Systems Administrator Interview Q's
Describe your career trajectory? How you began? Why you moved from position to position?
I started off in USD as an HelpDesk Coordinator where I managed the Helpdesk and co-ordinated technicians, delegating as needed. This position developed my organizational, technical, and people skills. And after 3 months I was promoted to being the fulltime IT administrator for the School of Nursing + Manchester Conference Center, where I improved business operations and streamlined communications with the implementation of an AD domain, streamlined the Imaging of lab PC's using multicast, trained endusers on PC sec, introduced a Sony Video Conferencing Systems and secured lab PCs using Faronics Deep Freeze to snapshot a computers desired configuration state.
Next I moved to SDSU where they needed a Systems Analyst (with Windows Server Administration + programming experience) where I was responsible for a portion of the SDSU Student Services network including: security, aidlink web applications and databases, servers, backups, user support, and equipment procurement.
I achieved compliance with SDSU Information Security Plan, while overseeing strategic IT planning and department-wide IT infrastructure and operations, aligning IT with CSU priorities, implementing secure systems configurations in accordance with the Campus Info Sec Plan.
I upgraded the Win infra + Servers to x64 Win7 + Server2008
+ implementing Secure Server builds, streamlining Vul Mgmt Processes (with McAfee EPO + CounterSpy Spyware scanning), introducing the Solidus VoIP phone system, and improving DR / BC by following a 3-2-1 rule based backup + recovery strategy).
I provided leadership and mentoring to my work study techs + endusers and handled all security incidents (99% of which were false positives).
I optimized and refined departmental business applications, while automating and optimizing EDI processes and reporting, scripting Oracle PL/SQL jobs, reducing processing time, troubleshooting software issues, and improving quality control of CBRS Campus Billable and Receivable Systems, Fee Deferment processing, Waiver Subsidy processing, and NSLDS Quality Control and Transaction Monitoring systems. Working with DBAs on query optimization.
While I continued my self education learning web dev.
I went back to Ireland to help out with a family emergency and while there I was indep IT consultant primarily for Sherlock Brothers Furniture where I put together a H+S VPN network (5 locations) using Untangle FWs, HP Switches, Dell Servers, and implemented an AD Domain, and improved security by upgrading their antiquated CCTV security camera's to ip-based Axis Security Cameras recording to DVR.
Upon returning to the USA I worked at Align General Insurance underwriters where I was part of a 2-man IT Admin team where we took care of everything for the company: Win/Linux/Unix Servers, the Network (a Multi-Site WAN/LAN), RDS Server with Remote users, FreedomVoice Cloud based VoIP, P to V server migrations (VMWare+Hyper-V).
I helped design + implemented BCP and DRP strategies to insulate the company against events, incidents, and unexpected disasters.
I cultivated an environment of collaboration and efficiency, by streamlining Office communication, with the migration to O365 (from Ex 2010) and the introduction of FreedomVoice Cloud based VoIP.
I enhanced the company’s digital presence with a refactored modern website using HTML5, CSS3, PHP, Apache web server, port forwarding, PSAD Port Scan Attack Detector IDS using Snort Signatures, Sendmail mail server, Linux Bind DNS name servers, a MySQL database servers, while using Git for version control.
While in my spare time I kept going with prog, learning PHP + joining the SDPHP study group, learning more Linux / DB / Web Server administion + Web App security.
Finally progressing to SRG where I'm part of a 4 person team, 2 Directors, Me the Sys Mgr of 2 helpdesk analysts, managing the network of a 33 site senior living community network that consists of (36 Firewalls, 600 Switches, 800 Wifi APs, 15,000+ Data Ports) .
I deal with the day to day running of systems + engineering of network equipment, supervising vendor mgmt,
Monitoring our DR + BC systems (DFS, FC SAN, AWS Backup, VMWare virtualized Exchange DAG and SQL Server FCI and AG), maintaining Network Security, handling Incident Response, providing senior management with status, issue, and resourcing reports.
I provide technical leadership + mentoring to our support analyst's (Jake+Paul) while supervising the Helpdesk, consult on IT architecture solutions, and procure equipment + implement solutions.
I am responsible for and throughly enjoy being responsible for companywide security ensure the adoption and implementation of information security best practices with a view to securing assets, educating users, and reducing incidents.
Its been an enjoyable career and has brought me to the point where I feel I am ready to take on a position as an IT Manager.
1 Why are you applying for this position / what interests you about this job? What is your IT Dept Structure?
Working as a Senior IT Admin or IT Manager would be a step up for me, I currently work under 2 IT dirs one who supervises contracts (accountant) while the other controls budgets + tech strategy.
I deal with the day to day running of systems, supervising the Helpdesk, vendor mgmt, net security, and incident response.
While making equip purchase recs + implem, and mon DR + BC systems.
Plus I will have less of a commute by working locally.
Working as an IT Mgr / TAM would represent professional growth allowing me to tailor technical strategy (BCP+DRP) + controls to mgmt risk (counter threats + vuls), control budgets, and mgmt vendor contracts while having final say on all technical decisions.
Working at ScaleMatrix would allow me to grow professionally by working in a fast paced DC environment on the latest public + private cloud technologies, HA solutions + LBed clusters while the opportunity to make architectural recommendations + perf upgrades excites me!
1 Why do you want to leave your current position?
I want to leave my current job as I believe I've out grown the role, having gained more experience + accomplished my CISSP, VMW, AWS, Server16 + Fort certs, so I'm testing the waters to see what else is out there + am looking for professional growth. I was going to switch before COVID hit
1 Tell us about your long-term career goals.
My long term career goals are to get more specialized Public/Private cloud, working on App Arch + Sec, before growing into a DevSecOps / SRE / IT Manager role.
In the meantime I have plenty of certs to take (CCNA, O365, Azure, Python) and would like to work in a co. with
a bigger Public/Priv cloud presence with more chall work.
I got interested in sec following a Cryptol attack, while a friend in InfoSec recommended Security+,CISSP
1 Describe your typical day? current workload?
I get in just before 8am and check in with our helpdesk guy (they work a staggered schedule one starts at 7am-4pm and the other at 9am-6pm) to see what's going on, on the network (such as any events, incidents or Outages / Bottlenecks / contention / Latency),
There'll usually be some device flagged as being down (false positives) so I'll jump on that straight away (it could be an issue with the physical network, a Firewall, switch, ISP internet service or damaged cabling))
Or an issue with our virtual network topology.
I have WhatsupGold net mon setup to monitor
our physical + virtual network, while our team finds it's virtual overlay feature useful for pinpointing issues in our NW, SAN, storage, Exchange, SQL Server, and SharePoint apps.
We monitor our Ubiquiti Wireless net through Ubiquiti's own self hosted Unifi Controller SDN SW solution which monitors all our Switches and APs on our wireless network.
I'll initially solve any urgent tier 3/4 type stuff, that is impacting peoples ability to conduct business or that requires admin level changes (perms/rules) or re-configs.
While I deal with less urgent issues that require Vendor input, throughout the day where I often try to re-create a problem for root cause analysis.
With all emergencies out of the way, I check the logs from our nightly backups + Powershell scripting jobs to make sure everything is as it should be or for anomalies to look into.
Next I do a Daily analysis of service tickets + whether we have met our SLA goals (of all tickets being looked at within a day) and if there is anything that our analysts may have missed that needs to be looked at.
As systems manager, I manage + train our analysts, manage staff schedules, vacation time, and on call shifts.
Then I switch over to projects I'm working on such as:
- Researching any new HW or SW we are going to implement.
- Coordinating with our Vendors + Reviewing Vendor support issues (have we got support within SLA).
- Planning the HW replacement cycle (5 years on servers/4 years on PCs) and ordering new equipment.
- Planning the takeover/handoff of new/old communities.
- Collaborating with our IT Dirs on technical decisions and our technical direction. Establishing and improving dept policies, procedures, and guidelines.
After lunch:
I schedule any appointments or meetings as there is less chance I will be pulled onto something else.
Coaching our Analysts + working with remote techs (remote hands) we engage to swap out net equipment.
Our Analysts deal with:
Desktop, laptop, phone connectivity issues.
Replacing parts on malfunctioning PCs under warrantee.
Account lockouts + password resets,
Drive mappings
Lobby stations not working
Anything preventing someone from working takes priority!
Describe your monthly? current workload?
I review and test all system updates on a monthly basis before scheduling them to run that night through WSUS.
I handle all imaging through WDS.
I do a quarterly analysis of analyst perf (tickets closed).
I do 2 monthly site visits to geographically dispersed communities for Onboarding and training of new employees (Security Awareness), Installation of equipment, Site surveys and maintenance of existing systems (network, telecoms, POS, medical alerting, PBX/phones, AV Equipment, Security Camera, ADP timeclock, printer, PC, Mac).
1 What regional vendors do you use and how do you manage your vendor relationships?
vendors services: Fort, HP, Dell, Ubiq, VMWare, MS, Bitdefender, Mimecast, WhatsUpGold, Cisco, CDW, ADP, Dameware, Teamviewer, GoToMeeting.
ISPs\Telcos (VoIP & Data services): ATT, TelePacific, Cox
Cable TV services: ATT, Cox
Phone System: Shoretel, Nortel, NEC, Mitel
The Community Manager / Corp Manager takes care of:
In-House TV: ZeeVee, Thor, AVerKey, Creston
Where do you get regional techs from? What perms?
We hire regional techs from Field Nation.
1 What are your strong points / What are you good at?
I have great people skills + can articulate problems + sols
to non-technical people in an easy to understand manner while building good rapport. I believe good comm delivered in a timely fashion is key to great cust serv
I have great problem solving, multitasking + analytical ability,
being able to diagnose problems quickly while getting the user working again.
1 What do you like to work on / find most interesting?
At the minute Public + Private Cloud services and the innovation happening in that space (Smart NICs) along with Web App Sec, attack surface reduction, net defense, SASE + SDWAN, Identity + ZTNA, and MP-BGP eVPN VxLAN and the
latency in network connections, connecting to the cloud.
1 Whats the biggest mistake you’ve made? How recover?
The biggest mistake I made was at SDSU, when demoting an old file server, assuming my boss knew the local admin password but didn't! Luckily we had everything backed up off there before hand so there wasn’t a problem, so now I always make sure to set the local password before removing from the domain.
1 How have you handled situations where you have had an excessive work load?
I regularly have situations where I have an excessive work load. In a situation like that its essential to prioritize what needs to be solved first, and then good communication between team members and end users is needed to keep everybody in the loop. If a lot of people have the same problem at the same time then a group email comes in handy.
1 Could you give 2 examples of stressful situations you have encountered at work, how you handled them?
A stressful situation for me was back at SDSU where one of the programs I was responsible for had a logic flaw on a production run messing up production data, it couldn't be rolled back, as subsequent programs had already run on that data, so we had to manually fix production data, unfortunately at the same McAfee threw up a false positive on someone computers which always needed to handled immediately. So it was a matter of having to juggle competing priorities.
And then of course there was the WorldIsYours ransomeware attack where 1400 Win PCs + Servers got encrypted as our AD Admin account had been compromised which put our entire team in a stressful situation. We went into a state of lockdown pulling 16 hour days until we had a functioning network again. It made me fully focus on security + attack surface reduction.
Give an example of where you had a conflict with a colleague and how you handled it?
In my time a ALignG myself and Jose had conflicting views on how to fix VoIP call clarity problem we were having, I was the point of contact working with the vendor FreedomVoice who had been recommending to me that we needed to use, their recommended and tested Dell Sonicwall TZ 215 UTM Firewall, however Jose wanted to maintain the Untangle NG UTM Firewall appliance, as it provided the OpenVPN site-to-site VPN connection to our datacenter Untangle FW.
I had already segmented out our VoIP and Data traffic onto 2 separate VLANs so the next logical step for me was to use the vendor recommended Dell Sonicwall appliance and switch to an IPSec site-to-site VPN as only open source firmware provides OpenVPN connectivity. At the end of the day Jose was the senior member and decided to run both FW's in tandem.
Everyone in the office says Internet does not work. What steps for investigation will you perform?
Ping 8.8.8.8 to see if you can get to google.
If no response, ping the on premise router of your ISP.
If no response, ping the public ip of your router.
If no response, ping the private ip of your router.
If no response, ping your switch.
If no response, ping your DC.
These steps will help to isolate where the malfunction and perform remediation.
What are the benefits of using a UPS versus What are the benefits of using a UPS versus a PDU??
A UPS has a battery and provides near-instantaneous protection from input power interruptions, by supplying energy stored in batteries. It provides emergency power to your devices for a short period of time when an outage occurs and allows you to gracefully power down your devices.
A PDU is an industrial grade power stripe used to remotely monitor, manage, and protect the flow of power to your devices, it can have built in switching capability which allows you to toggle the power on and off to specific power outlets.
They are used to multiply the number of power outlets available and are used to protect devices which don’t have redundant power supplies (single power cord devices).
Generally you use both together where Main - UPS - PDU.
You might bypass the UPS altogether and have a secondary power line running directly from the mains supply to PDU,
or
You might have dual UPSs with separate mains lines,
or
You might have one UPS being fed by dual mains lines.
2 Draw out your network diagram? What software do you use for creating network diagrams?
How do you manage your network documentation?
How do you handle late night equipment upgrades / patching.
2.1 Describe how you setup your Firewalls to give internet access to different subnets/VLANs?
2.1 Describe the use of VLANs in your environment? Describe how you configure VLANs?
2.1 What type of Routing have you configured for your network?
1 Describe your current network environment?
We have a H+Spoke VPN Topology (in a 2 tier architecture) providing redundant connectivity from each of our 33 communities back to our Head Office via IPSec VPN's running on Fortinet FTGW 60E NGFW Firewall devices (FortiOS 6.0) configured with fully redundant route based IPSec VPNs with Link Health Monitors + floating static routes over dual WAN interfaces from different ISPs at both the H+S FTGWs to providing redundant HA connectivity between our Head Office DC Hub and our remote Spoke Senior Living communities.
The Link Health Monitors configured on the IPSec VPN static routes are used to rapidly detect when a link goes down, providing sub-millisecond failover to the backup IPSec VPN running on our secondary WAN circuit.
Our FortiGuard security subscription services + UTM advanced threat protection we get automated protection against today’s sophisticated threats including 24/7 firewall support, application control, advanced threat protection, IPS service, VPN, and web filtering + Anti-Spam service, all from one device that’s easy to deploy and manage.
For regular internet traffic:
I allow load balanced internet access from the individual community locations through the use of ECMP Equal Cost Multipath Routing for redundancy over dual WAN interfaces configured with a weighted load balancing algorithm that distributes our regular internet traffic in a 70/30 split across WAN interfaces as our primary ATT WAN interface has more bandwidth and is less expensive than our secondary TelePacific WAN interface which is primarily used for VoIP phone service.
Back on the H+S VPN Topology, the fully redundant Route based IPSec VPN connections concentrate together at our Hub VPN Concentrator (a FTGW 600E unit) from the spoke remote VPN Gateways (a mix of FTGW 60Es, 90Ds, previously 110Cs) in each community.
The VPN Concentrator is a single, central FortiGate unit that acts a focal point to co-ordinate communication between IPSec VPN interfaces coming in from the remote spoke networks on one device in the network Hub, all VPN tunnels terminate at the hub's VPN Concentrator.
For IPSec connectivity
I configure the prim IPSec VPN with a static route exiting our HQ FTGW over WAN1 on our ATT Business Fiber link, entering our Branch FTGWs on WAN1. I configure the secondary IPSec VPN with a static route exiting our HQ FTGW over WAN2 on our TelePacific link and entering our Branch FTGWs on WAN2 also.
I have set both static routes of the IPSec VPNs with the same AD Administrative distance but I have set the static route of the Primary IPSec VPN to have a higher priority this way the Primary IPSec VPN handles all of our VPN traffic while keeping the default static route of our Secondary IPSec VPN active in the Routing table. Keeping the default static route of our Secondary IPSec VPN active in the Routing table, keeps the secondary IPSec VPN interface up, and available to respond to Link Health Monitor pings, however no traffic from the LAN or DMZ actively traverses this VPN unless the other static route fails out of the routing table, this config facilitates fast failover.
When there are multiple routes to the same destination with the same distance then the priority is checked, and the route with the most priority (lowest number) is given preference.
I put both IPSec VPN Interfaces in a VPN Zone in order to avoid duplication of Security Policy and to ensure seamless failover between IPSec VPNs.
I configure Link Health Monitors on the static routes of the Primary IPSec VPN that radiate out to each remote VPN gateway at the different communities. The Link Health Monitors control FO Failover from the active static route of the Primary IPSec VPN to the passive static route configured for the Secondary IPSec VPN.
I have added Blackhole Routes for subnets reachable using our IPSec VPNs to ensure that if a VPN tunnel goes down, unencrypted traffic is not mistakingly routed to our ISPs or the Internet. The Blkhole Routes are given the highest AD + least priority making it the last route hit when all other routes fail!
These Blackhole routes are not factored into our ECMP Load Balancing for regular internet traffic (non-VPN traffic) and are merely configured as a failsafe should the Static routes (WAN1 + WAN2) used by our IPSec VPNs to the private networks behind the remote VPN GWs fail.
This configuration avoids a SPOF (of only having one WAN link) and
provides availability through the rapid FO failover from one route to another in the event the primary WAN circuit goes down thanks to the Link Health Monitors,
while maintaining the highest IPSec security standard while in transit using the strongest possible AES 265 encryption and in the event both WAN circuits fail simultaneously, our routes over the IPSec VPNs fail safe to the Blackhole Routes preventing our traffic from leaving our network unencrypted!
For additional security I have segmented our network out into logically separate VLANs and use Policy based Routing to control the flow of information between the VLANs and what can get out to the internet.
With all of these in place Traffic can pass from our private networks (LAN/VLAN/DMZ) in the Corporate Head Office / Datacenter and remote Senior Living Communities to the other private networks in either the Corporate Head Office / Datacenter or remote Senior Living Communities.
Communication between remote private networks is facilitated by hairpinning traffic from one remote private network back through the hub before being directed out to the corresponding remote Spoke VPN Gateway on route to the private network of a different Community.
a spoke isn’t necessarily a FTGW, it could be VPN client software or it could be a Cisco device with a GRE VPN or a Windows device with an L2TP VPN.
Our switching infrastructure consists is a mixture HP 1820 48-port 24-port (half PoE ports for phones) and 8-port Switches, along with some legacy Procurve switches with extensive use of Vlans to segment our Corporate Business, VoIP and protected Server Networks while segregate our Web Application proxy / ADFS Proxy out onto our authenticated DMZ while also isolating our insecure Guest Wifi network out onto our unauthenticated DMZ.
