WAVE THEORY
TRANSVERSE AND LONGITUDINAL WAVES
TRANSVERSE WAVES
LONGITUDINAL WAVES
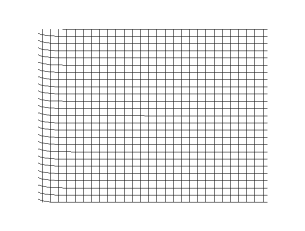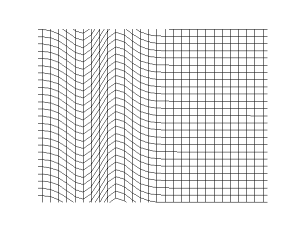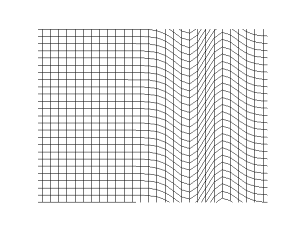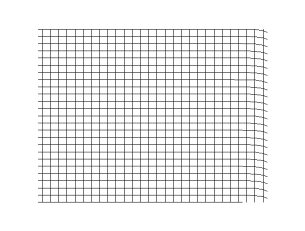
TRANSVERSE WAVES
TRANSVERSE WAVES: TIME DEPENDENCE
TIME DEPENDENCE
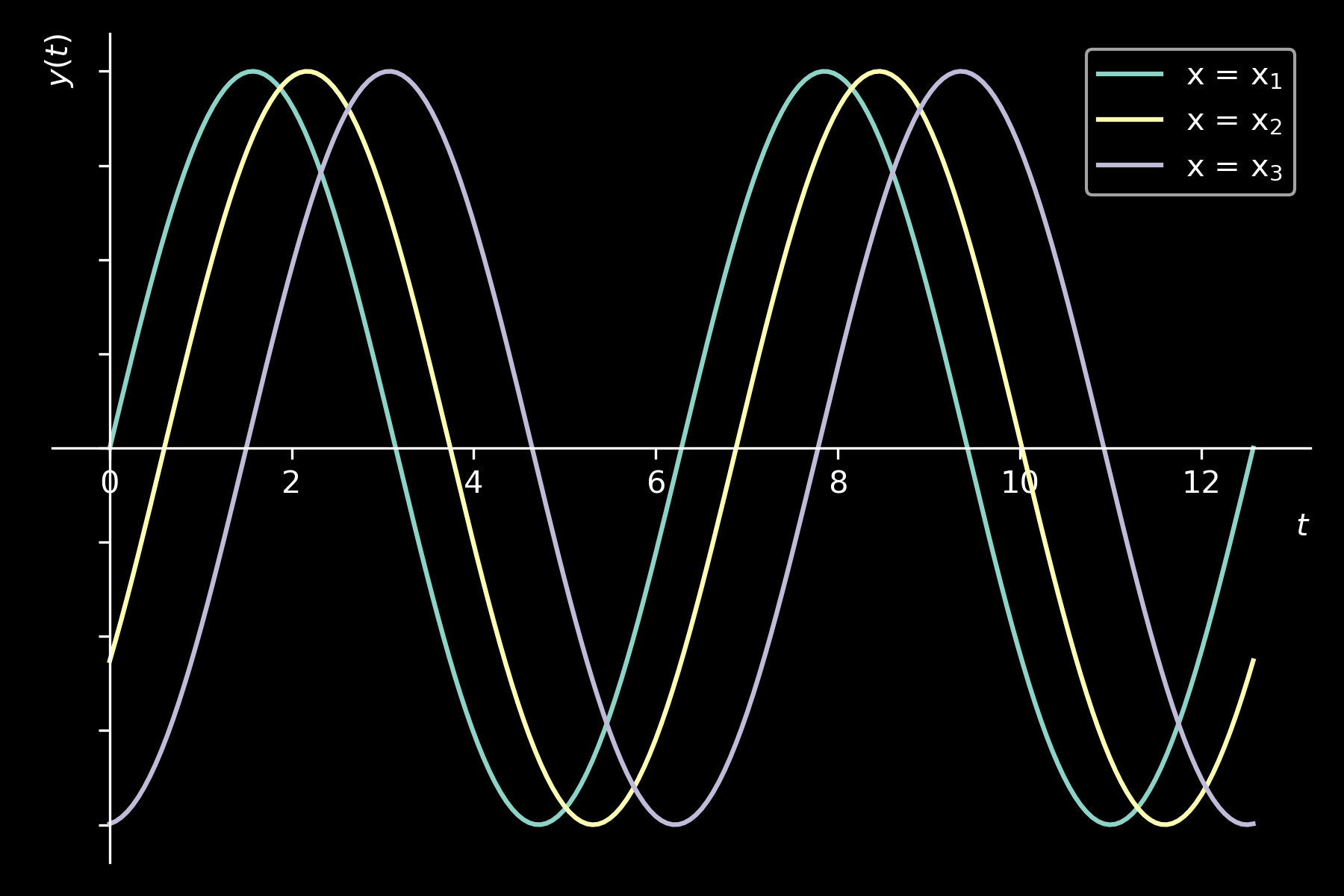
\( y(t) = y_{m} sin(\omega t + \phi_{x})\)
\( \omega=2 \pi \nu=\frac{2 \pi}{T} \)
\( \omega = angular \, frequency\)
