Hydroelectric Power
Jett & Emilie
Requirements For Hydroelectric Power
Map of world rivers:
- Good head
- Good flow
- Simple site layout with main parts close together
- Good grid connection
- Good site access
- Single ownership of the site, or cooperative neighbours
- Not too many environmental sensitivities
What is head?
The height difference between where the water enters into the hydro system and where it leaves it (in meters).
How does it work?
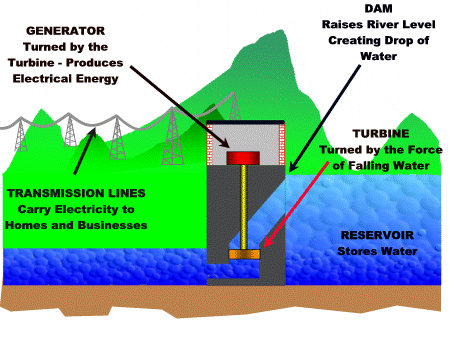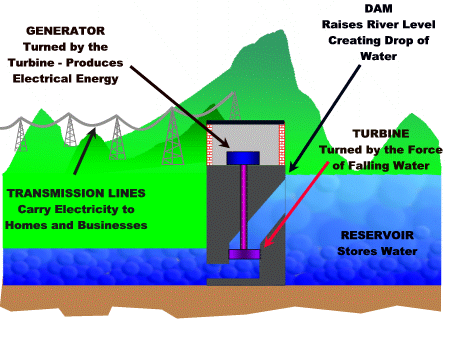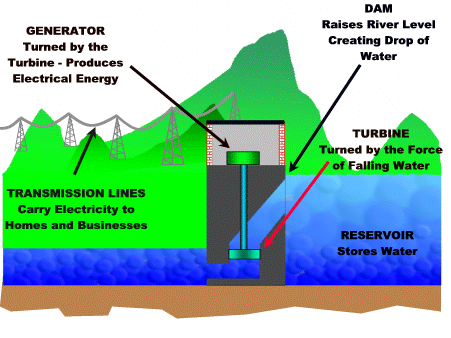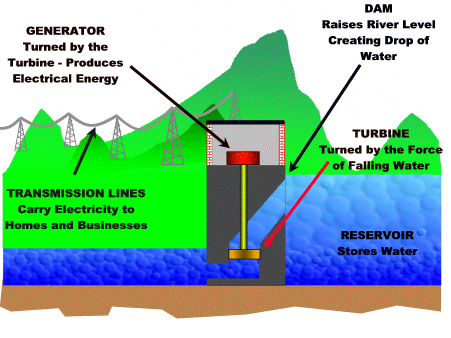
Visual representation (dam):
- Hydropower plants capture the energy of falling water to generate electricity.
- A turbine converts the kinetic energy of falling water into mechanical energy.
- A generator converts this mechanical energy from the turbine into electrical energy.
How much energy does it make?
Depends on:
- How far the water falls; the further the water falls, the more power it has.
- Amount of water falling; more water falling through the turbine will produce more power.
Fun Fact!
World-wide, about 20% of all electricity is generated by hydropower.
Case Study: Washington, US
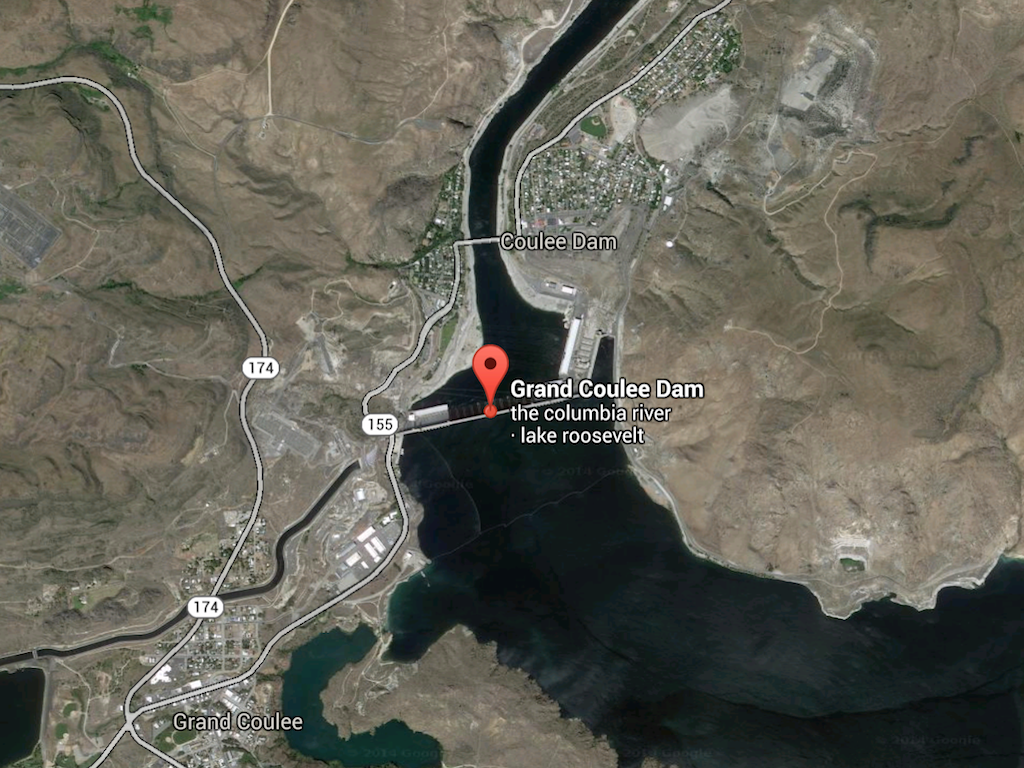
Grand Coulee:
- Grand Coulee hydropower project located on the Columbia River in Washington, US, is currently the world’s fifth biggest hydroelectric power station.
- Produces 6,480MW of energy.
- Located on the Columbia River, 145 km west of Spokane, Washington.
- It is three times the size of the Great Pyramid and two and a half times the volume of Hoover Dam.
- Constructed between 1933 and 1942, the Grand Coulee Dam was a major source of economic stimulus during the Great Depression (construction created 8 800 jobs).
- Consists of three power plants and a concrete gravity dam 168m high and 1,592m in length
Fun Fact!
Hydropower provides about 10% of the electricity in the United States.

