Electrostatics

The Electric Charge
Electrostatics
Background
...
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
Textbook Section 5.1
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
... is fundamental
Once upon a time ...
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
... is fundamental -- the phenomenological approach
Mr P explaining electric charge in terms of what it does.
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
... is fundamental
Once upon a time ...
in the 20th century ...
Experimental basis of QM
Discovery of the X Ray and the Electron
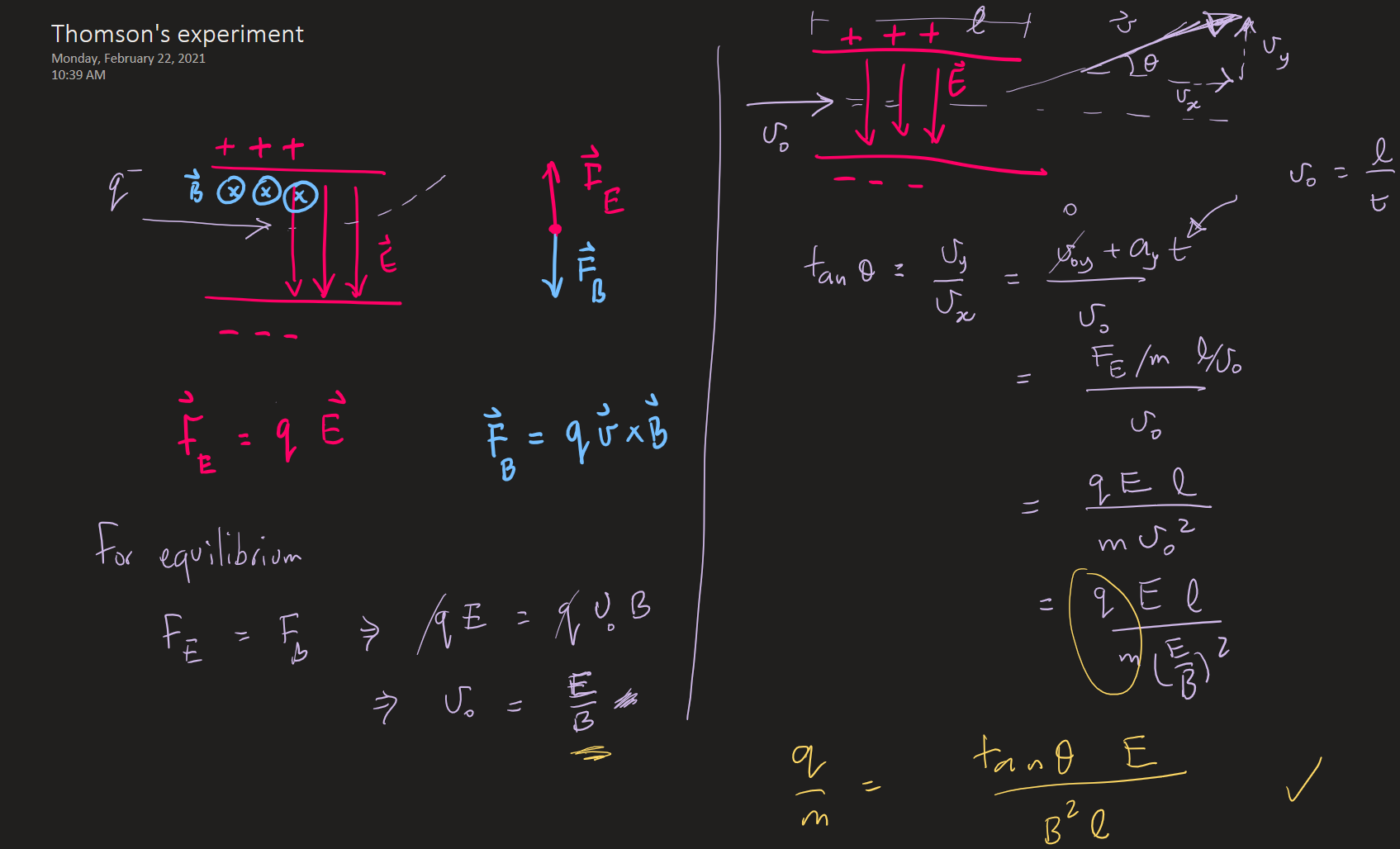
Thomson's experiment -- electron charge to mass ratio (1897)
From T & R, p 86
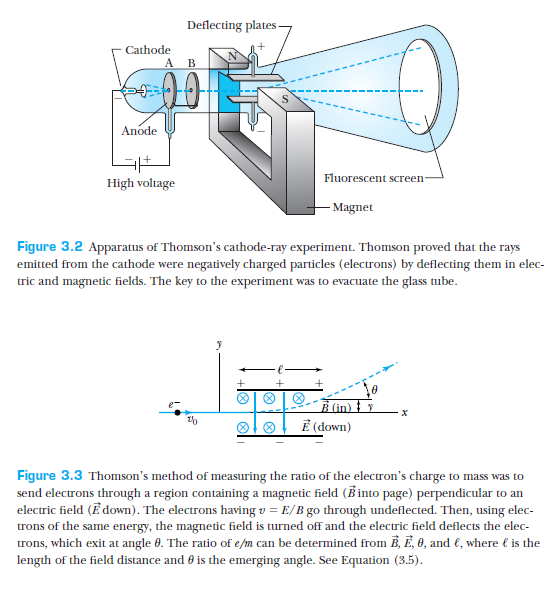
J.J. Thomson showed that cathode-rays were charged particles by showing their deflection in magnetic/electric fields.
Furthermore, he managed to measure the charge to mass ratio of the electron.
Experimental basis of QM
Discovery of the X Ray and the Electron
Thomson's experiment -- electron charge to mass ratio (1897)
From T & R, p 86
Experimental basis of QM
Determination of the electron charge
Millikan's experiment -- electron charge (1911)
From T & R, p 89
Millikan suspended oil drops between two plates by changing the potential difference across the plates.
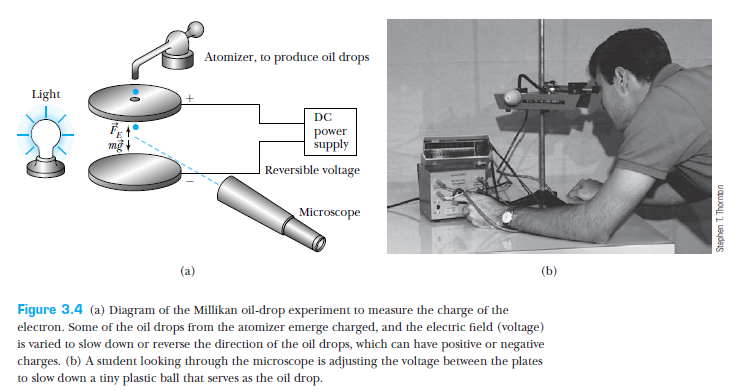
The equilibrium between the force of gravity and the electric force gave an estimate of the charge on the oil drop, in terms of its volume.
The volume was estimated from the terminal velocity.
Millikan found that the drops carried electric charge that was quantized!
The elementary charge, he found, was