\( T = period \)
\( \phi_{x} = spatial \, phase \)
TRANSVERSE WAVES: SPATIAL DEPENCENCE
SPATIAL DEPENDENCE
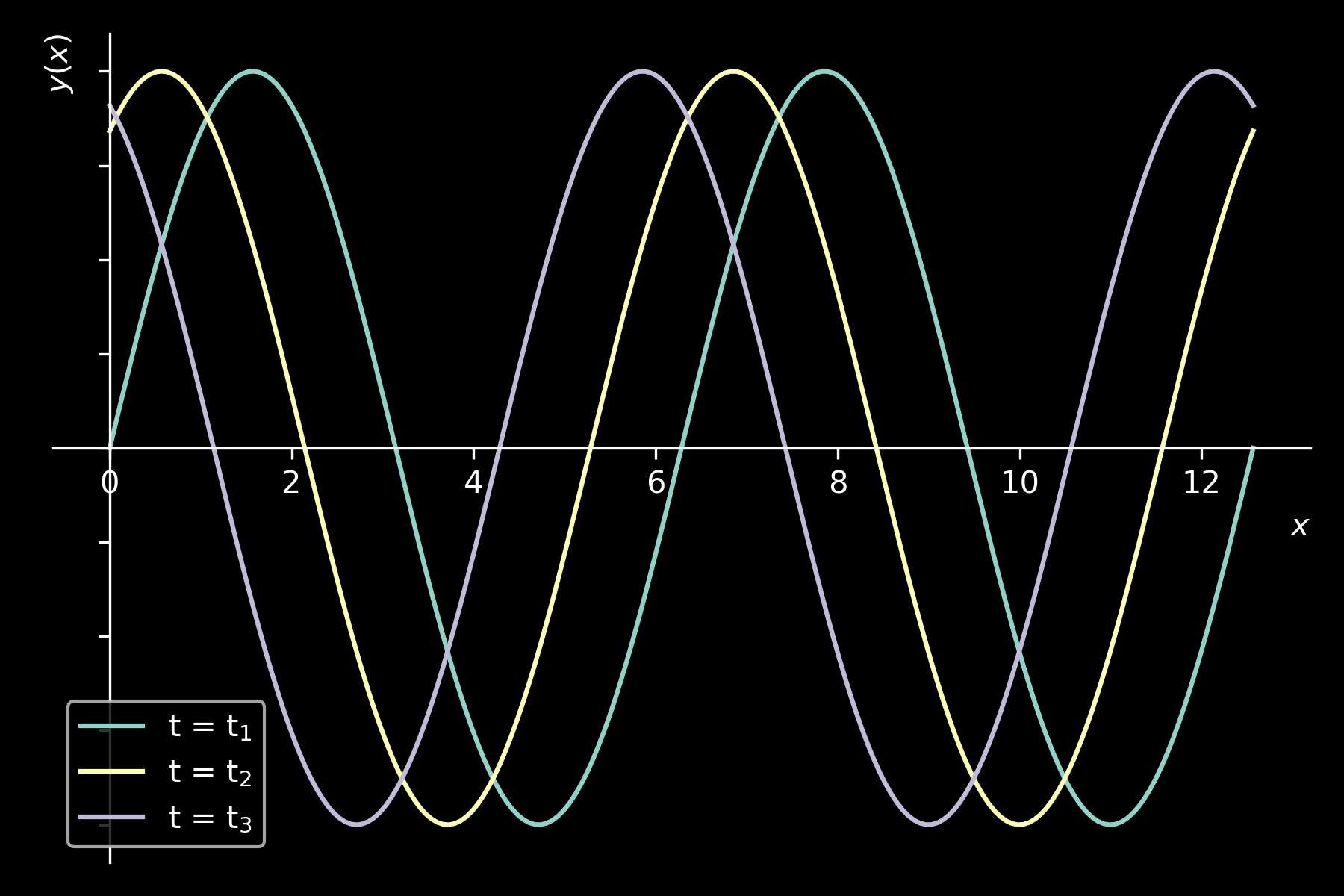
\( y(x) = y_{m} sin(k x + \phi_{t})\)
\( k = \frac{2 \pi}{\lambda}\)
\( k = wavenumber \)
\( \lambda = wavelength \, (spatial \, period) \)
\( \phi_{t} = temporal \, phase \)
TRANSVERSE SINUSOIDAL WAVE
\[ \phi_{x} = k x \]
\[ \phi_{t} = - \omega t \]
\[ y(x,t) = y_{m} sin (k x - \omega t + \phi) \]
