Kinematics
Description of Motion
What is Physics?
Overview
Contents
Herein, you will find resources related to the following topics:
Kinematics
Starring ...
Kinematics
Staring ...
Position

Kinematics
Featuring ...
Position and Time

relative position
All positions are relative.
Kinematics
Starring ...
Position & Time

relative position
Motion requires a change in position
Kinematics
Displacement & Distance
Kinematics
Featuring ...
Displacement & Distance

relative position
The object is displaced
from A to B
along the
shown path
Kinematics
Featuring ...

relative position
The Displacement is defined as the change in position
Displacement & Distance
Kinematics
Featuring ...

relative position
The Displacement is defined as the change in position
The magnitude of the displacement is the shortest distance between the two points, A and B.
The direction of the displacement is from the starting point, A, towards the end point, B.
Displacement & Distance
Kinematics
Featuring ...
Suppose we divide the path into little infinitesimal displacements along the path
Displacement
Distance Traveled
Displacement & Distance
Kinematics
Featuring ...
Displacement & Distance
In summary, distance is a path dependent scalar quantity, whereas displacement is a path independent vector quantity.
Kinematics
Velocity & Speed
Kinematics
Featuring ...
Velocity & Speed
The average velocity during some segment of motion is defined as
The "state of motion" is represented by a vector physical quantity denoted the Velocity
Kinematics
Featuring ...
Velocity
Consider the component of the motion in some direction:

The Average Velocity is defined as:
Kinematics
Featuring ...
Instantaneous Velocity

Consider the component of the motion in some direction:
The Instantaneous Velocity is defined:
Kinematics
Featuring ...
Instantaneous Velocity
Consider the component of the motion in some direction:
The Instantaneous Velocity is defined:
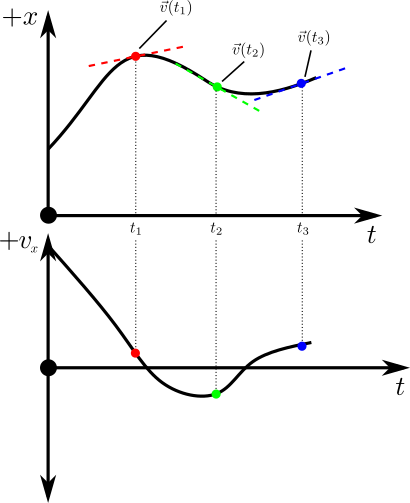
Kinematics
Featuring ...
Instantaneous Velocity
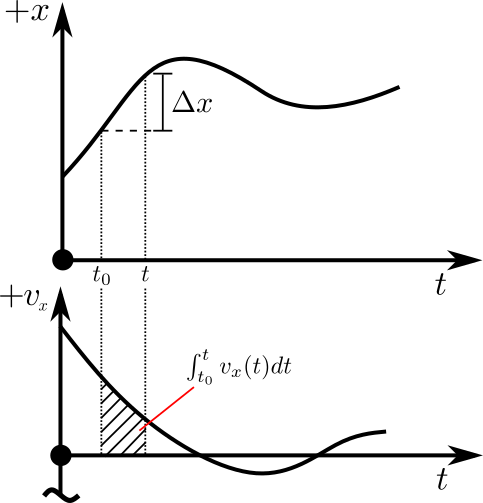
Kinematics
Acceleration
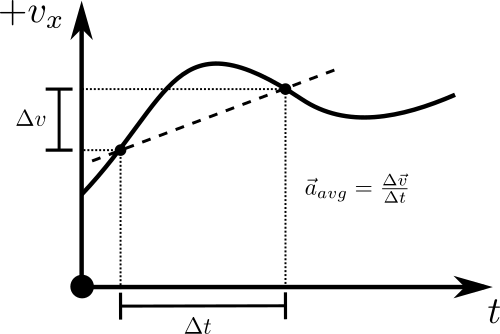
Kinematics
Featuring ...
Acceleration

Kinematics
Motion w/ Constant Acceleration
Kinematics
Motion in 1-D
Motion w/ Constant Acceleration