For our Wifi we use Ubiquiti Edge Switch XP switches with passive PoE(formerly ToughSwitch) and Ubiquiti UAP-AC-PRO UAP-AC-LR Access Points for both our Corp and Guest Wifi networks, both running on separate Vlans.
In each community:
we have dual Dell PowerEdge R720 servers (2 500GB SATA drives in a RAID1 config for the C drive and 5 1TB SAS disks in a RAID10 config for the data drive), which are VMWare ESXi v6 hosts to Win Server 2016 DCs.
From which we utilize AD Group Policy + DA Desktop Authority for config mgmt. Both servers get their power thru Eaton UPS's so they have backup power should there be an outage.
All communities have an internet lounge with 2 to 3 workstations and a printer.
All communities have a segmented corporate network running on its own Vlan.
All communities have Kiosk training computers where they can complete compliance based training courses for health care workers.
Back at Headquarters:
We house the majority of our VMWare (vCenter) virtualized corporate server infrastructure, SAN, FC Fabric and Dell SC8000 Storage Array in our purpose built DC with dual mains lines + FM200 fire suppressant system.
We use Windows DFS Distributed File System to replicate community files back to our head office where they are be backed up using block level replication.
We use WDS for building / capturing images (with driver injection), deploying images (WIM) with WDS/PXE, and WSUS for scheduling patching (once a month) ) + reporting.
For Asset Management and tracking we used Cisco’s Meraki Systems Manager.
Tell us about your experience with network switches?
Our switching infrastructure consists is a mixture HP 1820 48-port 24-port (half PoE ports for phones) and 8-port Switches, along with some legacy Procurve switches with extensive use of Vlans to segment our Corporate Business, VoIP and protected Server Networks while segregate our Web Application proxy / ADFS Proxy out onto our authenticated DMZ while also isolating our insecure Guest Wifi network out onto our unauthenticated DMZ.
I have in the past had to manipulate the Voice VLAN feature + PoE to achieve VoIP Passthrough in certain communities where we use one ethernet cable to supply Voice + Data + Power to workstations as there may be limited ethernet cabling or in communities where it is prohibitively expensive to run new cabling.
We use Yealink T42G VoIP phones with integrated Dual Port Gigabit ethernet switch with Voice VLAN functionality + Power via 802.3af PoE (or local PoE injector) to supply both Voice, Data, and Power to troublesome collocated workstations.
we use the PoE injectors to supply power to the VoIP phones in locations where our main switch doesn’t supply PoE or doesn’t supply the correct voltage (this saves on the cost buying a new 48 port switch to supply the correct PoE).
The Voice VLAN feature allows me to send Voice VLAN tagged traffic to the VOIP phones Dual Port Gigabit ethernet switch while using the Access Port to passthrough untagged data traffic on the default VLAN to the Client PC, bypassing the need to use a trunk port and the Native VLAN with their drawbacks to accomplish the same task.
VLAN1 - LAN / Default VLAN - untagged by default
VLAN51 - Native VLAN for Legacy Equip, blocked from other VLANs - tagged
VLAN52 - MGMT VLAN - Net Equip Mgmt VLAN - tagged
VLAN2 - Faux VLAN - for unused ports - tagged - FW Policy blocks this from going anywhere
VLAN5 - SRG Business Network - tagged
VLAN6 - VoIP Network - tagged
VLAN10 - Office Guest Internet Network (wired) - tagged
VLAN11 - Training Network - tagged
VLAN20 - VMW Management traffic
VLAN21 - VMW vMotion Network
VLAN22 - WSFC Heartbeat Network + AG Cluster Replication traffic (ethernet VLAN)
VLAN23 - VMW FT logging for vSphere fault tolerance
VLAN 40 - Ubiquiti Mgmt Net (DMZ port) - tagged
VLAN 41 - Guest Wifi + Internet Lounge Computers (DMZ port)- tagged.
VLAN 42 - IOTCRAP / Camera Network - tagged
2.2 Describe the controls you have put in place to secure Guest Wifi access + IoT devices? How do you manage your Unifi Controller / Network?
I have setup + administer a Ubiquiti Unifi SDN Wifi Network for 33 Senior Living communities, consisting of
1 cloud base UniFi Controller + 200 Ubiquiti ToughSwitches +
600 Ubiquiti WAPs (Unifi AP AC PRO / LR)
I segment our Guest Wifi VLAN41 + IOT device VLAN42 networks into its own DMZ with its own dedicated Ubiquiti ToughSwitch switching equipment in order to completely separate insecure traffic out onto its own infra + VLANs this
allowing better bandwidth mgmt with QoS,
ensures Ubiquiti PoE devices receive the correct PoE voltage and secures us from VLAN hopping attacks.
VLAN40 Ubiquiti Mgmt Net / VLAN41 G_Wifi / VLAN42 IOT
this VLAN is used to centrally manage all Ubiquiti devices from our AWS hosted Unifi SDN Controller which itself is hosted in an isolated AWS account and is only contactable from the public IP addresses of our Corporate Firewalls, creates maximum separation from our corporate systems + network ensuring their security.
In order for the Ubiquiti Switches + WAPS out in the different communities to receive their configurations from and be managed by the Unifi Controller in AWS, I have configured FW Security Policies to allow communication from VLAN40 through the WAN interfaces to the Unifi Controller in the AWS.
I created a Custom Unifi Profile on the Unifi Controller to deliver both VLAN 40 + VLAN41 + PoE to Ubiquiti switches + WAPs in hard to reach places, while I modified the flat Unifi Profile for VLAN42 for the IOT/Camera devices network to deliver only VLAN60 + PoE to the end point device they are connected to.
Custom Unifi profile (VLAN40 + VLAN41)
The custom profile was necessary here because I was implementing a non-standard configuration where I needed to pass 2 VLANs out a trunk port while also configuring the port to send PoE to other Ubiquiti switches and Ubiquiti WAPs.
VLAN1 Default VLAN / Native VLAN:
For security reasons I move the Native VLAN to our Faux VLAN2 to ensure no untagged traffic travels on our net.
VLAN40 for the Ubiquiti Mgmt net (Switches + WAPs)
VLAN41 for the Guest Wifi + Internet Lounge network
Our WAPs (UAP HD Access Points) are configured to dispense IP Addresses in separate DHCP ranges according to the VLAN that SSID is configured to run on.
PoE:
I also use Custom Unifi profile to supply PoE to WAPS + IOT/ Camera devices so separate power lines are not required to be ran to hard to reach places and so the devices can easily be rebooted with a bounce of their switch port.
To power our Yealink T42G VoIP phones, I enable Active PoE (802.3af/A) / PoE+ (802.3at/A 25.5 watts) which allow the devices to auto negotiate the proper voltage + pins to use for the transfer of electrical power between the 2 devices using Active PoE (802.3af/A) which is supported on both ends.
PoE PassThrough Switches
can operate as both a Powered Device (PD) and Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE).
This means that the switch can be powered by PoE while simultaneously providing power by PoE to other devices such as IP phones or WAPs wireless access points.
I have configured Security policies to
allow traffic inbound/outbound on port 8080 for the Inform protocol only from communities public WAN IP addresses after I have adopted new Unifi devices via Ubiquiti Cloud Access portal,
allow traffic inbound + outbound on port UDP 3478 for the STUN protocol only from communities public WAN IP addresses as it allows the Unifi controller to initiate contact with Unifi devices, so it doesn't have to wait for the WAP to send an inform packet before communication can begin which speeds the entire process up.
FW Policy blocking IOT use of its own insecure DNS:
The order of the rules is important here as (we generally place the most restrictive rule higher in the list so it is enforced before the less restrictive rules lower down the list)
DNS traffic from any source is allowed in to VLAN42,
so the default Fort DNS server is able to communicate with VLAN42, then directly after this
DNS traffic from any source is blocked to all interfaces, preventing external DNS sources from being used.
You always want to use your own DNS servers.
Securely Adopting Remote Unifi devices over the public internet
Finally with our Unifi Controller setup + configured for mgmt via the Ubiquiti Cloud Access portal at unifi.ubnt.com we can securely adopt our remote Unifi devices over the internet
the UniFi Cloud Access Portal at https://unifi.ui.com/
the Cloud Access Mgmt feature (that we temporarily enabled when configuring our Unifi Controller)
a computer on the same VLAN as the Unifi devices to access our UniFi Cloud Access Portal, via a Chrome Browser with the Ubiquiti Discovery tool plugin installed.
The Ubiquiti Discovery tool plugin allows the UniFi Cloud Access Portal to discover any locally-available unmanaged UniFi Devices and adopt them once we login with our Ubiquiti SSO account with 2FA which ensures secure authentication.
Using the Ubiquiti Chrome Plugin to adopt WAPs:
Mitigates the inherent risks of remote L3 adoption of Unifi devices and is an entirely more secure process than allowing direct web access to the Unifi controller using the unencrypted insecure inform protocol, because
TLS is used to encrypt the communication between the laptop (same VLAN) and the UniFi Cloud Access Portal,
meaning the unencrypted inform protocol is only exposed locally and never travels over the internet until secure encryption keys have been established and the adoption process is complete.
What type of perf / net monitoring do you have? what features do you like about it?
I introduced WhatsUpGold net monitoring to provide real time alerting of network issues + is also a log management tool that delivers advanced visualization features that enable our team to pinpoint + remedy net anomalies minimizing downtime for optimal availability while lowering MTTR.
It provides App monitoring, network traffic analysis, discovery and net + virtual env monitoring.
Nagios net mon is cheaper + more complicated to install, it monitors Switches, Routers, Servers, and Apps using SNMP.
2.1 Describe the VPN Topology of your Network and what type of Redundancy / Availablility + Security you perform between Branch + HQ Locations ?
2.4 Describe how you configure a H+S VPN Topology?
Takes place at the Hub / VPN Concentrator + at the Spokes, and with essentially the same 3 part configuration necessary in both places where I
Define Route based IPSec VPNs Phase1+2 configs in order to establish secure IPSec VPN connectivity
Define Routing thru the secure IPSec tunnels with FO (thru Link Monitors) + LB (thru PBR)
Define Security Policy to allow traffic to flow between the connected networks.
2.4.1 Describe the Phase 1+2 configuration of your HUB FTGW 600E unit + How it interacts your Spoke 60Es/90Ds(avoid like the plague-FortGu)?
2.4.2 Describe how you have configured Routing (with LB+FO) in your H+S Topology?
At the Hub I configure static routes from the local interfaces (LAN/VLAN/DMZ) to the VPN interface which sends traffic via VPN to each comm remote VPN GW
I configure Link Health Monitors to trigger fast FO.
3 Describe the Sec Pol / PBR on the Hub / VPN Concentrator to permit traffic to flow between the Corporate Private Networks and the Community Private Networks?
2.4.2 Describe how you have configured Routing (with LB+FO) in your H+S Topology?
2.4.2 At the Spoke Describe the Phase 1+2 configuration of your Spoke 60Es/90Ds + How it interacts with your HUB FTGW 600E unit?
2.4.2 Describe how you have configured Routing (with LB+FO) at the Spoke's in your H+S Topology?
I configure Link Health Monitors to trigger FO.
2.4.2 Describe the Sec Pol / PBR at the Spoke Remote VPN GWs to permit traffic to flow between the Spoke Private Networks and the Hub Private Networks?
2.3 Describe how you use FW Rules / Security Policies (Proxy Options) / PBR - by Service (NAT mode) on your Firewalls to secure + optimize traffic flow in + out of each network segment (VLAN/subnet) on your network?
2.3.2Describe your use of DPI / full SSL/SSH Inspection in your Security Policies?
2.3.1 What are your 9 major Egress Policies?
2.3.2 What are your 7 major Ingress Policies?
2.3.2 Describe your use of VIPs + WAP/ADFS Proxy / F5 LB in securing inbound server traffic?
2.3.3 What are your 4 major Internal Traffic Policies?
2.2 Describe how you have segmented your network using VLANs + Subnetting?
2.2 Describe the Vlan tagging / Switching setup of your network?
2.2 What's the difference between a VLAN and a subnet?
2.2 Describe your use of VLANs and DMZ's in securing your business Servers + Data?
What type of dynamic routing protocols have you used?
I use OSPF dynamic routing at one of our locations where the community is in a forrested location with private chalets distributed about 1000 feet from the main community building, making running cables too expensive. As a work around I setup a wireless network bridge configured with authenticated single area private OSPF routing to share routing info out to the internet between all routers so the chalets have highly available access to the internet.
I use a Ubiquiti LightBeam AC (LBE-5AC-23, with 23dBi of antenna gain (giving us a range of 50 miles or more) to create the wireless network bridge between several buildings at our Narrow Glen community.
We dont use a great deal of dynamic routing as we have been able to get away with IPSec VPN Static Routing, Policy based Routing, and ECMP Equal Cost Multipath routing with Link Health Monitors and a weighted Load Balancing Algorithm for high availability + Failover of our active + passive routes, and to control the flow of traffic between our Locations + VLANs.
2.5 How would you maintain 24/7 network uptime / HA / IT service availability? five 9's (99.999% uptime)?
Active redundancy where redundant items of the same kind, a method to detect failure + auto FO systems to bypass failed items in a HA FT design to maintain uptime.
- Hot swapping of components, no need to power down.
- Temp sensors to throttle operating frequency on servers.
- Redundant Power Supplies on servers + UPS
- RAID arrays on all servers to provide data redundancy,
- Data Backups locally and to remote warm sites for DR.
- HSRP (Hot Standby Routing Protocol) to FO to hot standby router. HSRP allows host servers in DC to use a single virtual router (multiple routers) to maintain connectivity even if the first hop router fails.
We have designed our systems using a fault-tolerant design following Active redundancy principles using Load Balanced Clustered Virtual servers to ensure maximum uptime.
Active redundancy is used in complex systems to achieve high availability with no performance decline. Multiple items of the same kind are incorporated into a design that includes a method to detect failure and automatically reconfigure the system to bypass failed items using a voting scheme.
A fault-tolerant design enables a system to continue its intended operation, possibly at a reduced level, rather than failing completely, when some part of the system fails. FT systems are typically based on the concept of redundancy.
HSRP (Hot Standby Routing Protocol) fail over internet connections should the main connection go down. HSRP is a routing protocol that allows host computers on the Internet to use multiple routers that act as a single virtual router, maintaining connectivity even if the first hop router fails, because other routers are on "hot standby" - ready to go.
Hot swappable of components dont have to power down.
Temperature sensors to throttle op frequency on servers.
RAID arrays on all our servers to provide data redundancy, Data Backups locally and to remote locations. 3-2-1-1-0 Rule
Power: - Redundant Power Supplies on servers.
- UPS Uninterruptible Power Supply power supplies,
DRP: - have redundant remote network configured to
take over in the event of a natural disaster.
How did you handle the impact of COVID?
What Remote working solutions did you implement?
What type of secure remote access / VPN / RDP have you configured?
It didn't impact our IT team that much as we handle everything remotely anyway and had corporate users working remotely via our pre-autheticated Load Balanced Server 2016 RDS Farm where users connect through a web browser to our WAP Web Application Proxy / ADFS Proxy before being redirected to our RDS Farm via our F5-LTM Load Balancer where they can access their workspace and work remotely.
Out in the communities they scaled down to a skeleton crew and had strict cocooning regulations in place while providing a meal delivery service and temperature readings on all people attempting to access the buildings
2 Give an example of an instance of a technical problem which tested your problem solving / technical skills and were happy to solve.
2.5 What difficult networking problems have you encountered and how did you resolve them?
2.5 Describe some networking / systems issues you have had to resolve?
Give an example of an unexpected IT support issue you discovered and how did you handle it?
2.5 What difficult networking problems have you encountered and how did you resolve them?
SRG getting PC’s with no wired connectivity onto our corporate network so I had to get connectivity through the legacy wifi network in the building. Initial I tried piggybacking our corporate IP range on the legacy wifi network by setting static IP and DNS settings on the computers in question (while setting up Static IPs on the DHCP server) this gave connectivity for a period of time but then would lose their ability to communicate with the DC. This can happen fairly regularly when a network is setup with a DC not on the same Vlan as its clients, eventually a computer local to the Vlans subnet takes over as the master browser for that subnet.
To overcome this I setup a separate DHCP scope and used DHCP reservations on that scope, while also using reverse blocking rules on the legacy DHCP scope to prevent the Corporate computers from pulling an IP on the legacy DHCP scope and then I had consistent connectivity.
SRG Getting ADP timeclocks to connect back to headquarters as part of a takeover that was going on, before we got a chance to put our network equipment in place. We placed one of our Firewalls on the Vintage network next to the ADP Timeclocks and setup an IPSec VPN back to our HUB Concentrator and had their network admin put rules in place to allow the traffic.
2.5 SRG Troubleshooting DHCP Scope issues where PC’s were intermittently losing connectivity, it appeared as though there was an IP conflict as both devices showed as having the same IP in Dameware and DNS.
Both MAC addresses were showing on our Switches so they were online. So I checked the Firewall and could see the Host Name and IP were showing on there so it looked like it was getting out to the internet.
I set a static IP on one of the computers and it updated in DNS. I plugged it into her Shoretel phone which had pass thru enabled + it pull an IP from the VoIP DHCP scope.
It was at this point that I checked DHCP scope for the corp wifi and could see it had been used up by devices that shouldn’t have been on their (namely peoples phones), so corporate users had used the Corporate password to get on there.
2.5 SRG Packet Shaping
I had a problem in one of the recently acquired communities where I had limited bandwidth on our WAN links while we were waiting for new Broadband links to be installed. This meant that the Corporate VLAN we put in was saturating all our bandwidth and not leaving any service for our Guest Wifi network leading to complaints.
To overcome this I enabled packet shaping on the internet connection in order to give a dedicated amount of bandwidth to the wifi network so guests could access their email.
Describe a network crisis and how you handled it?
I have encountered 2 ransomware attacks in my time where corporate files were encrypted and ransomware payments demanded. The second attack was by far the worst resulting significant downtime, it was known as TheWorldIsYours Ransomware where attackers managed to brut force our publicly exposed Citrix server, gain administrative access to our network, wiping out all AD Domain Servers and computers! Luckily we follow the 3-2-1 backup rule and had snapshots of our data and server configurations replicating at the block level between our dual storage controllers so no data was lost. We got all our Servers backup and running using Thinware vBackup within 24 hours but had to engage external contractors to help re-install all 1600 client PCs which took about a week.
1 What recent network projects / Improvements have you architected / managed the implementation of recently that you are proud off?
What Systems Integration / optimizations have you made + how did they improve company performance?
Give an example of where you have leveraged technology for process improvement?