Experimental basis of QM
Determination of the electron charge
Millikan's experiment -- electron charge (1911)
The atomic nucleus
What lies within?
The variety of nuclei
Atomic Nucleus
Nucleons & their structure
Rutherford
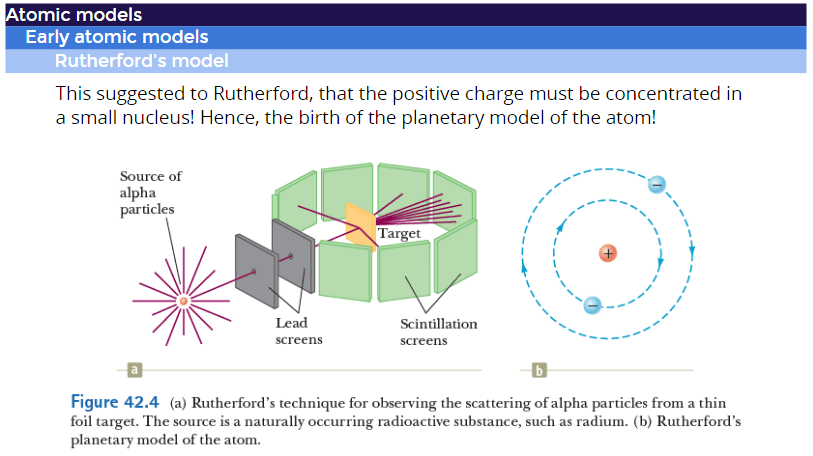
Atomic Nucleus
Nucleons & their structure
Discovery of the neutron (1932)
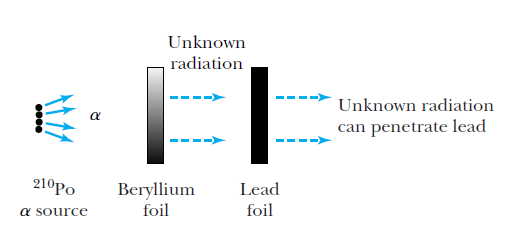
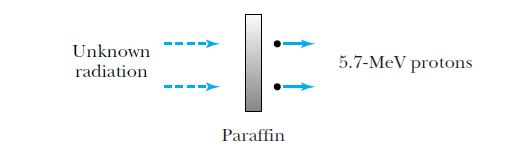