Kinematics
Motion in 1-D
Motion w/ Constant Acceleration
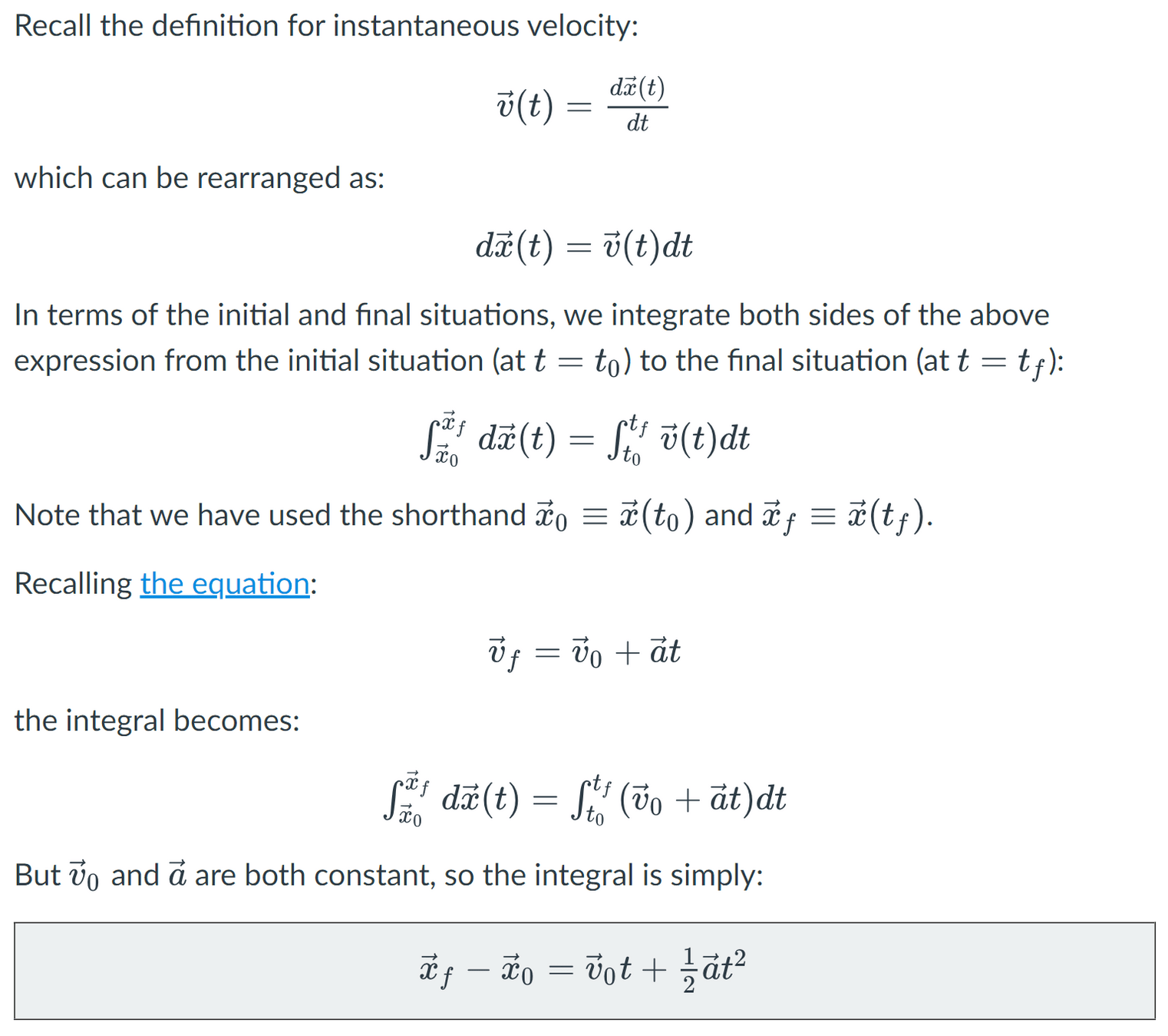
Kinematics
Motion in 1-D
Motion w/ Constant Acceleration
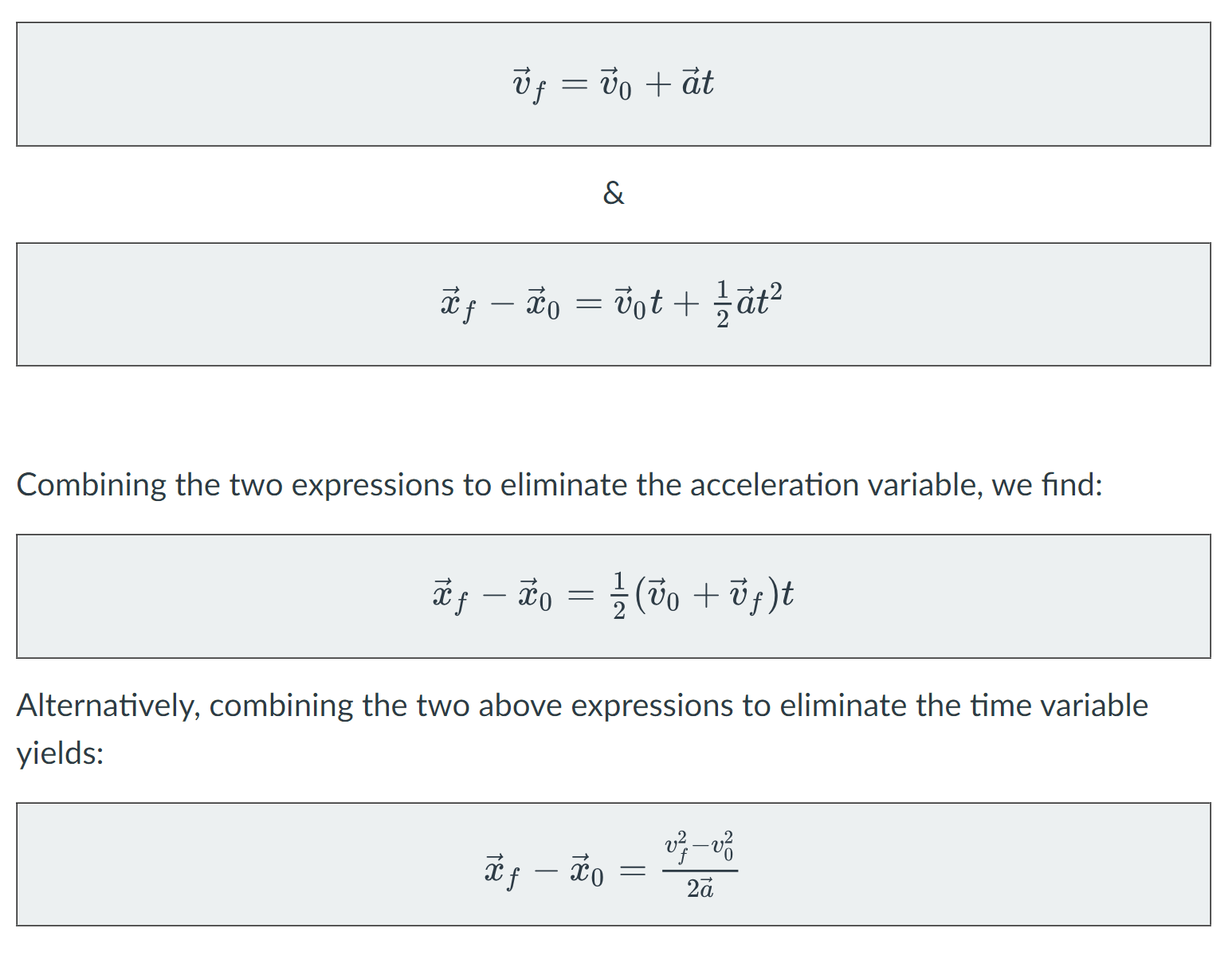
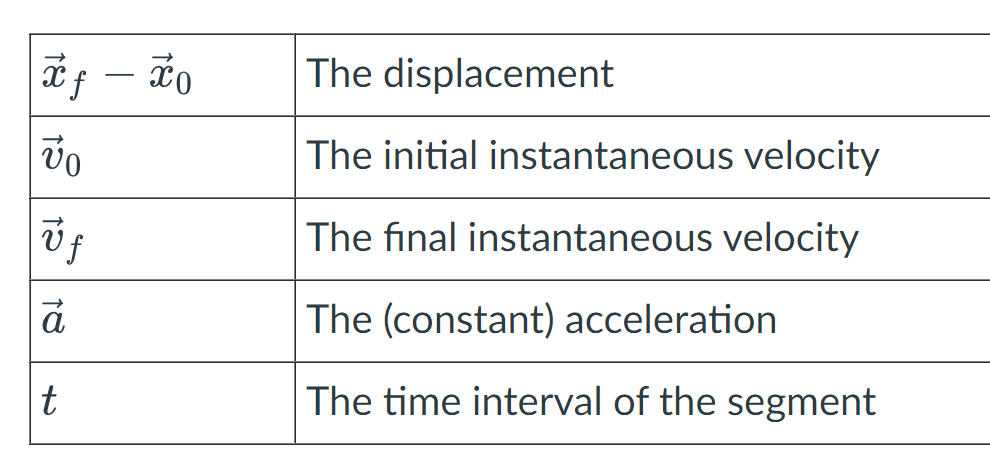
Kinematic Equations
Kinematic variables
Kinematics
Motion in 1-D
Motion w/ Constant Acceleration


