CH3
THE RELATIONAL MODEL
Introduction
-
A collection of one or more relations
-
Each relation is a table with rows and columns
- Consists of a relation schema and a relation instance
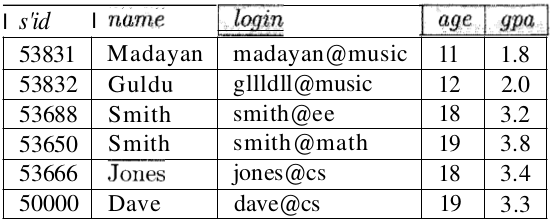
Students(
sid: string,
name: string,
login: string,
age: integer,
gpa: real
)
Create and modify relation using SQL
CREATE TABLE Students (
sid CHAR(20),
name CHAR(30),
login CHAR(20),
age INTEGER,
gpa REAL
)Create relation
INSERT
INTO Students (sid, name, login, age, gpa)
VALUES (53688, 'Smith', 'smith@ee', 18, 3.2)Insert record
DELETE
FROM Students S
WHERE S.name = 'Smith'Delete record
UPDATE Students S
SET S.age = S.age + 1, S.gpa = S.gpa - 1
WHERE S.sid = 53688Update record
Integrity Constraints
A condition specified on a database schema and restricts the data that can be stored in an instance of the database
Integrity constraints are specified and enforced
- When user defines a database schema
- When running a database application
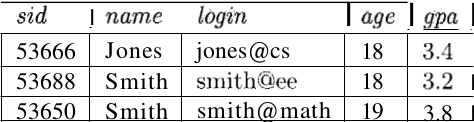
Key Constraints
Unique identifier for a record
CREATE TABLE Students (
sid CHAR(20),
name CHAR (30),
login CHAR(20),
age INTEGER,
gpa REAL,
UNIQUE (name, age),
CONSTRAINT StudentsKey PRIMARY KEY (sid)
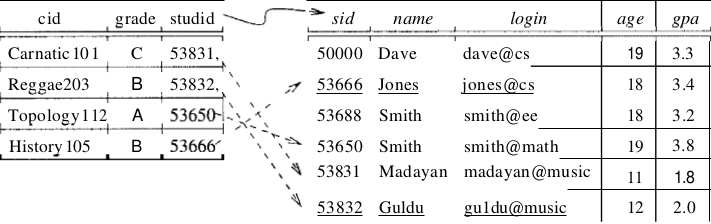
)Foreign Key Constraints
CREATE TABLE Enrolled (
studid CHAR(20),
cid CHAR(20),
grade CHAR(10),
PRIMARY KEY (studid, cid),
FOREIGN KEY (studid) REFERENCES Students
)
General Constraints
Ex: Student must be at least 16 years old
Enforcing Integrity Constraints
Key Constraint
If a command causes violation, it is rejected.
- null
- Duplicate
Foreign Key Constraint
If insert, update causes violation, it is rejected.
What if a Students row is deleted?
- Delete all Enrolled rows refering to the Students row
- Disallow the deletion of the Students row
- Set the studid column to a default value
Foreign Key Constraint
CREATE TABLE Enrolled (
studid CHAR(20),
cid CHAR(20),
grade CHAR(10),
PRIMARY KEY (studid, dd),
FOREIGN KEY (studid) REFERENCES Students
ON DELETE CASCADE
ON UPDATE NO ACTION
)NO ACTION CASCADE SET DEFAULT SET NULL
Transactions and Constraints
SET CONSTRAINT ConstntintFoo DEFERRED
SET CONSTRAINT ConstntintFoo IMMEDIATEVIEWS
CREATE VIEW B-Students (name, sid, course)
AS SELECT S.sname, S.sid, E.cid
FROM Students S, Enrolled E
WHERE S.sid = E.studid AND E.grade = 'B'Updates on Views
Only views that are defined on a single base table using just selection and projection,
with no use of aggregate operations
CH3THE RELATIONAL MODEL
By Gordon Ueng
CH3THE RELATIONAL MODEL
- 661



