Surviving Web Security
Gergely Nemeth

github.com/gergely | twitter.com/nthgergo | gergely@risingstack.com
RisingStack - Enterprise Node
https://risingstack.com
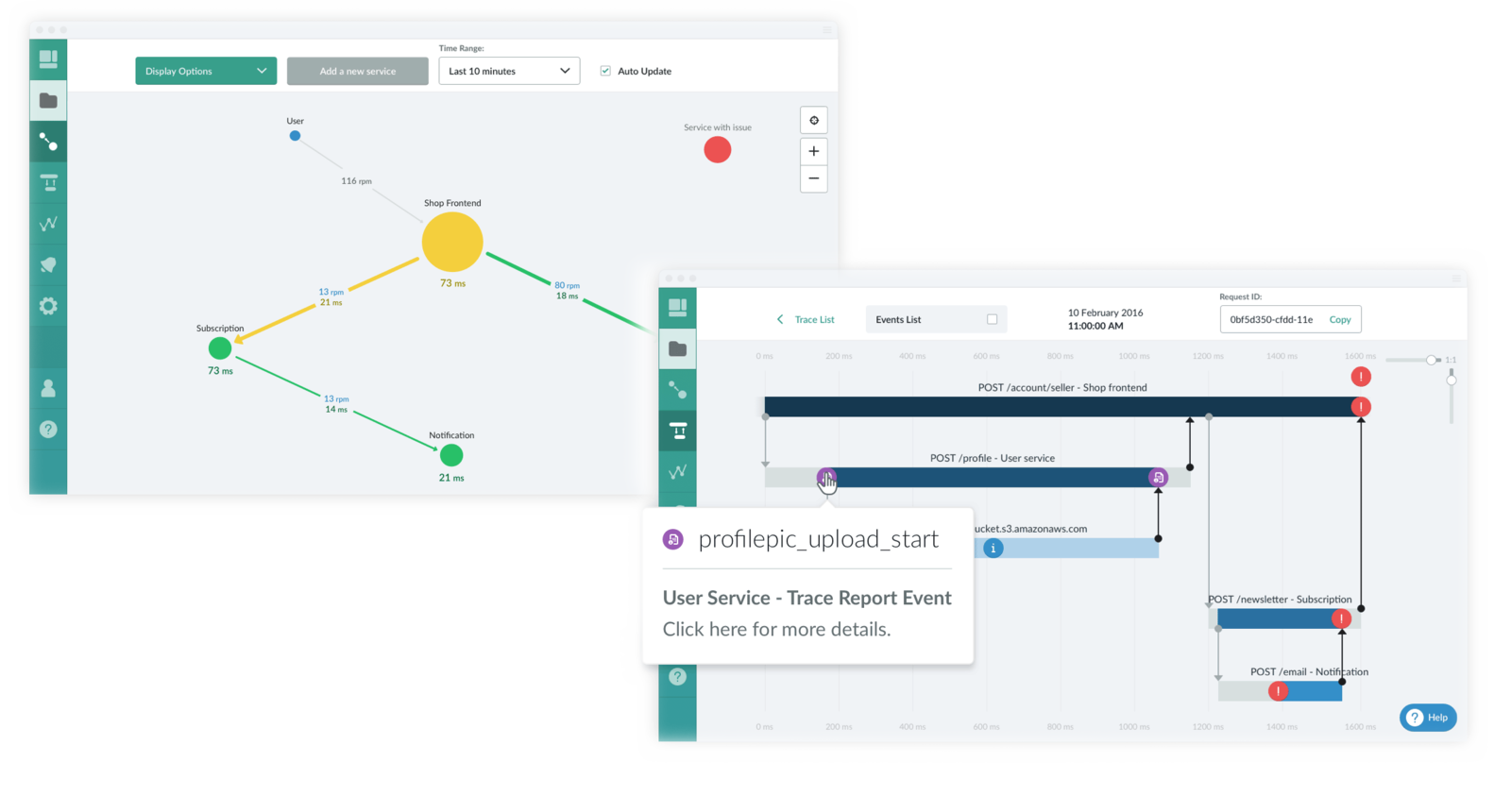
Trace - Microservice Monitoring
https://trace.risingstack.com
2015 In Retrospect


Heartbleed, Shellshock
lots of high-profile vulnerabilities such as
158 days time-to-fix security issues
an average of
open for more than 2 years
in some industries security tickets may be
XSS 47%
CRFS 24%
of all web apps.
affects
affects
Surviving Web Security
-
The Human Factor
-
Application Level Security
-
Network/Infrastructure Level Security
-
Node Security
The Human Factor
The Human Factor
-
95% of all security incidents involve human error
-
People are the weakest link
-
Train employees to withstand social engineering attacks
Application Level Security
Cookies - flags
-
secure - this attribute tells the browser to only send the cookie if the request is being sent over HTTPS.
