .house bind a key and class attribute to the current house index.
- Replace the img src with the currently looped house sigil property.

Events
III
III
Events
Events in Vue
- Events can be Native or Custom Vue events
- Events are handled using v-on directive
v-on:click has a shorthand as just @click
<button @click="counter++">
Increment
</button>Expression
Event Name
III
Events
Events in the Wild
<div class="vueDog vuePet"
@click="vueDog = !vueDog">
<img v-if="vueDog"
src="vueDog.jpeg">
<div class="text"> Tap the doggy </div>
</div>
<div class="vueReprtile vuePet"
@mouseenter="vueReptile = true"
@mouseleave="vueReptile = false">
<img
v-show="vueReptile"
src="vueReptile.jpg">
<div class="text"> Touch the gecko </div>
</div>
<div class="vueReprtile vuePet"
@mousedown="vueLeo = true"
@mouseup="vueLeo = false">
<div class="text"> Keep finger on the leo </div>
<img v-show="vueLeo"
src="https://image.ibb.co/cD9xMV/Vue-Leopard.jpg">
</div>III
Events
Event modifiers
- Take care of repetitive event specific actions that are easy to forget, like event.preventDefault.
- Can augment the event handler behavior.
- Makes event handlers responsible for handling event only
- @click.prevent - Executes event.preventDefault.
- @click.stop - Executes event.stopPropagation.
- @click.self - Handles events emitted only by the element it is attached to and not its children.
- @click.once - Executes only once.
- @click.ctrl - Executes only with combination with ctrl key.
III
Events
V-MODEL explained
<input type="text" v-model="username"><input
:value="username"
type="text"
@input="username = $event.target.value"
>Intelligently handles different form element components by listening and handling data in the required way
<input type="checkbox" v-model="isVisible"><input
:checked="isVisible"
type="checkbox"
@change="isVisible = $event.target.checked"
>Expand under the hood to
III
Events
Vue Lifecycle Diagram
III
Events
Things to watch for
- @event.stop - To stop event propagation (bubbling)
- @submit - Add on forms to prevent page refresh when submitting.
- $event - Use in template event expressions to access event payload
III
Events
Challenges
- Create a members dropdown
- Visualise each member inside the members dropdown
- Add currentHouse: null in the data property of the Vue instance.
-
Show the .members dropdown when clicking on a house
- Hide the .members dropdown when clicking away

Methods and Computed Properties
IV
IV
Methods and Computed Properties
What are Methods
- Functions that are bound to the Vue instance.
- Useful for extracting complex logic away from directives.
-
Make templates easier to read and manage.
- Methods have access to all the instance properties.
- Methods can be used inside Lifecycle Hooks and Watchers.
-
Can be used inside moustache expressions or dynamic bindings
data: {
counter: 0
},
methods: {
increment() {
this.counter = this.counter + 1
}
}<button @click="increment">Add one</button>
<div>{{ counter }}</div>IV
Methods and Computed Properties
Method Examples
<button @click="increment">+1 boringness</button>
<button @click="incrementBy(10)">+10 boringness</button>
<button @click="incrementTimes(5)">x5 boringness</button>
data: {
boringMeter: 0
},
methods: {
increment(){
this.incrementBy(1)
},
incrementBy(number = 0){
this.boringMeter = this.boringMeter + number
},
incrementTimes(times = 2) {
this.boringMeter = this.boringMeter * times
}
}IV
Methods and Computed Properties
What are Computed Properties
- Functions that act as dynamic property getters on the Vue instance.
- Recomputed every time any of its inner dependency values is changed.
- Cached to be very performant.
- Computed properties are bound to the Vue instance and have access to data properties, methods and other computed properties
// ...
data: {
firstName: 'John',
lastName: 'Doe'
},
computed: {
fullName() {
return this.firstName + ' ' + this.lastName
}
},
<div>{{ fullName }}</div><div>John Doe</div>IV
Methods and Computed Properties
Computed Properties Examples
<input v-model="search" type="text">
<div
v-for="chilli in filteredChillies"
:key="chilli"
class="pepper"
>
{{ chilli }}
</div>data: {
search: "",
chillies: [ "Cayenne", "Habanero", ... ]
},
computed: {
filteredChillies() {
return this.chillies.filter(chilly => {
return chilly
.toLowerCase()
.includes(this.search)
}
);
}IV
Methods and Computed Properties
Computed Properties vs Methods
- Executed only when dependencies change
- Cached
- Support defining a Getter/Setter functions.
- Does not take parameters
- Must be sync
- Should never mutate other properties in getters.
- Executed every time in templates
- Not cached
- Takes parameters
- Can be async
- Can return other functions or data types.
- Can mutate other properties or call other functions
IV
Methods and Computed Properties
Things to watch for
- Computed Property must return a value!
- Computed Property cannot be called as a function.
- Computed Property cannot be written over. Need to define Get/Set pair to do so.
- Computed Properties, Methods and data properties cannot share the same name.
- Be careful with this context when working with Methods.
IV
Methods and Computed Properties
Challenges
- Transform the @click expression on .house to a method.
- Hide the .members dropdown when you click on .map
- Transform the visibility check on the .members div to a isVisible method that accepts a houseId parameter.

