what is Agile?

How we used to do things - whaterfall
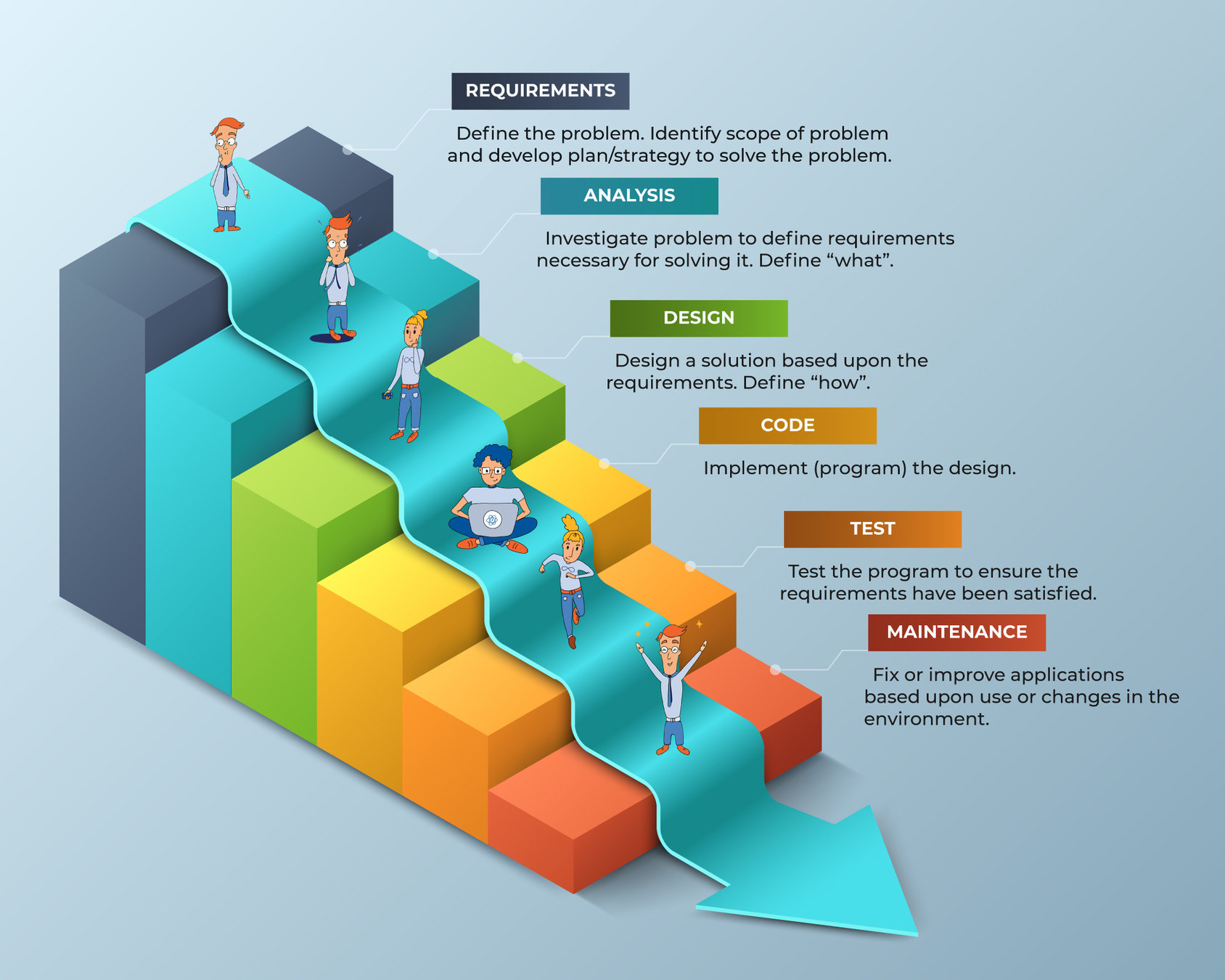
Vs Agile
It's the story how we went from

To
The Agile Manifesto
A bit of History
In 2001 this new management paradigm begin to pick up - agile was formalized when 17 people met at a ski resort in Utah and created the agile manifesto
what is agile?