Kinematic Equations
Kinematic variables
Kinematics
Freefall
Kinematics
Motion in 1-D
Freefall
If a bowling ball and a feather are dropped from the same height, would they reach the ground at the same time?
Independent of
the direction of motion!!!
Kinematics
Motion in 1-D
Freefall
Independent of
the direction of motion!!!
"During the final minutes of the third extravehicular activity [of the Apollo 15 mission,] a short demonstration experiment was conducted. A heavy object (a 1.32-kg aluminum geological hammer) and a light object (a 0.03-kg falcon feather) were released simultaneously from approximately the same height ... and were allowed to fall to the surface. Within the accuracy of the simultaneous release, the objects were observed to undergo the same acceleration and strike the lunar surface simultaneously, which was a result predicted by well-established theory, but a result nonetheless reassuring considering both the number of viewers that witnessed the experiment and the fact that the homeward journey was based critically on the validity of the particular theory being tested."
Watching the footage, I estimate the time interval from 'release' to 'touch ground' to be around ___ seconds or so, and I estimate the displacement to be about ____ or so, downwards.
Using these values, I can estimate the moon's gravitational acceleration to be ____ m/s^2, which is _____% away from the accepted value of _____ m/s^2.
Kinematics
in 2+ Dimensions
Kinematics
Motion in 2+ D
In general
Describe the motion using vector mathematics.