\[ \phi = additional \, phase \]
PHASE SPEED OF A WAVE
\( k x - \omega t = \frac{\pi}{2} \)
\( x(t) = \frac{\pi}{2 k} + \frac{\omega}{k} t \)
\( x(t) = \frac{\lambda}{4} + \frac{\omega}{k} t = x_{0} + v_{phase} t \)
\( x_{0} = \frac{\lambda}{4}; \)
\[ \boxed{v_{phase} = \frac{\omega}{k} = \lambda \, \nu} \]
\[ \boxed{\omega =c \, k, \; c=\lambda \, \nu} \]
For Light
SUPERPOSITION PRINCIPLE FOR WAVES
"If two functions are a solution of the wave equations, then their sum is a valid solution"
\[ y_{1}(x,t); \; y_{2}(x,t) \Rightarrow y_{1}(x,t) + y_{2}(x,t) \]
\[ \frac{\partial^{2}[y(x,t)]}{\partial t^{2}} = v^{2}_{phase} \frac{\partial ^{2}[y(x,t)]}{\partial x^{2}} \]
INTERFERENCE BETWEEN SINUSOIDAL WAVES
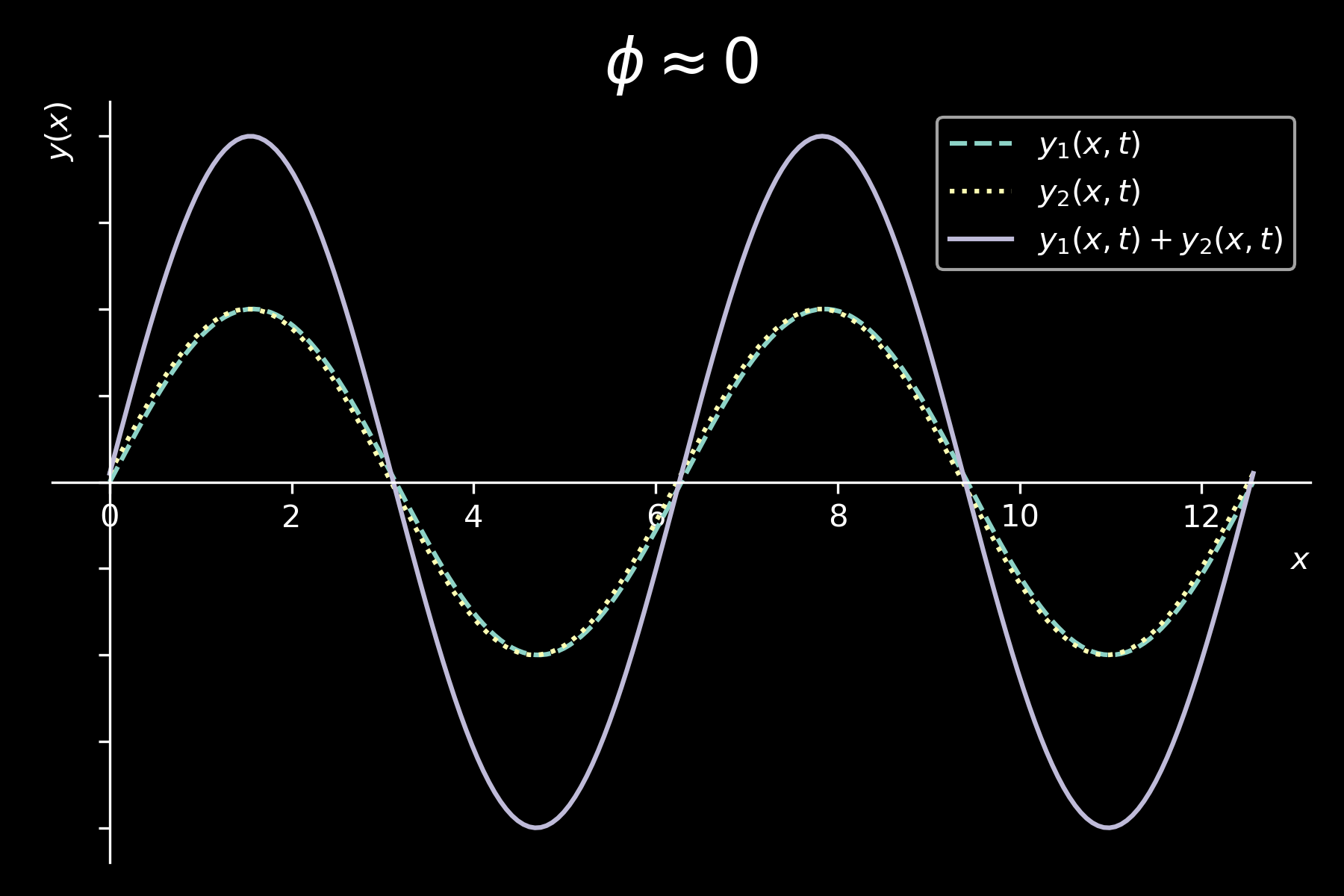
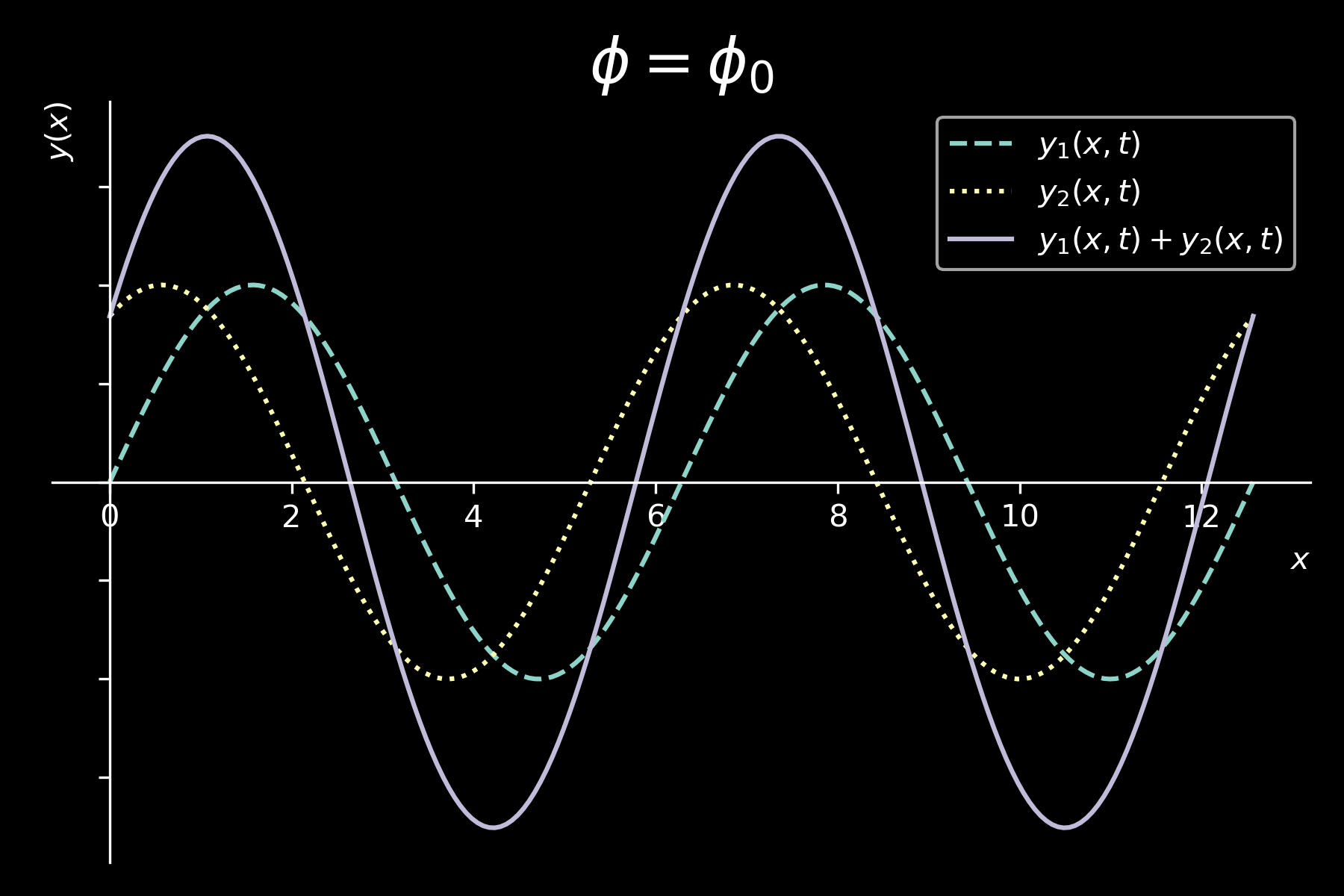
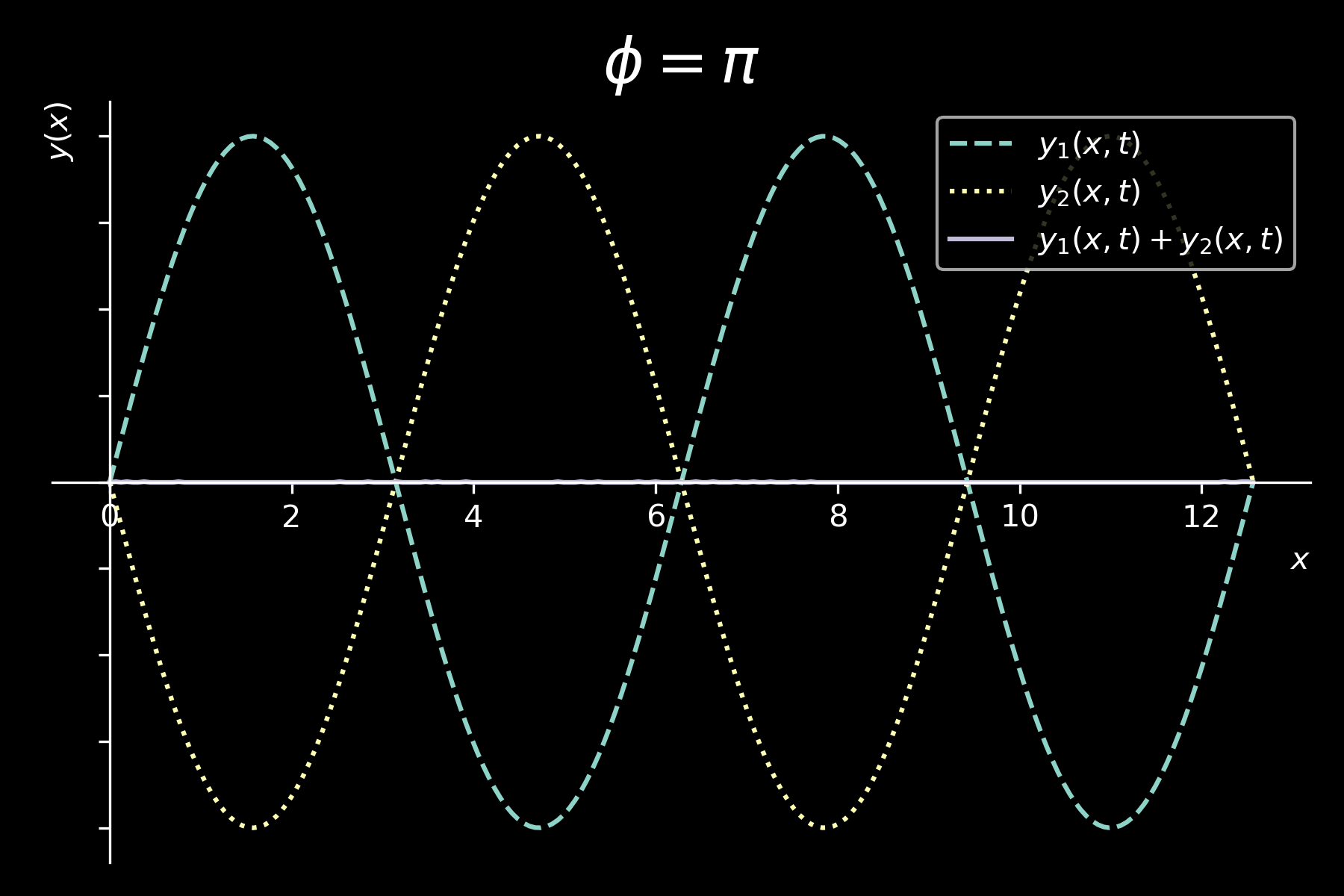
\( y_{1}(x,t) = y_{m} sin(kx - \omega t) \)
\( y_{2}(x,t) = y_{m} sin(kx - \omega t + \phi) \)