Chadwick suggested the radiation was a neutral particle
of about the same mass as a proton.
Atomic Nucleus
Chart of the nuclides

The variety of nuclei
Atomic Nucleus
Chart of the nuclides

The variety of nuclei
Atomic Nucleus
Chart of the nuclides
The variety of nuclei
Atomic Nucleus
The variety of nuclei
Definitions
Isotope:
Atoms with same Z but different A
Nuclide:
A nuclear species with a given Z, N, and A
Isotone:
Atoms with same N but different A
Isobar:
Atoms with same A but different combination of Z and N

Atomic Nucleus
Size of the nucleus
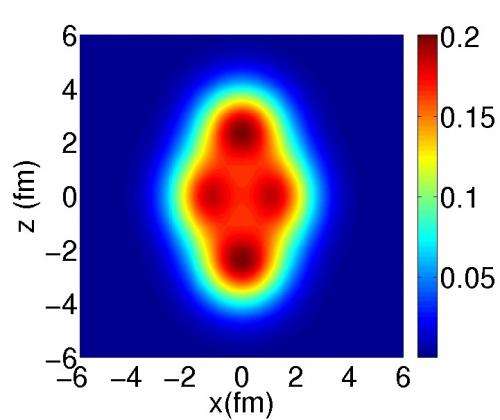
Atomic nuclei are bound states of protons + neutrons
Probability density for the presence of neutrons and protons predicted for the neon-20 nucleus. It can be seen that this is not homogeneous: the neutrons and protons are distributed in clusters. © Jean-Paul Ebran/CEA
Nucleons & their structure

The spatial extension of a typical nucleus is ~ fm
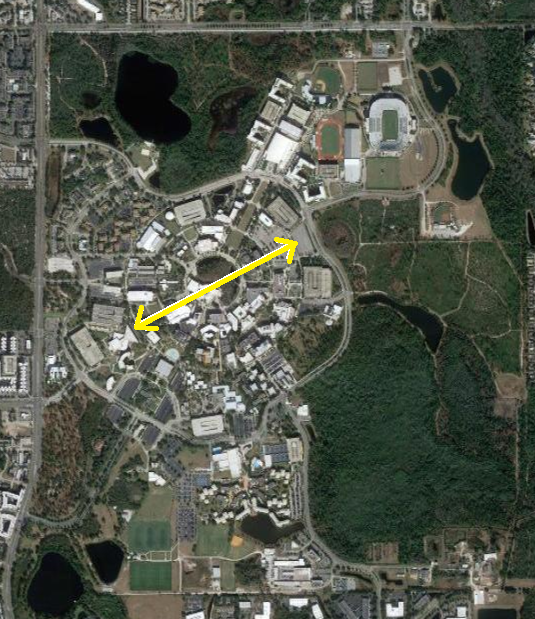
The comparative spatial extension of the atomic nucleus to the spatial extension of the electronic cloud in an atom is of the same order as the ratio of the size of your thumb compared to the size of UCF campus.
Atomic Nucleus
Underlying structure
Atomic nuclei are bound states of protons + neutrons
Probability density for the presence of neutrons and protons predicted for the neon-20 nucleus. It can be seen that this is not homogeneous: the neutrons and protons are distributed in clusters. © Jean-Paul Ebran/CEA
protons & neutrons
have internal structure
Nucleons & their structure
proton



