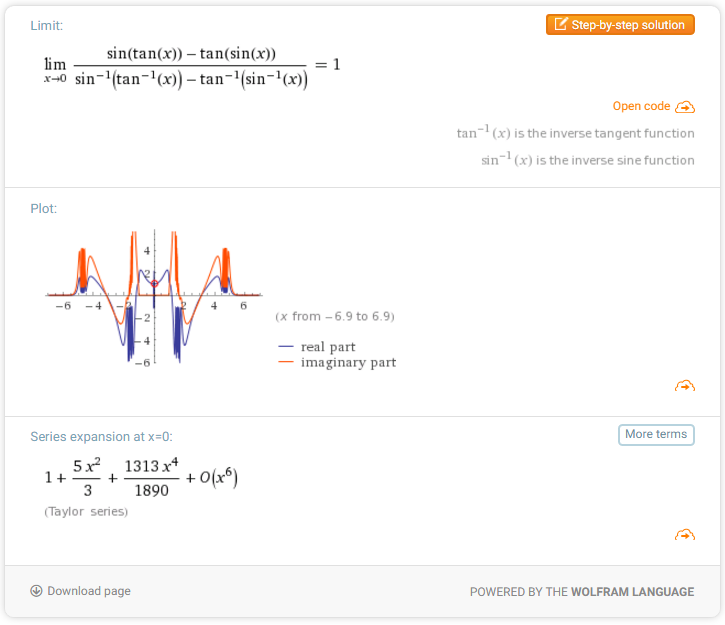
An Elusive Limit
f(x) = \frac{\sin(\tan x) - \tan(\sin x)}{\arcsin(\arctan x) - \arctan(\arcsin x)}
f(x)=arcsin(arctanx)−arctan(arcsinx)sin(tanx)−tan(sinx)
\displaystyle\lim_{x\to 0}f(x)=?
x→0limf(x)=?
1.Use your computer algebra system to
evaluate \(f(x)\) for \(x = 1, 0.1, 0.01, 0.001, 0.0001\)
Does it appear that \(f\) has a limit as \(x \to 0\) ?
f (1) = 1.183832...
f (0.1) = 1.016736...
f (0.01) = 0.989637...
Wolfram
f(0.001)=0?
*Infinite expression \(\frac{1}{0}\) encountered
f(0.0001) = Indeterminate
Excel
f(0.001) = 0
f(0.0001) = 0

2. Use the CAS to graph \(f\) near \(x=0\).
Does it appear that
\(f\) has a limit as \(x \to 0 \) ?
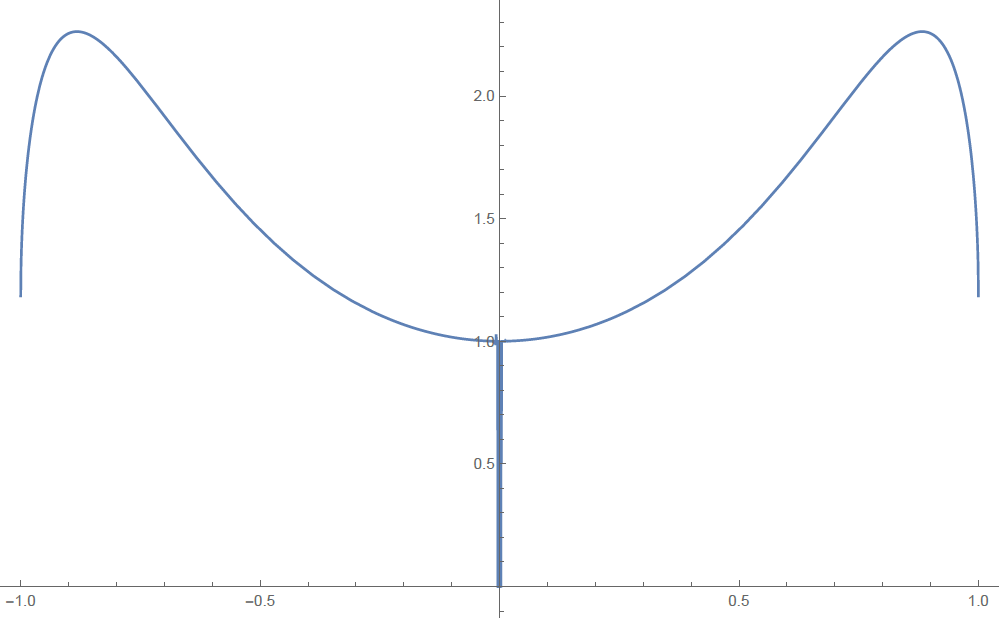