\[ \boxed{y(x,y) = y_{1}(x,t) + y_{2}(x,t) = 2 y_{m} cos \left( \frac{\phi}{2} \right) sin \left( kx - \omega t + \frac{\phi}{2} \right)} \]
INTERFERENCE, STATIONARY WAVES AND RESONANCES
\( y_{1}(x,t) = y_{m} sin(kx - \omega t) \)
\( y_{2}(x,t) = y_{m} sin(kx + \omega t) \)\( y(x,t) = y_{1}(x,t) + y_{2}(x,t) \)
\( \Downarrow \)
\[ \boxed{y(x,t) = [ 2 y_{m} sin(kx) ] cos( \omega t)} \]
\[ \boxed{ \lambda = \frac{2 L}{n}; \; n=1,2,3...} \]
INTERFERENCE, STATIONARY WAVES AND RESONANCES
WAVES: COMPLEX FORMALISM AND PLANE WAVES
\( y(x,t) = y_{m} cos(kx - \omega t + \phi) \)
\( \omega=2 \pi \nu=\frac{2 \pi}{T}\)
\( k = \frac{2 \pi}{\lambda}\)
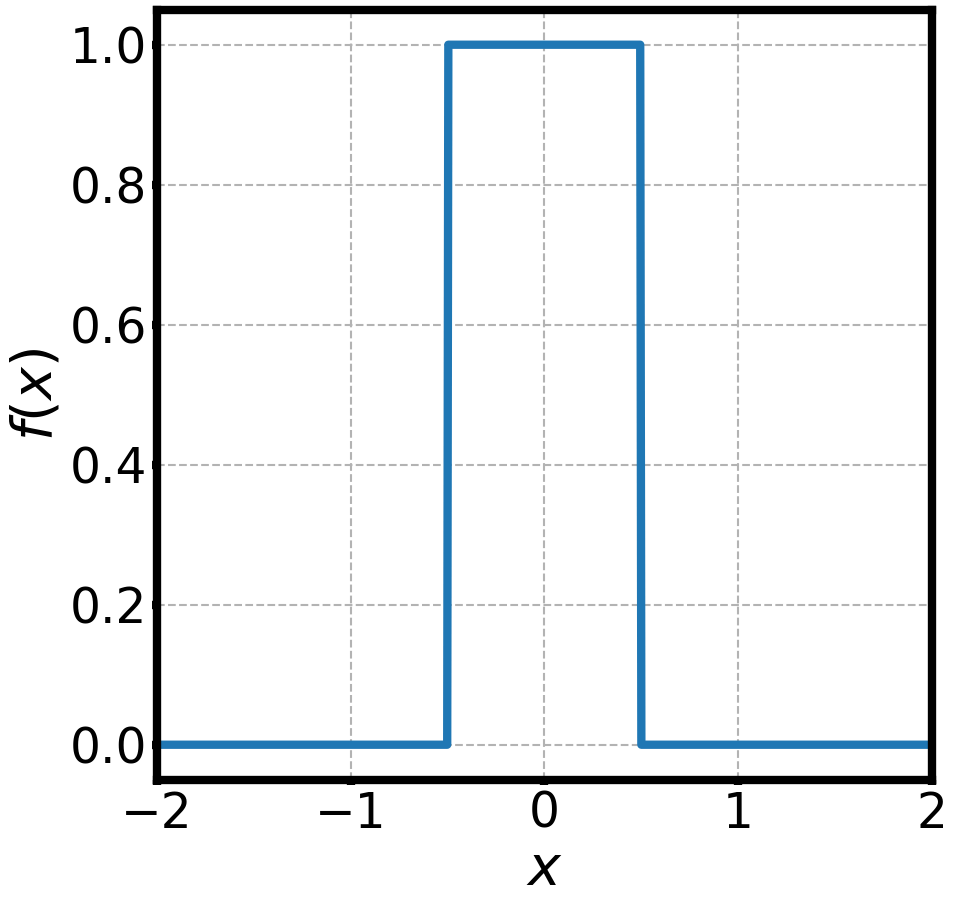
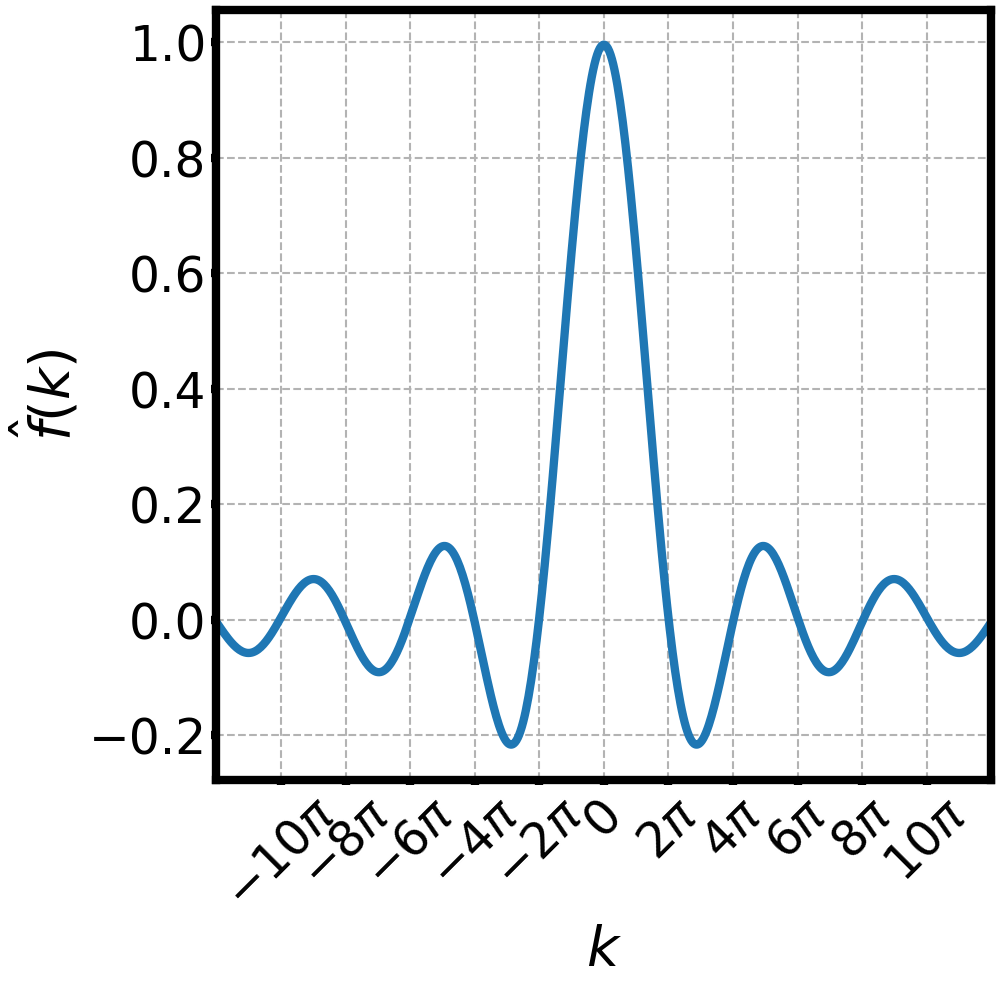
is a well behaved function
is its Fourier transform
is its inverse Fourier transform
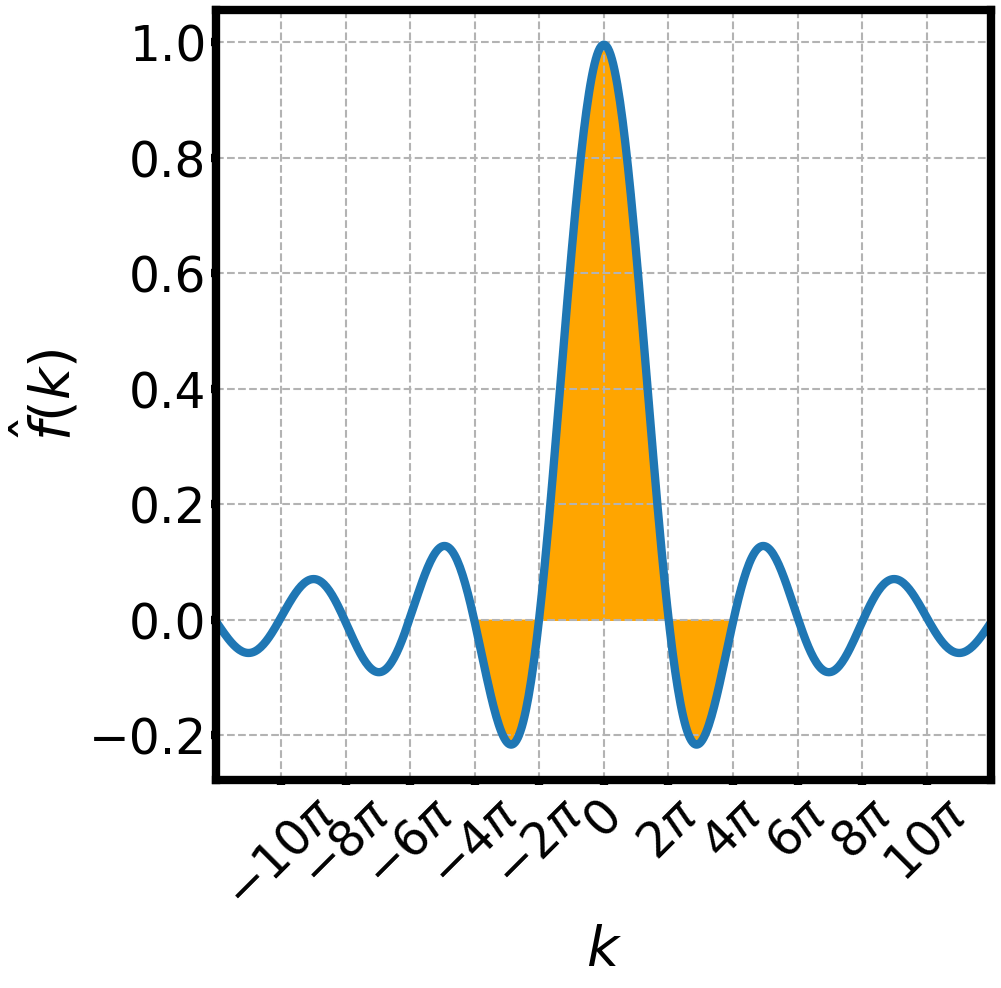
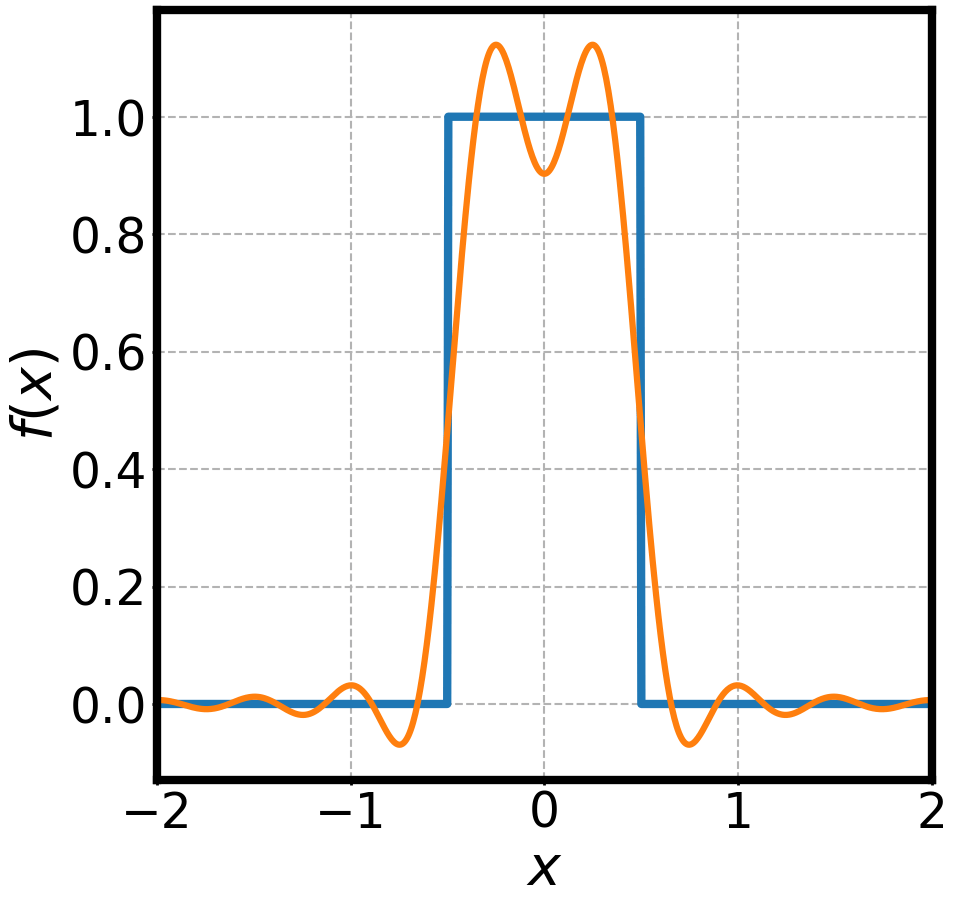
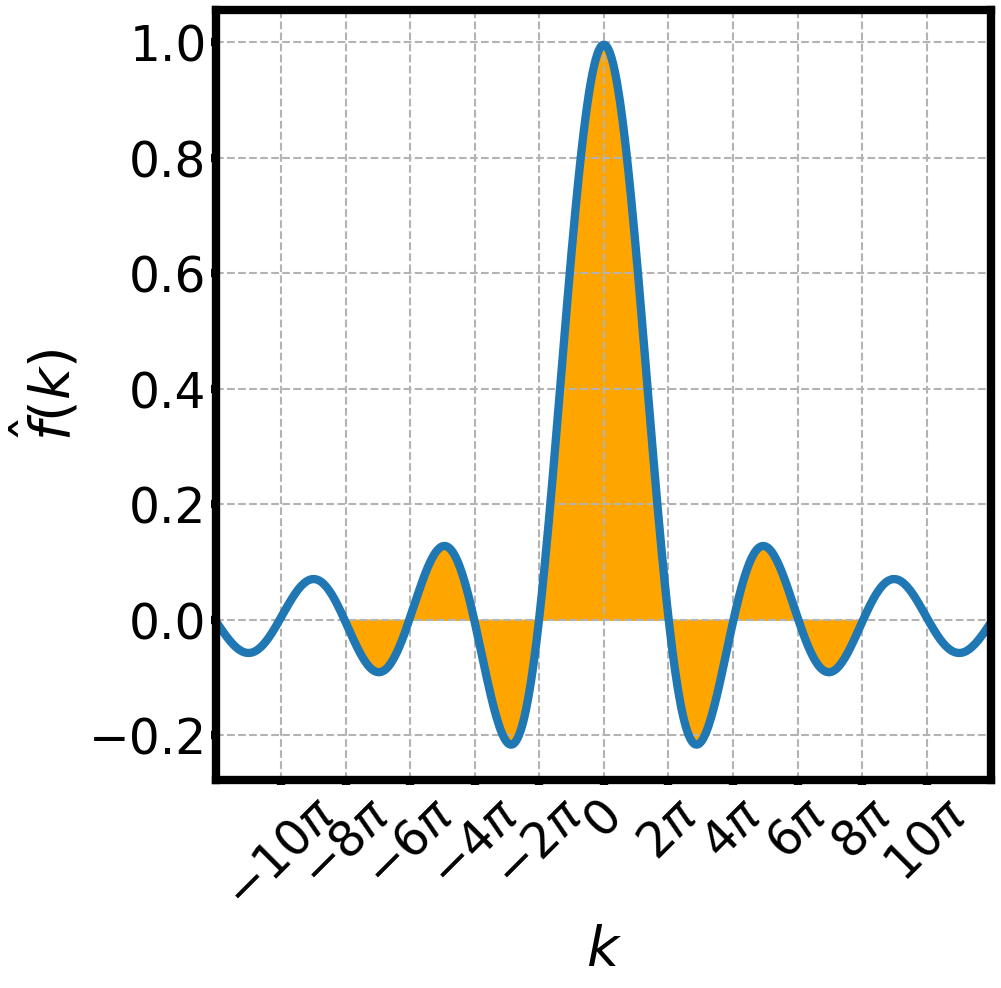