neutron



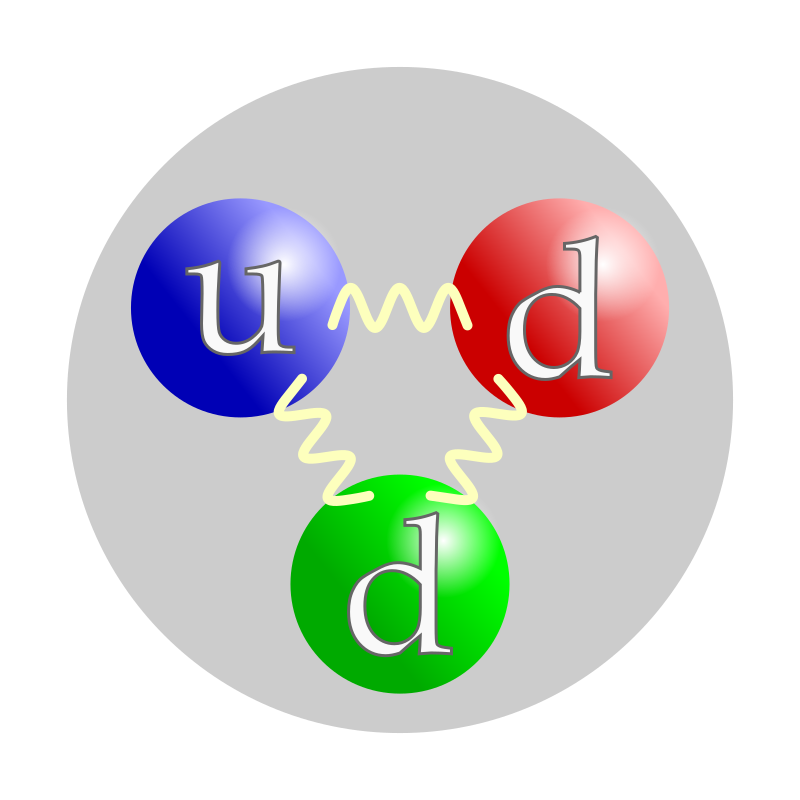
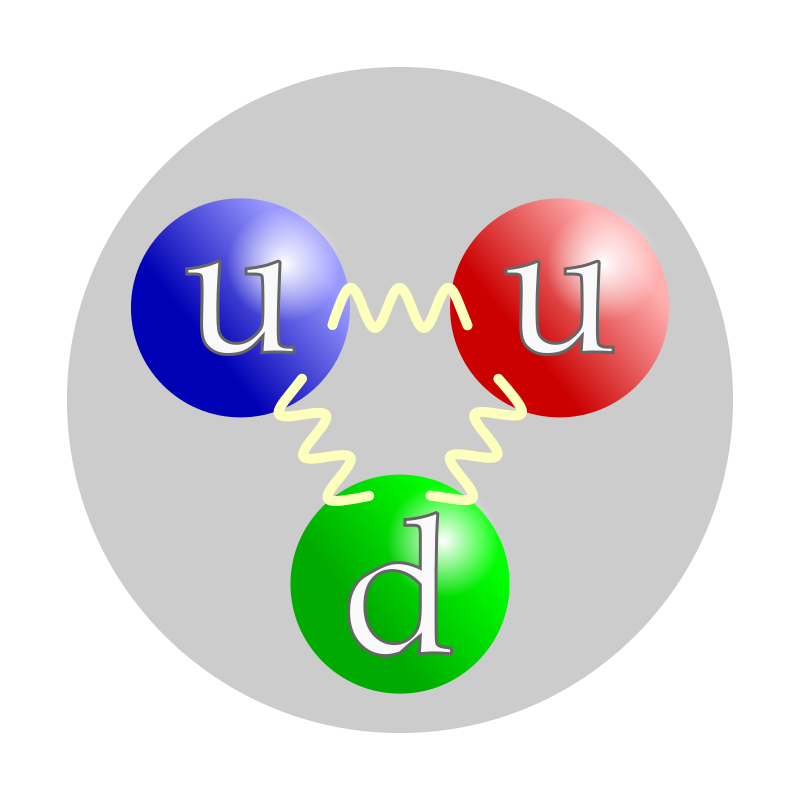
Atomic Nucleus
Underlying structure