| Physical Quantity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Displacement | ||||
| Velocity | ||||
| Acceleration | ||||
| Time Interval |
Kinematics
Motion in 2+ D
In general
Independence of the components
Describe the motion using vector mathematics.
Kinematics
Motion in 2-D
Projectile Motion
An object under the influence of gravity alone, experiences the acceleration:
Independent of
the direction of motion!!!
Kinematics
Motion in 2-D
Projectile Motion
Suppose a ball is launched with speed of 5.15 m/s at an angle of 53 degrees above the horizontal, from a point that is 90.0 cm above the ground. And suppose that we start a clock at the moment the ball is launched. Find the location of the ball and its direction of motion at the following times: (0.1s, 0.2s, 0.3s, 0.4s, 0.5s, 0.6s, 0.7s, 0.8s, 0.9s, 1.0s)
| index | Time after launch [s] | horizontal displacement of the projectile [m] | vertical position of the projectile above ground [m] | horizontal component of the velocity [m/s] | vertical component of the velocity [m/s] | speed of the projectile (magnitude of the velocity) [m/s] | direction of motion of the projectile (degrees above/below horizontal) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0 s | ||||||
| 2 | 0.10 s | ||||||
| 3 | 0.20 s | ||||||
| ... | ... |
Kinematics
Motion in 2+ D
Uniform Circular Motion
Kinematics
Motion in 2-D
Uniform Circular Motion
Imagine the motion of an object on a circular arc of radius R with constant speed v
towards the center of the motion

Kinematics
By drmoussaphysics
Kinematics
- 282