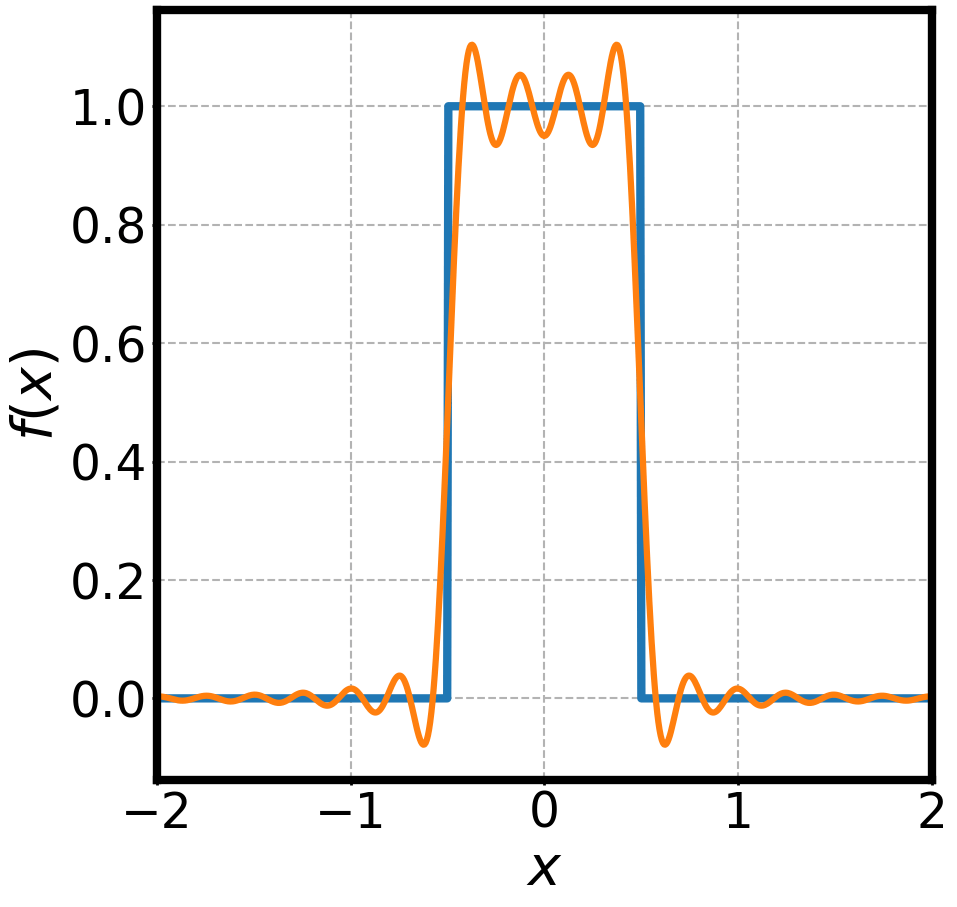
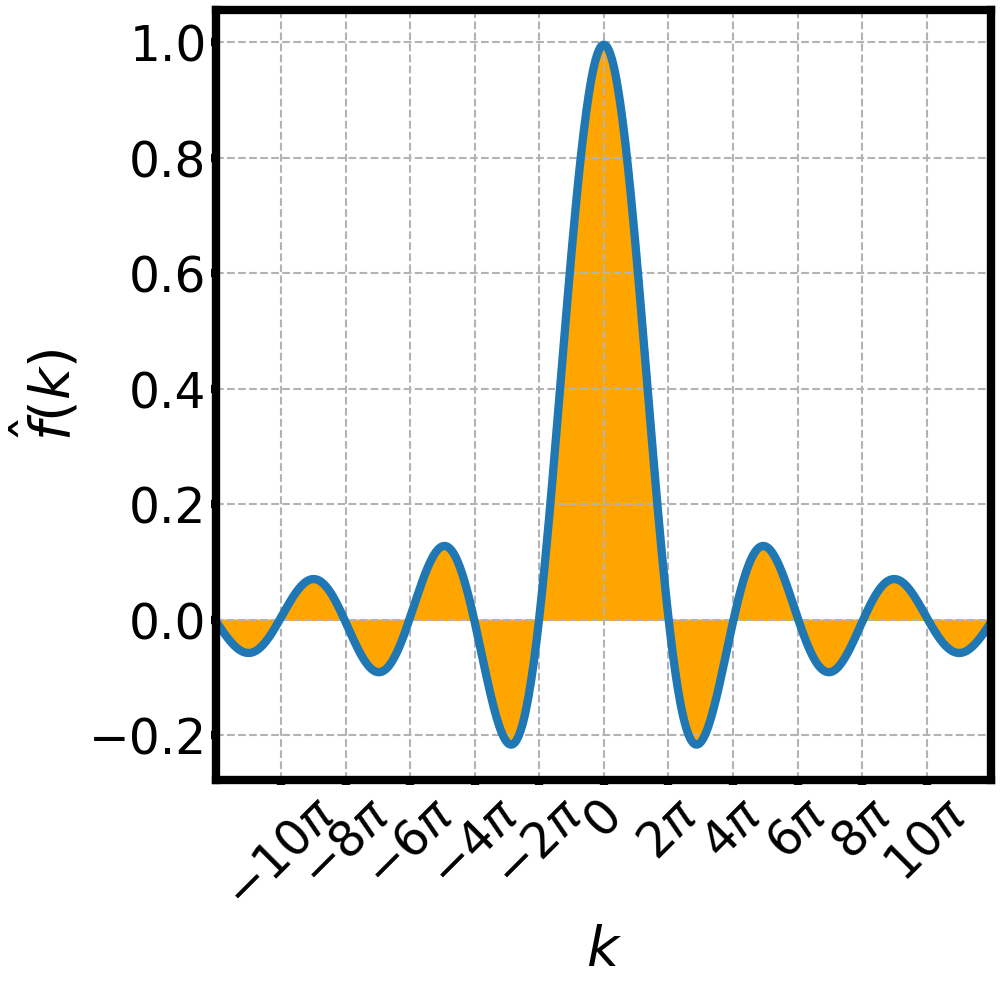
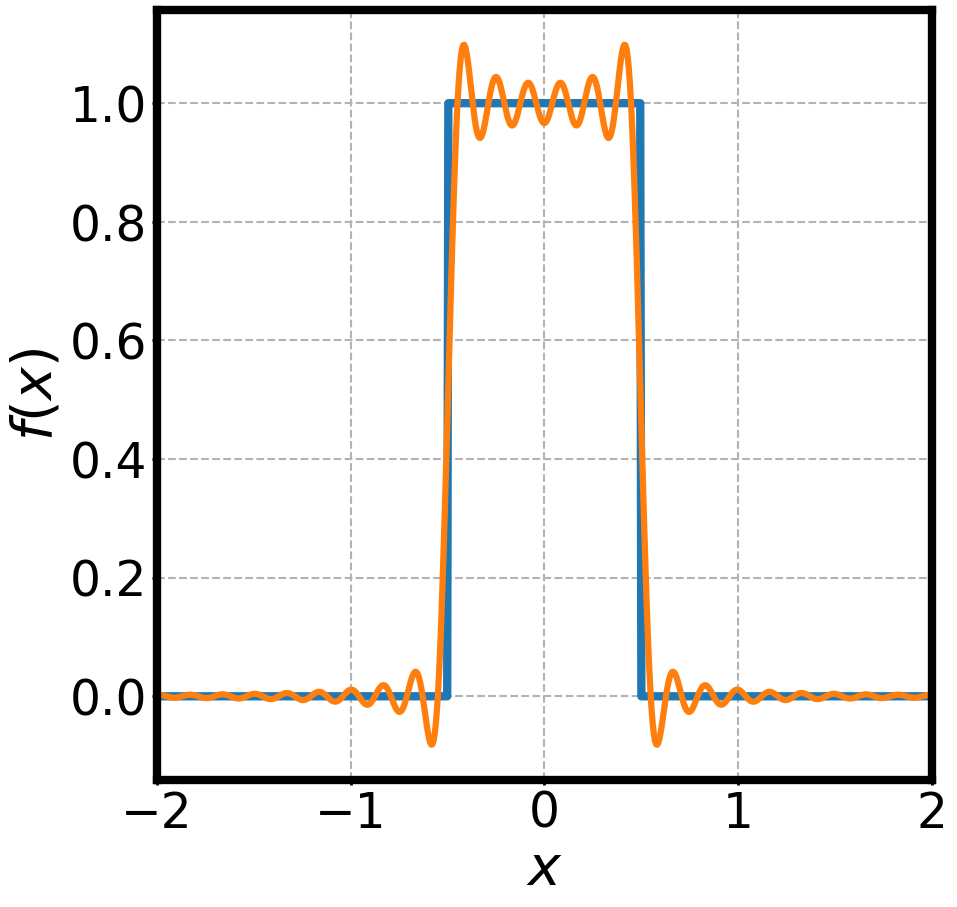
WAVES AND FOURIER TRANSFORMS
WAVES AND FOURIER TRANSFORMS
is a well behaved function
is its Fourier transform
is its inverse Fourier transform
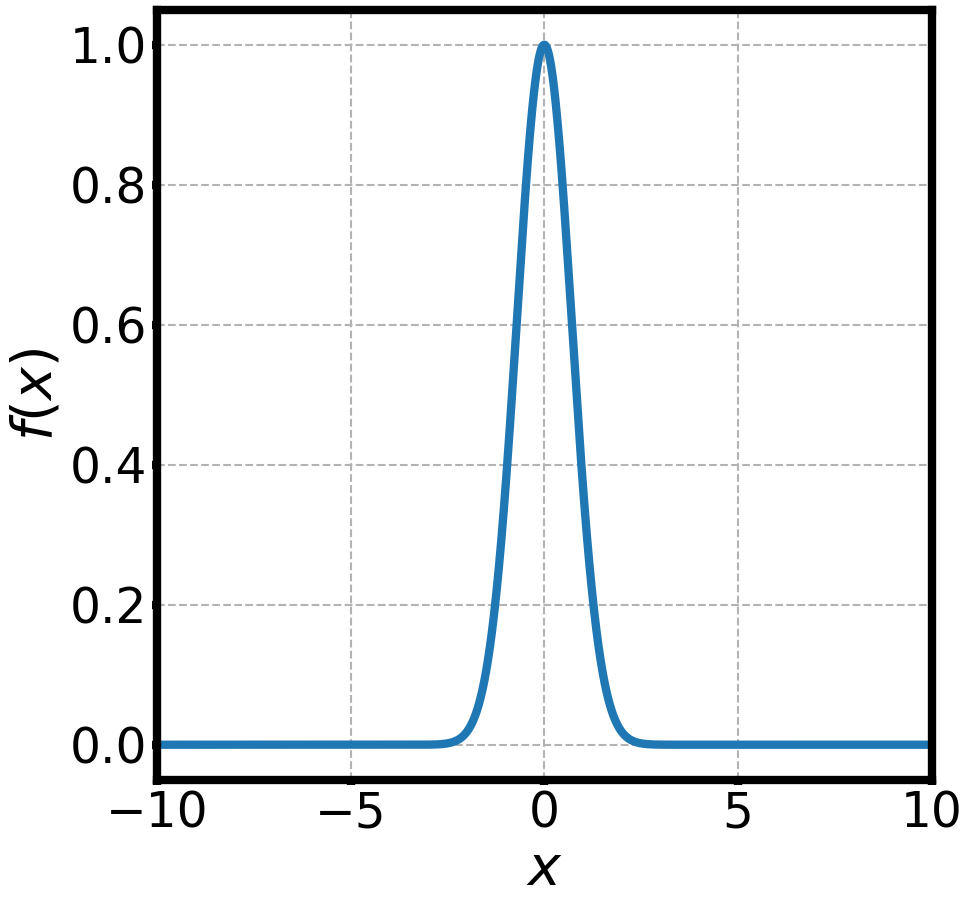
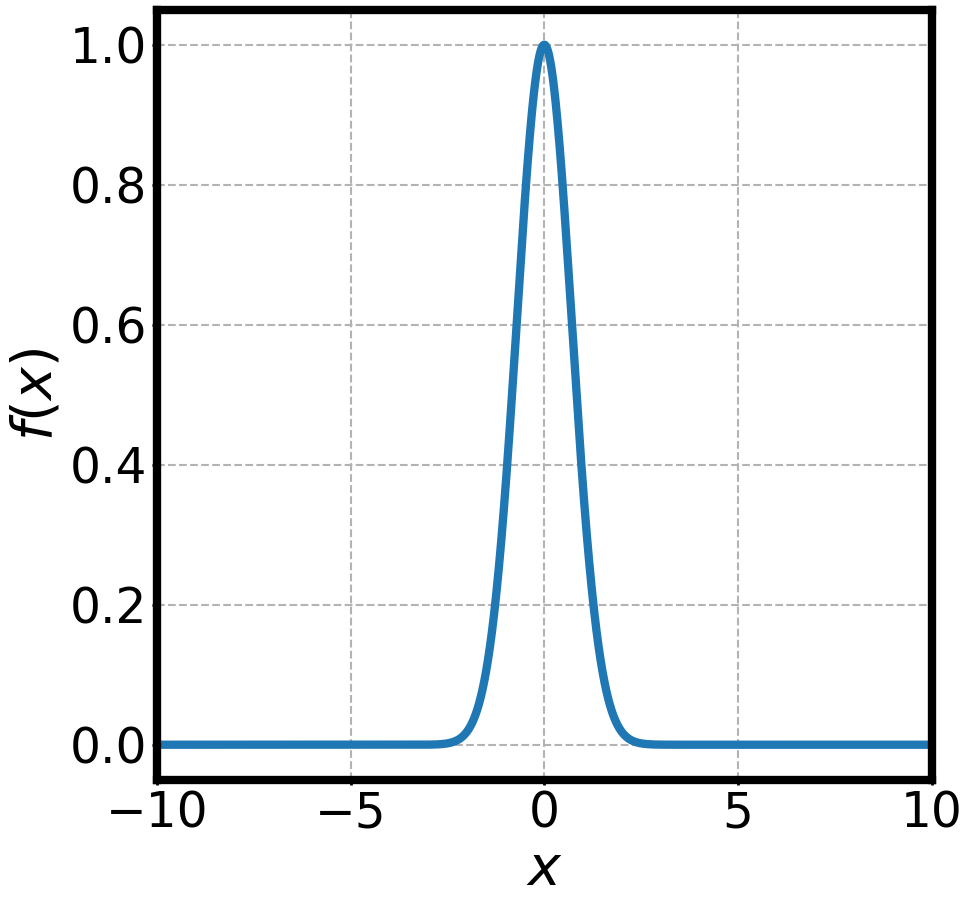
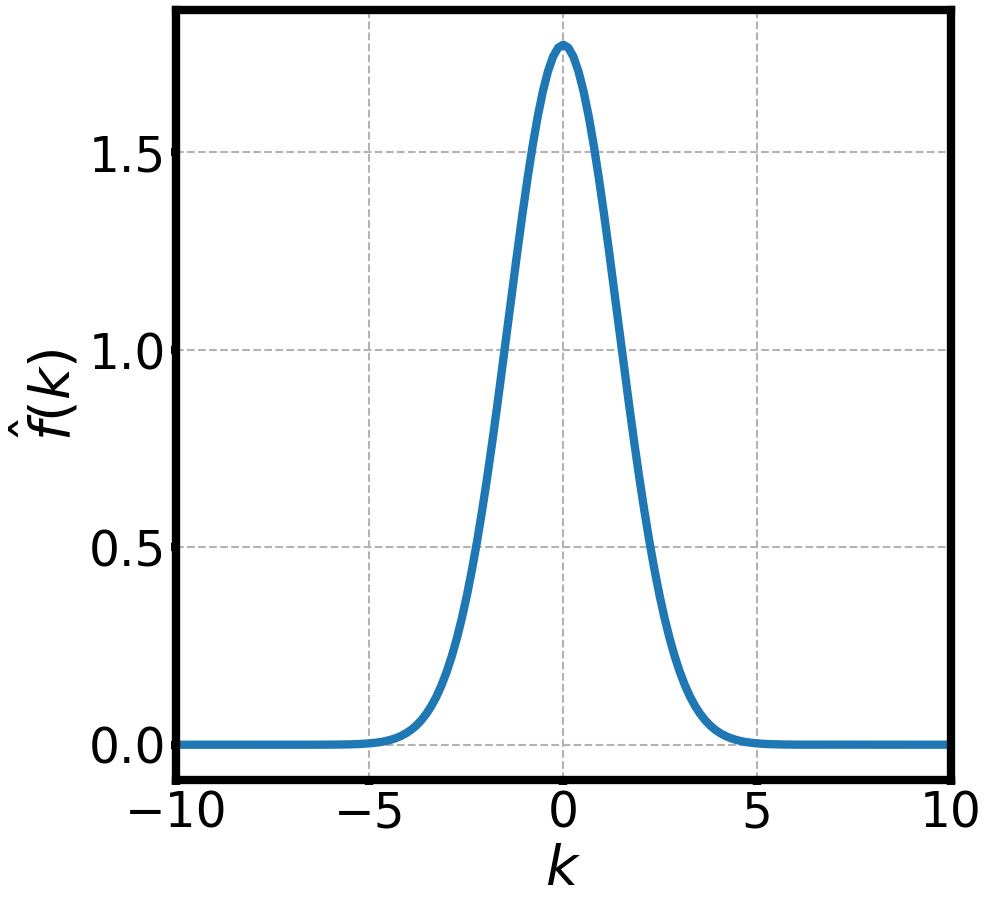
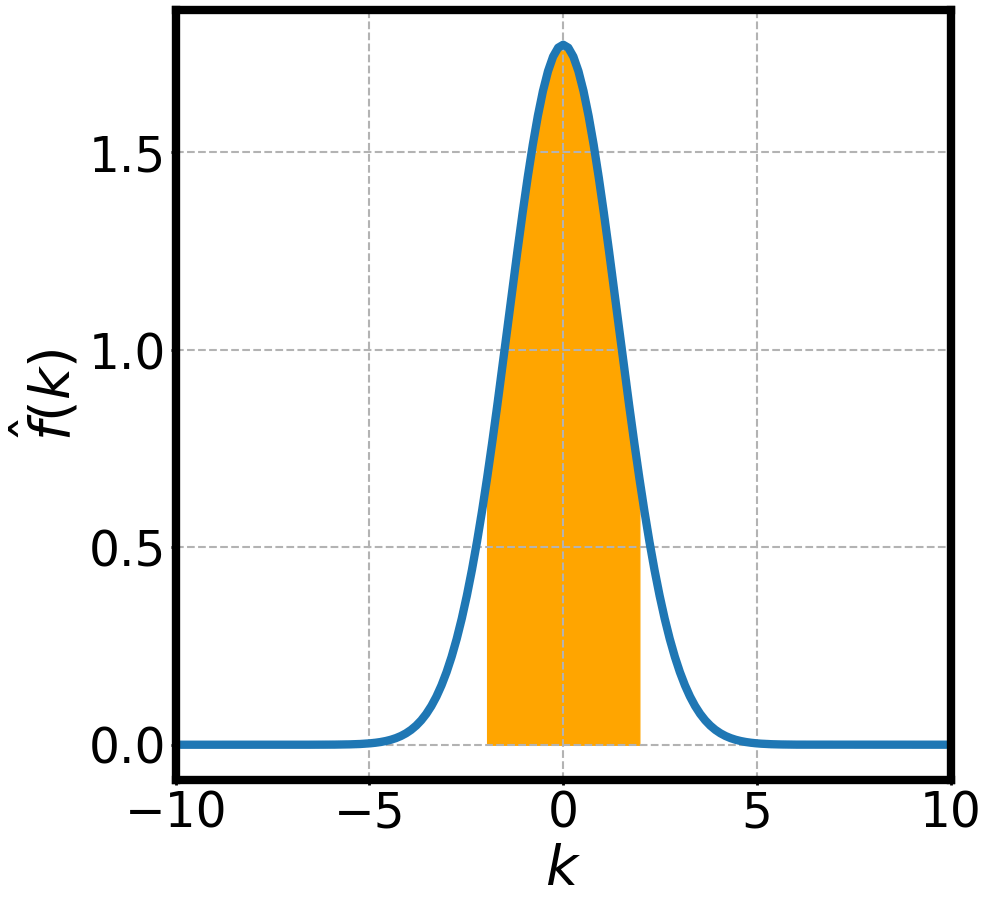