-
HttpOnly - this attribute is used to help prevent attacks such as cross-site scripting, since it does not allow the cookie to be accessed via JavaScript.
Cookies - flags
Cookies - flags
Cookies - (CRFS)
CROSS-SITE REQUEST FORGERY
This attack vector forces a user to execute unwanted actions on a web application in which they're currently logged in.
<!-- we are on real-website1.com -->
<!-- this is how an attacked could expose it -->
<form method="post" action="https://real-website.com/item/1/delete">
</form>
<script>
// submit the form onload
</script>Cookies - (CRFS)
CROSS-SITE REQUEST FORGERY
<!-- we are on real-website.com -->
<form method="post" action="https://real-website.com/item/1/delete">
<input type="hidden" name="crfs_token" value="random-token"/>
</form>
<script>
// submit the form onload
</script>Defend against it with cryptographically secure crfs tokens!
Cookies - (CRFS)
CROSS-SITE REQUEST FORGERY
const csrf = require('csurf')
const csrfProtection = csrf({ cookie: true })
app.get('/form', csrfProtection, function(req, res) {
// pass the csrfToken to the view
res.render('send', { csrfToken: req.csrfToken() })
})
app.post('/process', csrfProtection, function(req, res) {
res.send('data is being processed');
});Cookies - (CRFS)
CROSS-SITE REQUEST FORGERY
-
https://www.npmjs.com/package/csurf
-
http://expressjs.com/
Cookies - (CRFS)
CROSS-SITE REQUEST FORGERY
Data Validation - XSS
-
Reflected Cross Site Scripting occurs when the attacker injects executable JavaScript code into the HTML response with specially crafted links
-
Stored Cross Site Scripting occurs when the application stores user input which is not correctly filtered. It runs within the user’s browser under the privileges of the web application.
Data Validation - XSS
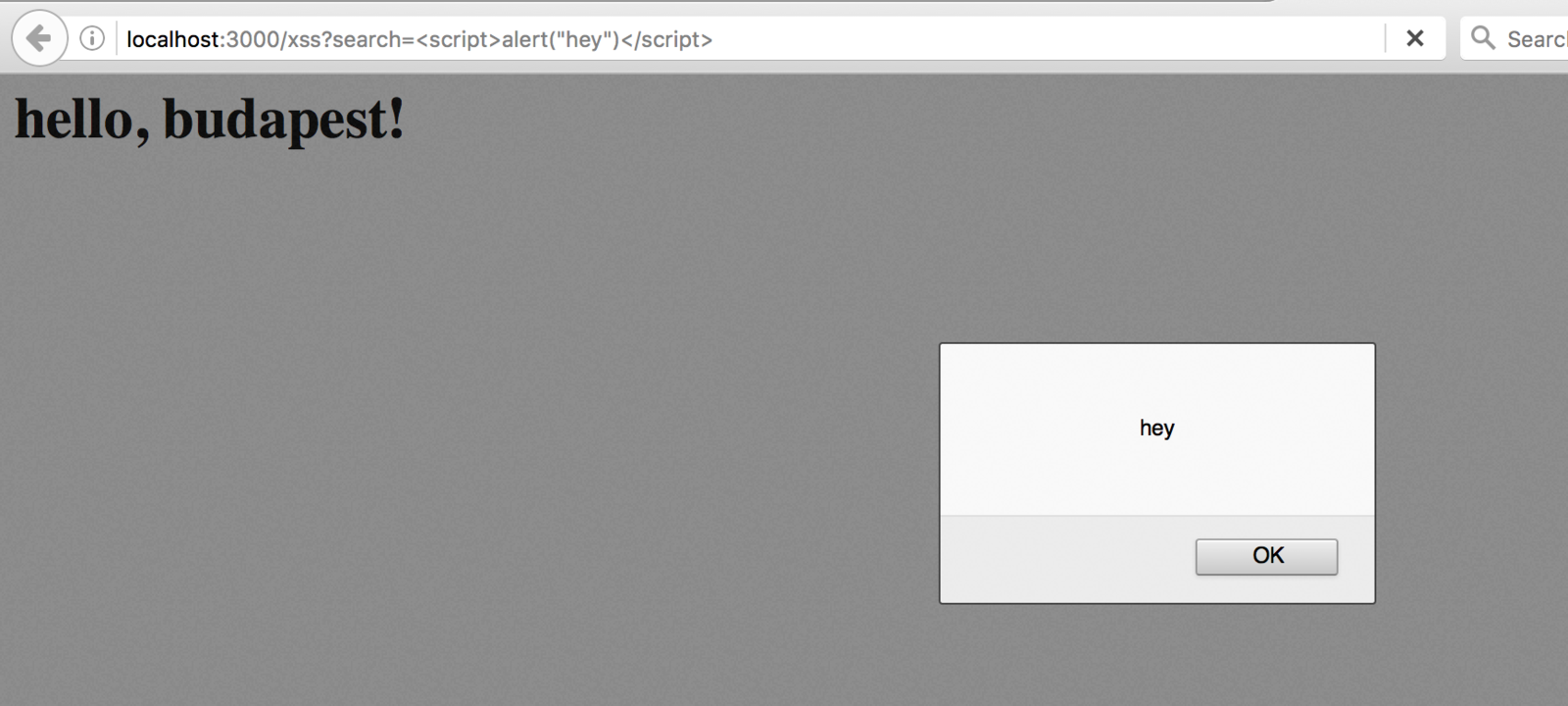
Defend against it with
input validation and security headers.
Data Validation - XSS
-
https://www.npmjs.com/package/validator
Data Validation - XSS
Data Validation -
SQL Injection
This attack vector consists of injection of a partial or complete SQL query via user input.
select title, author from books where id=$id
-- can become:
select title, author from books where id=2 or 1=1
Data Validation -
SQL Injection
Defend against it with