Components, Props, Custom Events
V
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
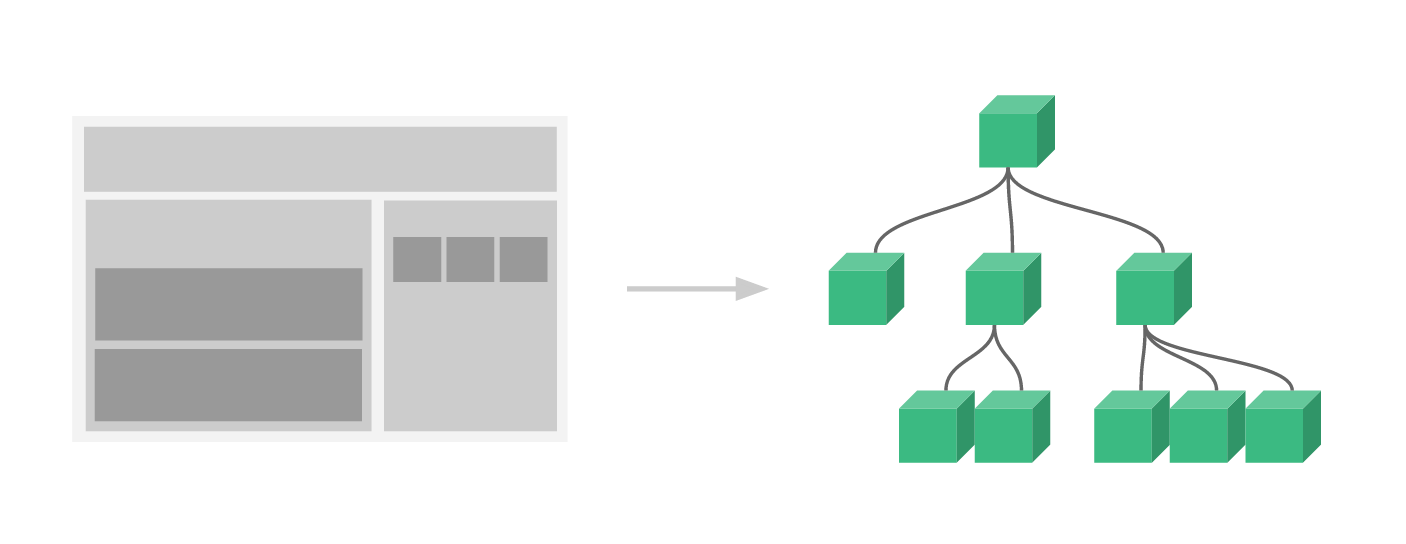
What are Vue Components
- Reusable Vue instances with a name.
- Tend to be small, isolated and testable.
- Accept same parameters as main Vue instance.
- Can accept properties, called Props.
- Can emit Events.
- Can be registered as Global or Local components
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
Composing Components
Vue Component Definition
var counter = {
template: '<button @click="increment">{{ count }}</button>',
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
methods: {
increment(){
this.count = this.count + 1
}
}
}
Vue.component('VCounter', counter) // Global component registration<div>
<v-counter></v-counter>
</div>V
Components, Props, Custom Events
Vue Component example
var VCounter = {
template: '<button @click="increment">{{ count }}</button>',
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
methods: {
increment(){
this.count = this.count + 1
}
}
}
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: {
VCounter: VCounter // Local Component registration
}
})V
Components, Props, Custom Events
Types of Templates
var component = {
data: () => ({ title: '' }),
template: '<div class="someClass">{{title}}</div>'
}<script type="text/x-template" id="unique-id">
<div class="someClass">
{{ title }}
</div>
</script>
<script>
var component = {
data: () => ({ title: '' }),
template: '#unique-id'
}
</script>String or template literal
X-template template tag
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
const component = {
data: () => ({ title: '' }),
render() {
return <div class="someClass">{ this.title }</div>
}
})JSX
const component = {
data: () => ({ title: '' }),
render(createElement) {
return createElement('div', {
class: ['someClass']
},
this.title)
}
}Render Function
Vue Component Specifics
- Components can be registered globally or locally.
- Can be nested inside other components.
- Each component's state is isolated from other components.
- A component can have multiple instances on a page.
- Components receive data from parents via Props.
- Components send data to parents via Events.
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
Things to watch for
- Template - only one top level element.
- Data - must be function returning an object.
- Cannot* access state or properties of other components.
- Name must not collide with HTML5 elements.
- Name format - TheCounter, VCounter, VueCounter, BaseCounter, AppCounter etc.
- Use kebab-case to write component tags. PascalCase only in CLI.
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
What are Props
- Way to pass data from parent down to child components.
- Dynamic data is passed via v-bind syntax.
- Props can have type validation.
- Props can have default values
- Props can have custom validation
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
<counter :min="5" :step="5" :max="100"></counter>Ways of Defining Props
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