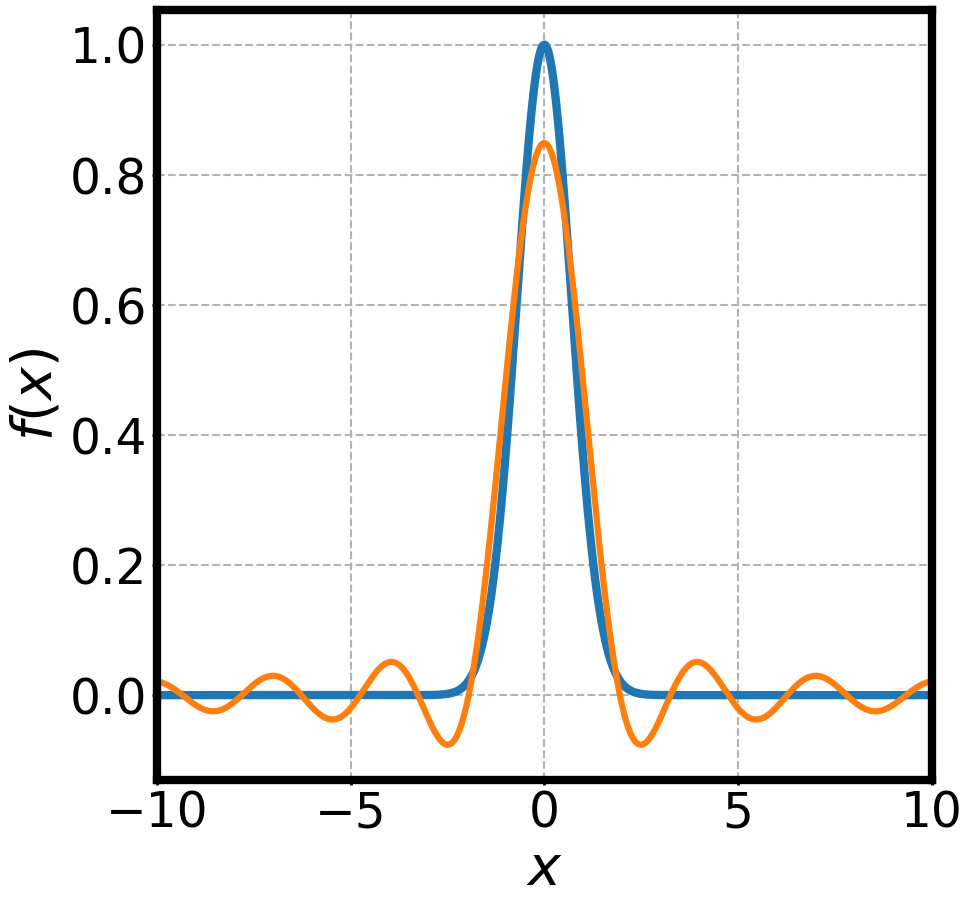
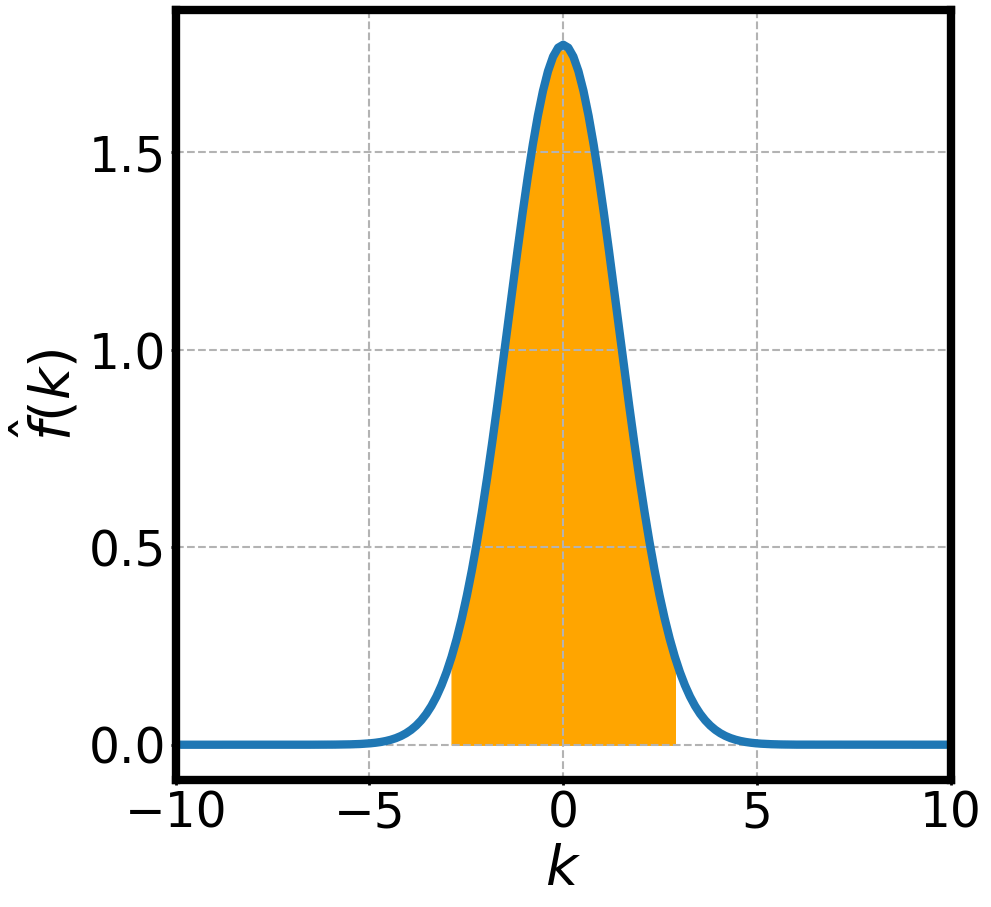
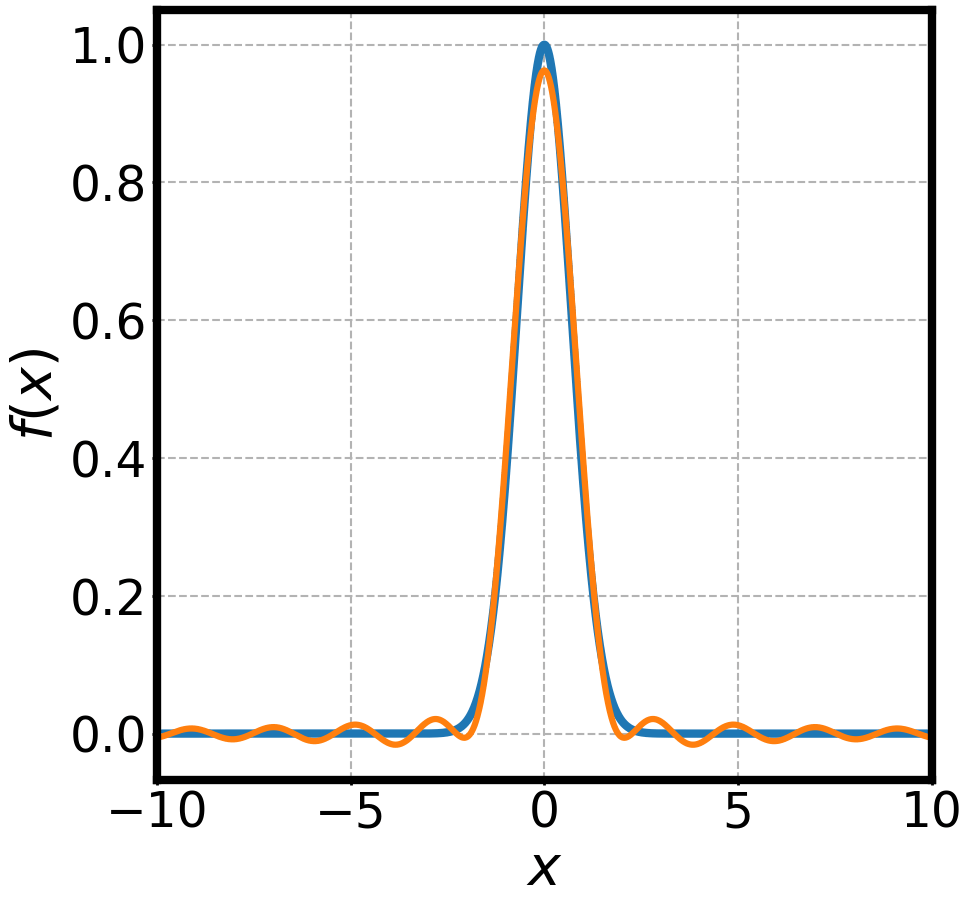
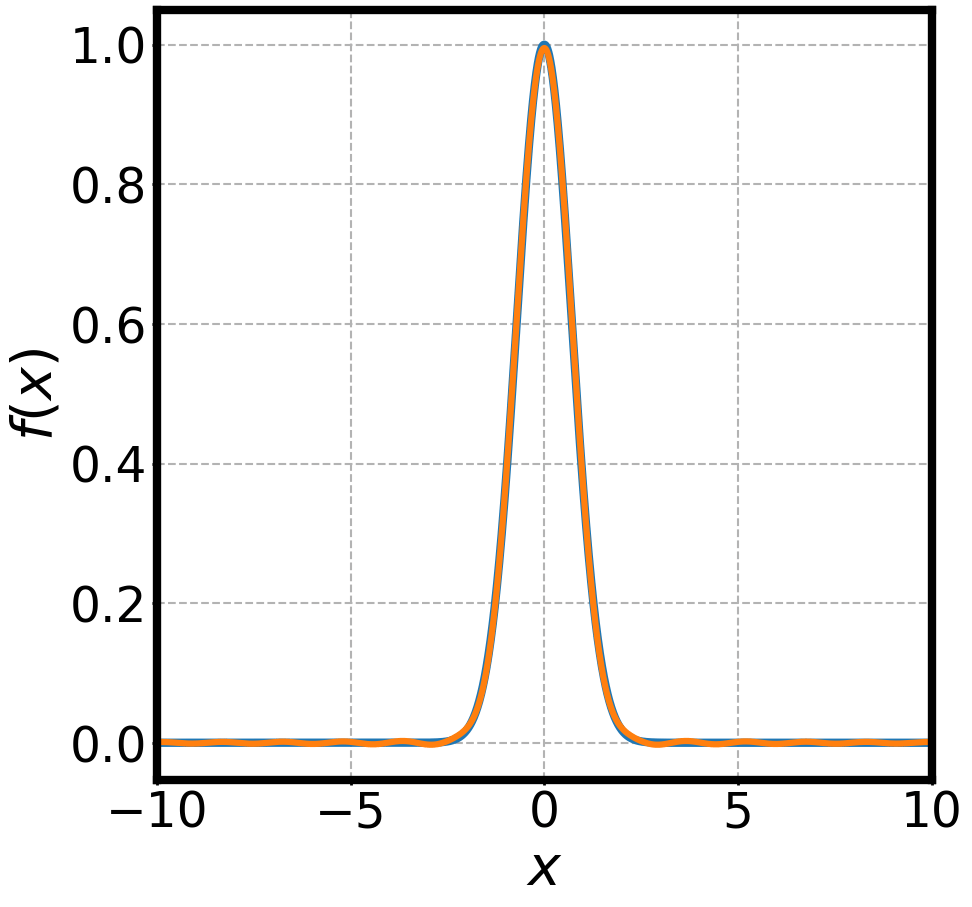
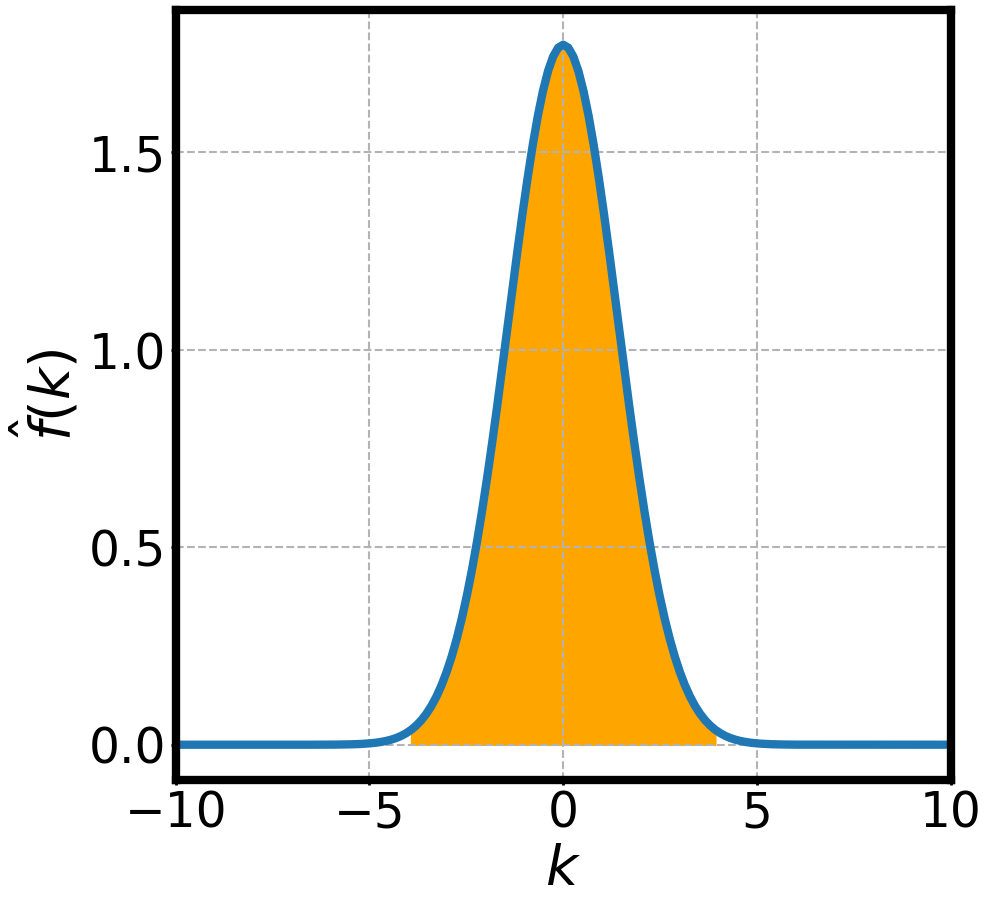
NON-DISPERSIVE WAVES PACKETS AND FOURIER TRANSFORMS
Group Velocity
NON-DISPERSIVE WAVES PACKETS AND FOURIER TRANSFORMS
DISPERSIVE WAVES PACKETS
Materials and Platforms for AI - Wave Theory
By Giovanni Pellegrini
Materials and Platforms for AI - Wave Theory
- 97