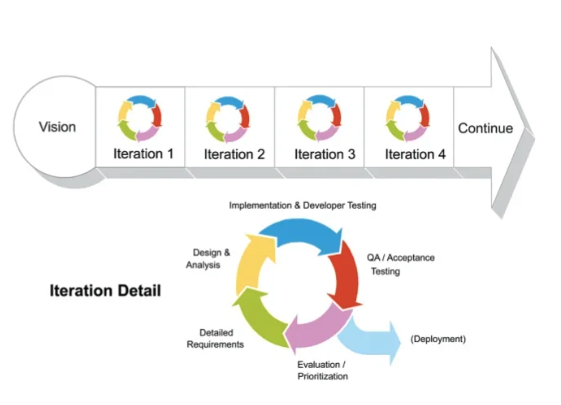
- In a nutshell, it’s incrementally delivery vs all at once
- Agile is a time-boxed iterative approach to software delivery, that builds software incrementally instead of trying to deliver it all at once near the end
- It works by breaking projects down to little bits of USER functionality, called User Stories, prioritizing them, and continuously delivering them in a short week cycle iterations
Why we use Agile methods?
- Improves customer involvement
- Increase Quality
- Simplify Releases
- Drives down risk
Advantages
- Customer satisfaction is rapid
- People and interactions are emphasized rather than process and tools (customers/developer/product/tests are constantly interacting)
- Regular adaptation to changing circumstances
- Even late changes in requirements are welcomed - NOT in waterfall
Disadvantages
- Sometimes in big projects, it’s difficult to assess the effort at the beginning
-
Projects can easily get taken off track if the customer is not clear what the final outcome they want - they can change it so often
- You need seasoned developers to drive this process
The agile manifesto
| Individual and Interactions | Over | Processes and Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Working Product | Over | Comprehensive Documentation |
| Customer Collaboration | Over | Contract Negotiation |
| Responding to change | Over | Following a plan |
That is, while there is value in the items on
the right, we value the items on the left more
Agile software development principles
- Customer satisfaction by early and continuous delivery of valuable software
- Welcome changing requirements, even in late development
- Deliver working software frequently (weeks rather than months)
- Close, daily cooperation between business people and developers