props: ['PropA', 'PropB']
props: {
PropA: Object,
PropB: String
}
props: {
PropA: {
type: Object,
required: true
},
PropB: {
type: String,
default: 'Lorem Ipsum'
}
}
Shortest - mostly for demos
Slightly Longer
Longest - recommended, most detailed
Prop example
<v-counter :increment-by="5"></v-counter>{
template: '<button @click="increment">{{ count }}</button>',
props: {
incrementBy: {
type: Number,
default: 1
}
},
data() {
return { count: 0 }
},
methods: {
increment(){
this.count = this.count + this.incrementBy
}
}
}V
Components, Props, Custom Events
What to watch for
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
-
Props are considered immutable to child components
-
Default value for a prop of type Object or Array, it should be a factory function returning the required data.
-
Use as kebab-case in templates, but as camelCase inside methods and computed properties on the component.
What are Custom Events
Way for child components to communicate with parent components.
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
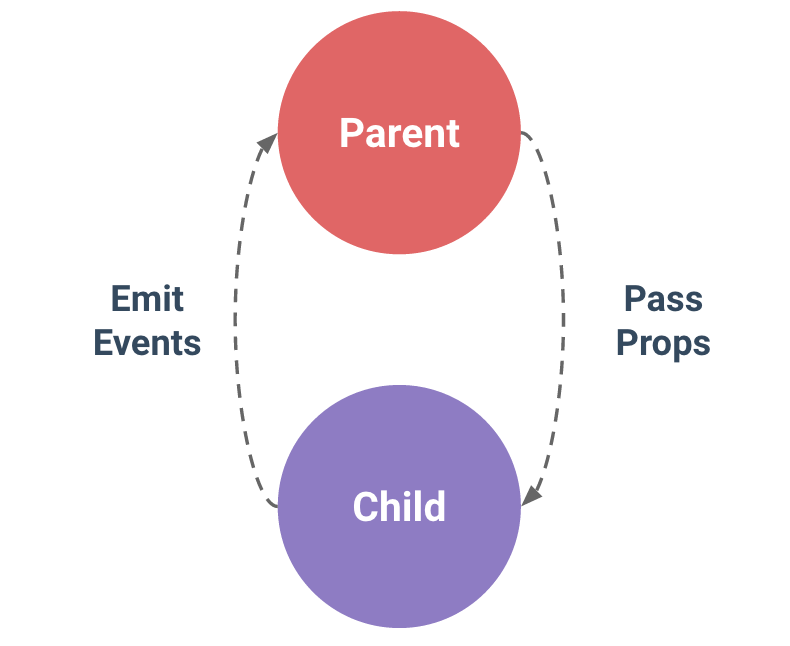
Working with Custom Events
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
template: '<button @click="notifyParent">click me</button>',
data: () => ({ count:0 }),
methods: {
notifyParent() {
this.$emit('change', this.count)
}
}<counter @change="handleChange"/>methods: {
handleChange(count) {
// handle event
}
}Parent Component
Child Component
- Events can pass data as payload.
- Emitted via $emit('event-name') from child components.
- Handled in parent component via events i.e. @event-name="action".
Custom Event Example
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
Custom Event Code Example
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
{
props: {
incrementBy: {
type: Number,
default: 1
},
value: {
type: Number,
required: true
}
},
methods: {
increment(){
const value = this.value + this.incrementBy
this.$emit('input', value)
}
}
} <v-counter
:increment-by="5"
:value="currentCount"
@input="handleInput"
></v-counter>Child Component
Parent Component
{
data() {
return {
currentCount: 0
}
},
methods: {
handleInput(emittedValue){
this.currentCount = emittedValue
}
}
}<button @click="increment">{{value}}</button>Things to watch for
V
Components, Props, Custom Events
- Always use kebab-case for event names. They are transformed to lower case in templates (HTML5 is case insensitive)
- Native event payload is HTML Event. Vue Events carry what you pass as payload.
- Custom events do not bubble up the chain like normal events.
Challenges
- Extract .house into a House component
-
Props:
- house - Object
- currentHouse - String
- houseId - String
- Move isVisible from the Vue instance to a computed property on House.
- $emit a house-change event on @click.stop on the .house.
-
Props:
- Extract .members into a Members component
-
Props:
- members - Array
-
Props:
-
Bonus: Extract .member into a Member component
-
Props:
- member - String
-
Props:
V
Components, Props, Custom Events