2 How did you have to adapt your network for:
Vintage Community Takeovers / Net Integration:
Community Wifi / Cameras Systems:
- Axis / Vitek / Hik / Geovision / ExacqVision IP based Security Camera’s.
Facilities Access Control:
- DKS Doorking, DXS, Viking, Vingcard, Maxxess.
In-House TV:
- ZeeVee, Thor, AVerKey, Creston
2 What Network Hardware have you configured and what features did you like / dislike about each?
2 What do you like / dislike about FortiGate's FortiOS?
2 Describe how you harden / upgrade a Firewall?
2 What sort of power control / backup power equipment have you used?
Are you using SDWAN yet?
How do you envision integrating SDWAN into your network?
And what benefits do you believe SDWAN will bring?
The move to SDWAN and a fully Software Defined Network (with increased opportunities for network automation) is on my plate for next year.
Describe the Layered Defense strategy / network segmentation strategy you used.
What is the difference between a threat, vuln, + a risk?
What's the difference between IDS v IPS? Give examples.
What are the steps to securing a Linux server?
Describe how a SIEM platform works.
How would you triage if something is high/med/low severity
At what point do you determine that a widespread malware outbreak is taking place versus a singular incident?
What sorts of anomalies would you look for to identify a compromised system?
What security measures have you implemented on your FWs?
What type security cert administration (PKI) have you done?
What sort of Vuln Mgmt / scanning do you do? Name at least 3 diff Vuln scanners and patterns to identify them
How do you increase Security Awareness across the company?
How have you improved the sec of your organization?
I drove a companywide security initiative to ensure the adoption + implementation of info sec BPs with a view to securing assets, educating users, + reducing incidents in the short, medium, and long term. MFA, SSO, SIEM and EDR
Exchange with mimecast filtering for spam control.
CarbonBlack / Bit9 whitelisting. BitDefender Anti-V + GravZo
I disabled use of SMB1, TLS 1.0 + 1.1 through GPO.
Syslog Servers to ingest logs from our servers.
I implemented a new secure password policy with password complexity rules + setup a Password Self–Service website (ManageEngine’s AD self-service plus product)
I implemented new account, account modification, and account termination procedures to bring us in line with SOX Compliance.
7 What Security Products / Equip have you used + configured?
Fortinet NGFW v6.0 / Untangle NG UTM Firewall v12.1 / Dell Sonicwall TZ 215 UTM Firewall / pfSense SG-4860 Sec GW.
Win Server FW, Linux Iptables/ufw firewall, Kali Linux.
WhatsUpGold / Nagios Core with MTRG integ for Net Mon
7 What Security experience do you have?
I recently drove a company-wide sec initiative to ensure the adoption + implementation of info sec BPs with a view to
- securing assets,
- educating users, and
- reducing incidents in the short, med, + long term.
- MFA, SSO, SIEM, + EDR,
- 3-2-1-1-0 Backup Rule (3 copies, 2 media, 1offsite/airgap)
3.2 How is encryption used to secure your data at rest?
I use Bitlocker Drive Encryption to encrypt at the VM level, so every volume gets encrypted (a key is required when mounting the volume), and stays encrypted so the whole volume is protected from offline attacks, even if a virtual disk gets stolen it still protected.
It protects at the file volume level so when the DB server is online, the volume is unlocked, though not decrypted. If a malicious party stole the whole drive, they still would not be able to attach + use it.
Detaching or Backing up a database to a different volume that is not protected by BitLocker causes any protection the file currently has to be lost.
For Servers in remote communities + Corporate laptops I enable Bitlocker FDE Full Disk Encryption so if a physical hard drive gets stolen the data stored on it is protected.
For our SQL Server instances I enable TDE Transparent Data Encryption, were the DB files themselves are encrypted (as well as backup files of the TDE-encrypted DBs).
Therefore, if either file is copied or stolen via a network share, the attacker still cannot read it.
With TDE you can encrypt the sensitive data in a DB and protect the encryption keys with a certificate.
TDE performs real-time I/O encryption and decryption of the data and log files to protect data at rest.
Backup files of DBs that have TDE enabled are also encrypted by using the DB encryption key. As a result, when you restore these backups, the cert protecting the DB encryption key must be available.
I use GP Restricted Groups to explicitly set and control the membership of a local group by replacing existing memberships with ones defined in the GPO, thus limiting who has administrative access. While also implementing LAPS Local Administrator Password Solution to manage the local account password of domain joined computers, it sets a unique password for every local administrator account and stores it in AD (limiting lateral movement if there’s a breach)
I have Advanced Audit Policy Configuration configured to log Success and Failure events.
3 How would you manage the configuration + security settings of computers on your domain?
3 How do you control all the Office 2013 / 2016 / 2019 settings on a network?
I use AD GPO in conjunction with Dell DA (Config Mgmt) + Bit9 process whitelisting to lockdown PCs,
while I monitor + defend our workstations using
Bitdefender (Win + Mac)+Gravityzone Cont Center +
CarbonBlack endp file behavior mon + real-time threat det.
While also doing a significant amount Powershell scanning to mon + detect suspicious activity across our AD, Servers, PCs
Secure Win Laptops using TPM+BitLocker Encryption
I use VirusTotal suspicious file + URL analysis - root cause analysis
I also integrated the ADSelfService Plus: Password Self-Service Portal which integrates with our AD domain + Ex email accounts to allow the user to register + set security questions before being able to reset their password and / or
unlock their accounts (network + email are linked together).
Introduced Config Mgmt + Sec Baselines + Golden Image to document, track, improve + approve network changes.
Introduced Meraki Systems Manager for Asset Management, which was very convenient to use through its browser based dashboard giving a detailed view of all pc and laptop assets.
MS CAL Management through the use of a KMS server.
AD Group Policy restrictions,
disabling legacy protocols (SSLv2).
password complexity requirements.
7 Give me an example of where you evaluated a risk and what control did you put in place to mitigate it?
While implementing new security controls + processes as part of our company wide digital transformation + security awareness program to simultaneously achieve refine our line of business tasks, improve security, while reducing OpEx .
ZT remote access to line of business apps using TLS/SSL based ADFS Federated Identity SSO solution.
Worked with AD as an LDAP repository, and wrote a number of powershell scripts for admin of data within AD. Automatically disabling User Accounts after 30 days
I've always approached IT with an eye on Security but it was in my role as a Systems Analyst at SDSU that I developed a deeper understanding of how a secure environment handling PII data should function.
I was part of the newly developed Campus Security Framework initiative, where I designed and implemented several new security controls such as:
McAfee EPO Anti-Virus + SunBelt Counterspy Anti-Spyware for centralized scanning, mgmt, + reporting of possible threats, compromises, + breaches.
I worked with the campus Info Sec Dept to developed + implement secure Server + PC builds.
Maintained our Software Licensing Inventory.
Implemented WSUS auto Patch Mgmt for our AD domain
MBAC MS Baseline Sec Analyzer.
SAST Code Analysis + Pen Tested Aidlink Web Portal
Any suspected security breach had to be reported to Info Sec Office and we had to send them copies of the logs of the suspected machine. We never had a security breach but McAfee popped false positives to be investigated, we took it off the network + shut it down.
We physically had to keep track of licenses for SW.
We had to educate all our users of the importance of not emailing or storing SSNs on their computers.
Any documents with social sec info were collected daily and sent away to be shredded.
Always using secure FTP.
We passed audits twice by outside auditors to see if we were in compliance.
How do you handle AntiVirus alerts?
Check the policy for the AV and then the alert. If the alert is for a legitimate file then it can be whitelisted and if this is malicious file then it can be quarantined/deleted.
The hash of the file can be checked for reputation on various websites like virustotal, malwares.com etc.
AV needs to be fine-tuned so that the alerts can be reduced.
What sort of attacks / Security incidents have you experienced? And how did you counter them?
What is your incident response plan / what incidence response methodology do you follow?
What is an incident and how do you manage it?
Any event which leads to compromise of the security of an organisation is an incident. The incident process goes like this:
- Identification of the Incident
- Logging it (Details)
- Investigation and root cause analysis (RCA)
- Escalation or keeping the senior management/parties informed
- Remediation steps
- Closure report.
Explain phishing and how it can be prevented.
List the steps to data loss prevention.
Describe what SQL Injection is ?
This is a server-side attack that takes advantage of vuls in web applications to send unauthorized DB queries
What's XSS and why is it bad? How would you rank it's severity?
Whats the difference between XSS v XSRF?
XXS Cross site scripting is a JavaScript vulnerability in the web applications. The easiest way to explain this is a case when a user enters a script in the client side input fields and that input gets processed without getting validated. This leads to untrusted data getting saved and executed on the client side.
Countermeasures of XSS are input validation, implementing a CSP (Content security policy)
C/XSRF Cross Site Request Forgery is a web application vulnerability in which the server does not check whether the request came from a trusted client or not. The request is just processed directly. It can be further followed by the ways to detect this, examples and countermeasures.
DDoS stands for distributed denial of service. When a network/server/application is flooded with large number of requests which it is not designed to handle making the server unavailable to the legitimate requests. The requests can come from different not related sources hence it is a distributed denial of service attack. It can be mitigated by analysing and filtering the traffic in the scrubbing centres. The scrubbing centres are centralized data cleansing station wherein the traffic to a website is analysed and the malicious traffic is removed.
Countermeasures:
- Implementing detection mechanisms, especially signal analysis techniques
- Deploying HA solutions and redundancy resources
- Disabling non-required service
- Traffic pattern analysis
Explain how the TCP handshake works. How is it different from UDP?
TCP is connection oriented, while UDP is connectionless.
The data exchange is done, thanks to a three-way handshake technique, shown here. The first step is the client sending an SYN packet to the server. The server then responds with an SYN-ACK packet, if the target port is open. Finally, the server receives an ACK packet and a connection is established.
SYN: Starts the connection
ACK: Acknowledges the reception
RST: Resets a connection
FIN: Finishes reception
URG: Indicates urgent processing
PSH: Sends immediately
Chain of custody?
For legal cases the data/device (evidence) needs to be integrated, hence any access needs to be documented – who, what when and why. Compromise in this process can cause legal issues for the parties involved.
CIA triad?
Confidentiality refers to protecting data by granting access to data (for example Personal identifiable information PII of clients) only to authorized persons and groups.
Integrity refers to the fact that data should be protected during every process. Simply is ensuring the trustworthiness, consistency and accuracy of data
Availability refers to ensuring that the data is available by authorized users when it needed.
7 Whats more important Security or Operations?
it's a balance! Sometimes ops takes priority + security might need to take a back seat, but that’s only for an accepted risk, or sometimes Security is going to lead.
You have to make sure you right size + put the investment in the right place to make sure your users are protected.
7 What Compliance Standards do you have experience off?
At SRG we had to deal with Sarbannes Oxley as one of our partner organizations was a publicly quoted company.
Short-Sighted Compliance:
Many organizations feel they can get away with doing the bare minimum by meeting compliance standards. What compliance really does is give a false sense of security without ensuring protection. It is checking a box rather than solving a problem.
3 What sort of Config Mgmt / Asset Inventory do you do?
For Asset Management and tracking we used Cisco’s Meraki Systems Manager.
7 Introduced Meraki Systems Manager for Asset Management, which was very convenient to use through its browser based dashboard giving a detailed view of all pc and laptop assets giving its connectivity status, SSID, Name, Serial Number, Model, Warranty, BIOS, installed software and performance.
What are the various ways by which the employees are made aware about AUP / info sec policies and procedures?
Employees should undergo mandatory information security training post joining the organisation. This should also be done on yearly basis, and this can be either a classroom session followed by a quiz or an online training.
Sending out notifications on regular basis in the form of slides, one pagers etc. to ensure that the employees are kept aware.
What are your views on usage of social media in office?
Social media is acceptable, just ensure content filtering is enabled and uploading features are restricted. Read only mode is acceptable till the time it does not interfere with work.
Not sure if the data is secure or not but users can take steps from their end to ensure safety.
- Connect with trusted people
- Do not post/upload confidential information
- Never use the same username password for all accounts
What are your thoughts on BYOD?
If it's being going to be used for work purposes then it needs to enrolled as a managed device.
2.5/7 What Net Mon experience do you have?
2.5 We don’t use Security Fabric as we use VDOMS for FW virtualization and Security Fabric doesn't work with VDOMs!
7 WhatsUpGold Net Infra monitoring:
mon+alerting services for SAN, servers, switches, apps.
Customizable dashboard so you can see whatsup!
Network maps / (live net topology shows outages location).
virtual overlay shows virtual network connectivity, as it differs from the physical connectivity of your physical network.
Heat maps identify choke points or interfaces with restricted throughput, by become amber or red .
Sends realtime alerts via email, text before users report.
Captures the NetFlow data (traffic patterns) from our routers.
It also monitors Ex, SQLS, + SharePoint apps.
7 What sort of log Management do you do?
7 What sort of Security, Logging, Log Analysis Solution have you used?
2.5 Describe how you do auditing and Logging in your current network?
Data Collector sets:
Performance counter can be used to monitor the amount of replication that has taken place.

Describe how you do auditing and Logging?
We configure auditing and logging to send our encrypted logs to FortiAnalyzer as our SIEM for logging and event analysis as Logging on the Fortigates themselves is somewhat limited.
FortiAnalyzer allows us a central pane of glass to view reports and system event log messages in one place, while expediting our daily auditing schedule (to inspect logs for signs of intrusion and probing).
Why is DNS monitoring important?
Name 4 types of DNS records and what they signify.
What information would you include in a SOC report?
Do you have any experience SIEM / SOAR Solutions?
How do you secure your publicly available Web Services? (Yardi, Exchange OWA / ECP?)
How do you secure your AWS Cloud Presence (CASB/SASE)?
What sort of Identity Mgmt (ZTNA) do you do?
2.5 What sort of packet and protocol analysis have you done and why?
2.5 What Wireshark experience / Packet sniffing do you have?
2.5 Describe the difference between a Network SPAN and a Network TAP.
2.5 What of network test equipment have you used to test / put load on switches, routers, and wireless bridges.
2.5 How have you configured your home network / lab?
7 What sort of Server Monitoring do you do?
What are the steps to securing a Linux server?
Use Logwatch to monitor logs on our file servers.
Get daily emails from all our backup jobs.
Get daily security reports from our remote servers.
Get weekly emails from our untangle router.
Get security alerts / log extracts from our Sonicwall VPN.
Use DenyHosts on our web server to block suspicious ip's.
Symantec Cloud Alerts when there are PC issues.
Use VMs to decrease the severity of op sys sw faults.
DMZ Monitoring / dedicated IDS
To securely monitor activity in our DMZ I use a separate ZoneRanger monitoring appliance from Tavve inside the DMZ to monitor all servers, devices and applications with access from the internet,
it creates a secure conduit through the firewall to proxy encrypted SNMP data back to our centralized network management / monitoring station, for logging and has the ability to send a notification via e-mail, pager or other immediate alerting method to administrators and incident response teams.
I do not open firewall ports so that the existing network management and monitoring software can communicate with the DMZ devices as that opens up a new attack vector from the DMZ as the ICMP + SNMP protocols used to poll devices and keep track of availability are in fact not secure and can be exploited.
Honeypot
I also place a honeypot (Thinkst Canary / Dshield Honeypot ) in the DMZ, configured to look like a production server that holds information attractive to attackers.
The idea is to divert attention from your "real" servers, to track intrusion patterns, and even trace intrusion attempts back to the source and learn the identity of the attackers.
Binary Canary
Website monitoring, Server monitoring, Email monitoring, FTP Monitoring, DNS Monitoring, SMTP Monitor, PING monitor, Uptime Monitoring, router monitoring
3 How much Windows Server / Active Directory / Group Policy Experience do you have?
I've ran AD Controllers and Win File servers since 06.
3.3 Explain your use of ADMT AD Management Tool?
3.1 Do you employ any kind of SSO Single Sign-on solution on your domain?
3.1 What is Active Directory + How is your AD Infrastructure backed up?
It is the MS's authentication service + directory service for centralized management of domain user accounts, groups, and computers (objects) access rights.
To backup AD I use scheduled tasks running on our dedicated backup server to run Powershell scripts using WBAdmin cli of Windows Server Backup to reach out to our virtualized DFS Hub File servers + primary and secondary DCs in our HQ Datacenter and pull full data volume backups + system state backups on a nightly basis.
In addition to our centralized backups in the DC I also schedule distributed backups of All field domain controllers to local, secure disk storage in each community office, where WBAdmin backs up to a dedicated virtual disk which it actually takes over and removes from view anywhere on sys.
This dedicated invisible virtual disk contains only the most recently backed up copy of the system state of the DC, so should the DC operating system fail, this copy can be used to quickly restore the machine.
the only way you can dedicate a disk to our backups is through a scheduled backup, it is not with manual one time backups.
The dedicated disk is completely overwritten the first time it is written too, while Windows Server Backup prevents the disk from being visible in, as it's entirely dedicated to backups.
To make this method secure, configure backup share perms so that only domain admins can access this shared drive.
AD backups are very disk-intensive operations, backups may need to wait until weekends or other less busy periods.
I use dedicated backup agent service accounts with service admin credentials that are only used to perform backups for DCs to maintain separation of accounts from those used to backup application servers because the service account that is used to back up domain controllers must be a highly privileged service administrator that is part of the Backup Operators group.
Members of this group are considered service admins, because the group’s members have the privilege to restore files, including the system files, on domain controllers.
Individuals who are responsible for backing up applications on a member server should be made members of the local Backup Operators group on that server — as opposed to the Backup Operators group in AD. If the same backup agent service account is used for backups on both DCs as well as other appservers, then the app servers could potentially be compromised to gain access to this highly-privileged account.
The System State Backup is expedited as I have virtualized writeable DCs that include the GC, DNS, + FSMO flexible single master operation roles , not WDS - trimarc) in our HQ DC and backups run between VLANs over our 10 g/bit ethernet, in order to logically air gap our backups as they contain sensitive information such as
The KRBTGT account password
which is set when created & practically never changes.
The krbtgt account is the domain service account. This account is disabled but is used for KRBTGT Kerberos Tickets.
if an attacker was able to compromise one of our AD Backups and learn the password to the domain service account they could create golden tickets that would allow them to generate auth material for any account in AD and so subvert Kerberos auth by forging Kerberos tickets (assigning new authentication tokens at any level) to enable unauthorized access with a view to taking over the domain in a Pass the Ticket attack.
I archive our backups for a maximum of 180 days, as they become useless for restoration after that due to the AD Tombstone Lifetime being set to 180 days by default or >
If AD Recycle Bin is enabled, the backup lifetime is equal to the deletedObjectLifetime value or the tombstoneLifetime value, whichever is less.