- Projects are built around motivated individuals, who should be trusted
- Face-to-face conversation is the best form of communication (co-location)
- Working software is the primary measure of progress
- Sustainable development, able to maintain a constant pace
- Continuous attention to technical excellence and good design
- Simplicity—the art of maximizing the amount of work not done—is essential
- Best architectures, requirements, and designs emerge from self-organizing teams
- Regularly, the team reflects on how to become more effective, and adjusts accordingly
Agile methodologies
- Scrum (Our focus)
- Extreme Programming (XP)
- Dynamic Systems Development Method (DSDM)
- Feature Driven Development (FDD)
- Lean and Kanban Software Development
- Crystal
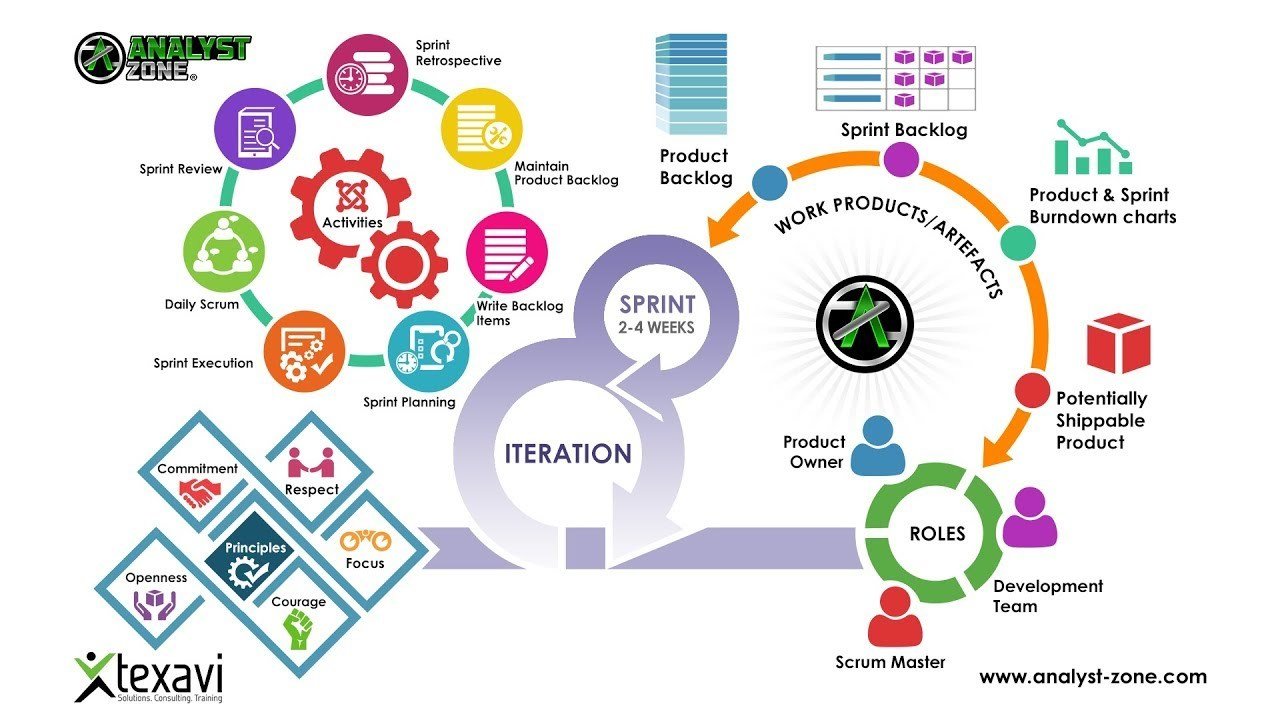
scrum
scrum roles
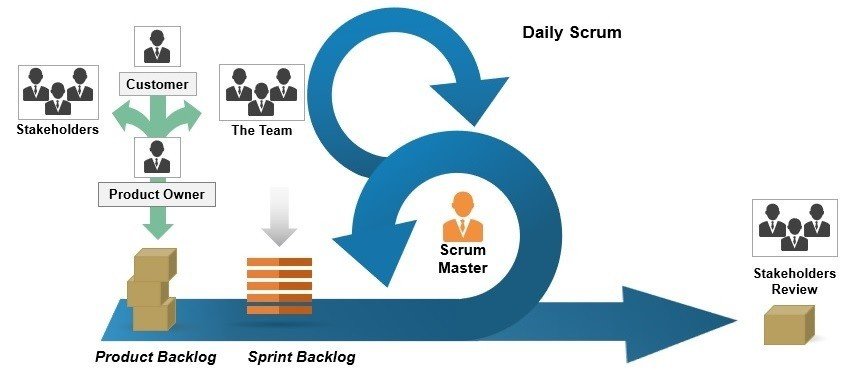
Product owner (po)
- Responsible for maximizing the ROI of the development effort
- Responsible for Project Vision
- Responsible for re-prioritizing the backlog, and adjusting long-term expectations (release plan)
- The final arbiter of requirement questions and conflicts
- Decides whether to ship
- Consider stack-holder interests
- Has a leadership role
scrum master
- Is the core of the team
- Responsible for the Scrum planning for a sprint
- Manages impediments/conflicts
- Part of the team - does not need to be the manager
- Responsible for scrum ceremonies (daily stand up, demo, retro)
scrum team
- Works to achieve sprint goals
- Takes part in ceremonies
- Attend Daily stand up
- What was done yesterday?
- What is the plan for today?
- Any impediments?
The Process & Ceremonies
- Sprint planning meeting
- Sprint execution
- Daily Scrum
- Sprint review/retro
- What to continue?
- What to change?
- What to drop?
QA
What is Agile
By Eyal Mrejen
What is Agile
- 170