Vue Plugins and Vue Router
VI
VI
Vue Plugins and Vue Router
What are Plugins
- Distributable bundles that extend Vue's functionality.
- Can be used both in Browser and in Bundle mode.
- Can register global components.
- Can attach properties to the Vue prototype.
- Can add extra functionality to components.
VI
Vue Plugins and Vue Router
What is Vue Router
- Official Vue multi-page routing plugin
- Allows for website navigation without refresh in the Browser.
- Connects URL structure to component definitions - Pages
- Pages are defined in a Routes list
- Pages can have dynamic parameters in URL user/:userId
VI
Vue Plugins and Vue Router
Vue Router Instance
// 1. Define some routes
const routes = [
{ path: '/', component: HomePage },
{ path: '/user/:id', name: 'users', component: UserPage, props: true }
]
// 2. Pass the routes
const router = new VueRouter({
routes: routes
})
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
router: router
})website.com/user/:idwebsite.com/user/1VI
Vue Plugins and Vue Router
Child Pages
- Each page can have many subpages.
- URL can extend from it's parent or have separate structure.
- Child pages are rendered only inside the router-view custom component of parent pages.
- Child page change does not affect the parent component.
- Child pages can receive props from URL params, route config, and parents.
<div id="app">
<the-header></the-header>
<div class="main-wrapper">
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
<the-footer></the-footer>
</div><div id="app">
<the-header></the-header>
<div class="main-wrapper">
<!-- child is injected -->
<user-page></user-page>
<!-- parent template continues -->
</div>
<the-footer></the-footer>
</div>VI
Vue Plugins and Vue Router
Router Link
- Dynamic component used for creating links to pages defined in the router config.
- Auto registered by Vue Router
- Can intercept clicks to stop browser from refreshing the page.
<router-link to="/about">Go to About</router-link>
<router-link :to="{ name: 'about' }">
Go to About
</router-link>
<router-link :to="{ name: 'user', params: { id: 1 } }">
Go to About
</router-link><a href="/about">Go to About</a>
<a href="/about">Go to About</a>
<a href="/user/1">Go to User 1</a>
VI
Vue Plugins and Vue Router
History vs Hash
- Requires server setup to redirect all requests to index.html
- Uses HTML5 History Api
- Nice, SEO friendly URLs.
- Id navigation for sections is possible.
- Default mode
- Just works
- Adds # to routes
- Can conflict with id navigation to page sections
vuebulgaria.com/stark/eddard-stark
vuebulgaria.com/#/stark/eddard-stark
VI
Vue Plugins and Vue Router
Challenges
-
Move the main Vue instance template and functionality to a new WesterdosMapPage component.
-
Assing it as a page with name of home and / path.
-
- Change the main Vue instance’s template to a single router-view
- Create a MemberPage component
- Assign it as a page with name of member, path /:houseId/:memberId
- Add a router-link linking to the MemberPage on the Members template.
- Display the currentMember's name on the MemberPage template
- Add a back button to the Westeros Map.