I run System State Backup for our AD Infra in order to
- back up the registry,
- back up our boot files,
- back up our system files, and
- back up application specific things such as AD
AD is all stored in system state so when you backup system state you are in fact backing up AD as well
If you have AD Domain Services, it'll backup both ntds.dit (AD database) as well as the SYSVOL directory.
If you have AD Certificate Services installed on your Domain Controller / Certificate Authority, it will back up the DB.
The thing you really need to remember, though, is when you perform a restore of AD. You will want to make sure that you reboot your DC into AD Restore Mode, so DSRM Domain Services Restore mode as we call it. And then you can perform an authoritative restore of the DB.
if we wanted to perform a non-auth restore of this node, we can just simply perform a system state recovery restore on this node. Once we restarted this node then, it would receive its DB from another node in the cluster.
Cluster Database on a cluster node.
IIS on a web server.
IIS metabase - C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv + any websites you have (C:\inetpub\wwwroot)
Hyper-V VMs + Host Component
on a Hyper-V Host machine, will get all host level settings + all VM configuration settings.
In addition to the backups themselves I also:
archive the Admin account and DSRM password history in a safe place for as long as the backups are valid, that is, within the tombstone lifetime period or within the deleted object lifetime period if AD Recycle Bin is enabled.
I also synchronize the DSRM Domain Services Restore mode password with a domain user account (Administrator or Domain Admins or Enterprise Admins groups) in order to make it easier to remember, this synchronization must be done as preparation in advance of the forest recovery.
The Admin account is a member of the built-in Admins group by default, as are the Domain Admins and Enterprise Admins groups. This group has full control of all DCs in the domain.
I also generate + keep detailed daily reports on the health of our AD DS infra using a scheduled task + my AD Health Check Powershell script to email me a report on the status of our AD DS components, such as NTDS, Netlogon, DNS, etc.
so that, if there is a forest-wide failure, the approx time of failure can be identified, so an accurate backup can be identified that holds the last safe state of the forest .
The script checks the following AD DS components:
- Pings all the DCs in the forest
- Verifies that the Netlogon service is running
- Verifies that the NTDS service is running
- Verifies that the DNS service is running
- Runs the DCdiag Netlogons test to ensure the appropriate logon privileges allow replication to proceed
- Runs the DCdiag Replications test to check for timely replication between directory servers
- Runs the DCdiag Services test to see if appropriate supporting services are running
- Runs the DCdiag Advertising test to check whether each DSA is advertising itself, and whether it is advertising itself as having the capabilities of a DSA
- Runs the DCdiag FSMOCheck test on the DCs that hold the FSMO roles and the enterprise tests on the domain itself
3.1 What measures do you take to secure AD?
To counter a possibly compromised krbtgt password I:
Change krbtgt password 2x every year (DoD STIG requirement)
+ after any AD admin leaves or
To contain the impact of a compromise of a previously generated golden ticket, reset the built-in KRBTGT account password twice, which will invalidate any existing golden tickets that have been created with the KRBTGT hash and other Kerberos tickets derived from it.
Enable AES Kerberos encryption (or another stronger encryption algorithm), rather than RC4, where possible.
Ensure strong password length (ideally 25+ characters) and complexity for service accounts and that these passwords periodically expire.
Also consider using Group Managed Service Accounts or another third party product such as password vaulting.
Limit domain admin account perms to domain controllers and limited servers. Delegate other admin functions to separate accounts.
Limit service accounts to minimal required privileges, including membership in privileged groups such as Domain Administrators.
3.3 Describe the 5 types of Win Serv backup using WBAdmin?
wbadmin start systemrecovery
BMR+SystemState+all vols+all apps
BMR (system components, system drive+vols)
Windows Recovery environment. No OS.
Wbadmin systemstaterecovery (2012)
Registry, boot files, system files,
AD on DC (SysVol, ntds.dit)
DSRM AD Restore Mode - auth restore
IIS metabase + websites
Hyper-V Host + VMs
Cluster Host. Certificate Services
3.3 Describe the 5 types of Win Serv backup using WBAdmin?
Azure Backup (dom controllers + BMR, only NTFS,
cannot copy VHDXs to the cloud (2012)
MARS MS Azure Recovery Service agent (2012)
3.2 What type of File Server setup do you have? And how do you have its storage configured?
3.2 What MS DFS experience do you have?
3.2 How are Files / data replicated and backed up?
3.2 How do you monitor your DFS replication + your backup infrastructure?
3.1 What type of AD Security Model (Shares + NTFS Perms see below) do you use and why?
3.1 How do you control Share Permissions v NTFS / Folder permissions (AD groups / Inheritance (sub-folder perms) / Effective Permissions)?
3.2 What sort of Archiving / Backup / Recovery of User Data / Data Recovery do you perform?
3.2 How can files be recovered from the ConflictAndDeleted or PreExisting folders?
3.2 What’s the difference between standalone and fault-tolerant DFS installations?
3.2 Where exactly do fault-tolerant DFS shares store information in Active Directory?
3.2 What problems have you encountered with DFS?
3.3 How do you handle Win Updates / Patch Mgmt?
SCCMs integration with WSUS for scheduling patching (once a month) + reporting.
2.5 What type of print solutions have you administered?
3.2 What type of File Server setup do you have? And how do you have its storage configured?
In each of our communities, we use dual virt Win2016 file servers distributed across all our communities to provide locally redundant file services while also utilizing FT Domain-based DFS Namespaces + replication for HA and BC.
by storing DFS Namespace info in AD and having AD replicate that DFS Namespace info to all DFS subscribing DCs, making it highly available without having to use WSFC !
To make a domain-based namespace fault tolerant, you need at least 2 namespace servers + 2 DCs.
We have dual DC's in every Site with DFSN, DFSR, AD sites and services (with local subnet mapping to localize resource access) all configured appropriately and running on our DCs which is beneficial as they are already running other services like DHCP, DNS and AD sites and services which improves our namespace site awareness and the perf of domain queries.
Having dual DCs / DFS Namespace servers in every Site
providing DFS Client referral resolution within each community, as the AD site configuration is used to determine the nearest namespace server which clients can get their DFS referrals from.
DFS allows us to organize many geographically distributed SMB file shares into logical namespace folders (DFS Roots) in a distributed file system, so users can access files using a single path to files located on multiple servers without needing to know their physical location.
DFS provides location transparency by automatically redirecting users to the nearest copy of the data using Windows AD Sites + Services least cost calculations.
I use FSRM File Server Resource Manager to manage user file quotas, file perms, screening policies, while also using it to monitor volumes that are involved in DFS Replication.
Right now we give corp staff a 10GB quota.
Much of what is stored is office files (Word, Excel, Powerpoint) along with larger files from the Adobe CS suite and Autodesk products. To do quotas you would have to enable it on the volume in windows.
DFS replication
provides data redundancy by replicating community files back to our head office datacenter in a H+S replication topology with dual Hub Servers doing Data Collection and from there we do block level backups using our SC8000 SAN.
All spokes (Branch servers) can replicate with our dual Hub Servers and vice versa but spokes cannot replicate with each other, active file writes only happen at the communities.
If one Hub Server goes down, the other takes over and replication continues until the Hub Server comes back online, minimizing the impact of any outages.
We also use our DFS Replic H+S top to publish data out to comms for use in software installs and client PC patching.
To prevent branch clients from being able to browse to other branch servers, I have created one namespace for each branch server / hub server pair
I have created one replication group (set of members / servers) + one replicated folder per community, and put all other folders into the replicated community folder because we have a fast network.
Creating a single replicated folder with many subfolders is a way to throttle the amount of data replicated concurrently and minimizes disk I/O. This simplifies the process of deploying replicated folders because the topology, schedule, and bandwidth throttling for the replication group are applied to each replicated folder, as opposed to creating multiple replicated folders which would increase the number of concurrent downloads with higher throughput, but can potentially cause heavy disk I/O usage for staging file creation, staging folder cleanup, and so forth.
The DFS replication group schedule is set to replicate every 15 minutes, Monday to Friday, 7 days a week.
In the datacenter
we have 2 virtualized Win 2016 servers with DFS namespace in a VMWare HA Cluster running separately on 2 VMWare ESXi 6.0u1a Hosts connected to our Dell SC8000 array for all of our storage needs.
The advantage of this is that when we need to upgrade a server or apply a patch or compensate for a crash, we can do them all without requiring downtime as we have redundancy at the application level.
We use virtual servers as far as possible so that we can start with less resources, + add resources as we expand.
A minimum of 2 servers should be deployed for HA, load balancing, and redundancy.
In a small or mid-sized environment, DFS-N and DFS-R both can be deployed on 2 servers.
VMWare Datastore Configuration + Dedupe
I have dedicated disks for each file servers vmdk (for dfsr) and use 2012R2 for ease of management to dedupe the data on the file servers themselves.
I paravirtualize my disk controllers and spread storage disks across all the controllers for redundancy
As for backup, we use Unitrends appliance and we use hourly snapshots on the SC8000 which is block replicated to the secondary array.
Net Performance -
insure there is enough network bandwidth to support access - you can gauge by looking at how the current NetApp is configured - as well as IO throughput to your SAN
My new setup will have 10GB at the core so I certainly will not be saturating my network connection.
Storage Performance
Depending on your SAN and disk config (raid levels) you will get much better read/writes from the SAN disk.
Note – I use RDM’s for better I/O for disk intensive apps, servers, (obviously you will loose some of the flexilbly with vmdks, but its a balancing act)
Availability -
this is really going to rely on a number of things - redundancy built into the SAN infrastructure and network, and employing HA in the VMware environment.
You can administer namespaces by using
DFS Management,
the DFSN DFS Namespace Cmdlets in Windows PowerShell ,
the DfsUtil command, or scripts that call WMI.
Advantages of using DFS:
- Using DFS-R provides both DR + HA.
- DFSN abstracts the data out from where it is stored, allowing you to swap out servers without having to worry about Server names, as people access data through the DFS Namespaces which point to shares. name/server changes are transparent to the user, and if one of the VMs go down, only the depts segmented on that VM lose access, whereas before it was the whole org that would be affected if the file server went down.
- Data duplication occurs to dual virtual servers running on premise while also being replicated back to our Corp HQ via DFS + then backed up to auxiliary partitions on our SAN.
- SW + WSUS Updates are replicated out to remote communities using our DFS share Srg-llc\itupdates\Software
so then when our installation process (SCCM with WDS/PXE / WSUS for patching +updating) needs them they are already available locally.
In SCCM Local DP Distribution Points in each community are used to minimize the WAN impact on remote communities.
DFS is configured on the local dc to replicate certain folders with corporate office.
Dfs is setup on the DCs the main thing it is used for is to replicate the it updates directory over to the communities and are then used by DA to install bitdefender and other programs.
- DFS allows me to manage smaller File Servers that are 2-3TB a piece in each community, rather than having entire 10TB volumes out there.
We don't have full domain access to create DFS replication, nor do we have VMware license for HA, so this was the easiest way to allow for storage without making too many accessibility challenges or extensive downtimes.
The file servers are balanced over 2 hosts, so it's a lot easier to migrate a single 2tb server to a new host if there's a host failure rather than try to migrate a 10tb.
Dis-Advantages of DFS
- DFS Replication was designed for use over low-bandwidth nets, and sometimes the high-latency involved means that replicas are hours or even days out of sync with each other.
- DFS-R also requires that files be closed before they can be replicated, meaning that the newest files are the least likely to be replicated in a timely manner.
SRG WSUS uses DFS for deploying updates:
Srg-llc\itupdates\Software - also has SW which gets installed.
DFS is configured on the local dc to replicate certain folders with corp office. If you right click on the Software folder and go to the DFS tab, it shows the servers that replicate this folder.
the software folder is the largest folder DFS replicates as it is 2.66 GB and so can eat up a lot of bandwidth when a dc first starts DFS replication.
Dfs is setup on the DCs the main thing it is used for is to replicate over the it updates directory which is used by DA to install bitdefender and other programs.
3.2 How do you monitor your DFSR replication?
To monitor DFS I use Powershell scripts (using the Dfsrdiag.exe) to generate and email me DFS Reports only if there are any issues with the basic health of DFS, such as
the DFS Replic Backlog Count + DFS Replication completion.
I test DFS Replication completion in both directions using DFS Propagation tests to make sure replication is happening in both directions.
Conflicts occurring in DFS Replication.
The body of the sent emails for the alerts now includes the basic issue info in it, saving you troubleshooting time, as you now know where to zero in.
Alternatively you could manually check this info using
the DFS Management snap-in to generate a DFS diagnostic report to monitor the health of the
replication backlog,
the replication efficiency, and
the number of files and folders in a given replication group.
is suitable for monitoring up to 50 servers; however if used for monitoring > 25 servers, the diagnostic report might take a long time to generate, and the resulting file can be quite large and slow to open in a Web browser. So to monitor >50 servers I would use the DFS Replication MOM Microsoft Operations Manager Pack is designed for monitoring 50 or more servers.
Powershell scripts + Dfsrdiag.exe with WhatsAppGold to monitor the DFS replic backlog between servers.
3.2 What sort of Archiving/Backup/Recovery of data do you do?
Backups are essential for a highly available DFS, because restoration from backup is the ultimate recovery method.
To backup DFS I use Dfsutil.exe to export the DFS namespace configuration.
The recovery process involves creating a new namespace root + then using Dfsutil.exe to import the namespace configuration.
Dfsradmin.exe to create an inventory of DFS Replication settings.
This inventory includes a list of all replication groups, replicated folders, and their respective attributes.
Windows Server Backup on the Hub servers in our HQ Datacenter to
- back up the replicated data.
- back up Active Directory
on a nightly basis using WBADmin commandline tool + Windows Server Backup Role for AD to do full System State Backups.
Configuration information for DFS Replication is stored in Active Directory which is why I back it up.
In order to successfully restore DFS namespace and replication in case of accidental deletion, AD system state and below registries need to be backed up
Active Directory System State -
both DFSN and DFSR configurations are stored in AD.
DFS name space configuration -
need to be exported with Dfsutil utility:
dfsutil /root:\\domain.com\dfsnameSpace /export:C:\export\namespace.txt
Shares registry on each DFS Namespace server for DFS Root Share -
HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Shares
DFS namespace registry key on each server -
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\DFS
There are multiple ways available to restore DFS based on what backup you have.
3.2 How can files be recovered from the ConflictAndDeleted or PreExisting folders?
To recover lost files, restore the files from the file system folder or shared folder using File History,
To recover files directly from the ConflictAndDeleted or PreExisting folder, use the Get-DfsrPreservedFiles and Restore-DfsrPreservedFiles Windows PowerShell cmdlets (included with the DFSR module in Windows Server 2012 R2), or
the RestoreDFSR sample script from the MSDN Code Gallery.
This script is intended only for DR and is provided AS-IS, without warranty.
the Restore previous versions command in File Explorer, or
by restoring the files from backup.
DFS can not replicate files that are encrypted with EFS encryption.
What problems can you have with DFS installed?
2 users opening the redundant copies of the file at the same time, with no file-locking involved in DFS, changing the contents and then saving, meaning Only one file will be propagated through DFS.
You can’t make DFS fault-tolerant using WSFC, instead just Install a standalone one.
A fault-tolerant DFS root node - stores the Dfs topology in the AD, which is replicated to other DCs.
Thus, redundant root nodes may include multiple connections to the same data residing in different shared folders.
3 What Powershell scripting / automation of system management tasks have you done?
3 What scripting experience (Windows DOS / Linux Bash / PHP / Perl / Python) do you have?
Please list your experience with Powershell scripts and what you use them for?
I've been working with PowerShell for about 7 years to automate systems admin + security related tasks. My favorites script's are:
AD Inventory, AD Health check, AD domain doc,
DHCP inventory, DNS Enumeration, Network discovery,
Creating a Full Database Backup,
Monitor DFS replication backlog between servers, DFSR health report,
Converting a physical server to a virtual machine,
Scanning for Windows 10 updates,
Deleting Old User Profiles in Windows,
Audit permissions after a Windows migration,
Configuring Sysmon config files,
Monitoring AD Group Membership,
O365 Email hard to block all forwarding rules proactively,
Scripting LAPS to set random local admin passwords in a domain and using the LAPS Reporting PowerShell script to audit the use of the LAPS toolkit,
determine if machines are able to support Exploit Guard, Application Guard and Credential Guard,
Finding inactive computer accounts,
Scanning Live Networks for MAC addresses/OUI Oddness,
Hunting for Malicious Office Files (Macros), and
Monitoring the use of Command-Line Browsers (wget.exe/curl.exe).
3 How did you secure your Powershell scripts?
What kind of hashing did you use?
I secure all powershell scripts using Code signing certificates as it is the only way we can ensure that 99% of the scripts are not malicious and are doing what they are intended to do.
Code signing enables you to set the PowerShell execution policy to a more secure level like the AllSigned option.
To implement code signing in PowerShell, we can either use ADCS AD Certificate Services or buy an actual code signing certificate from a CA like GoDaddy or VeriSign.
What happens when you type google.com into your browser's address box and press enter?
• The "g" key is pressed
• The "enter" key bottoms out
• Interrupt fires [NOT for USB keyboards]
• (On Windows) A WM_KEYDOWN message is sent to the app
• (On OS X) A KeyDown NSEvent is sent to the app
• (On GNU/Linux) the Xorg server listens for keycodes
• Parse URL
• Is it a URL or a search term?
• Convert non-ASCII Unicode characters in hostname
• Check HSTS list
• DNS lookup
• ARP process
• Opening of a socket
• TLS handshake
• If a packet is dropped
• HTTP protocol
• HTTP Server Request Handle
• Behind the scenes of the Browser
• Browser
• HTML parsing
• CSS interpretation
• Page Rendering
• GPU Rendering
• Window Server
• Post-rendering and user-induced execution
X 3.4 How familiar are you with Hyper-V?
3.4 Whats the difference between a Basic Disk v Dynamic Disk?
3.4 What is a CSV Clustered Shared Volumes?
3.4 What is Storage Spaces Direct (SoFS)?
3.4 Whats the difference between VHD(VHD Sets) / VHDX / Cluster with shared VHDX / Pass-through disk?
3.4 Where would you use Data Deduplication?
3.3 Explain what the following Hyper-V concepts are?
3.3 Gen1 Hyper-V v Gen2 Hyper-V
SLAT required for Hyper-V (rec. 2012)
DEP Intel XD bit. AMD NX bit.
