GSM
"The Wake up call"
Duarte Monteiro C-days 2018

Chantam house rule

education purposes only

$whoami
- Security Automation Engineer @ PaddypowerBetfair
- Information Security Specialist @ Euronext
- Head of Infosec Assessment & Exploitation Team @ Euronext
- Security Research @ Cobalt



Masters in Information Security @ FCUP


INTRO

GSM - "The wake up call"
What is this talk about?
- What is GSM?
- How GSM works?
- GSM Security Principles
- Breaking the Security Principles
- "PoC"
Objective: Awareness
Probably to much information for 45 min talk. + Plus I' not an GSM Expert --- just a curious guy
WHAT IS GSM?

GSM - "The wake up call"
GSM ARCHITECTURE AND PROTOCOL
WHAT IS?

GSM - "The wake up call"

- Standard for over the radio cellular communications protocol for voice
- Lack of standardisation in Europe in PSTN
- Firstly called: Groupe Spécial Mobile (1983)
- Adopted by ETSI: Global System for Mobile communications (1989)
- World's first GSM call on July 1, 1991
- 3 Billion users in 2008
WHAT IS?

GSM - "The wake up call"
-
Main Features:
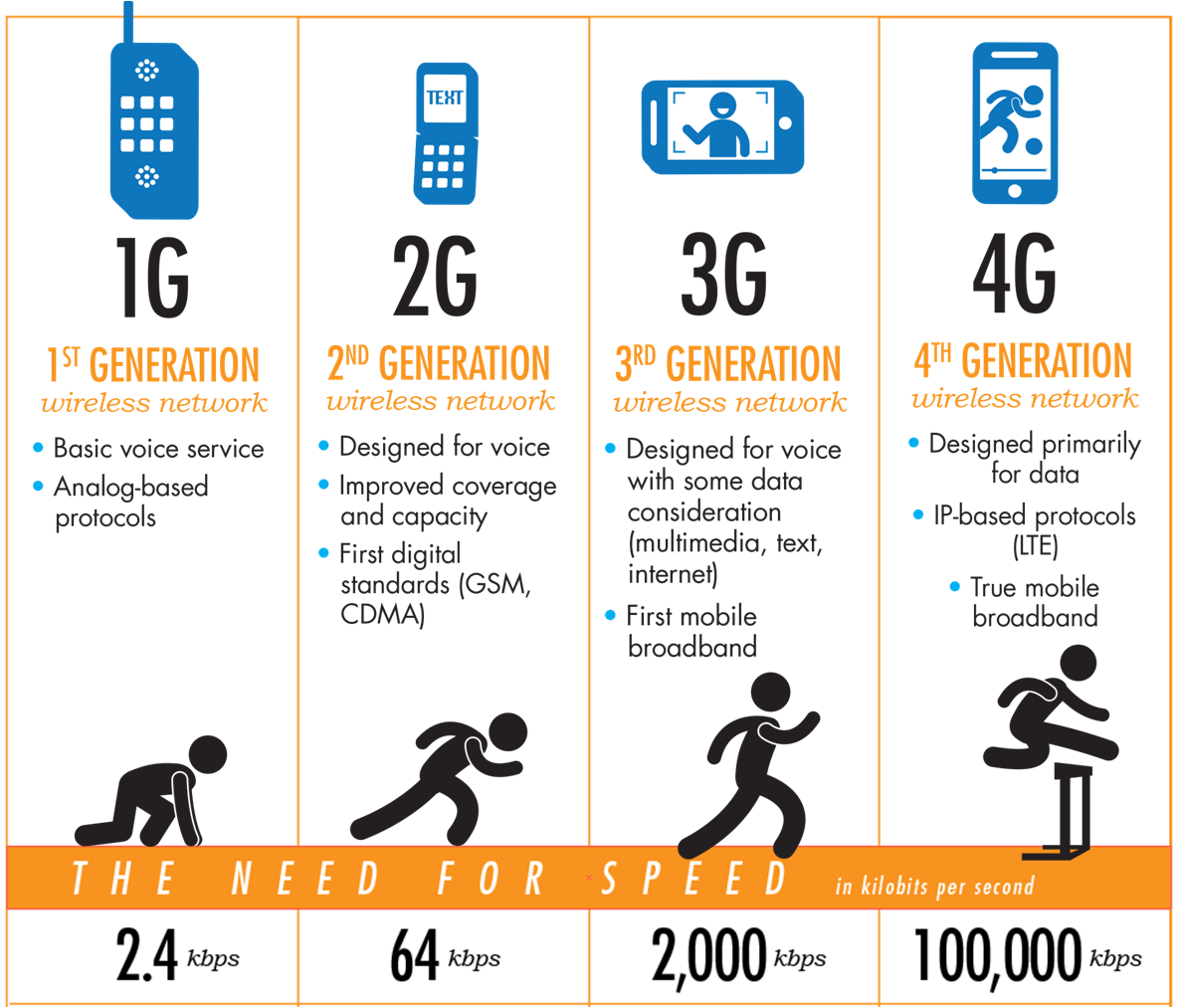
- Good subjective speech quality
- Low terminal and service cost
- Support for international roaming
- Ability to support handheld terminals
- Support for range of new services and facilities
- Spectral efficiencity
- ISDN Compatibility (RDIS)
WHAT IS?

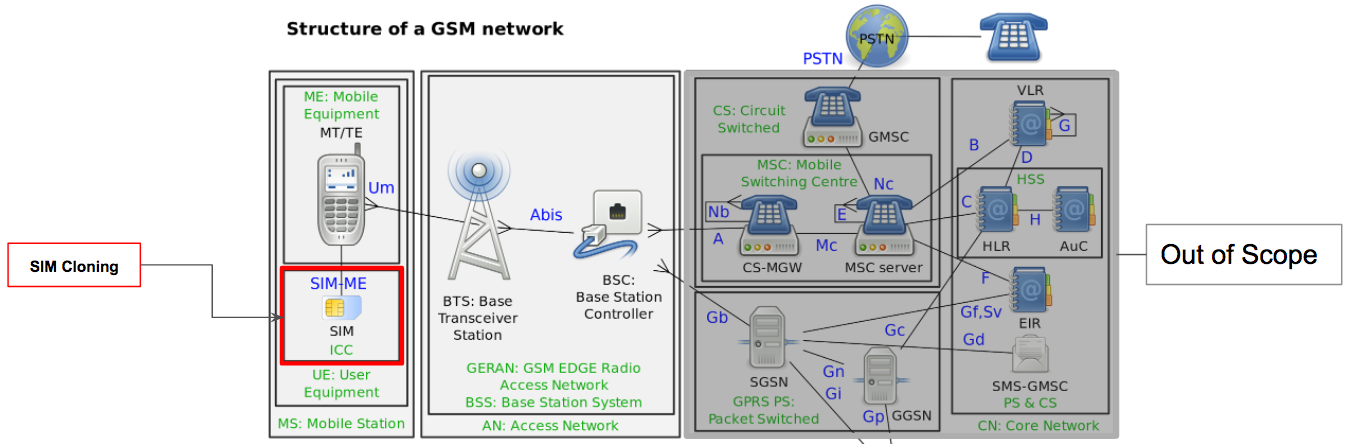
GSM - "The wake up call"
-
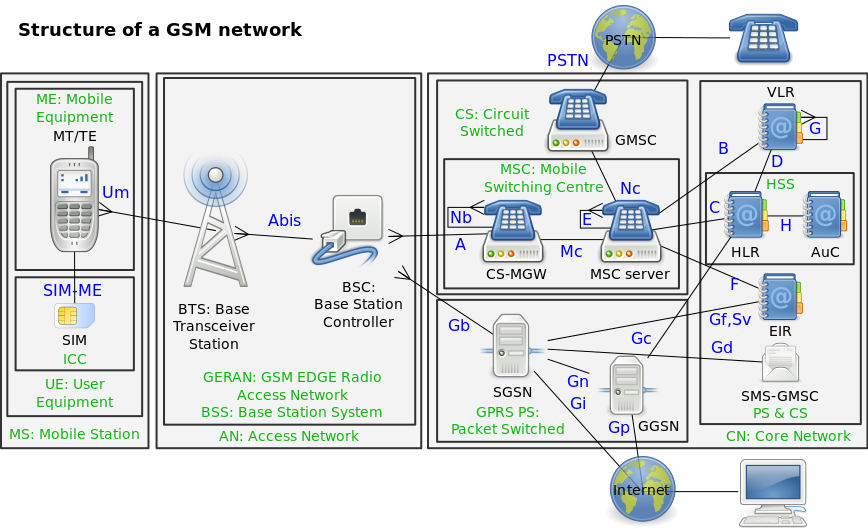
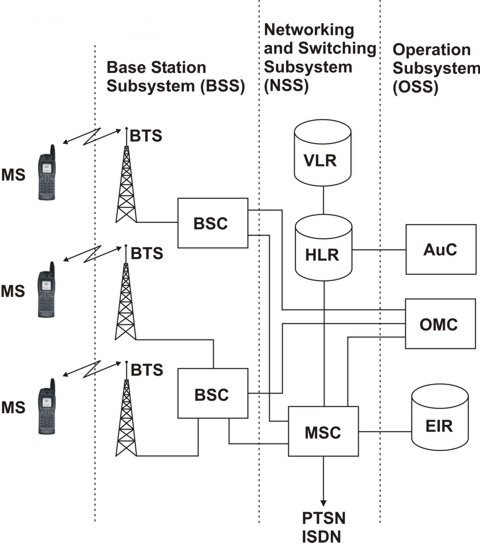
Functional Elements
-
Base Station Subsystem
-
Network SubSystem
-
Operation Subsystem
-
-
Databases
-
Home Location Register (HLR)
-
Visitor Location Register (VLR)
-
Authentication Center (AuC)
-
Equipment Registry Identity (EIR)
-
WHAT IS?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Scope

-
Interfaces
-
Um Interface
-
Abis Interface
-
WHAT IS?

GSM - "The wake up call"
We know the architecture but does the user connects to the network?
super-high-level
WHAT IS?