parameterized queries / prepared statements
Data Validation -
SQL Injection
// paramaterized
query( "select name from emp where emp_id=$1",
[123] )
// prepared
query( {
name:"emp_name",
text:"select name from emp where emp_id=$1",
values:[123]
})Data Validation -
SQL Injection
-
https://www.npmjs.com/package/pg
Data Validation -
SQL Injection
Data Validation -
CMD Injection
This is a technique used by an attacker to run OS commands on the remote web server.
https://example.com/downloads?file=user1.txt
can become:
https://example.com/downloads?file=%3Bcat%20/etc/passwd
Data Validation -
CMD Injection
Password Equality Check
// the bad solution
if (userEnteredPassword === passwordFromDb) {
return true
}
return false// the good solution
var cryptiles = require('cryptiles')
if (cryptiles.fixedTimeComparison(
userEnteredPassword,
passwordFromDb)
) {
return true
}
return falsePassword Equality Check
-
https://www.npmjs.com/package/cryptiles
Password Equality Check
Password Storing
Never store plaintext passwords - but hash them with a salt.
Use bcrpyt or scrypt!
-
https://www.npmjs.com/package/bcrypt
-
https://www.npmjs.com/package/scrypt
Password Storing
Denial of Service -
Evil Regex
Most Regular Expression implementations may reach extreme situations that cause them to work very slowly.
-
Grouping with repetition
-
Inside the repeated group
-
Repetition
-
Alternation with overlapping
-
-
([a-zA-Z]+)*
Denial of Service -
Evil Regex
-
https://www.npmjs.com/package/safe-regex
Denial of Service -
Evil Regex
Network/Infrastructure
Level Security
Secure Transmission - SSL
HTTP is a clear-text protocol:
traffic served through it can be read by anyone.
Always use HTTPS.
Security Headers
-
Strict-Transport-Security enforces secure (HTTP over SSL/TLS) connections to the server
-
X-Frame-Options provides clickjacking protection
-
X-XSS-Protection enables the Cross-site scripting (XSS) filter built into most recent web browsers
-
Content-Security-Policy prevents a wide range of attacks, including Cross-site scripting and other cross-site injections
SECURITY IS PART OF YOUR JOB
Where to START?
-
https://www.owasp.org/index.php/OWASP_Top_Ten_Cheat_Sheet
-
https://nodesecurity.io
Questions!

Surviving Web Security
By Gergely Nemeth
Surviving Web Security
- 1,462