Case Study: Washington, US


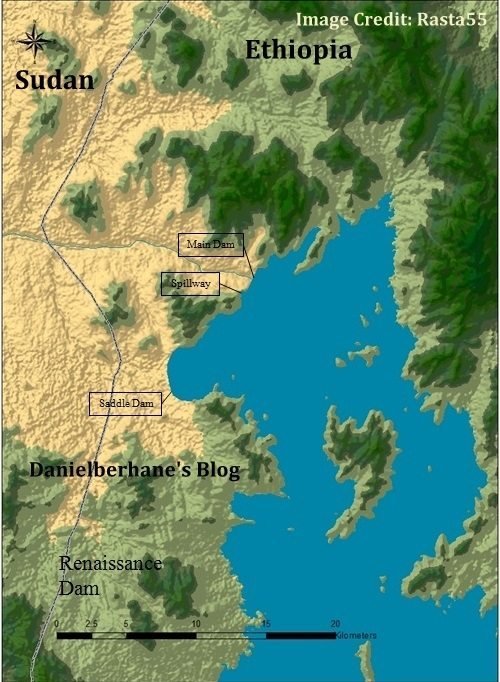
Case Study: Ethiopia (LIC)
- Grand Ethiopian Renaissance Dam, formerly known as the Millennium Dam (sometimes referred to as Hidase Dam), is a dam on the Blue Nile River in Ethiopia, which is located about 40km east of Sudan. The project is owned by Ethiopian Electric Power Corporation.
- Has been under construction since 2011.
- Aimed primarily at generating power, with an expected capacity of 6,000MW, the main and saddle dams will also create reservoirs with an impounding capacity of 74 billion cubic metres.
- The dam will be capable of handling a flood of 19,370 cubic metres per second.
- Total value: € 3,377.05 million.
- The project involves the construction of a main dam, with 2 power stations at the foot of the dam.
- total installed power of 6,000 MW and estimated production of 15,000 GWh per year.
Fun Fact!
Hydropower prevents the burning of 22 billion gallons of oil or 120 million tons of coal each year.

Case Study: Ethiopia (LIC)


Advantages & Disadvantages
- Fuelled by water, a clean source.
- Very efficient, renewable method of generating electricity without producing air pollution.
- Increased agriculture & irrigation.
- Can be a domestic source of energy.
- Creates reservoirs, that offer a variety of recreational opportunities, notably fishing, swimming, and boating.
Advantages
- Costs to human and wildlife populations
- Adverse affects to the health of humans and animals.
- Diverts waterways.
- Changes in water and food security.
- Social disruption caused by construction of dam.
- Loss of biodiversity.
- Humans, flora, and fauna may lose their natural habitat.
- Create water pollution: chemicals & heat pollutants.
Fun Fact!
The United States is the second largest producer of hydropower in the world. Canada is number one.
Disadvantages
Evaluation of Hydropower
As the world’s dams become more efficient, they will begin to generate more and more power, for example the 3 Gorges Dam, in China (largest HEP plant in the world), which generates massive amounts of power, supplying power for millions of people. Ghana also has a large dam. Additionally, the artificial lakes (reservoirs) that dams create can be used to make irrigation for agriculture. With the combination of improving agriculture and generating more power, jobs in the thousands will be created, improving the quality of life for many people, while providing sustainable energy at the same time.
Quick Quiz:
1. How is electricity generated in hydropower plants (dam)?
2. What is one disadvantage of hydroelectric power?
3. What is the largest HEP plant in the world?
Fun Fact!
Norway produces more than 99% of its electricity with hydropower. New Zealand uses hydropower for 75% of its electricity.

Hydroelectric Power
By emilie356
Hydroelectric Power
- 1,043