GSM - "The wake up call"
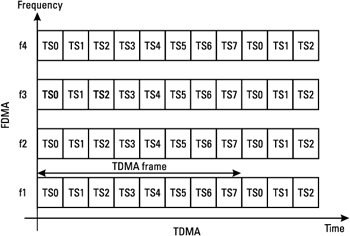
- GMSK modulation
-
It uses Frequency and Time Division Multiple Access (F/TDMA)
- TDMA For access scheme
- FDMA For frequency allocation
- Full-Duplex Transmission (FDD TDD)
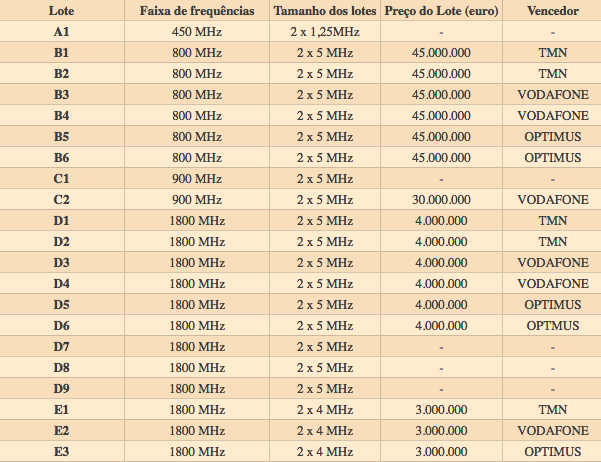
@Anacom
WHAT IS?

GSM - "The wake up call"
-
How does it send data?
- Sending/Receiving GSM Frames
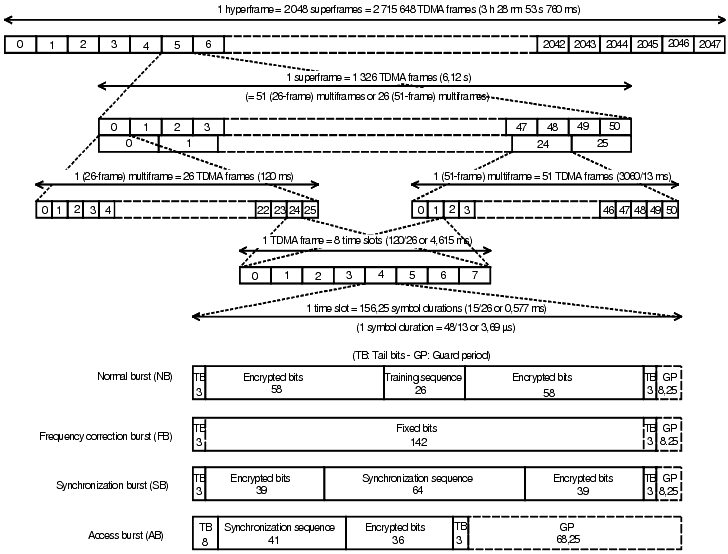
WHAT IS?

GSM - "The wake up call"
-
Channels
- Physical Channels - Medium which the information is carried
-
Logical Channels - It consists of information carried over a physical channel
- Traffic Channels
- Control Channels
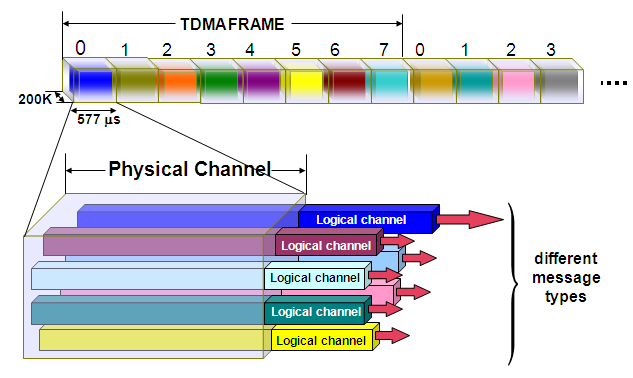
WHAT IS?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Layer 1
- Channel Combinations
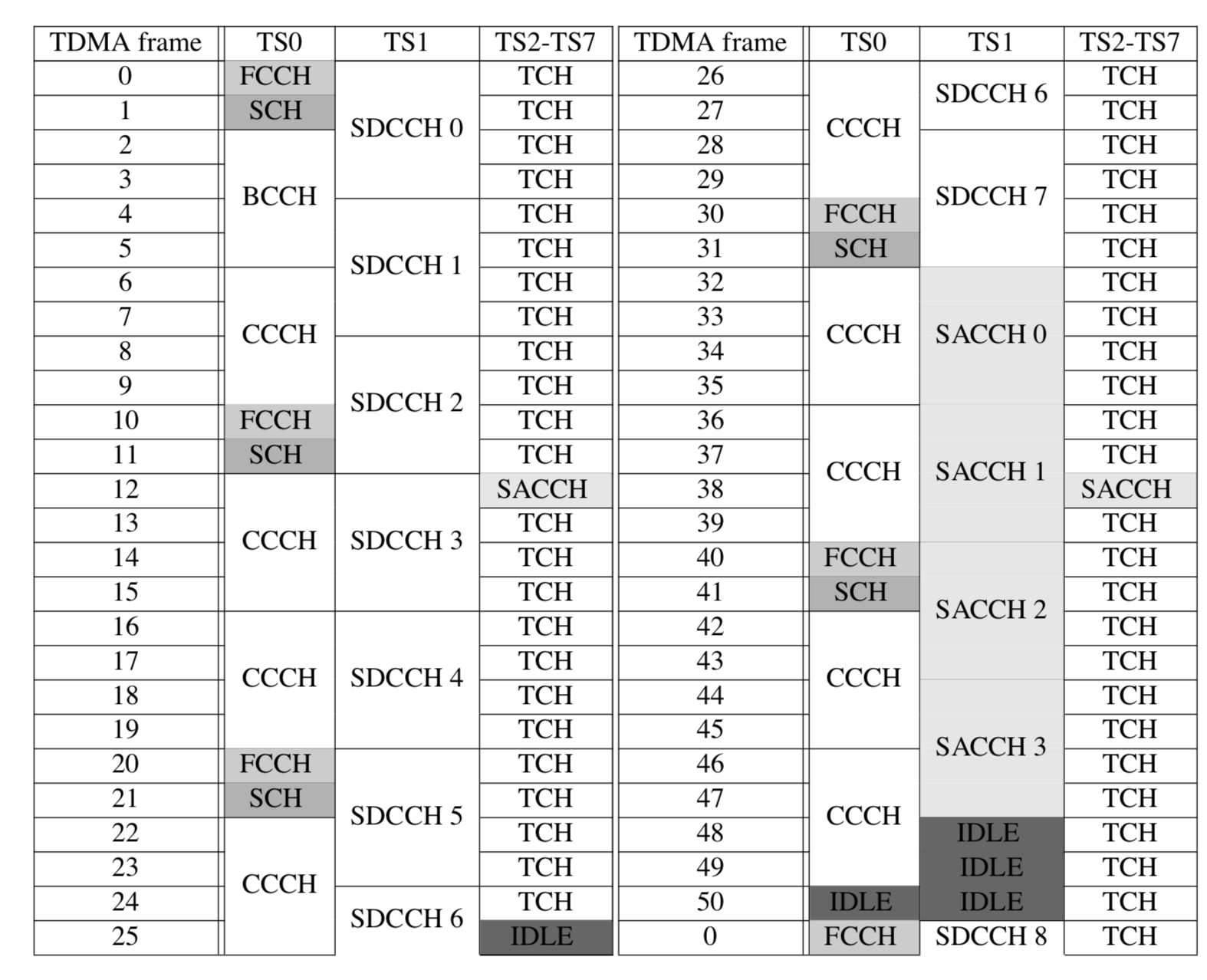
WHAT IS?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Geographical Hierarchy
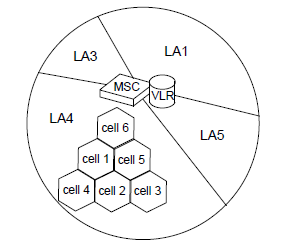
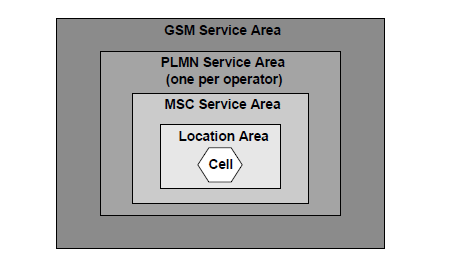
Physical
Logical
WHAT IS?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Protocol Stack

WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Motivation and Introduction
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
- It's old (1989)