of Elementary Particles





Nucleons & their structure
Electrostatics
The Electric Charge
... is fundamental
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
TL;DR
- Electric Charge is an intrinsic property of matter.
- Electric Charge is quantized (i.e. manifests in nature in integer multiples of the elementary charge:
- We have identified two types of charge -- ka positive and negative.
- "Ordinary" matter is made up of atoms, who are themselves made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
- Neutral objects have equal number of protons and electrons. (neutral does not mean without charge.)
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
The Net Electric Charge
- Each Proton has a net charge of +e
- Each Electron has a net charge of -e
- Objects are charged by losing or gaining electrons.
- Every ordinary object will carry a net charge that depends on the difference between the number of protons and electrons:
- Thus, an object will carry net negative charge if it has an excess of electrons, while a deficiency of electrons results in an overall positive net charge.
Electrostatics
The Electric Charge
How to "charge" an object
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
Charging by contact
- Electric Charge is conserved in a closed system.
- When two objects are in "contact", they could exchange electrons, leaving one object positively charged and the other negatively charged.
Move John's feet against the carpet and see the charges jump from the carpet to his body.
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
Conductors & Insulators
In conductors, some electrons are free to move
In insulators, electrons are bound to the nuclei
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
Conservation of charge
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
Polarization
- You can induce a charge on an object by performing a series of steps, that typically start with polarization.
- Polarization means separating the charges to different "poles"
- Polarization means separating the charges to different "poles"
- Rub the balloon against the sweater to pick up some charge.
- Notice the charge sits in place on the balloon -- why? (hint: is it made out of a conducting or insulating material?)
- Bring the balloon close to the wall -- the charges in the wall polarize.
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
Charing by induction
Electrostatics
The Electric Charge
Charge Distribution
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
Charge Distributions
Linear Charge Density
Surface Charge Density
Volume Charge Density
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
Point Charge
Charge distribution A
Charge distribution B
What do we mean by point charges?
Electrostatics
Electric Charge
Di-pole
What is an electric dipole?

Two equal but opposite charges separated by a small distance.
The electric dipole moment p is a vector whose direction is from -q to +q and whose magnitude is given by p=qd
Electrostatics
The Electric Charge
... and the rest of the cast
Electrostatics
The influence & interaction of electric charges
The Cast
potential
potential energy
field
force
charge
flux
influence
interaction
Electric ....
Electrostatics
The influence & interaction of electric charges
The Cast - relationship map
Electric ....
influence
interaction
Electrostatics
The influence & interaction of electric charges
The Cast - relationship map
Electric ....
influence
interaction
influence
interaction
gravitational....
analogus to
Electrostatics
The influence & interaction of electric charges
The Cast
influence
interaction
Physical Quantities
Electrostatics
The influence & interaction of electric charges
The Cast
electric charge
electric charge influences
interaction between charges
Physical Quantities
Electrostatics
The influence & interaction of electric charges
The Cast
recurring roles
Electrostatics
The influence & interaction of electric charges
The Cast
charge
influence
interaction
Physical Quantities
recurring roles
Parameters
Electric Charge
By drmoussaphysics
Electric Charge
- 331