x \in[-1, 1]
x∈[−1,1]
x \in[-0.1, 0.1]
x∈[−0.1,0.1]
x \in[-0.01, 0.01]
x∈[−0.01,0.01]
3.Try to evaluate \(\displaystyle\lim_{x \to 0} f(x) \) with l'Hospital's
Rule, using CAS to find derivatives of
the numerator and denominator.
What do you discover?
How many applications of l'Hospital's
Rule are required?
g(x)=\sin(\tan x) - \tan(\sin x)
g(x)=sin(tanx)−tan(sinx)
h(x)=\sin^{-1}(\tan^{-1}x) - \tan^{-1}(\sin^{-1}x)
h(x)=sin−1(tan−1x)−tan−1(sin−1x)
\text{let }f(x) = \frac{g(x)}{h(x)}
let f(x)=h(x)g(x)
g'(0)=g''(0)=g'''(0)=g^{(4)}(0)=g^{(5)}(0)=g^{(6)}(0)=0
g′(0)=g′′(0)=g′′′(0)=g(4)(0)=g(5)(0)=g(6)(0)=0
h'(0)=h''(0)=h'''(0)=h^{(4)}(0)=h^{(5)}(0)=h^{(6)}(0)=0
h′(0)=h′′(0)=h′′′(0)=h(4)(0)=h(5)(0)=h(6)(0)=0
g^{(7)}(0)=h^{(7)}(0)=-\frac{7!}{30}
g(7)(0)=h(7)(0)=−307!
4.Evaluate \( \displaystyle\lim_{x \to 0} f(x) \) by using the CAS to find
sufficiently many terms in the Taylor series of
the numerator and denominator.
(Use the command taylor in Maple or Series in Mathematica.)
\sin(\tan x) - \tan(\sin x)
sin(tanx)−tan(sinx)
=-\frac{x^7}{30}-\frac{29x^9}{756}-\frac{1913x^{11}}{75600}+O(x^{13})
=−30x7−75629x9−756001913x11+O(x13)
\sin^{-1}(\tan^{-1}x) - \tan^{-1}(\sin^{-1}x)
sin−1(tan−1x)−tan−1(sin−1x)
=-\frac{x^7}{30}-\frac{13x^9}{756}-\frac{2329x^{11}}{75600}+O(x^{13})
=−30x7−75613x9−756002329x11+O(x13)
5. Use the limit command on your
CAS to find \(\displaystyle \lim_{x \to 0}f(x)\) directly.
(Most computer algebra systems use the method
of Problem 4 to compute limits.)
6. In view of the answers to Problems 4
and 5, how do you explain the results of
Problems 1 and 2?
Precision, Oscillation
>>> (sin(tan(t))-tan(sin(t))).series(t, 0.001)
2 3
- 6.99960922556642e-16⋅(t - 0.001) - 1.16678888772981e-12⋅(t - 0.001)
4 ⎛ 5 ⎞
- 1.16667149988666e-9⋅(t - 0.001) + O⎝(t - 0.001) ; t → 0.001⎠
>>> (asin(atan(t))-atan(asin(t))).series(t, 0.001)
2
2.16840434497101e-19 - 7.00286183208387e-16⋅(t - 0.001)
3 ⎛ 4 ⎞
- 1.16670562100296e-12⋅(t - 0.001) + O⎝(t - 0.001) ; t → 0.001⎠Tayler series at 0.0001 ?
$ isympy
>>> (sin(tan(x))-tan(sin(x))).series(x, 0, 13)
7 9 11
x 29⋅x 1913⋅x ⎛ 13⎞
- ── - ───── - ──────── + O⎝x ⎠
30 756 75600
>>> (asin(atan(x)) - atan(asin(x))).series(x, 0, 13)
7 9 11
x 13⋅x 2329⋅x ⎛ 13⎞
- ── + ───── - ──────── + O⎝x ⎠
30 756 75600

Calculus
By doraeric
Calculus
- 132