8.0.0 Version - 1999
From: European Telecomunication Standards Institute (ETSI)
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
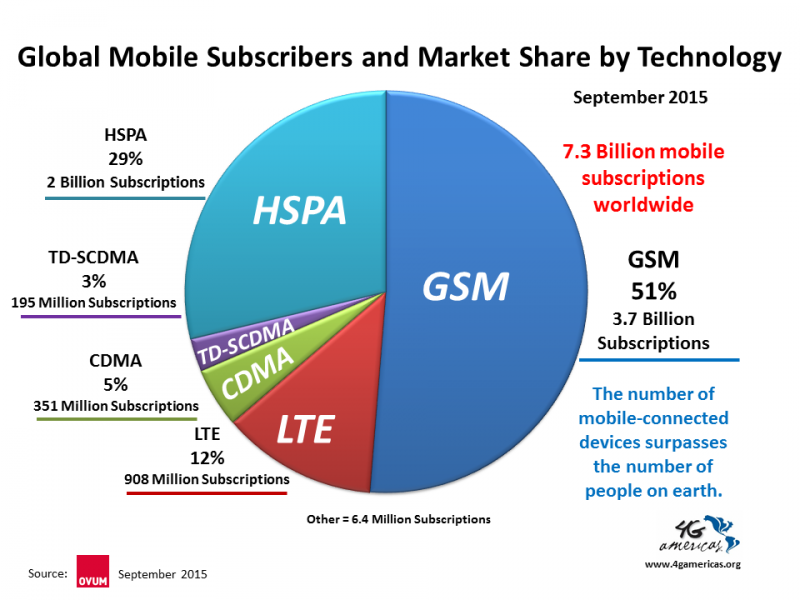
- Everyone still uses
Failover
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
- It's everywhere...
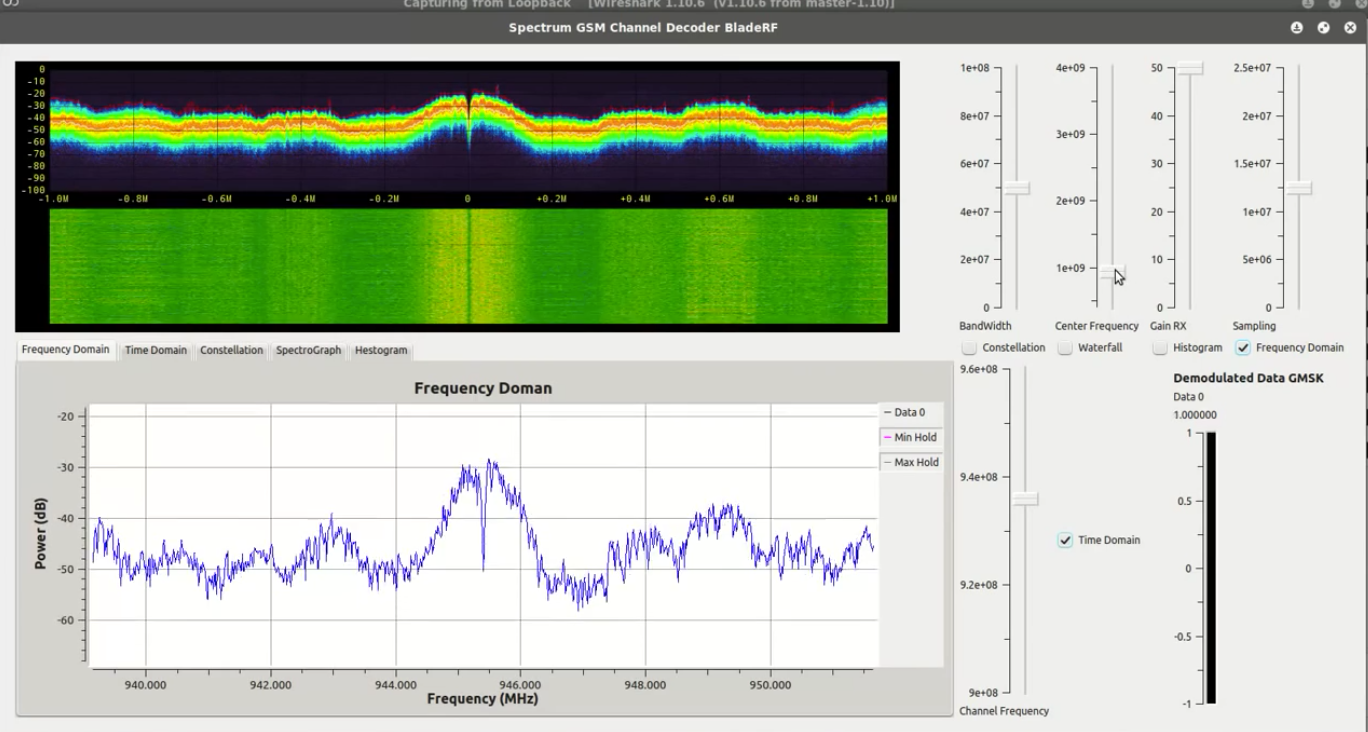
Meaning: anyone can take look :)
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
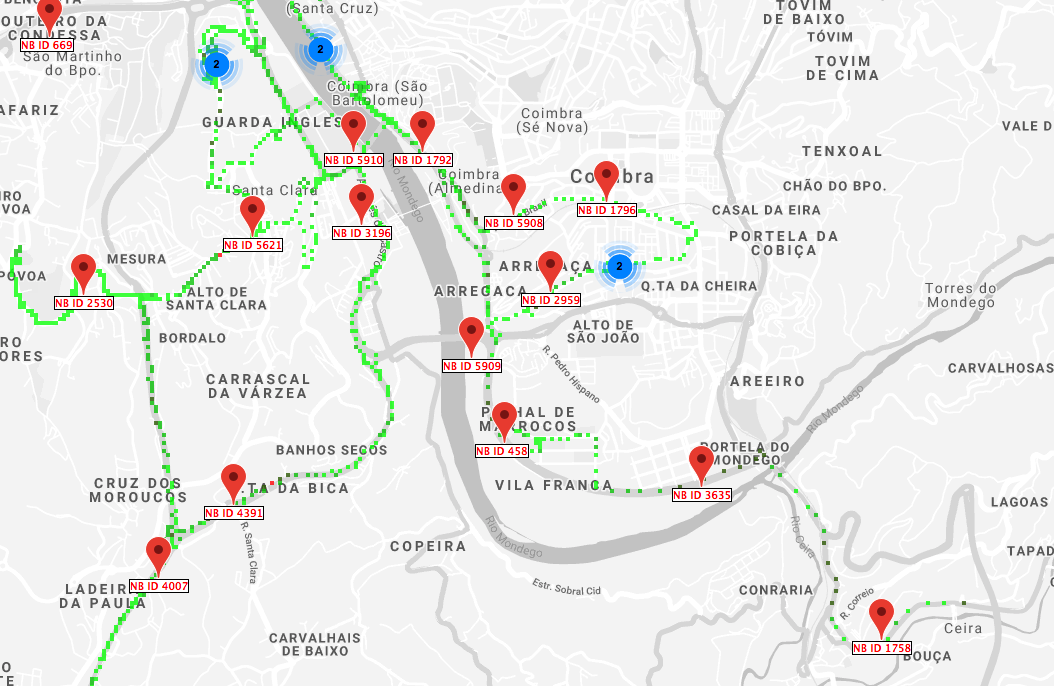
It's literally everywhere.
SECURITY PRINCIPLES?

GSM - "The wake up call"
WHAT ARE THE MAIN CONCERNS AND THREATS
SECURITY PRINCIPLES

GSM - "The wake up call"
-
Security Concerns:
- As an Operator how can do I guarantee the Subscribers identity?
- As an user, is my data safe from eavesdropping or impersonification?
SECURITY PRINCIPLES

GSM - "The wake up call"
-
Security Principles:
- Subscriber Identity Confidentiality
- Subscriber Identity Authentication
- User data confidentiality on physical connections
- Connectionless user data confidentiality
- Signalling Information Element Confidentiality
AUTHENTICATION
CONFIDENTIALITY
ENCRYPTION
...they don't care about availability
SECURITY PRINCIPLES

GSM - "The wake up call"
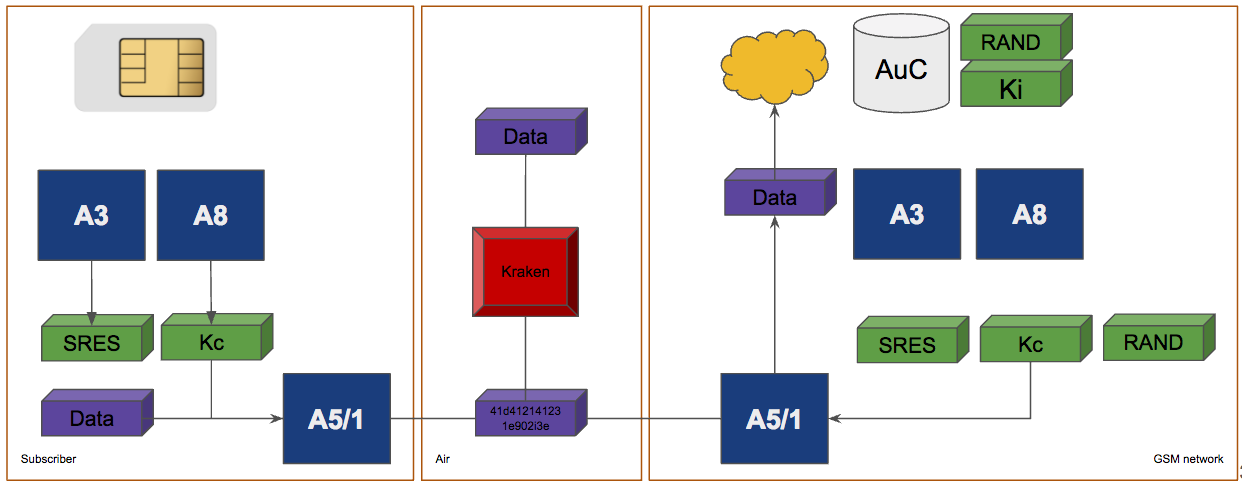
1. Subscriber Identity Confidentiality
Who are you?
IMSI - International Mobile Subscriber Identity
TMSI - Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity
Random 8 Digits
| IMSI | ||
|---|---|---|
| MCC | MNC | MSIN |
| 3 Digits | 2/3 Digits | MSIN |
SECURITY PRINCIPLES

GSM - "The wake up call"
2. Subscriber Identity Authentication

IMSI
is shared by the SIM and Operator
SECURITY PRINCIPLES

GSM - "The wake up call"
2. Subscriber Identity Authentication
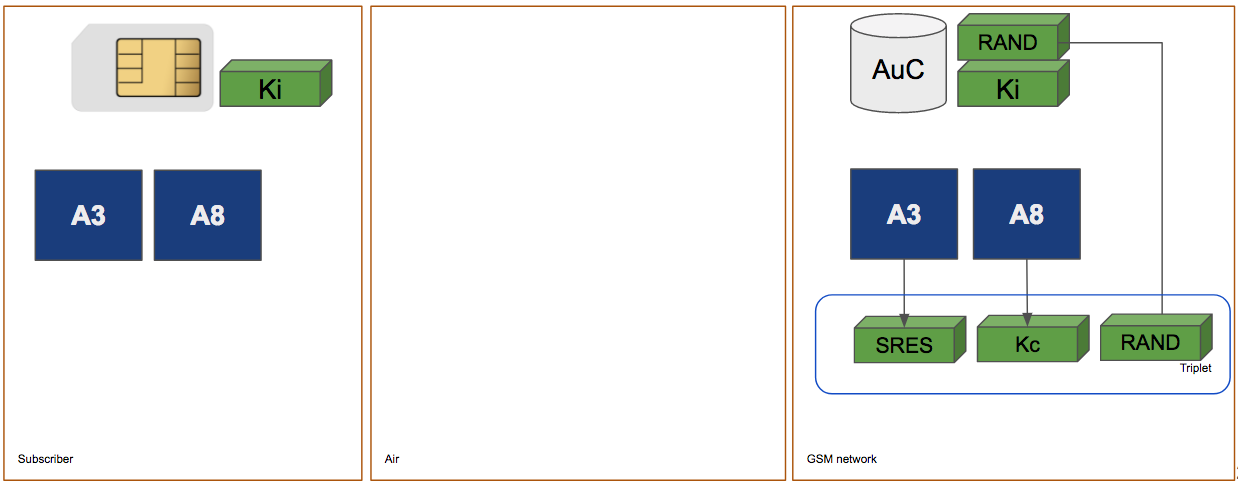
A3/A8 Algorithms are used to start the process