Vue CLI and Single File Components
VII
VII
Vue CLI and Single File Components
What is Vue CLI
- Complex set of build tools for fast and painless app development
- Feature rich - Babel, TypeScript, ESLint, PostCSS, PWA, Unit Testing & End-to-end Testing
- Extensible - allows installing external plugins
- Instant Prototyping - build and run Vue files without scaffolding projects
npm install -g @vue/cli
vue create my-project
# OR
vue uiVII
Vue CLI and Single File Components
Vue Single File Components
- Files with .vue extension.
- Template, script and style are in one file.
- Encourage writing small, isolated modules.
- Ability to use pre-processors - TypeScript, Sass, Less, Pug etc.
<template>
<button @click="inc">{{ count }}</button>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
methods: {
inc(){
this.count++
}
}
}
</script>
<style lang="scss">
.button {
background: red;
&:hover {
background: pink;
}
}
</style>
VII
Vue CLI and Single File Components
Why precompilation is necessary.
- Browsers don't know what .vue extension is.
- Need to compile to .js files.
- Compilation requires a configured Webpack or Browserify build chain.
- Using latest ECMAScript features requires transpilation based on target browser.
- Browsers cannot* resolve separate components dynamically.
- PostCSS and style preprocessors need extra configuration.
All of the above are solved by Vue CLI out of the box.
VII
Vue CLI and Single File Components
Challenges
- Add our style.css to the index.html inside the public folder.
- Delete everything from components and views folders.
- Move House, Members and Member* components each to a separate SFC vue file inside components folder.
- Move the houses data to a file inside src/data/houses.js.
- Move WesterosMapPage and MemberPage to views folder each in a .vue file.
- WesterosMapPage.vue should expose the houses data
- MemberPage.vue should expose the houses data
- Move the router definition to the router.js file.


Special thanks to the Vue Bulgaria Team

Nedyalko
Dyakov


Elena
Gancheva
Hristiyan
Ivanov
Find me at
dobromir-hristov
d_m_hristov

dobromir_hristov


dobromir-hristov

Dobromir Hristov
Where to next?
Vue Mastery
Vue School
Vue JS 2 - The Complete Guide
Learn Vue 2: Step By Step
Vue Beginners Workshop
By Dobromir Hristov
Vue Beginners Workshop
- 2,123