Intel VT or AMD-V
Bitlocker (Gen1+Gen2)(uses new key storage feature)
Bitlocker (vTPM-Gen2 only) Requires Basic disk with at least 2 partitions + Needs NTFS.
vTPM (host needs to be on physical TPM)
Guarded Host Role (for shielded VM)
Shielded VM (Gen2)
3.3 Gen1 Hyper-V v Gen2 Hyper-V
|
|
Gen1 |
Gen2 |
|
support the synthetic NIC but not for PXE booting synthetic network adapters go through the VMBus |
x |
x |
|
Boot from a device attached to SCSI controller |
|
x |
|
Boot from VHDX (up to 32GB in size) |
|
x |
|
online resizing |
|
x |
|
uses UEFI firmware = secure boot (signed drivers) Shielded VMs (has a vTPM and uses bitlocker) |
|
x |
3.3 Gen1 Hyper-V v Gen2 Hyper-V
|
uses UEFI firmware = secure boot (signed drivers) Shielded VMs (has a vTPM and uses bitlocker) |
|
x |
|
GPT GUIed Partition Table needed for UEFI |
|
x |
|
enhanced session mode |
|
x |
|
Linux (LIS) and FreeBSD (BIS) VMs with secure boot |
|
x |
|
export and import VMs |
|
x |
|
DDA Discrete Device Assignment Requires Intels EPT Extended Page Table/Intel VT-d AMD NPT Nested Page table / IO MMU To expose IO MMU |
|
x |
3.3 Describe the process for an In-Place Cluster Migration?
3.3 Describe the process for an Cluster OpSys Rolling Upgrade?
3.3 Describe the process to Create a Cluster with SoFS?
3.3 What is an AD- detached cluster?
3.3 What is a Global Update Manager?
3.3 What are the different Quorum Modes and what is a Quorum Dynamic Witness?
3.3 Explain Cluster Storage Replication for
a Stretch Cluster?
Cluster to Cluster?
Server to Server?
3.3 What is a Storage Replica?
3.3 What are Live Migrations?
3.3 What are Simultaneous Live Migrations?
3.3 Explain Hyper-V (default) Dynamic Load Balancing?
introduced in server 2012 R2 - now the default, and it's what Microsoft recommends-- is dynamic.
It uses the best of both Address hash and Hyper-V (static) port balancing.
It uses address hash for outgoing traffic,
Hyper-V port balancing for inbound traffic.
7 How do you handle PC Imaging?
3 What Imaging Experience do you have?
3 How do you setup a group of computers at the same time?
3.3 Explain your use of Win ADK Assessment + Deployment Toolkit, DISM, WDS and SCCM?
We use SCCM 2012 for building / capturing images (with driver injection),
deploying images (WIM) with WDS/PXE,
and SCCMs integration with WSUS for scheduling patching (once a month) + reporting.
GPO's + Custom Powershell scripts for custom configuration + some software deployment.
However for config mgmt we use Desktop Authority.
3.3 What are the different Windows Licensing Option?
Essentials: replaced small bus serv, can be dom serv
25 users / 50 devices, comes with 1 phy/virt OS license.
Does not use CALs, uses the Specialty Servers model.
Standard: unlimited number of win server conts.
per Core/CAL core based licensing model.
All phy cores must be licensed
In 2012 standard license gave you 2 cores = 2 VMs.
In 2016 min of 8 core licenses per physical CPU, and 16 core licenses per VM Server.
Uses CALs / Max 2 OSEs Op System Environments.
DataCenter: unlimited No of win server conts.
All phy cores on the standard edition must be licensed, uses the per Core/CAL core licensing model.
Uses CALs / Unlimited number of OSEs Op Sys Env.
Advanced Feature (Storage Spaces direct, Storage Replica, Shielded VMs)
SDDC and software defined storage.
you must deploy Software Assurance.
Nano: you must deploy Software Assurance.
Software Assurance is a comprehensive Volume Licensing program that includes a unique set of technologies, services, and rights to help you deploy, manage, and use your MS products more efficiently.
3.3 Explain how you activate + keep track of your Win Licensing?
ADBA AD-based Activation v KMS Key Mgmt Service
for larger networks of >50 machines.
- is the MS recommended activation method + also uses VAS Volume Activation Service within Domain but without having to have a KMS Host.
similar to KMS, you install the CSVLK Customer Specific Volume License Key as an AD activation object.
Then as soon as computers are joined to the domain, they are activated while they can comm with the DC.
You'll use KMS for your older OSs (pre 2012/ Win8), and ADBA here to support your newer operating systems.
Requires > Server 2012 + >Windows 8
X What type of print solutions have you administered?
I administer metered Canon imageRUNNER multi-function copier / printers (with Uniflow tracking installed)
The Uniflow system tracks copier/printer usage by employee for departmental billing. We only pay for actual usage and are invoiced quarterly by Canon Business Solutions.
Communities receive a monthly report showing usage by employee, which has acted as a deterrent to excessive minimize copying/printing to only what is necessary.
While in the past I have administered networked HP + Dell multi-function printers, MICR Check Printing, Ricoh, Brother + Epsom multi-function printers.
How much experience do you have with Linux / Unix?
I setup a Backuppc system installed on Ubuntu / FreeBSD 9 on a HP Proliant MicroServer with a RAID-Z zfs software raid.
Backuppc is a high-performance, enterprise-grade system for backing up:
Linux, Windows and Mac PCs + laptops to a server's disk.
It is configured to extract backup data via rsync from client computers running Cygwin configured with SSH for secure connectivity and the backuppc client to connect via rsync over our data network. BackupPC's web interface automatically fills incremental backups with the corresponding full backup, so there is no need to do multiple restores from the incremental and full backups: BackupPC does all the hard work for you.
7 On a side Project I put a PSAD Port Scan Attack Detector IDS + log analysis system with fwsnort integ
which lets you pull in snort rules from http://www.emergingthreats.net/? providing active protection as opposed to passive monitoring and alerting.
It even allows you to analyze the transport headers using string matching to find application layer signature matches, to more accurately analyze traffic.
List the basic components of Linux
What is Linux? How is it different from Unix?
What is the difference between absolute and relative path?
What is Samba? Why is it used?
Which command shows you free/used memory? Does free memory exist on Linux?
What is the difference between soft and hard mounting points?
What is SSH? How to connect to a remote server via SSH?
What is virtual memory?
What does the command env do?
What is the difference between a swap partition v swap file?
What is a zombie process?
3.4 What type of Clustering / Virtualization have you done?
Currently I am using VMWare ESXi 6.5 + vCenter to host a virtualized Exchange CAS Array + 4 node DAG cluster, spread across two storage controllers for HA of our mailbox data, while protecting it in an application consistent state, minimizing downtime + improving our RPO.
while also hosting a SQLS FCI Cluster (CaB) with shared storage (pRDM shared LUNs on our Dell SC8000 array) which I have extended with an SQL Server AlwaysOn AG for multiple controller / multiple site HA.
While in the past I used ESXi 5.5 to host a warm DR site at a remote datacenter in Canada. I have also previously used Hyper-V to host Domain Controllers, a Utility Backup Server and lightly used Linux web servers.
5 How is your Exchange Server configured, backed up, and secured? What type of Redundancy is built in?
I use a single site HA Virtualized Ex Server hosted in our VLAN20 Server network and protected by a WAP / ADFS Proxy in our Auth DMZ to secure all access to our internal Mail + Web servers.
For external access, I configure our public DNS Zone to point our domain MX (MTA) mail records to our Mimecast Public IP address
DNS Records: A, CNAME, MX, SPF, DKIM, DMARC.
I do not enable NAT for inbound traffic unless it is required by an application.
If for example, NAT is enabled for inbound traffic, the SMTP server might act as an open relay.
For internal access + to cut down of admin overhead I have configured pinpoint DNS config to separately resolve internal queries directly to our LB.
The name of the Pinpoint DNS zone is the same as that of the External DNS Zone (srg-llc.com), while the name of the DNS records are all the same except for the ones I manually configure (no dynamic updates) to resolve to local ip addresses.
Keeping the internal and external namespace URLs identical makes it easier for users to locate resources.
And it reduces the number of certs required to secure SSL/TLS communication between clients and servers.
Why are you using a WAP/ADFS Proxy to authenticate HTTP requests to the CAS array?
I use our WAP/ADFS Proxy located in our auth DMZ, to securely publish our web services, and pre-auth access to our OWA & ECP/EAC using ADFS claims-based authentication, while using simple pass-through pre-auth for OAB, MAPI over HTTP, OA Outlook Anywhere, PS, AD AutoDiscover, Web Services, AS Active Sync.
We also use our ADFS server / ADFS Proxy to facilitate SSO through claims based Federate Identity with our extranet SW dev partner Yardi who externally host our Sharepoint Training + Comp website.
Explain how the Claims based SSO Authentication process works?
ADFS identity federation is setup by establishing a trust between two orgs with different security realms, allowing one org to allow controlled access to its services without requiring a shared ID DB.
On the source Accounts side, the federation server authenticates the user using AD Domain Services RBAC then issues an OAuth access token containing a series of claims about the user including their identity.
On the dest Resources side, another federation server validates the token and issues another token for the local servers to accept the claimed identity.
What are the benefits of claims based authentication?
Centralized authentication makes it easier to manage accounts, by removing the mgmt of authentication from the individual applications, while also making it
making it easier to upgrade auth methods in the future.
OWA and EAC are no longer responsible for authenticating users, storing user accounts + passwords, looking up user identity details, or integrating with other identity systems.
Internal users are authenticated directly through our internal ADFS Server via our F5-Big-IP LTM LB using WIA/IWA Windows integrated authentication.
Explain the function of your F5-BigIP LTM Load Balancer?
I use a one armed F5 Big-IP LTM LBalancer (v HA) that performs pure connection-proxying of stateless
client request using L4 source IP lbing of
HTTP / MAPI over HTTP requests (RPC-over-HTTP, Outlook Anywhere, Web Services, and ActiveSync) to our CAS array (accepts+forwards to anchor mailboxes).
I use L4 LBing as we only require TCP affinity (v session affinity) for Ex 2013, while network health grabs
determine available servers improving perf + scalability.
Single namespaces per client protocol are load balanced across the CAS array (or DCs where each DC is its own AD site) using our F5 L4 HW Load Balancer and per protocol VIPs.
The LB gets an internal IP address by MAC address reservation in the DHCP + while I also register the LB DNS hostname in our internal DNS servers.
I Config the LB for HA of SMTP + HTTPS (port 443) using the Exchange HTTPS LB Template.
I created VSs Virtual Services for every LBed protocol + point the FW per protocol VIP address at the Assigned VSs, rather than the LBalancer itself.
I add all Ex Servers to the VS for HTTPS HA so requests can be load balanced to all of them.
I add the Ex SAN / * cert to the VS to validate requests.
I change the Mail + autodiscover internal DNS host records to the IP Address (VIP of LBed protocols) of the Load Balancer.
Ex Namespace HA Design
I use a single generic namespace srg-llc.com for both our public and private messaging protocol needs, with single namespaces per client protocol + per protocol health checking requiring only a single cert for all services to connect users to their mailboxes.
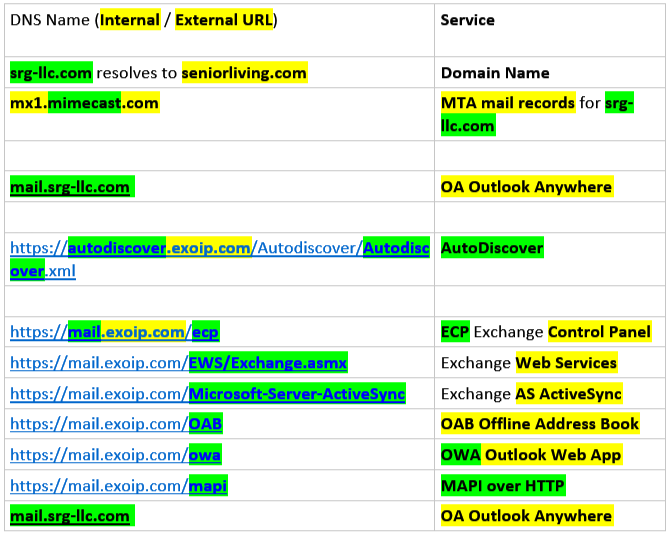
How is your single site HA Virtualized Exchange Server is backed up?
Our Exchange installation is backed up using:
- our 4-node DAG spread across two storage controllers for HA of our mailbox data, while protecting it in a application consistent state, minimizing downtime + improving our RPO.
+
- VMWare virtualized Ex VMs + our Dell SC8000 Array with its VSS based backups to counter OS + HW failures.
- A DAG ensures nothing is lost in the event that the source server dies as frequently copied logs + the Mailbox transport safety net catch everything else.
With non DAG replication solutions such as Veeam Replication or Hyper-V replica you may lose all mail sent since the last replication interval.
My DAG deployment consists of 3 non-lagged copies + one lagged copy of our mailbox DBs meaning I'm not solely relying on RAID or VSS-based backups.
In my design, Each DB has 4 DB copies,
which are distributed across our dual Storage Controllers + are isolated from each other:
reducing failure domains + increasing availability, + ensuring that mailbox data is protected from SW, HW and even DC failures.
Only 3 of the 4 copies are configured as highly available, with the 4th being a lagged copy to counter
human error: accidental deletion of mailbox or user data
storage logical corruption: that has replicated to all non-lagged copies in the DAG, restore from Lagged.
Recovery from a lagged copy: can be faster than restoring from a backup because lagged copies don't require a time-consuming copy process from the backup server to the Exchange server. Significantly lowering TCO + improving RTO by reducing downtime.
While using the lagged database copy to restore data, it is important to remember that the lagged database copy is not a guaranteed point-in-time backup.
Lagged DB copies = availability threshold around 90%
Exchange 2013 is optimized for 8TB disks.
The source of data in a reseed operation is always the bottleneck, however now that you are reseeding from multiple sources that bottleneck is gone and you are fully utilizing your disks.
In DAG installations with continuous replication, I enable CCRL Logging (Ex Replic service)(v ESE circular logging) to generate closed log files meaning the current log files aren't truncated or deleted so log shipping + replay can still occur.
- VMW virtualized Ex VMs + our Dell SC8000 Array (VSS based backups) counter OS + HW failures.
Virtualized Ex VMs streamlines DR Recovery + testing of DR environments a lot easier, whilst reducing cost by reducing HW reqs + consolidating Ex Server roles and AD components on a few Hosts.
Ex VMs reduce our RTO in a disaster as VMs are more easily spun up at the DR site + have fewer HW reqs,
while maintaining a RPO of < 2 minutes.
I use our Dell SC8000 Array with its Dell Replay Manager 7.8 for Microsoft SW agent backup solution to generate near-instant, VSS app-aware SC series snapshots of all volumes hosting Ex DBs + trans logs for backup + DR.
Ex-aware agents use the Ex VSS writer to create local VSS SC series snapshots that are then used to create backup images.
the VSS snapshot taken uses the VSS snapshot cache local in the Op System + so is appl aware. This is superior to the snapshots / clones taken at the array level that are not Ex aware + only crash consistent.
I create my Dell Replay Mgr 7.8 Backup sets
run everyday at 12am, with 1 retry, after 1 minute
Ex verification service runs during backup/restore ops.
the VSS Full Backup setting is disabled, in order to flush Ex Trans Logs after the backup completes, as my Mimecast sync require use of the trans logs.
Delete Old Restore Points (keeping only the last 2)
successful snapshot creation: emails me on completion
Our local DB backup images are then cloned offsite to AWS S3 Glacier storage for archiving + compliance,
while also being replicated to our warm standby servers in AWS for DR recovery purposes.
For eDiscovery + fast restores of individual mailbox items, I use a combo of our Mimecast Cloud Archiving features + Ex's built-in restore options such as
In-Place eDiscovery: discovery manager searches archive mailboxes in eDiscovery searches.
In-Place Archiving (archive mailbox): regain control of your org's messaging data by eliminating personal store (.pst) files and allowing users to archive mail.
Recoverable Items folder: (Single Item Recovery) protects against accidental deletion using the Deleted Item Retention window to retain deleted data.
Litigation / Legal Hold (Hold Policy): new In-Place Holds are obsolete, only Hybrid Deployments can create new In-Place Holds, instead use eDiscovery cases or O365 retention policies. Litigation Hold is still available.
Public folders: public folders (mailbox DB->DAG for HA)
Explain how you dealt with Exchange Server 0-Day Mass-Hack campaign and the ancillary Mimecast certificate compromise + F5 Big-IP Vulnerability that recently hit the headlines?
I got lucky on that one in that I got my Servers patched on March 2nd, the day the patches came out!
I switched our Mimecast SEG into Continuity Mode and air gapped the CAS Servers while I was remediating + investigating for IOCs.
I checked my Backup Set was still intact.
Our FTGWs got updated WAF/IPS/AV signatures on March 3, to detect exploits targeting these vuls, while I also do SSL/TLS DPI of all traffic to/from our CAS Array.
I use an WAP/ADFS Proxy in our DMZ to pre-auth users
Remediating + Investigating for IOCs.
Remediation was easy, as I already had the Exchange Servers updated to CU23 which we had applied back in June 2019 (Health Checker script).
Next I ran the Test-ProxyLogin.ps1 - All clean
I checked for IOCs released by Volexity + Az Sentinel.
I also ran the Nmap Script to detect whether our URLs were vulnerable to the Ex Server SSRF Vulnerability.
Finally I done an Anchor Mailbox check to make sure they weren't compromise.
Subsequently I ran MSERT Tool (MS Support Emergency Response runs MS Safety Scanner) + EOMT.ps1 script (Exchange On-Premises Mitigation Tool) All clean.
I also regularly run PowSh scripts to monitor AD Activity, Task Scheduler for rogue tasks, and Registry Run locations for any SW persistence.
For Extra Vigilance, I done some extra Attack Surface Reduction + Hardening,
I rotated the AD credentials on all key AD accounts
I will implement an AD Split Permissions model when we get all servers upgraded to Exchange 2016 or 2019.
I plan to look at implementing a UEBA User and entity behavior analytics solution, to monitor the use of identities + doing Behavior-based detection so malicious activities (web shells) can be blocked!
I plan to implement a cloud based EDR Solution (always current threats+mitigations as they occur) for all Tier Zero assets such as Exchange + ID services, ensuring we are protected and secure in the timeliest fashion.
I plan to implement a SIEM / SOAR solution for faster log analysis + event response, while ensuring our IIS logging preserves Source IP Address in Header, not LB IPs.
Explain how you dealt with F5 Big-IP Management Interface (Port) / iControl REST interface unauthenticated RCE vulnerability that recently hit the headlines?
This wasn't a major issue for us as I had already restricted access to specific ports (port lockdown feature) on the management interface + self IP address (packet filtering functionality)(and subsequently the iControl REST interface) to only trusted devices on our network, insulating us from the public internet, reducing our attack surface, improving our sec posture.