SECURITY PRINCIPLES

GSM - "The wake up call"
2. Subscriber Identity Authentication
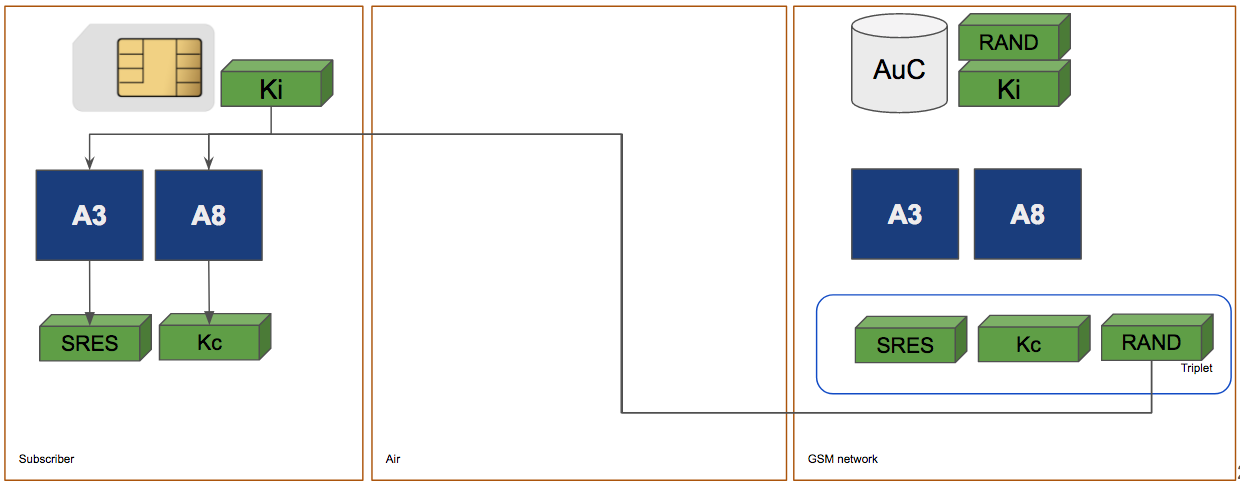
Authentication Triplets are generated: SRES, KC and RAND
SECURITY PRINCIPLES

GSM - "The wake up call"
2. Subscriber Identity Authentication
RAND is sent to the subscriber via the Um Interface
SECURITY PRINCIPLES

GSM - "The wake up call"
2. Subscriber Identity Authentication
SRES' is sent over the radio and NSS will check if it's match.
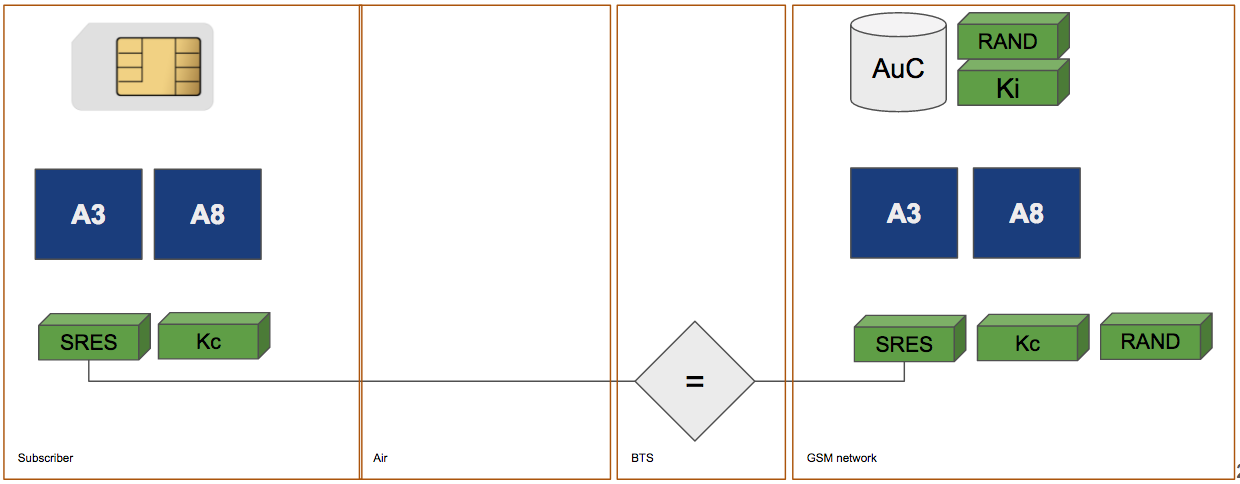
SECURITY PRINCIPLES

GSM - "The wake up call"
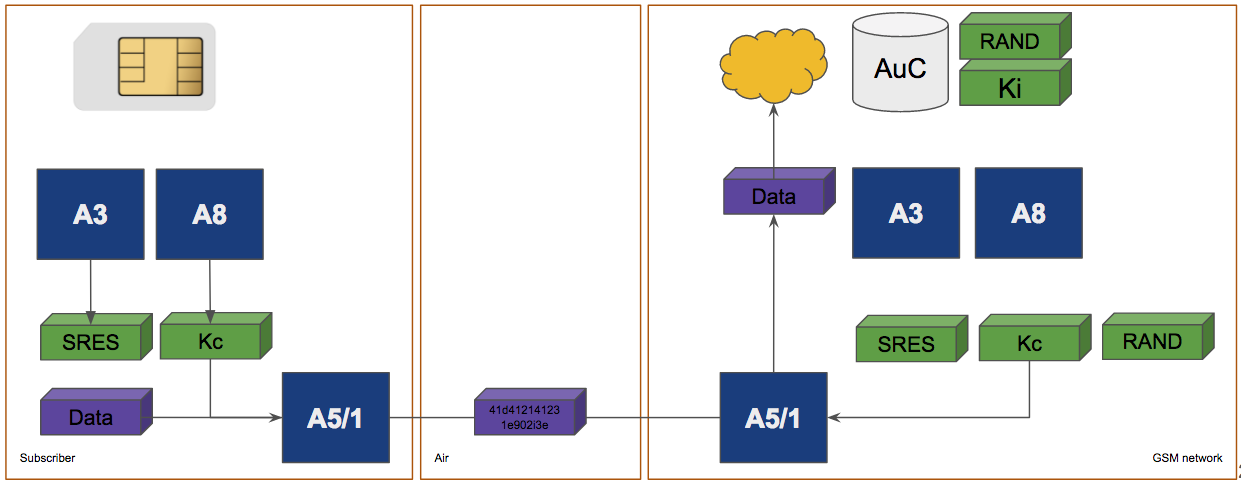
3. User data confidentiality on Physical Systems
GSM Symmetric Encryption Algorithms:
- A5/0 - No encryption
- A5/1 - Commonly used
- A5/2 - Broken
- A5/3 - 'KASUMI' currently used in 3G
Remember, encryption is optional.
SECURITY PRINCIPLES

GSM - "The wake up call"
3. User data confidentiality on Physical Systems
BREAKING THEM

