JavaScript Fundamentals
var isMale = true; // is_male 🙅
// Introduced from ES6 (2015)
let name = "Fadzil";
const age = 30;# PRESENTING CODE
Variables
Data Types: String, Number, Boolean, Object, Array, Function, Null, Undefined.
Operators: +, -, *, /, %, ++, --, ==, ===, !=, !==, <, >, <=, >=.
if (age > 18) {
console.log("Adult");
} else {
console.log("Minor");
}
console.log(age > 18 ? "Adult" : "Minor");
# PRESENTING CODE
Control Structures
if-else, switch
Loops: for, while
// || (or)
result = '0' || 1
// && (and)
result = '0' && 1
// ! (not)
result = !'0'
// ?? (nullish coalescing)
// - when the value is not 'null' or 'undefined')
result = '0' ?? 1# PRESENTING CODE
Logical Operators
const person = {
firstName: "Fadzil",
lastName: "Jusri",
age: 11110,
fullName : function() {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
}
};# PRESENTING CODE
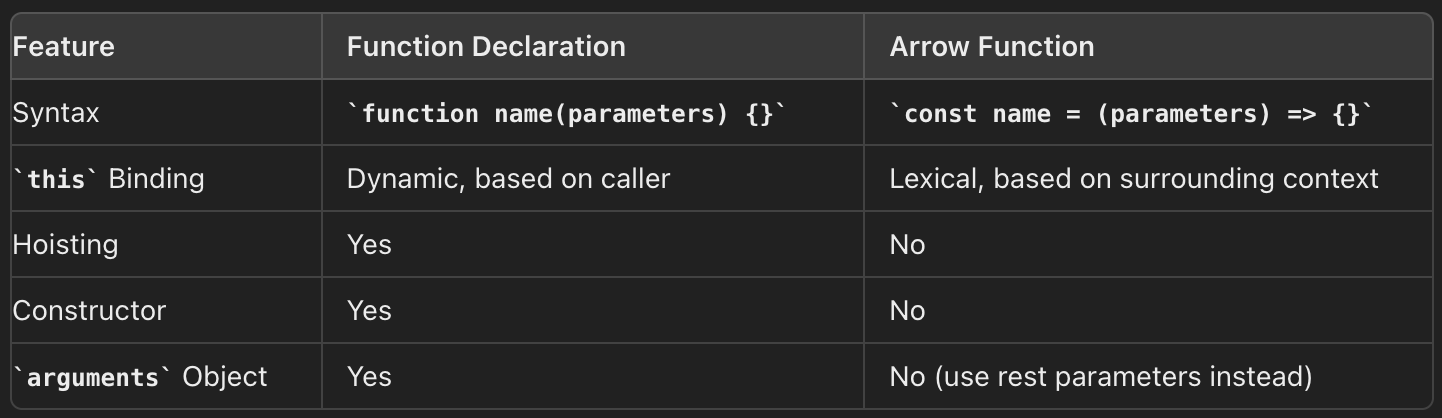
What is this?

const person = {
firstName: "Fadzil",
lastName: "Jusri",
// function declaration
fullName : function() {
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`;
}
};
const person = {
firstName: "Fadzil",
lastName: "Jusri",
// arrow function (ES6)
fullName : (args) => `${args.firstName} ${args.lastName}`
};# PRESENTING CODE
Functions
// Immediately Invoked Function Expression
// function that is called immediately after it is defined.
(function functionName() {
console.log("function logic");
}());
(async function () {
console.log("function logic");
})();
(() => {
console.log("function logic");
})();# PRESENTING CODE
IIFE
// Creation
let user = new Object(); // "object constructor" syntax
let user = {}; // "object literal" syntax
// Can initialize properties as “key: value” pairs:
let user = {
name, // when variable 'name' same as property name
[agePropertyName]: 30, // let agePropertyName = "age";
"likes JS": true // multiword property name
};
// remove property using 'delete' keywords
delete user.age, delete user["likes JS"];# PRESENTING CODE
Objects
let user = { name: "Fadzil" };
let admin = user; // copy the reference
admin.name = 'Hacked'; // changed by the "admin" reference
console.log(user.name); // 'Hacked'
console.log(user == admin); // true, both variables reference the same object
console.log({} == {}); // ??# PRESENTING CODE
Objects Referencing
A variable assigned to an object stores not the object itself, but its “address in memory” – in other words “a reference” to it
let user = {
name: "Fadzil",
measurements: { cap: "m", shoes: 7 }
}
// Object.assign
let admin = Object.assign({}, user)
// Destructuring
let admin = {...user}
// structuredClone // _.cloneDeep (lodash)# PRESENTING CODE
Objects Cloning
"use strict";
const user = Object.freeze({
name: "Fadzil",
measurements: { cap: "m", shoes: 7 }
})
user.name = "Hacked"; // throws an error in strict mode# PRESENTING CODE
Immutable Objects
JavaScript
By fadziljusri
JavaScript
- 73