In addition I was made aware of the RCE vul on the morning of March 10th, meaning I had our F5 devices patched well ahead of Rapid7s PoC exploit on March 16
Patching is facilitated by being able to switch our Mimecast SEG into Continuity Mode, to ensure continuity of email services while bringing our F5 Load Balancers and subsequently our main Email system offline for patching.
After reviewing the details of this exploit I further secured our network by blocking unecessary access (TCP port 443 default or 8443 alternate) to the iControl REST interface from most IP addresses in the VLANs defined in self IP addresses that are allowed to communicate with the F5 LTM Local Traffic Manager.
I also monitor login attempts to our F5 on an ongoing basis for the possibility of any unauthorized access.
2.2 Describe your Email Flow in / out of your network, and within your network? Particularly your DNS config.
2.2 Describe how you secure your publicly accessible IIS Web servers + Exchange Email Servers?
What type of IIS Web Server administration have you done?
I administer + protect a load balanced IIS/ASP.net Web Server Farm + Exch CAS Array by pre-authenticating requests
through our WAP / ADFS Proxy (Win 2016) before they reach our IIS Servers. I logically + physically segment our Servers out onto their own VLAN20 Server Network on its own switching equipment, in order to prevent any malicious broadcast traffic from ever reaching our servers.
While our IIS/ASP.net Web Server Farm + Ex CAS array, are themselves highly available services running on
clustered backend DBs (Ex DAG + SQLS FCI/AG) accessing
Fast Redundant storage on our Dell SC8000 SAN via our FC Fabric.
I protect our Web + ADFS servers (config data / private keys) from direct access from the internet by directing all requests to our published IIS web services to pre-authenticate with our WAP / ADFS Proxy (auth DMZ-VLAN30)
before they are redirected to our Web Servers in VLAN20.
This configuration provides extra layers of defense such as:
- against malicious HTTP requests originating from the Internet. As HTTP traffic arrives from the internet, the WAP terminates those HTTP Requests and initiates new requests to the published applications.
- providing DDOS protection by stopping attacks at the perimeter before they can hit our backend servers.
- Reducing our attack surface by selectively publishing specific applications making identity rather than our Firewall our security perimeter.
-
MFA, Multifactor Access Control + Workplace Join so unmanaged devices can use our web services.
2.2 By positioning the Reverse proxies in the DMZ and authenticating external access through our WAP / ADFS proxy we reduce our attack surface as we are:
- Minimizing the ports + protocols that traverse from the Internet to our DMZ and from our DMZ our intranet.
The Firewall between our authentication DMZ-1 network + our intranet allows me to impose strict ACLs so only authorized traffic Is allowed to reach our Exchange CAS array +
IIS10/ASP.net4.6 Web Server Farm.
I use WAP Reverse Proxy in the DMZ, to securely publish our Exchange web services such as
- OWA, ECP/EAC,
- MAPI over HTTP, AD AutoDiscover, AS Active Sync, OA Outlook Anywhere (RPC-over-HTTP), OAB, Web Services, PS
for remote access from the internet.
Our WAP / ADFS Proxy is configured to use ADFS Claims based PreAuthentication of authorized users to only allow authorized users access to our publicly exposed web services + prevent un-authenticated traffic from hitting our servers.
ADFS integrates with AD Domain Services using it as an IDP identity provider to generate claims based sec tokens from our users AD accounts. Our WAP / ADFS Proxy uses the edge security token containing a users claims (access grant approval permissions) from our ADFS Server and uses them for pre-authentication + grant access to a specific set of resources for a specified period.
The ADFS Proxy uses the MS ADFS PIP protocol to establish a Trust relationship with our ADFS server by exchanging client certificates and client header information which facilitates the ADFS Proxy to perform PreAuthentication for the domain.
PassThru Pre-Authentication
Claims based pre-authentication only applies to OWA + ECP published URLs, while I use PassThrough Pre-Authentication (aka application based authentication on the Web Server) for:
AD AutoDiscover, MAPI over HTTP,
AS Active Sync, Exchange OAB, Web Services, OA Outlook Anywhere (RPC over HTTP), PS Powershell
2.2 Our WAP / ADFS Proxy also provides Federated Identity services for SSO with our federation partner - Yardi who externally host our Sharepoint Training + Compliance App by sending them claims based identity tokens derived from our user Active Directory accounts.
I configure Claims Issuance Policies on the ADFS Server where I specify the claims that will be sent to relying trust parties (our ADFS Proxy or 3rd party ADFS Proxy) so our users can logon using their SRG credentials.
2.2 For internal access to our web services running on our Exchange CAS array + IIS/ASP.net Web Server Farm,
I have configured Pinpoint DNS (in VLAN20 + VLAN5) to resolve the private URLs for our Ex web services directly to the IP address of the internal load balancer before being distributed to our CAS Array which is configured to use ADFS based WIA Windows integrated Authentication that uses
users AD credentials for SSO access our Web Applications.
however the drawback of this is that there is no SSO should they then try to access the externally hosted Sharepoint website as they never obtained a federated Claims based token).
Pinpoint DNS handles all internal CAS access + Ex Web Access that goes from one computer on the internal network to another computer on the internal network, avoiding exposure to the Internet and improving perf.
To facilitate this I configure our internal DNS Zone with Pinpoint DNS, that allows me to manually configure internal DNS records to resolve our Exchange Web Services internal URLs to different ip addresses internally,
than the public IP Addresses the Ex External URLs resolves to,
while also removing the need to separately manage split DNS zones).
The Internal PinPoint DNS Zone is configured with mail + autodiscover DNS names that point directly to the IP address of the internal load balancer before being distributed to our CAS Array
2.2 A PinPoint zone
is created in the same way as any other DNS zone.
The only difference is that the name of the zone is the same as the name of the DNS record you want to assign a private IP address to internally.
The private DNS zone (Internal DNS)
will have a mail.srg-llc.com record + autodiscover.srg-llc.com that resolves to the load balancer internal IP address.
2.2 For Remote SSO + access to our Federated partner Sharepoint Training website,
we send ADFS claims based security tokens, so when Remote Users log into their OWA web app externally, our WAP places an SSO cookie in their web browser.
This SSO cookie is generated based on the ADFS claims based security token it recieves from our ADFS server and is used to identify that an active session has already been authenticated on the users browser, so when users visit any other externally hosted federated app (SharePoint Training website), it can check the SSO cookie to see a user's:
UPN (user identity) + access grant approval perms + expiry.
and log them into our federate partners externally hosted app.
For external access to our web services, I have moved our
authoritative external DNS Zone from our Domain name registrar to AWS Route 53 as its Healthchecks feature allows me to provide fast DNS Failover in the event that our primary ISP WAN connection and public IP address become unavailable,
our AWS Route 53 healthcheck will detect an outage of 10 seconds or longer and automatically failover the public ip address of web applications to point to the public ip address of our secondary ISP WAN connection ensuring continuity of service + avoiding the delays associated with
- Manual DNS Reconfiguration or
- Round robin DNS load balancing
Round robin DNS is inherently limited, because it depends on a timeout on the client side, and doesn’t take into account availability, load or latency, so the user might be routed to a dead or suboptimal destination.
2.2 To create the Route 53 healthchecks
I create Route53 healthchecks for both our WAN connections + their public IP addresses.
I create dual public DNS entries for each web service that I require to failover to the secondary WAN IP address in the event of a failure.
I associate the health check with the DNS entries configuring one as the primary and the other as the secondary.
Authoritative external DNS Zone records:
autodiscover DNS name / External URL:
points to our registered domain name for our public IP address which is then forwarded to our WAP / ADFS Proxy for pass thru pre-authentication before reaching our CAS array.
A Record
The main DNS A record for all our mail services, while all other External Mail URLs are registered in DNS as sub-domains, so for our Exchange services it is Mail.srg-llc.com
And then all other Exchange mail services are sub-directories / virtual directories accessed using
Mail.srg-llc.com/mapi, Mail.srg-llc.com/owa, Mail.srg-llc.com/acp
MX MTA mail record:
that points to our Mimecast SEG for inspection and archiving before being forwarded to the public IP address on the WAN interface of our Firewall that then forwards SMTP mail traffic to our load balancer ip (VLAN20) before being distributed to our CAS servers in our CAS array.
SPF record:
specify which mail servers are permitted to send email for that domain name, in our case the Mimecast mail servers.
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail) record
designed to sign + verify header info in SMTP messages.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) DNS record
ensures messages are correctly authenticated using the authentication identifiers that SPF + DKIM email auth standards provide to enforce policy, allowing the domain owner to decide who is allowed to send on their behalf.
(Mimecast SEG -> FW VIP -> WAP/ADFS -> F5-BigIP LTM LB -> CAS Array -> Mailbox Server -> DAG)
External Mail traffic coming from the internet first passes through our Mimecast SEG before making its way to the public IP of our WAN interface that's setup with a VIP forwarding all traffic for our mail.srg-llc.com domain to our WAP/ADFS Proxy in our authentication VLAN30.
We filter all our email requests through our Mimecast next-generation cloud based security, archiving, + continuity service to inspect + filter + archive email as it enters and leaves our network. Mimecast adds an extra cloud based layer of redundancy, improving our email cyber resilience (should our primary On-Prem email solution be taken down), which is essential if you have any compliance requirements to meet.
while also providing defense-in-depth by adding an extra layer of security from a different vendor, meaning attackers have multiple locks to pick for each vendor target.
Archiving to Mimecast
Backup + Archiving happens directly from the Exchange Mailbox Servers using Mimecasts journaling + synchronization technologies, while the Mimecast SEG simply inspects + sanitizes email as it ingresses+egresses our net.
The Mimecast for Outlook Plugin usually operates in Active mode where it is continuously monitoring your Outlook apps connection to your Exchange Server every 3 seconds, if it sees that you loose connectivity to your Ex server and your ability to send and receive emails then the it switches into Continuity Mode, whereby you use the Mimecast MTA + Servers to continue to send and receive email until your main Exchange servers comeback up, at which point synchronization occurs between the Mimecast Cloud Servers + our On-Prem Exchange Mailbox Servers.
F5-BigIP LTM Local Traffic Manager Load Balancer
Is located in our VLAN20 Server Network and is configured with a Round Robin load balancing algorithm to evenly distribute incoming requests at the TCP level while also doing SSL passthrough with SSL ending on either our
Web Server Farm or Exchange CAS Array.
Our F5-BigIP LTM LB performs pure connection-proxying (L4 load balancing) of stateless
HTTP / MAPI over HTTP requests
Outlook Anywhere, Web Services, and ActiveSync requests
to our either our Web Server Farm or Exchange CAS Array.
Co-Location of Servers in VLAN20 our Server Network:
We maintain 2 DMZs at headquarters with their own switching infrastructure + VLANs in order to separate traffic for our Corporate servers from our Guest Wifi / IOT / Camera networks.
I keep our IIS application servers + SQL Database servers + a Domain Controller, all in the VLAN20 as they all need to communicate with each other.
Out in our communities I keep dual servers acting as DC, DNS, DHCP, Printer + Ex Mailbox in our VLAN5 SRG Business network while I segment our Guest Wifi / IOT / Camera networks in the Communities DMZ
with its own switching equipment as the hardware for the Guest Wifi / IOT / Camera networks is easily accessible in public spaces.
All servers are further secured using Windows Firewall to limit connections to just the ip addresses of the IIS/ASP.Net application servers in our Web Server Farm (also in VLAN20)
the ESXi Host hosting the servers dedicates a separate VMNIC team to traffic from the internet.
I also use AppLocker to prevent malicious code from running on the DCs and is easy to implement on DCs as their workload is well defined and largely static.
I also run Device guard on Server 2016.
To get an accurate set of FW rules(ACLs/ACEs) between VLANs:
I had to monitor traffic using a Catch All Security Policy with Base Security Profiles for a number of months to get an accurate picture in Fortiview of the traffic traversing to and from our servers in order to build an accurate set of rules.
if the Catch All Security Policy is catching traffic that should be allowed, I create a rule to allow that traffic and places that rule above my Catch ALL Policy.
After 3 or 6 months of monitoring I disable the Catch All Policy and transitions to a DENY by Default stance (which is security best practice) where users have to submit a change request to get certain types of traffic allowed.
3.4+6.1 What type of SQLS Clustering / Virtualization have you done?
3.4+6.1 What is SQLS FCI / SQLS AG Availability Group?
3.4 What is VSS?
4 What type of IIS Web Server admin have you done?
4 Explain how your ASP.Net / IIS Web Servers are configured?
How do you provide secure access?
How do you ensure HA?
What is your backup process for your Web Servers ?
4 How much load does your IIS Web Server handle?
6.1 I've been running a SQLS FCI + AG for a little over 4 years now. When I began at SRG in 2016, I took over administration of a Yardi Sql Server 2012 FCI cluster (Active/Passive for HA) on bare metal Windows Server 2008 R2 machines (running on HP Proliant DL380 servers, in the same subnet) leveraging WSFC to host a SQL Server 2012 FCI for HA with shared storage on our Dell SC8000 SAN array (in a CaB configuration, not CiB).
FCIs abstract which node of the underlying cluster is hosting it, by assigning the cluster a unique name, however FCIs require shared storage, AGs do not.
DBs are only available after recovery is complete, meaning they have a longer RTO than AGs.
6.1 Whats the difference between SQL Server Native Backups v VSS based Backups
SQLS Native Backups (VDI Backup) = SSMS T-SQL backup
- Full / Increm / Differ backups that can be taken using BACKUP DATABASE T-SQL command or using
the SSMS Management Studio GUI.
VSS based Backups: use the VSS APIs to backup SQL DBs with the help of APIs exposed through SQLVDI Virtual Device Interface and SQL Writer.
6.4 Why do you use shared storage over Direct attached storage?
We use shared storage as a single datastore / Central repository can have multiple hosts/VMs accessing it concurrently - key for vMotion, HA, DRS.
It is scalable and recoverable implementations.
It allows clustering of VMs across physical hosts.
It facilitates Data replication + vMotion, HA, DRS, and DPM.
To get the most from shared storage, you must understand the storage performance limits of a physical environment so you do not overcommit resources.
I use vSphere Web Client navigator to install Cluster Nodes + mount the FC based pRDM shared LUNs as dedicated SCSI devices on member VMs.
The shared storage SCSI adapter for >=Server 2008 must be the LSILogic SAS type, while < 2008 versions must use LSILogic Parallel type.
Then I installed SQLS + the MS Cluster Service on both virtual nodes, so FO Cluster Manager can utilizes the storage mapped to the VMs to configure + manage:
storage for the SQLS FCI database files +
CL-Witness quorums disks
SQLS requires at least 3 clustered volumes:
one for system DBs, one for data files, one for log files.
Our SC8000 has redundant Storage Controllers that provide pRDM shared LUNs + block level storage for :
- our backend SQLS DB server FCI+AG in a RAID10 setup.
- our backend Ex DAG.
- the IIS / ASP.Net Web Server Farm (which accepts persistent connections from our WAP/ADFS Proxy via our F5 Big-IP LB.
- our virtualized Windows DFS file servers.
Windows SMB was used to provide file level connectivity between Client PCs and our DFS File Severs, while we use
MS DFS to replicate file changes back to the HQ File Severs
6.4 The advantages of using RDMs v VMFS datastores?
Workload Type determines VMFS v RDM:
For VMFS = random workloads, RDM = I/O throughput.
For sequential workloads, with small I/O block sizes, RDM has slightly better throughput. However as the I/O block size increases, the I/O gap decreases.
For all/mixed workloads, RDM has slightly better CPU cost.
6.4 RDM use cases:
are mapping files (proxies) that enable a storage LUN to be directly connected to a VM from the SAN / NAS.
RDM are used to improve perf in I/O-intensive applications.
1.Virtual compatibility mode: RDM acts exactly like a virtual disk file, including snapshots.
2.Physical compatibility mode: direct access of the SCSI device allowing lower level control.
to grant machines concurrent access to the same resources.
For MS cluster config in VM VtoV (CiB + CaB) or VM PtoV
conversion ops (avoid migrating data LUNs to VMDK).
A cluster’s data disks or quorum disks where vms have been set up as WSFC nodes.
For apps that use hardware-specific SCSI commands
6.2 SQLS FCIs in active/passive configs provide
local HA at the instance level, the advantages of this setup are that it provides low RPO + RTO objectives (zero data loss + seconds/minutes to recover)
counters possible software issues by insuring near instant App Consistent FO with zero data loss.
An FCI's normal FO + recovery process rolls back Incomplete transactions while complete transactions are rolled forward, leaving the DB in an application consistent state at the time of manual failover/failure ensuring zero data loss.
This is the same result as a VSS based backup without the acquiesce overhead that can slow a server down or trigger a failover in an AG
An FCI can participate in an AG as one of the instances hosting either a prim / secondary AG replica.
AGs rely on WSFC for FO policy or quorum mgmt and
have lower RTO with no shared storage. AGs provides protection at the DB level allowing
multiple DBs to FO as a single unit (v FCI Instance level).
However when you FO an AG, additional tasks are required to make a DB usable (SQLS Agent jobs) .
Having additional copies of the DB in sync is the tradeoff for ensuring redundancy.
AGs allow both HA + DR using a single feature that's not tied to shared storage, allowing AG Replica's to be geographically + logically distributed.
for HA, you can have AG replicas co-located in one DC,
for DR, you can have geographically dispersed AG replicas each with separate storage in remote DCs.
2016: Virtualization of FCI Cluster:
My first upgrade was to virtualize + upgrade the SQLS 2012 FCI cluster and get them off the aging Server 2008 machines (running on older Dell PE R720 machines) and onto ESXi 6.0 hosts (came out Feb 2015).
This was a staggered migration, where I done a P2V conversion (using vCenter Converter) on the secondary node first, I synchronized it, then I swapped roles making the virtualized node primary, then I virtualized the remaining secondary physical node.
So I had a SQLS 2012 FCI cluster running on virtualized Server 2008 VMs / ESXi 6.0 (Feb 2015) hosted on dual Dell PE R720s, with DRS Anti-Affinity rules to keep the FCI VMs separated on different ESXi hosts at all times.
2017: Upgrade to Server 2012R2 (Oct 2016)
Next I used a Cluster OS rolling upgrade to update my Server 2008 VMs to Server 2012R2 VMs.
Can you upgrade directly from Server 2008 to 2016? How did you handle your Quorum Witness during upgrade?
So I now had the SQLS 2012 FCI cluster running on Server 2012R2 VMs hosted on vSphere 6.0 hosts configured with shared pRDM storage mapped to our storage array for block level backup.
I use VMW VASA APIs + Storage Providers to allow my ESXi Hosts closer integration with our storage array.
Advantages of a virtualized FCI on VMW are that:
Our virtualized FCI facilitates FO + recovery at multiple levels including the App / Host / Array levels.