GSM - "The wake up call"
ATTACK SURFACE AND ATTACKS
road down the memory lane
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Attack Surface - SIM
SIMs use COMP128 algorithm to generate the Kc/SRES based on the Ki + RAND (A8 Algorithm)
COMP128v1 -> Leaked and exploited
COMP128v2 -> Safe
COMP128v3 -> Safe
DONT TRUST SECURITY BY OBSCURITY
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Attack Surface - MS
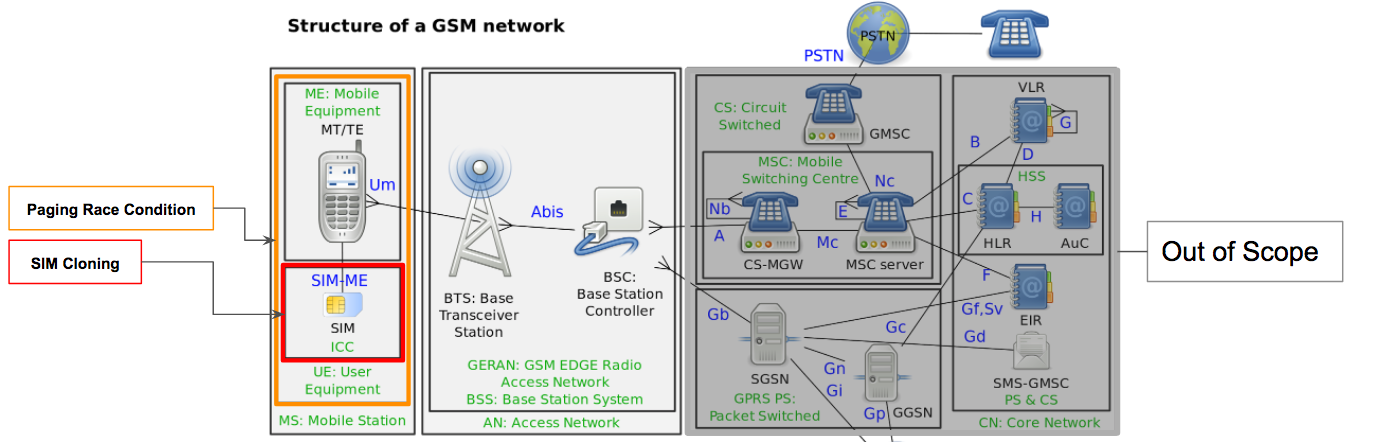
Silent SMS (Aka Type-0 SMS) - allows to undermine the subscriber location
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Attack Surface - Um Interface
-
Known-Plaintext Attack (KPA) on the encryption algorithm (A5/1)
- Rainbow-tables released (1.7Tb)
- Allows to retrieve the Kc of a encrypted communications
- A5/2 Broken in seconds.
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
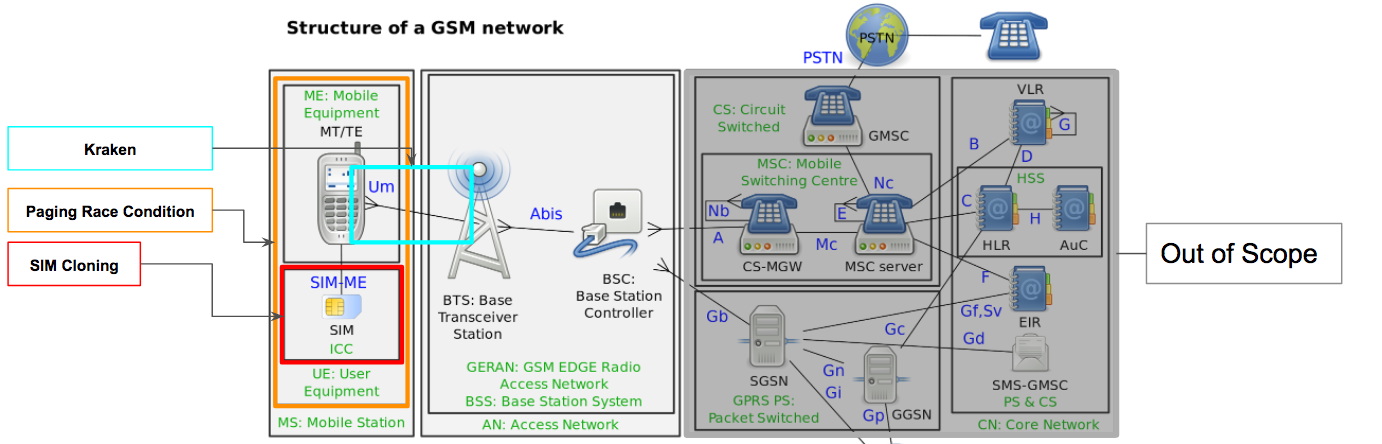
Attack Surface - Um Interface
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Attack Surface - Um Interface
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Attack Surface - BTS
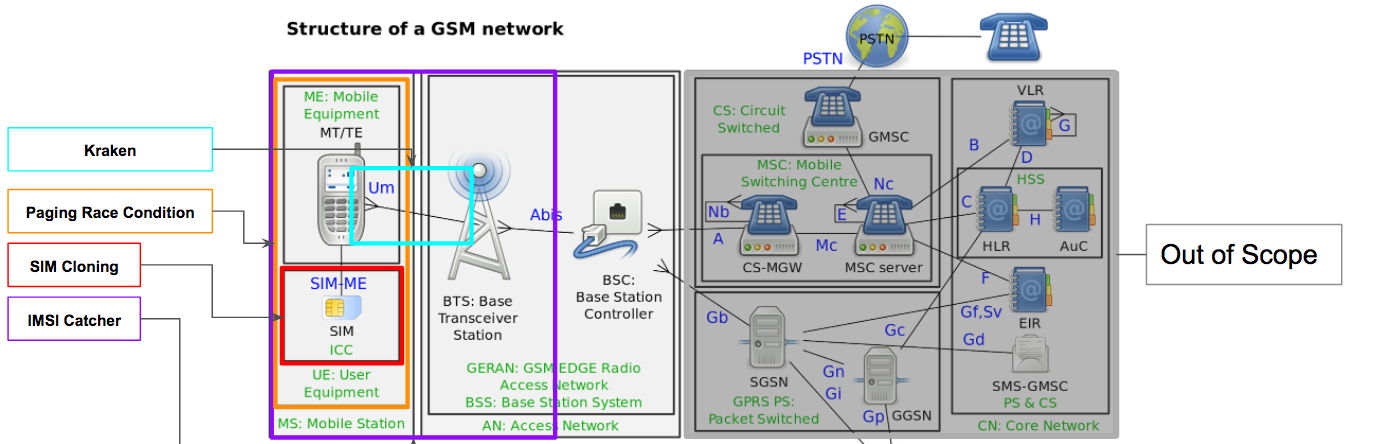
IMSI Catcher - Devices capable of simulating an BTS or sniffing GSM traffic (active or passive)
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Attack Surface - BTS
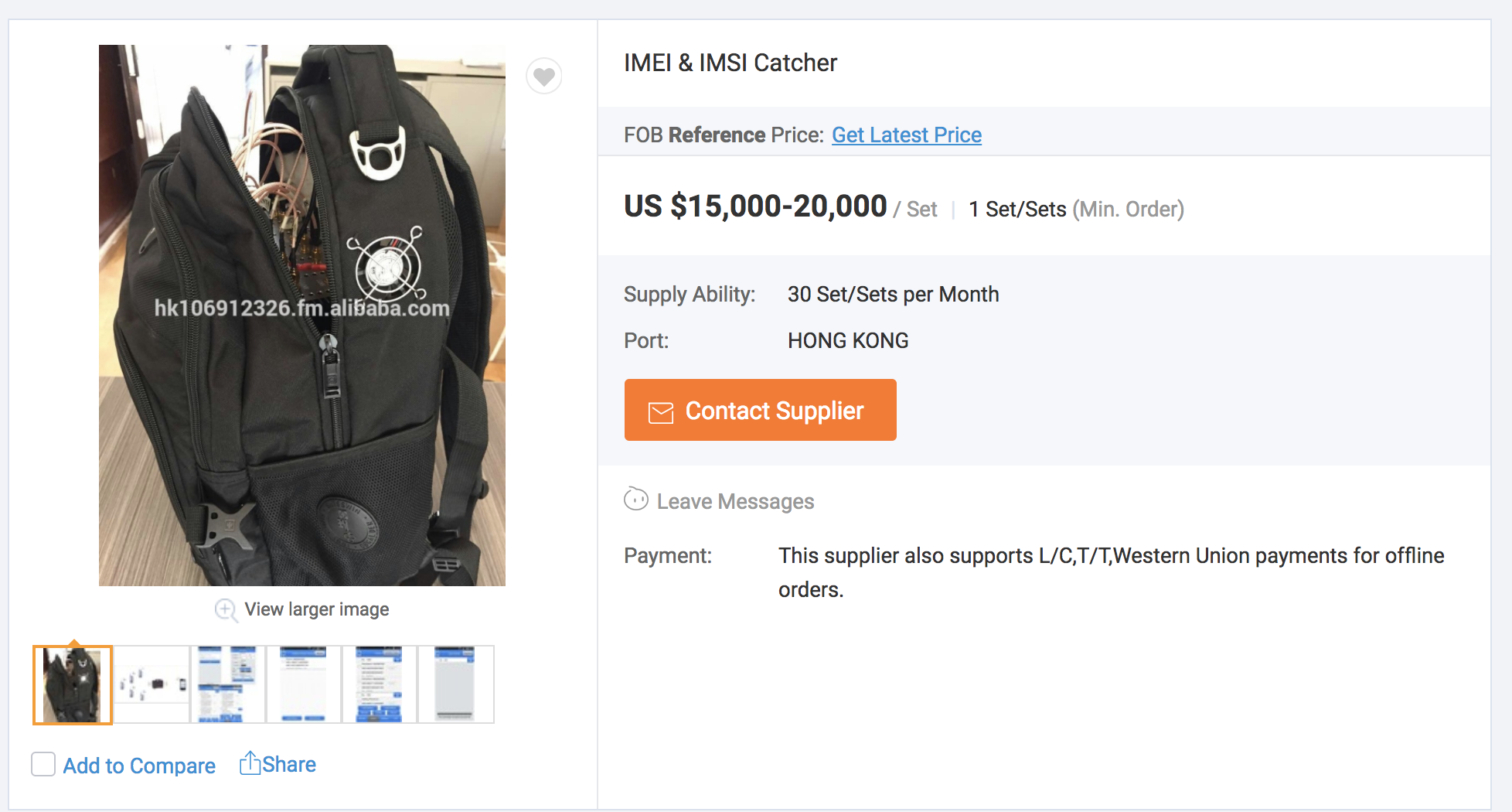
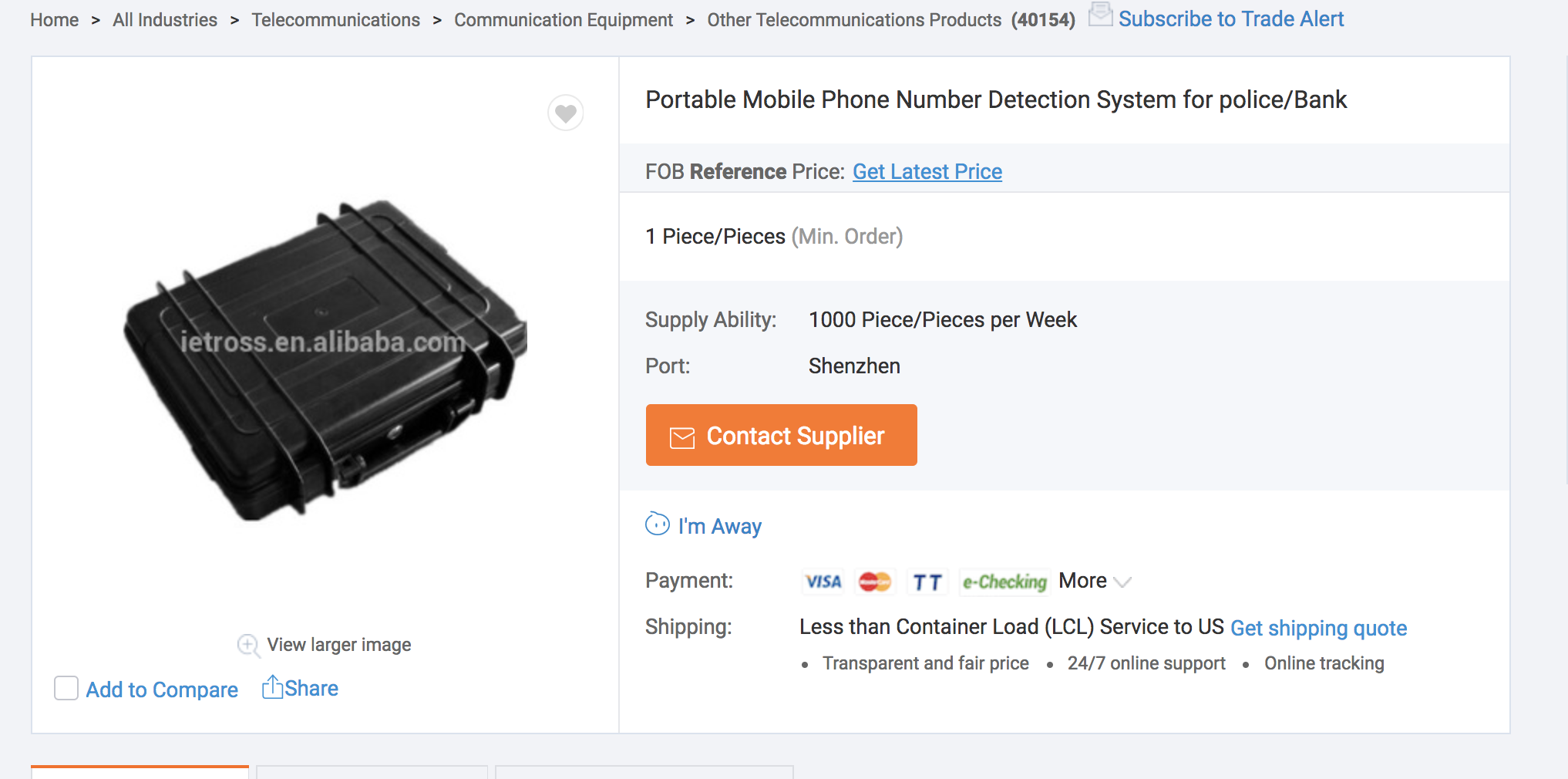

WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Attack Surface - Abis
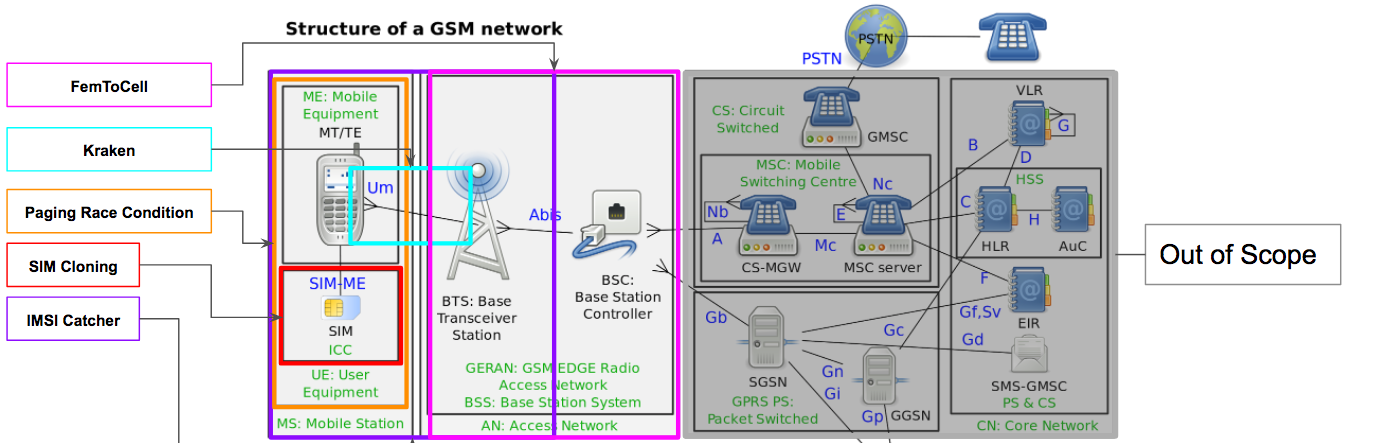
Femtocell - Operator devices that are corrupted for malicious activities.
- Dump traffic clear text from subscribers connected to the femtocell

POC

GSM - "The wake up call"
PROOF-OF-CONCEPT AND TOOLS
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
So, what is the problem?
- No hardware available to send/receive signals
- Code / Documentation of attacks is not shared/omitted
- No support, no replies, empty forums and wrong information
- Too much specifications
-
Partial Kerckhoffs's principle?
- Technical Specifications - Check
- Encryption and Hashing algorithms - Unknown
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Solution
-
Hardware:
- Motorola C123
- BladeRF



WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Solution
-
Software:
- OsmocomBB Project
- GR-GSM
- YateBTS