- The FCI Cluster counters possible software issues occurring at the instance level
- vSphere HA and DRS counters possible Host HW failures or Op Sys failures at the Host level.
- Synchronous Block level replication of the SAN LUNs at the HW Array level between the pRDM Live Volume and a backup DSM Live Volume to counter possible disk failure or ransomware encryption of the pRDM Live volume.
Our FCI creates a flexible environment allowing
easier patching, upgrading, and scaling while
increasing security by spreading SQL instances over several VMs and allowing easier migration.
VMWs Built-in multipathing + the advanced queuing techniques allow virtualized SQL Server installations to leverage advanced configuration options such as:
Controling, limiting, and guaranteeing IOPS to VMs to increase perf + service more clients.
Utilizing multiple SAN paths and SP ports to balance the workloads of multiple SQLS VMs to Storage.
2017: I upgraded our SqlS 2012 FCI cluster running on dual Server 2012R2 VMs hosted by ESXi 6.0 hosts (R720) to Sql Server 2014
while simultaneously extending the FCI Cluster running in our DC with a SQLS AlwaysOn AG as I needed to add DR + offsite Data Replication.
SQLS AlwaysOn AG (Node + File Share Majority) in order to provide redundancy + DR at the DB level, in addition to the FCI instance level protection.
I done this migration due to SQLS 2012 mainstream support ending on July 11, 2017, while SQLS 2014 was supported until July 2019 + allowed me to upgrade to Dell PE R920 servers with Intel Xeon Skylake-SP Scalable Processor for increased perf.
2019: I upgraded our SqlS 2014 FCI + ALwaysOn AG running on dual Server 2012R2 VMs hosted by ESXi 6.0 hosts (R720) to Sql Server 2017 FCI + Always On AG.
Here WSFC / AlwaysOn AG extends into AWS for DR, while VMWare HA clustering is used on a local level within our DC to counter Host/Op Sys level issues.
The prim DC hosts 2 AG replicas in sync commit mode (single site/metro area) for HA, where Log steams are sync replicated allowing auto/ forced FO. The secondary AWS DC hosts 1 replica, running in async mode for DR protection.
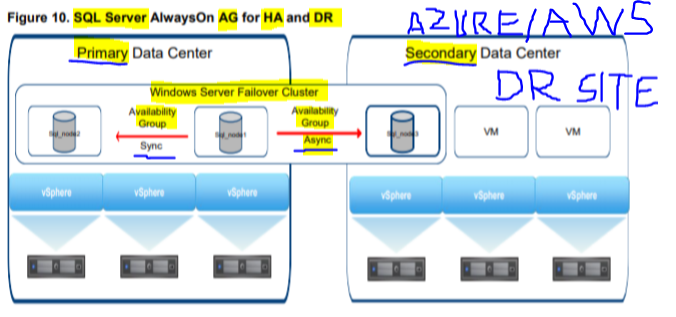
2020: I upgraded VMW installation from ESXi 6.0 to ESXi ESXi 6.7 (April 2018) / 6.5 (Oct 2016).
6.1 The net effect of a v-Motion or VSS based backup stun operation on FCI or AG Failover:
is that the stunned VM is unable to exchange heartbeats for the duration of the stun operation. If this lasts longer than 5 seconds + the VM is in a cluster then its cluster partners considers it unavailable and it FOs.
vSphere provides the ability to use multiple VMNIC interfaces to LB vMotion traffic while also countering unnecessary DB FOs due to missed heartbeats.
Enabling multiple VMNIC interfaces for vMotion requires configuring multiple VMkernel ports on different port groups. Each port group is assigned multiple VMNIC interfaces as either active or standby.
6.1 What are vSphere 6.7 new Security Features?
vSphere 6.7 provides a number of enhancements that help to lower a security risks for VMs hosting SQLS.
NOTE: vHardware v14 must be used to allow these features to be enabled.
• Support for a vTPM for the VM.
• Support for MS Virtualization Based Security .
• Enhancement for the ESXi “secure boot.”
• VM UEFI Secure Boot.
• FIPS 140-2 Validated Cryptographic Modules turned on by default for all operations.
6.2 Describe your Ethernet Net Config (VLANs, NIC Teaming, vMotion, WSFC Heartbeats) SQLS FCI + AG?
Cluster nodes SQLCLUSTER1+2 have 2*dual NIC teams (3 if you are using iSCSI)
- one for VLAN20 Server Network (Client Access),
VLAN21 VMW Mgmt traffic, VLAN22 VMW vMotion Network (all 3 are vmkernel interfaces (vmknic) )
- one for VLAN23 WSFC Heartbeat Communication + AlwaysOn AG Replication Network. SQLS clusters require a private heartbeat net for cluster keepalive / health checks as well as for intra-node comm, while you can also use this network for AG replication.
Synchronous AG Replication or DBM DB Mirroring which are sensitive to latency and requires a high-speed network.
-
one for the VLAN25 iSCSI storage network.
6.2 We have a non-converged LAN/SAN setup:
The LAN-side, our Dell PE R720 Servers are setup in active/standby configs with 4 * 10gb ethernet cards that connects (via 10Gbe) to redundant ToR Dell S4810 switches which are then configured with VLT Virtual Link Trunking up to our Dell core Z9000 switches.
Our FCI both Hosts have uniform access to the shared storage for HA, both Hosts use RAID1 local boot disks .
The SAN-side, our Dell PE R720 servers have dual Brocade 1860-2 2-port FC HBA Fabric adapters (16gbps FC connectivity + 10 gb ethernet DCB connectivity for virtualized environments) which connect via 8Gb FC to redundant Brocade 6505 FC Switches which relay traffic to our Storage Array that is composed of dual SC8000 storage controllers + 1 SC220 storage enclosure).
6.2 VMs in a hypervisor have different network needs.
SQLS AGs with WSFC nodes require dedicated physical network adapters (not virtual).
Use NIC teaming to provide redundant uplinks for vSS.
To use this capability, assign at least 2 physical NICs per vSS
Use the VMXNET3 paravirtualized net adapters to for
better throughput with reduced hypervisor CPU utilization.
For Ex 2013 DAG VMs configure at least 2 virtual network interfaces connected to different VLANs or networks,
to allow VMs to distinguish system v network failures.
Within VMs use 802.1q VLAN tagging and virtual switch port groups to logically separate traffic.
VMW recommends jumbo frames for vMotion/iSCSI traffic.
6.2/.6 To ensure uninterrupted AG synchronous replication :
a high-speed net with confirmed bandwidth + low latency,
sufficient to support the amount of SQLS trans traffic.
Make sure that WSFC vNICS (with separate pNICs VM, iSCSI, Vmotion) are connected to redundant physical switches, while putting VMs on same host/switch/subnet for comm
Use the VMXNET3 paravirtualized NICs that are
optimized for virtual environments + provide better throughput with reduced hypervisor CPU utilization.
Use vNIC drivers that are TSO Tcp Stack Offload-capable.
Update all drivers (VMW Tools, NIC) + Firmware
Use static IP addresses for network interfaces that are used for client connections + heartbeat links in a WSFC.
use traffic shaping + load balancing to ensure VMs get BW.
6.3 We use Multi-NIC vMotion interfaces for our heavily utilized OLTP SQL Server + our Ex Servers
Our testing showed an almost 25% increase in throughput achieved when multiple vSphere vMotion interfaces were used and no undue cluster DB failovers (without having to modify the cluster heartbeat settings)
Prior to implementing multi-NIC vMotion interfaces, we were having an issue with perf degradation during the vMotions where SDPS Stuns were slowing down the VM’s vCPUs to allow the vMotion operation to complete, this was not an acceptable risk for our SQL Server workloads.
With multi-NIC vMotion, every vMotion operation utilizes multiple port links, increasing perf + reducing the risk of SDPS related degraded perf on large, memory intensive VMs.
6.1 Heartbeat packets are Lightweight (134 bytes) in nature and sensitive to latency, if the cluster heartbeats are delayed by a Saturated NIC, or blocked due to firewalls, then unexpected DB FOs may occur.
In virtualized WSFC Clusters, Heartbeat thresholds are increased as the default 5 secs may be too sensitive.
In Hyper-V the default value changes when the 2nd VM is added to the 1st to form a cluster.
RouteHistoryLength setting (default 10) is a cluster service logging component that tracks dropped heartbeat packets + must twice the others so 40 here |
6.7 Describe the config of your vDS + Port Groups?
We use vDS switches as we use LAGs(LACP) / Nic Teaming
Uplink Port Groups->LAG Ports, PortGroup Pol->Nic Teaming
We use dedicated Port groups, VLAN tagging / 802.1q trunking, and separate physical interfaces to segment/ separate net traffic as it flows from our virtual network (VMs + vSS + ESXi hosts) to our physical switches + FWs,
so we can apply custom Port Group pols (Teaming+FO, Sec, Traffic Shaping, VLAN) to different virtual nets / traffic types.
I use 802.1q tagging + vDS port groups to separate traffic.
I use NIC teaming to provide redundant uplinks for vDSes,
where I assign at least 2 pNIC interfaces per vDS.
6.7 VMW Virtual Network Components:
Physical Uplink: from HW switch
VMNIC (pNIC):Physical net card in VMW, create subnets/VLAN
Uplink Port Group: uplink adapter on vSS to VMNIC.
vSS Port Groups: (connect VM, same level as VMKernel Ports),
- L2 connection from VMs to the vSSs. Prod/Test/DMZ.
- vSS Policies (Teaming, T Shaping, MTU, Sec)
- VNIC (VM) connects to a port in a port group + VLAN tags.
VMKernel P Group (VMKNIC): (same level as VM Port Groups), Mgmt, vMotion, Stor, FT, vSAN. TCP/IP Stacks/GWs
6.8 What type of VMW Network monitoring do you do?
I measure effective bandwidth between the VM+its peer looking for dropped transmit/receive packets.
Dropped packets indicate a bottleneck in the network.
Network perf: depends on your app workload + net config.
I use ESXtop, Resxtop, or the advanced perf charts to check the % RX or TX packets dropped.
6.6 What VM perf problems + how you solved them?
• If a VM is network-constrained, use net traffic shaping to give a VM more bandwidth during its peak hours.
• If a VM is constrained by memory, add memory shares or increase the VM’s memory reservation.
• If a VM is constrained by CPU, add CPU shares or increase the VM’s CPU reservation.
• If a VM is constrained by CPU or memory, increase the limits or reservations of the Res Pool the VM belongs to.
• Use NIC teaming to balance the network load across multiple physical network adapters.
• Use Storage Multipathing to balance the disk I/O load across multiple paths to a datastore.
• Use a DRS Cluster to balance VM load across hosts.
6.6 Give an example of a VMW problem you encountered?
Network Latency Issues:
Covered in previous slide
VMNIC (pNIC) Verify speed, duplex, wake on LAN settings.
To reduce dropped packets inside the SQLS guest:
to enable RSS Receive side scaling in the guest.
VM on the wrong port group issues:
the wrong security, the wrong traffic shaping, the wrong NIC teaming options, or a total lack of connectivity.
What Storage technologies do you have experience working with?
I'm currently using a Dell SC8000 with dual storage controllers (allowing block level replication between controllers) which has given solid performance for the most part, it integrates well with VMWare having registered the VASA 2.0 Provider (in vCenter) so I could import the vSphere Infrastructure + server objects into DSM Dell Storage Manager and register the FC HBAs (WWIDs) for those Hosts, it also imported the Cluster and Host hierarchy, so we could start presenting volumes to the Hosts/Cluster. DSM allows us to create the Storage Containers (which act as data boundaries) which map to vSphere endpoints within DSM allowing each of the ESXi Hosts to receive a PE pair + LUNs for their virtual datastores.
Each Controller has a 4-port FC HBA card with each port redundantly connecting to both FC Fabrics for redundancy of transport paths + multipathing to multiple controllers. With this setup there are, 4 paths available from each FC switch to each Controller, + 2 paths available from each server to each FC switches meaning 2 Fault Domains are configured on each FC Switches, finally we enable MS MPIO multipathing on our ESXi Hosts + Server VMs to complement the MS MPIO used on the Storage Controllers.
The only bad point about this storage array is that its limited to ‘Round Robin’ (Active/Active config) MPIO policy or ‘Fail Over Only’ (Active/Passive config) MPIO policy as it's not a true Active/Active Array nor is it an ALUA array as
Volumes are “owned” by a particular controller for mapping to servers, meaning the second controller will be active only during failure of primary controller resulting in a brief outage while failover occurs!
6.2 Describe your SAN Stor Network (FC Fabric) config use by your Server VMs to access their Storage?
Describe the Zoning of HBAs in your FC Fabric to control ESXi Host access to LUNS on the Storage Controllers?
Describe your use of MPIO/Multipathing between your Server VMs + Storage Controllers for load balancing + HA?
How did you configure your SC8000 to work with VMW?
We have dedicated storage net so our ESXi hosts(VMs) can access our SC8000 array + perform Datastore hearbeats.
6.2 We have a non-converged LAN/SAN setup:
The LAN-side, our Dell PE R720 Servers are setup in active/standby configs with 4 * 10gb ethernet cards that connects (via 10Gbe) to redundant ToR Dell S4810 switches which are then configured with VLT Virtual Link Trunking up to our Dell core Z9000 switches.
Our FCI both Hosts have uniform access to the shared storage for HA, both Hosts use RAID1 local boot disks .
The SAN-side, our Dell PE R720 servers have dual Brocade 1860-2 2-port FC HBA Fabric adapters (16gbps FC connectivity + 10 gb ethernet DCB connectivity for virtualized environments) which connect via 8Gb FC to redundant Brocade 6505 FC Switches which relay traffic to our Storage Array that is composed of dual SC8000 storage controllers + 1 SC220 storage enclosure).
6.4 How did you configure your SC8000 to work with VMW?
I registered the VASA 2.0 Provider (in vCenter) so I could import the vSphere Infrastructure + server objects into DSM Dell Storage Manager and register the FC HBAs (WWIDs) for those Hosts, it also imported the Cluster and Host hierarchy, so we can start presenting volumes to the Hosts/Cluster.
as a result of mapping vSphere 6.0 endpoints to DSM you will see the PEs (Each of the Hosts receives a PE pair + LUNs),
and then I create the Storage Containers in DSM, vSphere 6 doesn't recognize PEs until Storage Container created!
the storage container shows as a datastore and underneath it the container is a data boundary where Vvols will be created.
In VMW if we click on 1 of our Hosts they now show as having 2 PEs with LUN IDs. Each Host in the Cluster has different PEs!
The PEs are how each of the hosts are going to send read / write IO to the Vvols on behalf of the VMs.
VASA 2.0 vSphere APIs for Storage Awareness
are either supplied by 3rd-party vendors / VMW + enable communications between vCenter + Stor Controller.
VASA enables storage entities to inform vCenter about their
configurations, capabilities, health, + events.
In return, VASA can deliver VM storage requirements from vCenter to a storage entity + ensure storage meets the reqs.
ESXi uses a special VMkernel layer, the PSA Pluggable Storage Architecture (VMkernel APIs) aka vSphere APIs for Multipathing to manage storage multipathing.
VAAI vSphere APIs for Array Integration (HW Accel APIs offload certain storage ops to the array),
Array Thin Provisioning APIs prevent out-of-space conditions and to perform space reclamation.
6.4 Storage APIs - Data Protection (3rd-party backup sols)
When 3rd-party SW uses the VMW APIs to perform backups, it frees our ESXi hosts from the backup load and they are nondisruptive (no VM restart, no impact on backup window) + can be performed at any time as they use VMFS's snapshot capability.
6.4 What type of SP Storage Processor you use on SAN?
We use the SC8000 SP which we integrate into vSphere
/ vCenter using VASA VMWare API for Storage Awareness,
The SP / PE is a SAN component that processes HBA requests received from /routed through an FC switch and
handles the RAID/volume functionality of the disk array.
VASA APIs (registered in vCenter) integrate with 3rd-party SP's software that facilitates the export of PE Protocol Endpoints along with their associated Storage Containers
so vSphere can map them to Virtual Datastores (important for VVOLs) and become visible in vSphere Web Client + Host.
Storage Containers can be a pool of storage capacity or
an aggregation of storage capabilities (snapshot, replication, duplication).
6.2 Each Controller has a 4-port FC HBA card with each port redundantly connecting to both FC Fabrics for redundancy of transport paths + multipathing to multiple controllers.
The additional ports provide more connectivity (MS MPIO/Linux DM-MPIO) and enable LB + FO across HBA paths.
Each Controllers FC IO cards are configured as ‘Virtual Ports’ using NPIV N_Port ID Virtualization.
FC I/O module ports use 16Gb SFPs small form-factor pluggables. We recommend 16 Gb FC for the best perf, while all FC ports can negotiate to lower speeds.
With this setup there are, 4 paths available from each FC switch to each Controller, + 2 paths available from each server to each FC switches meaning 2 Fault Domains are configured on each FC Switches, finally we enable MS MPIO multipathing on our ESXi Hosts + Server VMs to complement the MS MPIO used on the Storage Controllers.
6.4 How did you access LUNS / what HBA naming conventions did you use?
To access LUNS on our SAN via HBAs + FC Fabric, I use a naming convention associated with a vmhba / Runtime name,
- A 1 runtime name is created by the host and is relative only to the installed adapters at the time of creation;
- it might be changed if adapters are added or replaced and the host is restarted.
- Uses the convention vmhbaN:C:T:L
2 Canonical name: The NAA ID, Network Address Authority that is a unique identifier for the LUN. This name is guaranteed to be persistent even if adapters are added or changed and the system is rebooted.
3 SCSI ID: The unique SCSI identifier that signifies the exact disk or disks that are associated with a LUN.
6.4 Why HBA Zoning v Masking on your FC switches?
With Zoning the switch fabric controls which HBAs can see which SPs (+ PEs) thru the SAN.
SPs is a SAN component that processes HBA requests received from the FC switch + handles the RAID/volume functionality of the disk array.
VASA APIs (registered in vCenter) integrate with 3rd-party SP's SW that facilitates the export of PE Protocol Endpoints along with their associated Storage Containers so vSphere can map them to Virtual Datastores to become visible in the vSphere Web Client + Host.
Zoning uses single-initiator-single-target zoning when zoning ESXi hosts to FC arrays.
With this type of configuration, fabric-related events that occur on one array do not impact other arrays.
6.4 Soft Zoning
(configured on the FC switches to control which WWNNs can see other WWNNs through the switch fabric):
Is where you use the WWNN names so any port connected to that WWNN is automatically zoned into whatever soft zone you put it in, so you just use the node name of the host and the node name of the array and it doesn't matter what the WWPN is they'll just be zoned automatically.