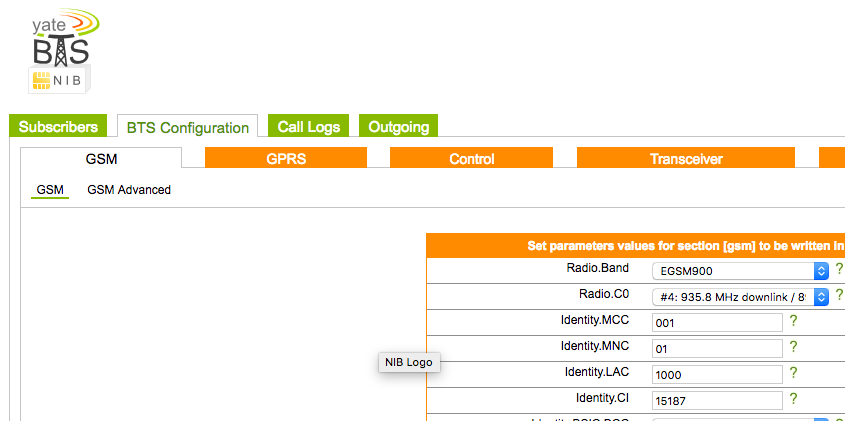
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Results - IMSI Catcher (Passive)
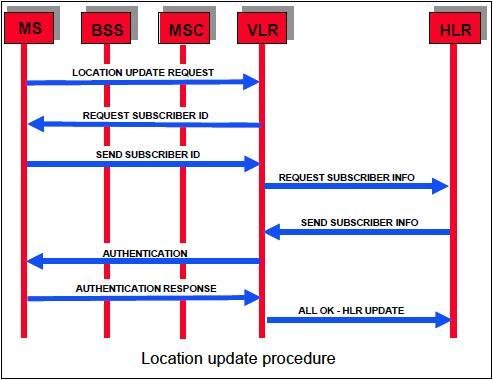
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Results - IMSI Catcher (Passive)
-
Rogue BTS:
- Catch IMSI from subscribers
- Send spoofing SMS
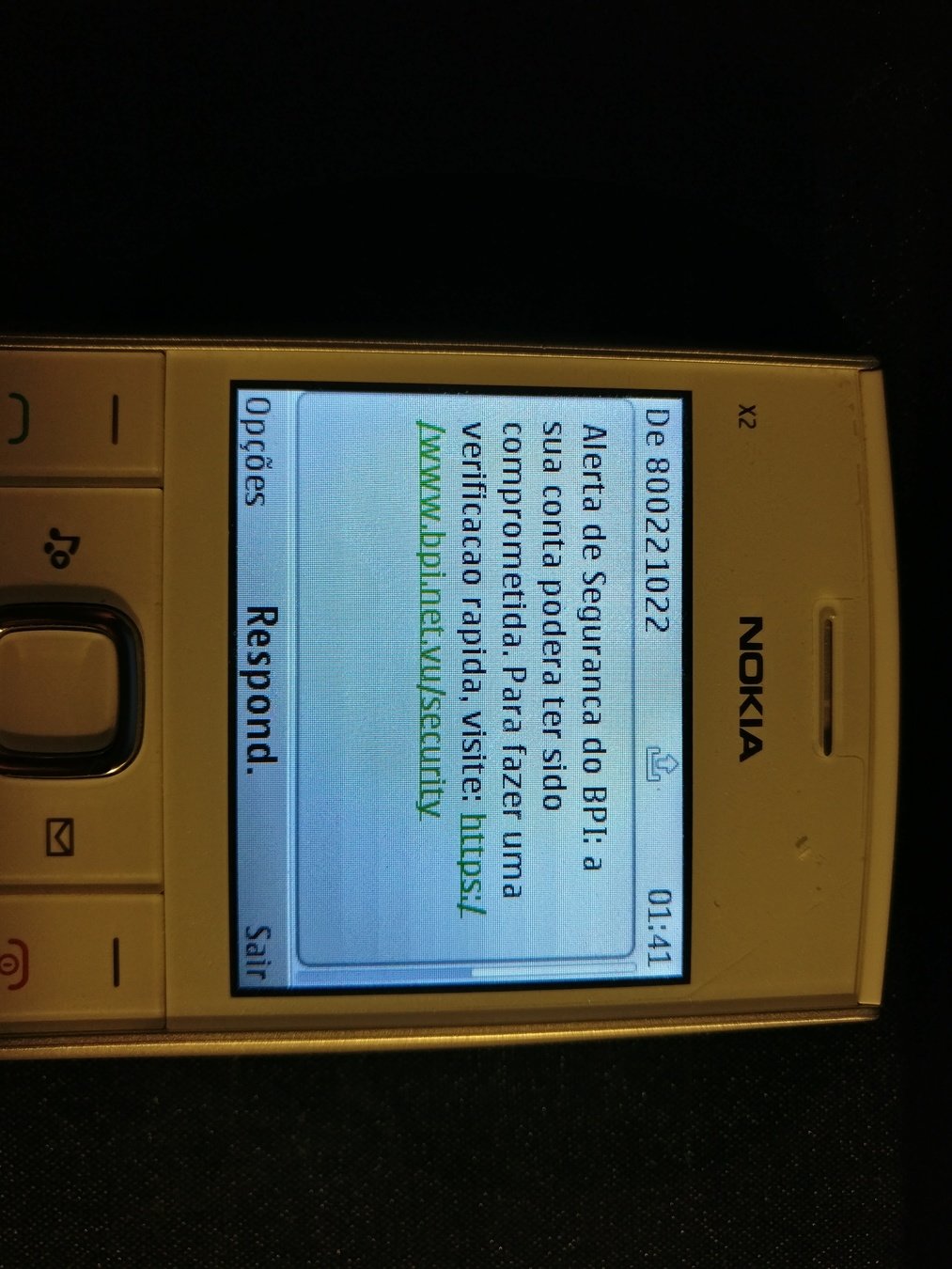
-
Attack Scenarios:
- deploy stagefright exploits (RPDU) -> Not tested
- Layer 7 exploits (SMS DoS/) -> Not Tested
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Results - IMSI Catcher (Passive)
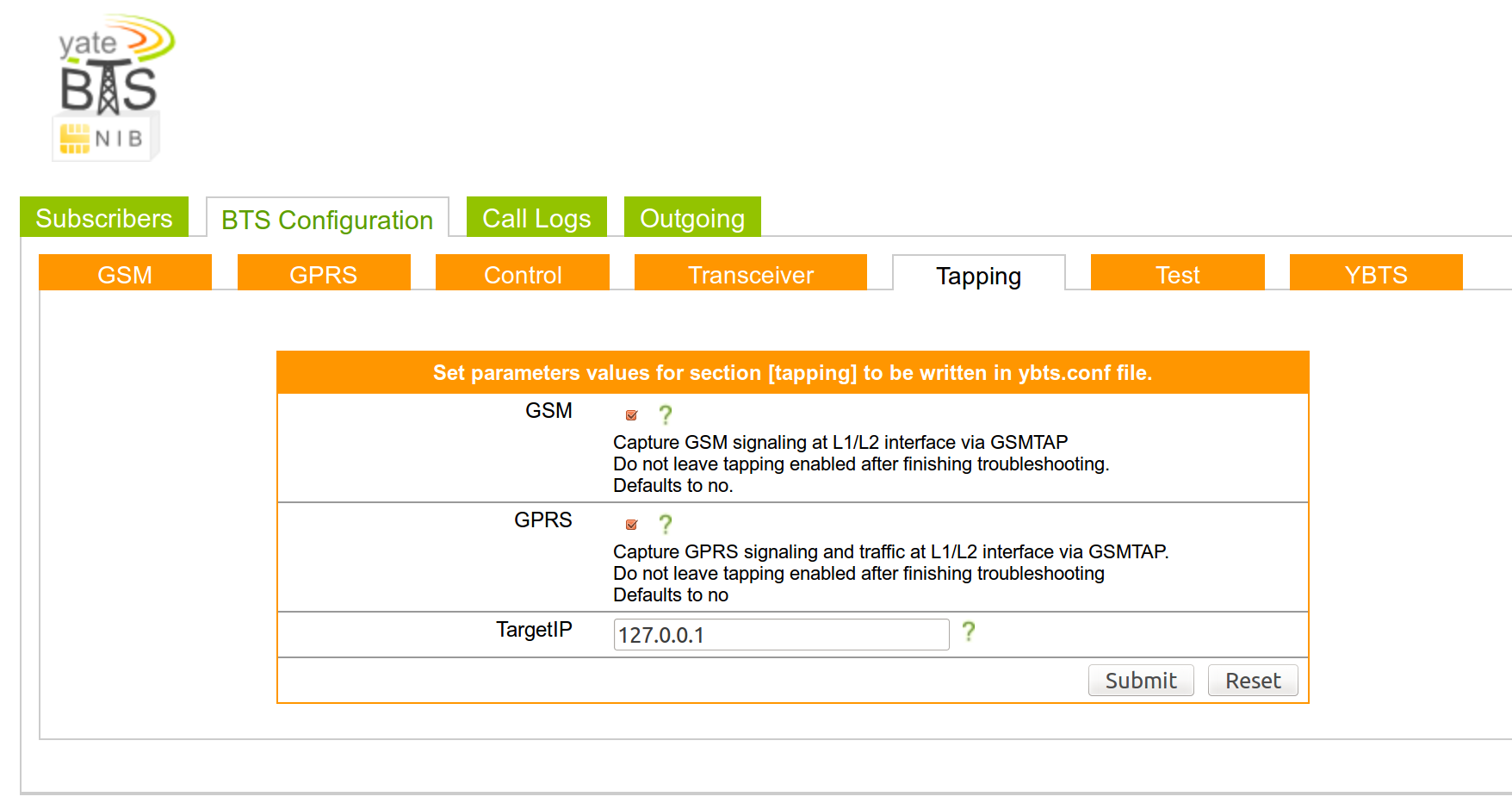
No access to the Operator network, meaning - The victim will only be able to send data but receive network failure.
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
GSM A5/1 Cracking
VERY HYPOTHETICAL
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
GSM A5/1 Cracking
Country Assessment
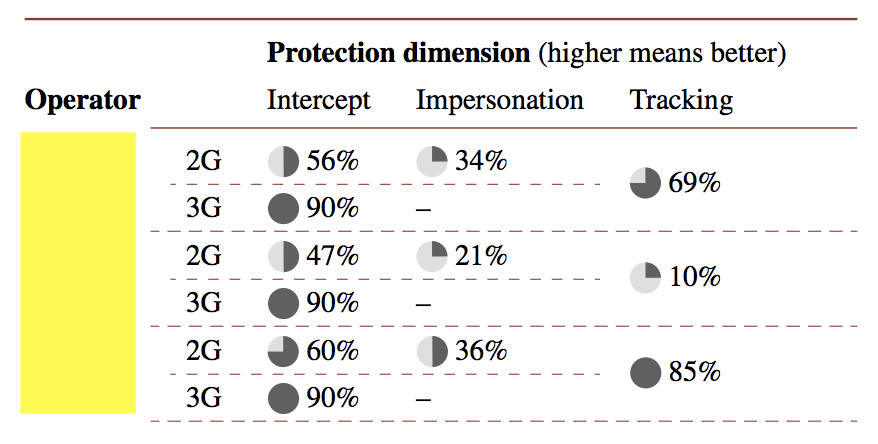
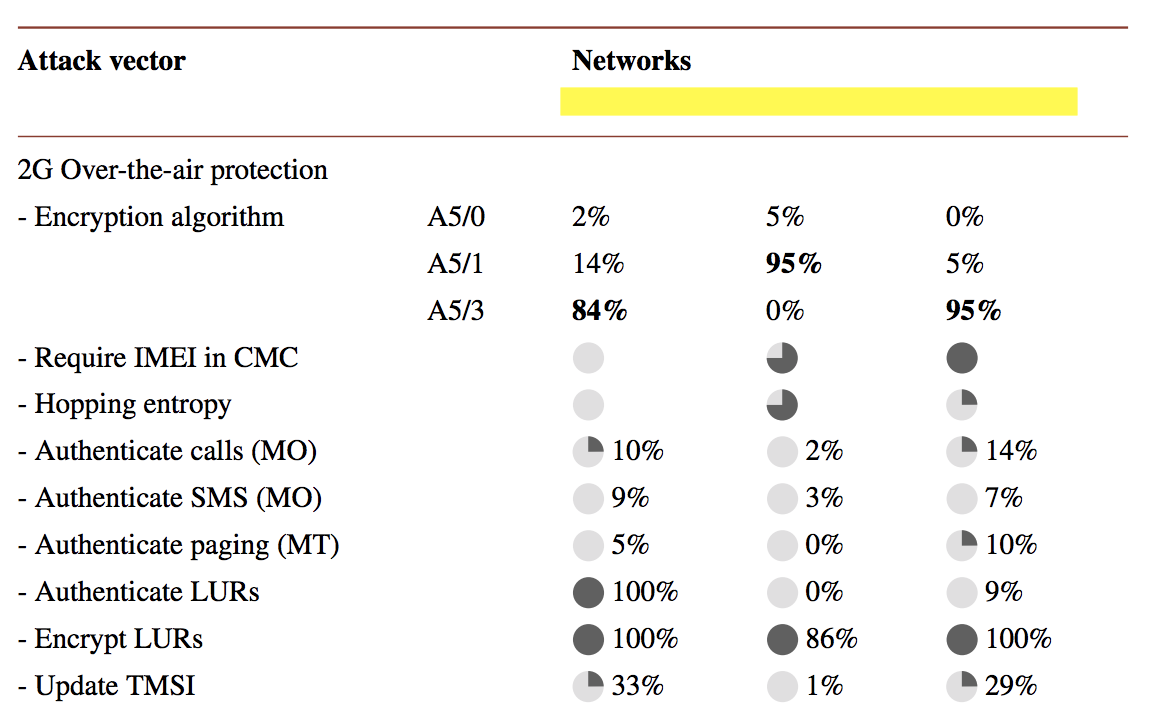
SRLabs - GSMMAP
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
GSM A5/1 Cracking
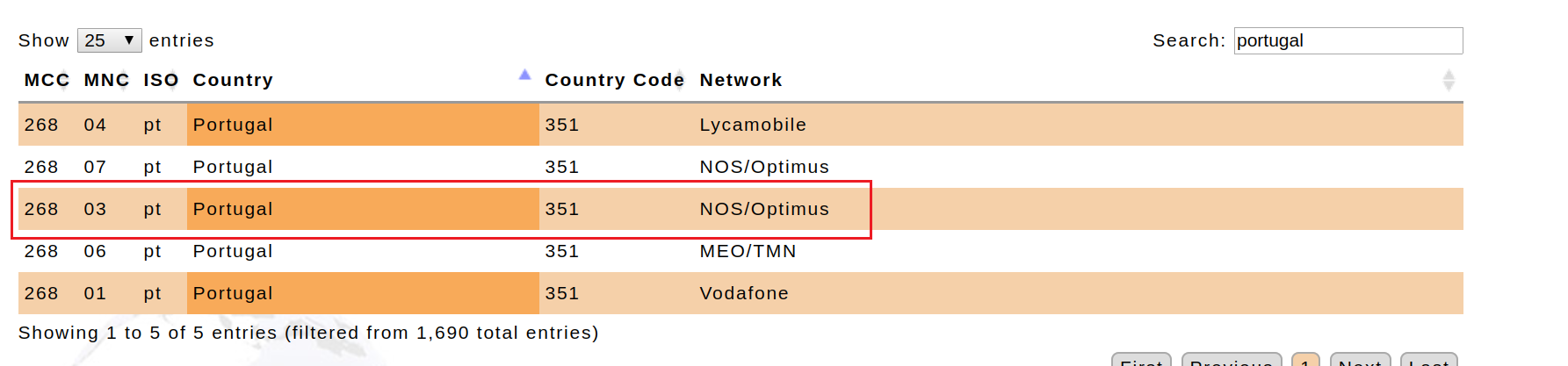
1. Environment RECON
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
GSM A5/1 Cracking
2. Environment RECON (2)
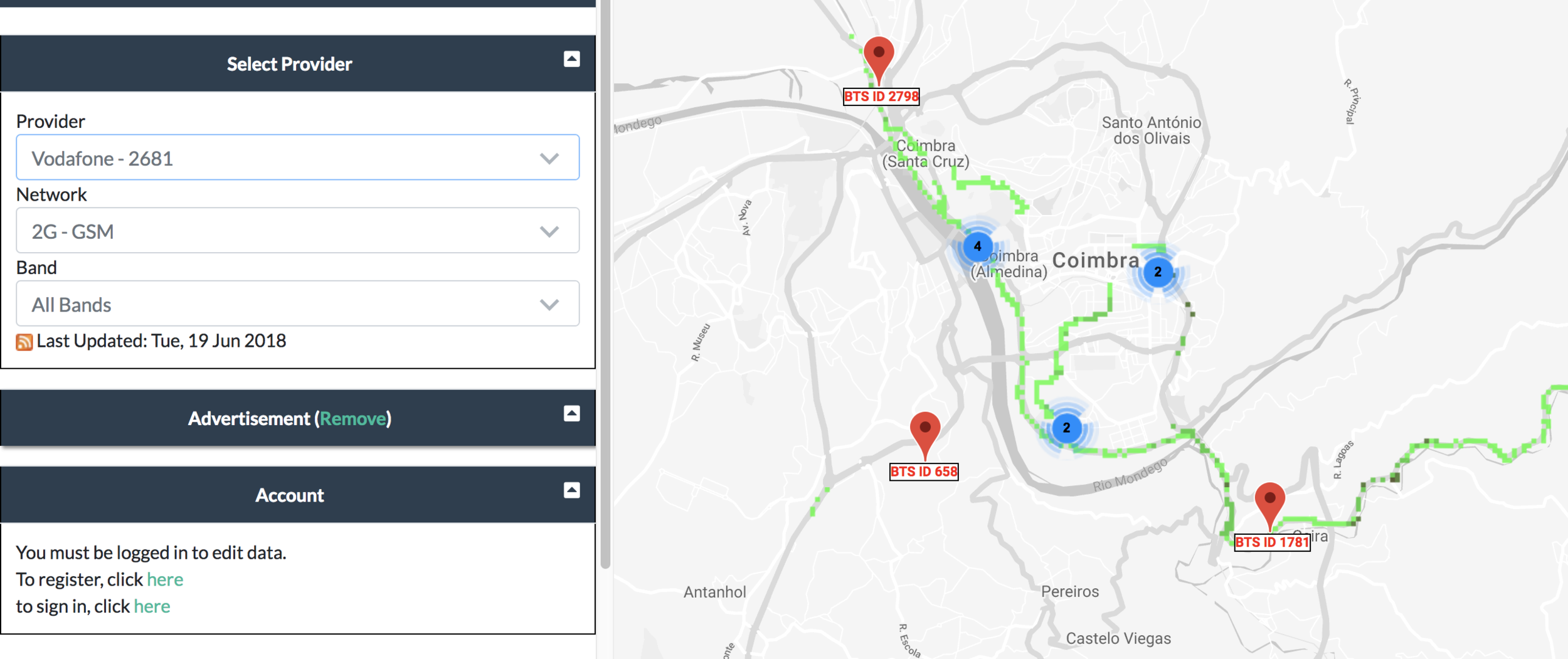
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
GSM A5/1 Cracking
3. Environment Details (GSEC)
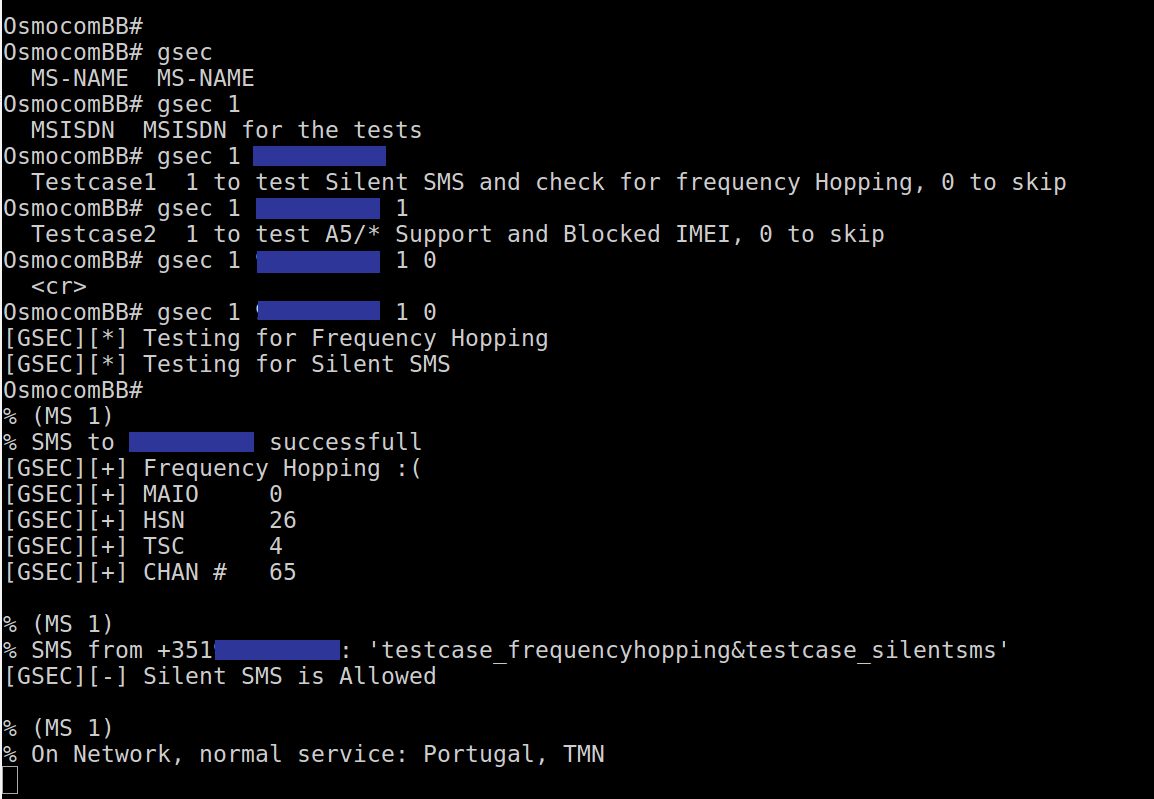
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
GSM A5/1 Cracking
4. Target + Identification
> Tracking + Dumping
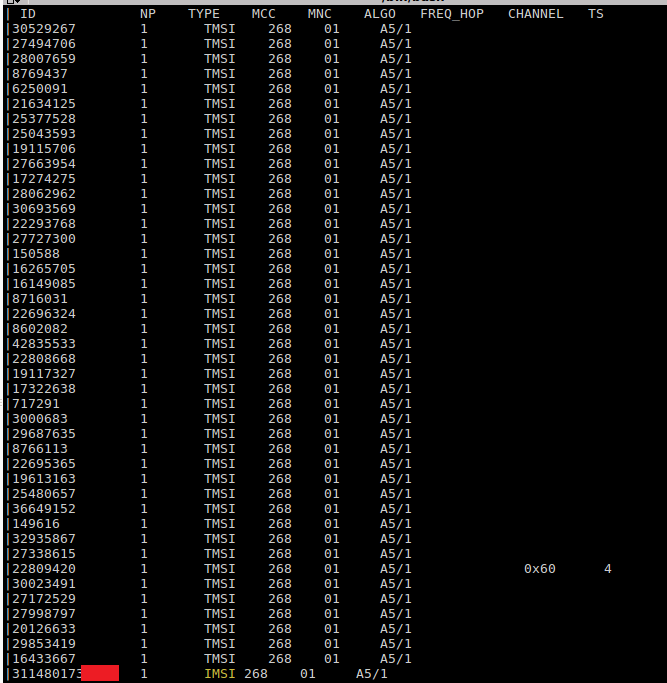
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
GSM A5/1 Cracking
4. Get Keystream
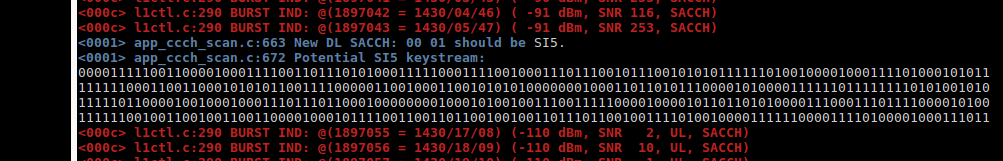
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
GSM A5/1 Cracking
4. Load Rainbow Tables + Kraken
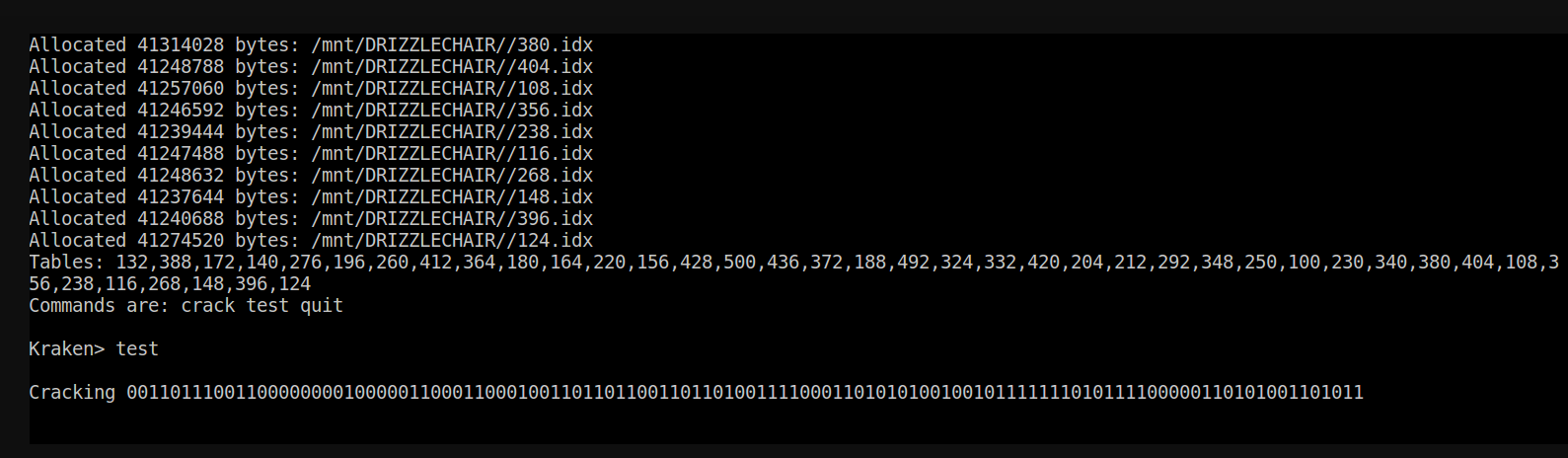
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
GSM A5/1 Cracking
6. Get Kc and crack comms!

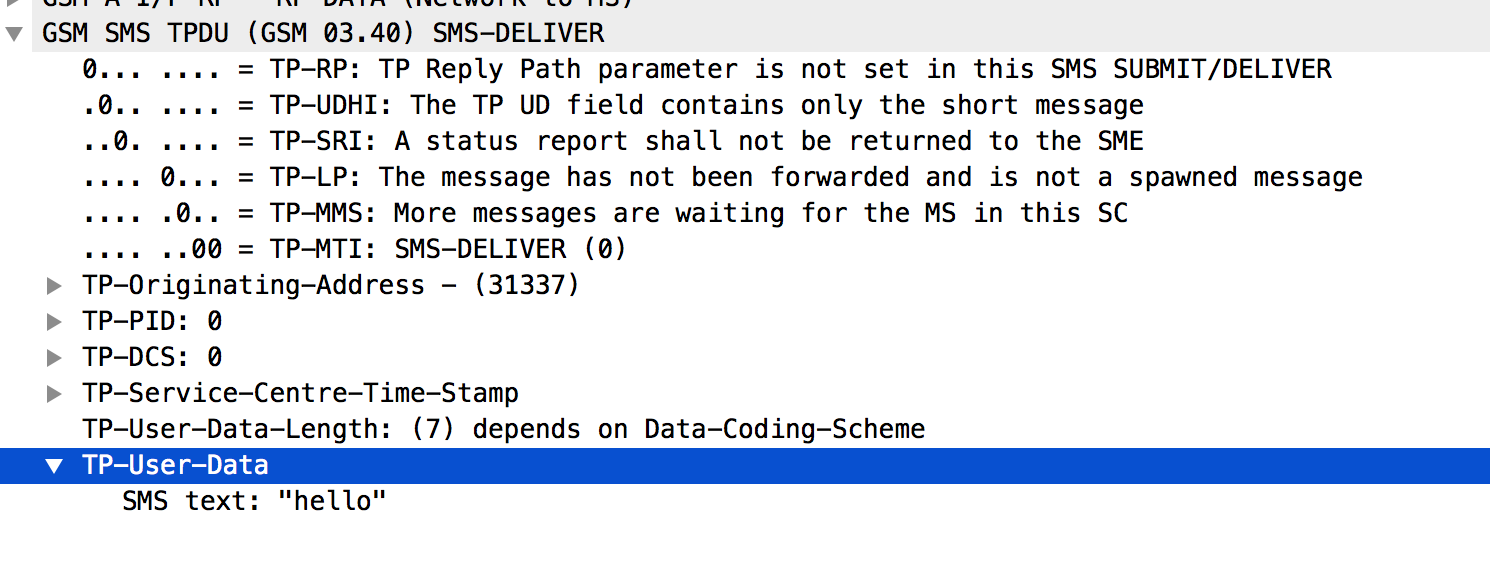
WHY?

GSM - "The wake up call"
Roadmap for the tools
-
GSEC:
- Increase tests
- Kraken requirements
-
Full automation:
- GSEK - GSM Exploitation kit
Q&A
Thank you.


...are you ready to answer the phone?
GSM - The Wake Up call
By Duarte Monteiro
GSM - The Wake Up call
- 670