VM Options - FC NPIV can see WWNN for vm
6.4 Hard Zoning
(uses WWPNs to determine which switch ports will connect to SPs storage processors).
6.4 Masking:
is controlling what the SPs tell the host with regard to the LUNs that they can provide. In other words, the SP is configured to lie about the LUNs it is connected to.
command line only. can be done on the SP.
VMW recommends doing any masking on the SP.
on the host:
MASK_PATH module of native multi-pathing arch.
on the array:
by not allowing some hosts to access a specific LUN.
boot from SAN:
certain LUNs are used to boot a host, meaning they need to be masked from other hosts that access an array.
6.2 The Dell Compellent SC8000 will only support
‘Round Robin’ (Active/Active config) MPIO policy or
‘Fail Over Only’ (Active/Passive config) MPIO policy.
MS LB policies are generally dependent on the controller design (ALUA or true Active/Active) of the storage array attached to Windows-based computers.
The other policies require ALUA Asymmetric Logical Unit Access support on the array and additional support through a DSM Device Specific Module. (These are not available on the Compellent as it is not a true Active/Active Array nor is it an ALUA array)
Volumes are “owned” by a particular controller for mapping to servers.
The second controller will be active only during:
- failure of primary controller.
- the primary can no longer take the workload
6.2 Creating Volumes on the Storage Array using DSM Dell Storage Manager + mapping them to Cluster Server Objects so Server VMs can write data to them and have it redundantly stored in a Live Volume on the array.
To make mapping storage to a cluster easier, DSM allows you to create cluster server object, where you can place individual server objects that will be used by cluster nodes.
So any volumes that are mapped to the cluster server object are automatically mapped to each server contained in the cluster server object.
During the process, you will be asked config a ‘Replay Profile’, which will determine how often ‘snapshots/recovery points’ of the storage volume should be taken.
6.3 How is Storage multipathing configured in VMW?
our ESXi host boxes dual 2-port FC HBAs meaning there are 2 paths from our ESXi boxes to each Fabric switch.
We use ESXi's NMP Native Multipathing Plugin (part of the PSA architecture)to manage multipathing. Our ESXi hosts use the default SATP Storage Array Type Plugin (VMW_SATP_ALUA) for use with SCOS 7.3.20 (Aug 2019) + DSM 2019 R1 (30 Aug 2019) to change the PSP path selection policy from the single path MRU (default PSP, LUN thrashing) to RR PSP as RR allows multi-paths where Data is alternately sent over different paths during same data transfer session.
Even though data is sent on only one path at a time, this increases the size of “the pipe” and therefore allows more data transfer in the same period of time.
6.2 Back on the Server 2012 VMs configured with MPIO,
as soon as the HBA on the Windows server detects storage available for it, it will be detected in the Windows disk management administration tool after performing a disk scan. You must right click the detected virtual disk and initialize it, so the volume setup on storage array displays in Windows just like a typical hard drive. Note, no special configuration was needed on the HBA.
6.3 Multi-pathing
is used both for load balancing and for HA.
Gives you more bandwidth + can increase perf
In an active-passive setup it is used only for HA, while
in an active-active setup it is used for both HS + LB.
6.3 What sort of optimizations did you make to your virtual network for SQL Server?
SQL Server demands Block Storage, we have our ESXi boxes hosting our SQL Server instances setup with redundant FC HBA's for accessing storage through our SAN.
Because of this I ensure we are always using the most up-to-date HBA Firmware, have configured multipathing between the ESXi hosts + Storage controllers (both with redundant FC connectivity configured in a ‘Round Robin’ MPIO policy (for an Active/Passive configuration), and have tuned the HBA driver settings to provide a deeper Queue depth so more transactions can be sent a once.
6.3 And what type of Driver Module setting tuning (Controller failover protection - Login Retry Count + Port Down Retry, Queue Depth tuning did you do? And why?
Queue depth is the number of commands that a LUN may concurrently operate on, when that number of outstanding commands is achieved, the LUN refuses to accept any additional commands (any additional commands are failed with the status of TASK SET FULL).
Queue depth denotes the number of I/Os that can pass through a storage path at one time, all other I/Os beyond this number are queued until the path has more room.
Device Driver Queue Depth is set on the host adapter to balance the IO load across LUNs so that a single busy LUN does not consume all available adapter resources.
6.4 What sort of LUN Formatting / LUN numbering / RAID Level did you implement?
I use our Dell DSM SW (OVA) for LUN Mgmt tasks such as:
LUN creation,
array cache management,
LUN mapping, and LUN security.
Setting up replic, check points, snapshots, or mirroring.

6.4 Mark sizes his LUNS for individual datastores and then clusters them together, in a SDRS Datastore Cluster to make sure all datastores in the cluster receive defined reqs.
Smaller LUNs for:
- Less wasted storage space.
- Different apps need different RAID characteristics.
- Flexibility, as multipath pol + disk shares are per LUN.
- Use of WSFC requires each cluster disk is in own LUN.
- Better perf because less contention for a single volume.
Fewer larger LUNs for:
- More flexibility to create VMs without asking for space.
- More flexibility for resizing virtual disks/doing snapshots.
- Fewer VMFS datastores to manage.
When Troubleshooting LUNs look at:
- the assignment of an array cache to a LUN,
- the number of disks per LUN,
- the RAID level of a LUN.
For data warehousing / DBMS systems that primarily perform sequential reads, set RAID5.
For transactional apps, with random I/O, set RAID10.
Do not mix different types of I/O on same RAID LUN.
However, today’s array technology can also automatically adjust for sequential and random I/O.
6.5 What Features of the SC8000 do you use / like?
Dell SC8000 is based on a Fluid Data architecture
it's storage profile's feature enables orgs to move data dynamically, intelligently, and efficiently among multiple storage tiers + RAID levels.
I created a Vols folder for volumes used on WSFC nodes, then created a Servers folder + Server Cluster folder.
Storage Types: virtualizes storage by grouping disks into pools, which hold small chunks of data known as pages.
We recommend:
- A default data page size of 2 MB, for most applications
- 2 storage tiers each for SQLS log and data volumes
Tier 1-WI SSDs + RAID10 single-redundant or redundant.
Tier 2-RI SSDs + RAID5-9 (striped across multitple drives).
6.5 On the SC8000, Blocklevel storage is allocated for use by defining volumes and mapping them to servers.
Storage profiles: - are a tiering policy feature.
simplifies tiering mgmt by enabling you to assign flash storage to active data while retaining the flexibility of storing cold data in a more cost-effective tier.
control how the array Storage Center manages volume data, so when a storage profile is assigned to a volume, the volume inherits the profile's tiering attributes.
The selected storage profile for a volume dictates which disk tier accepts initial writes as well as how data progression moves data between tiers to balance perf+ cost.
The storage type determines the available storage profiles.
Predefined storage profiles are the most effective way to manage data in the Storage Center.
a flash-optimized storage profile:
directs all write operations to high-perf Tier 1 storage―write-intensive (WI) SSDs in RAID 10.
On-demand data progression automatically converts replay and RI data to RAID 5 and places it on Tier 2 RI flash storage that has exceptional read perf characteristics.
v cost-optimized storage profile:
enables the admin to create a volume for applications such as backup and archive, as well as for low-priority apps.
Data Progression +Data Reduction (intelligent deduplication and compression) moves data to lower-overhead RAID levels. For example, data can be moved from high overhead RAID10 to space efficient RAID 5 and inexpensive RI read-intensive SSDs, finally to low overhead RAID6 7.2k SAS HDDs.
6.3 Do you use RDMA as part of your setup?
FC uses hardware based DMA to perform transfers without the need to make intermediate copies of the data, therefore RDMA is not needed for FC, and does not apply to FC.
RDMA is a part of a protocol through which memory addresses are exchanged between end points so that data is able to move directly from the memory in one end point over the network to the memory in the other end point, without involving the end point CPUs in the data transfer or allowing intermediate copies of the data to be made.
RDMA capable protocols RoCEv1 RoCEv2 iWARP InfiniBand
iSER iSCSI over RDMA protocol often uses iWARP or RoCE.
SRP SCSI RDMA protocol that runs only over InfiniBand.
6.3 What type of Storage Policy (Policy based Storage) do you have configured? And why?
Stor Pol outlines the QoS a storage system can deliver.
is a guarantee that the storage system can provide a specific set of characteristics.
A storage policy lists the storage capabilities:
that VM home files (.vmx, .vmsd, .nvram, .log, and so on) + virtual disks (.vmdk) required to run apps in the VM.
Stor Pols are used to determine the Storage compliance of a VM. You will then get notifications if your VM is not in compliance with the policy.
Vendor-specific storage capability comes from a SP.
User-defined / tag-based storage capability not represented by any SP, can assign to multiple datastores.
What type of Storage Mon / Baselining do you do in vCenter ?
DAVG Device Average: >20ms problem with your SAN.
Aka Physical SCSI device command latency,
array may be under designed.
KAVG Kernel Average: >2/3ms problem with your host/array.
aka VMkernel SCSI command latency,
6.7 What Storage Net problems have you encountered?
I have seen Excessive demand placed on storage devices causing Slow + Overloaded Storage due to:
- The storage load exceeding device specs as architects didn't fully understand the load of DB + Mail servers
- Excessive Swapping due to
- High Latency due to incorrect Queue depth, saturated links, badly configured RAID type, caching/prefetching algs
-
path thrashing causing a LUN to not be visible as 2 hosts try to access the same LUN through different SPs.
- Excessive disk throughput due to many vm operations on a VMFS drive + incorrect ResPool (Shares/Reserv/Limits)
- Misconfigured Storage Fabric wrongly zoned + strict acls
6.3 What type of SIOC + SDRS have you implemented + why?
SIOC allows you to control the amount of storage I/O resource allocation that is allocated to VMs during periods of I/O congestion, it throttles IOPS.
extends shares + limits to handle storage I/O resources.
You can use vSphere SIOC with or without SDR, however it is enabled when you enable vSphere SDRS.
RDMs are not supported with SIOC.
SDRS Datastore Cluster, Mark sizes his LUNS for individual datastores and then clusters them together, in a SDRS Datastore Cluster to make sure all datastores in the cluster receive the resources the cluster is defined as requiring.
LUNs with different perf characteristics can cause problem
Host + datastore clusters can coexist in the virtual infra.
6.4 Why do you use FC over iSCSI?
If a backup array is emulating a tape library, this is usually easier to do with FC than with iSCSI.
When designing topologies / architectures FC v iSCSI is an important consideration pure FC network are not routable while iSCSI is so it is useful in hybrid archs.
FC has a tightly-controlled oversubscription ratio
which is the number of hosts that we allow to access a storage device (typically 4:1 to 20:1, depending on app).
iSCSI can often be several dozen *12 :1 storage target.
FC can use fiber-optic cable or copper cable.
less overhead than TCP/IP, speeds of 1, 2, 4, 8, 10, 20 Gbps.
flexible + it doesn't put load on Ethernet LAN. Cost$$
when you add host, it auto scans 256 FC SAN LUNs (0–255).
6.4 Troubleshooting FC and iSCSI
Tools such as traceroute, ping, are common on both FC/iSCSI
FC’s troubleshooting tools are available at both the adapter level and the switch level, but since FC has the concept of a fabric, many of the tools are system-wide.
This allows for many common steps to be taken in one centralized management location.
iSCSI troubleshooting tools are very similar to FC since they both appear as SCSI + offer the same services.
6.7 Troubleshooting Tools
vCenter views:
- 1 Storage view: (Summary tab / Related Objects tab)
- 2 Hosts + Clusters view: (Related Objects - Datastores)
(Storage Adapters - what a host can see)
vSphere Client:
- Monitor the host’s event logs / ESXtop / remote ESXtop / WebClient (adv. charts) + compare to baseline.
- Storage Views tabs - hit Reports button. View storage info for any object except networking.
- Storage Views tabs - hit Maps button. Click Search, Storage Options - view all the storage options available.
Monitor from your storage HW: using the vendors tools
6.7 Solutions to slow / overloaded storage:
- rebalance the I/O workload across all available LUNs.
- VMs see all stor as “local SCSI, but it is the underlying stor where issues occur + are fixed, so not much to do in VMW.
- Multipathing / PSP Pol can enhance perf + availability.
Stor View-Manage-Settings-Connectivity+Multipathing
- Make sure your device drivers are correct and up-to-date.
- Fewer smaller LUNs + Ensure compatibility of devices.
- Set proper LUN queue depth from your stor vendor docs. reduce No of VM snapshots they can cause SCSI reservs.
-
follow the Config Maximums document + reduce the No. of VMs per LUN to the recommended maximum.
7 What BCP / DRP experience do you have?
BCP: have secondary systems in place to kick in should the main system fail.
(we have Open VPN should our Dell Sonicwall VPN fail).
DRP: have redundant remote warm site configured to take over in the event of a natural disaster.
How much Public Cloud AWS / Azure experience do you have?
I use AWS Route 53 Healthchecks to control FO of our WAN Interfaces in the event one of them goes down.
I run a SQLS Availability Group that's extended into our AWS VPC and asynchronously replicates transactions to out redundant Cloud based SQL Server instances. These SQL Server instances are configured with DB Volumes stored EBS high perf persistent block storage that ensures:
- 99.999 percent availability
- Crash-consistent point-in-time snapshot support
- Encryption support
I use gp2 general purpose volumes as they offer a good balance of price + perf for SQL Server workloads, such as single-digit millisecond latencies + the ability to burst to 3,000 IOPS.
To connect to VPC we use redund Accelerated Site-to-Site VPN
Accelerated S-to-S VPN is more consistent than regular S-to-S VPN as it uses the highly available and congestion-free AWS global network rather than the public network face were you can face inconsistent availability and perf as traffic traverses through multiple public networks which can be congested + each hop can introduce availability + perf risks before reaching the VPN endpoint in AWS.
Only Transit Gateway supports Accelerated Site-to-Site VPN. The VPN endpoint is created on the Transit Gateway.
For File Archiving we use
We use AWS Glacier API to create Glacier Vaults where we upload snapshotted Storage volumes for inexpensive long term backup + archiving.
The Unifi Controller is in its own AWS account separate from our AWS backup account.
however both are managed using AWS Organizations an AWS account management tool which allows you to consolidate billing and payment for all your AWS accounts in one location under your Root Account.
Having different accounts within AWS serving different purposes increases security as if one account was to get compromised your other accounts are insulated.
In addition to this the quickest way to spot a breach in one of your accounts is to monitor for spikes in your billing, as the AWS Billing system is Amazons number one priority, and its most accurate, most up-to-date, and most secure system. It monitors in minute detail down to every API and System call!
It is supremely accurate for compliance reasons.
Making it AWS's most important security tool!
To secure the Unifi Network in AWS
I use the AWS firewall to restrict inbound + outbound traffic
to the public IPs of each community + Head Office, while also locking down Ports to only those that are required, namely port 8080 for the Inform protocol and 3478 for the STUN protocol.
To secure the Unifi Network at the Community FTGWs
I also open ports 8080 inbound + outbound for the Inform protocol and 3478 inbound + outbound for the STUN protocol only from ubnt.com in the security policies allowing Unifi Management traffic to pass between the WAN interface + the DMZ interface, before allowing the traffic to pass onto VLAN 40 virtual interfaces where the Unifi devices are situated.
Striping EBS volumes
Stripe your EBS volumes to optimize perf + exceed the limits of a single volume’s perf.
There is no need to implement any RAID redundancy levels because EBS data is already replicated with 99.999 percent availability and designed for an annual failure rate (AFR) of between 0.1% – 0.2%. For example, implementing RAID1 would give you an unnecessary 50 percent reduction in both EBS bandwidth and capacity.
Taking EBS snapshots
Snapshotting your backup volumes to S3 is an effective strategy for long-term backup. Use Amazon DLM Data Lifecycle Manager to auto create and (optionally) delete snapshots. Also, EBS integrates with AWS Backup, a fully managed backup service.
You can take MS VSS–enabled snapshots through EC2 Systems Manager Run Command.
6.1 AlignGeneral (13-16) SQLS experience
I've ran AD Controllers and Win File servers since 06.
While I began administering SQLS 2008R2 + 2012 instances when I joined Align General in 2013.
I took over administration of 2 SQLS 2008R2 instances + 4 SQLS 2012 instances running on bare metal installs of Windows Server 2008R2 + 2012
The 2008R2 box ran on custom built Supermicro server using dual socket Intel Xeon E5506 processors with 32GB of RAM. Storage on the server was controlled by a LSI SAS 9211-8i hardware RAID controller. The C boot drive was configured in a RAID1 configuration mirroring across dual 2TB SAS drives, while the E data drive was setup in a RAID10 config (mirroring for redundancy then striping for speed) across 4 * 2TB SAS drives.
I migrated the SQLS 2008R2 instances running on Server 2008R2 machines to SQLS 2012 running on Server 2012, as SQLS 2008R2 was end of main stream support in July 2014 and our software vendor (Insuresoft) recommended the upgrade.
The Server 2012 boxes ran on a Dell PE R720 server using dual socket Intel Xeon E5-2650 processors with 64 GB RAM (DDR3+ECC),
Storage on the server was controlled by a PERC H710p HW RAID controller. The C boot drive was configured in a RAID1 config mirroring across dual 900GB SAS drives, while the E data drive was configured in a RAID 10 config (mirroring for redundancy then striping for speed) across 8* 900GB SAS drives.
6.1 What was your Backup Strategy at Align?
Originally we were using a dual (onsite / offsite) backup strategy, using nightly Native SQL Server Management tasks for full differential nightly backups Monday through Thursday, with a full backup every Friday night and hourly transaction log backups to our main File Server between 5am and 9pm, M-F.
Remote Backups were subsequently sent offsite on a week-nightly basis from our main File Server FS01 to our remote DCs in OVH Texas and OVH Ontario Canada either nightly or weekly using rdiff-backup or rsync.
I upgraded this backup process to use Idera SQL Safe to lower our RTO + RPO objectives, by using it's excellent compression features to reduce the amount of data we had to send, reducing the size of our Backup window, with the knock on effect of being able to decrease the trans log backup interval to15 mins.
Idera runs on a separate UTIL01 machine and is used to mirror all SQL DBs to SQL 03 (for DR purposes).
Idera's Patented Instant Restore technology brings your DB online immediately minimizing app downtime.
Pauses and restarts backup if there's a network outage.
The Idera SQLSafe management console is on UTIL01 + allows us to restore directly from file shares as source.
All of these backups are in the .SAFE file format (Idera SQLSafe proprietary) but you can convert to .BAK file
Systems Enginer Interview Q's
By donsheridn
Systems Enginer Interview Q's
- 540
