OPTIMIZATION, NEURAL NETWORKS AND INVERSE DESIGN
FROM NANOPHOTONICS TO COMPUTATIONAL IMAGING


Giovanni Pellegrini @

WHO AM I?
Giovanni Pellegrini
Associate Professor - Physics Department - University of Pavia
Research Interests
- Computational Nanophotonics
- Machine Learning and Optimization for Nanophotonics
- Machine Learning for Image Reconstruction
- Machine Learning for Signal Processing
Also interested in
- Industrial Automation and Robotics
- Deep Learning for Machine Vision
- Both @ Sinteco Robotics

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
OPTIMIZATION, NEURAL NETWORKS AND INVERSE DESIGN
FROM NANOPHOTONICS TO COMPUTATIONAL IMAGING
GENETIC MULTI-OBJECTIVE OPTIMIZATION FOR INVERSE DESIGN OF 1DPC
SUPERVISED NEURAL NETWORKS FOR DIRECT AND INVERSE DESIGN OF NANOHOLE ARRAYS
SUPERVISED, PHYSICS INFORMED NEURAL NETWORKS FOR PHASE RETRIEVAL
UNSUPERVISED, PHYSICS INFORMED NEURAL NETWORKS FOR PTYCHOGRAPHY


Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
GENETIC MULTI-OBJECTIVE OPTIMIZATION FOR INVERSE DESIGN OF 1D PHOTONIC CRYSTALS


Giovanni Pellegrini, Jonathan J. Barolak, Marco Finazzi, Michele Celebrano, F. Michelotti, A. Occhicone and Paolo Biagioni




Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
CHIRALITY (IN NATURE)
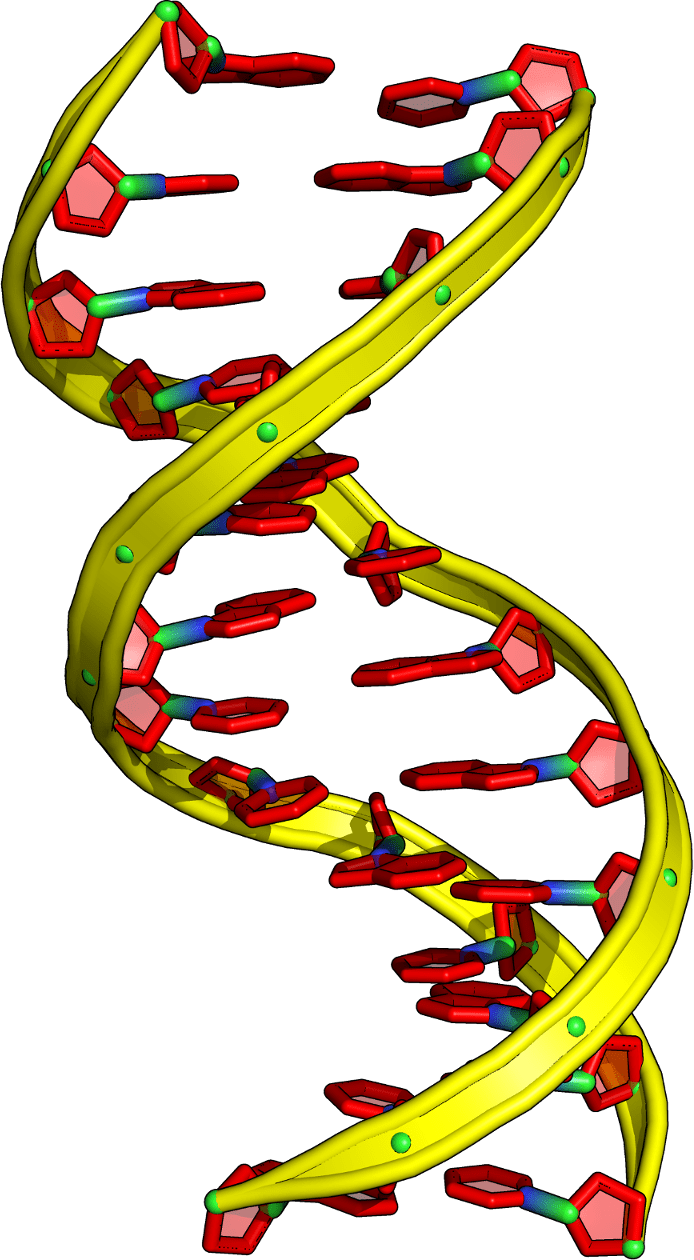
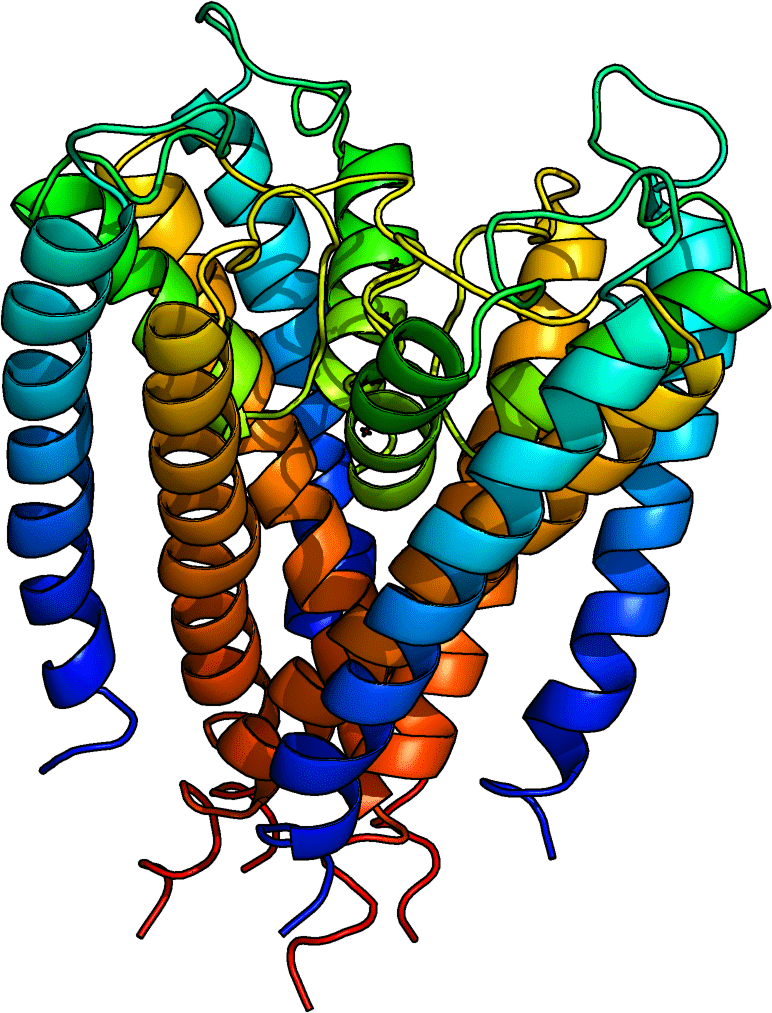
Molecules
DNA
Proteins
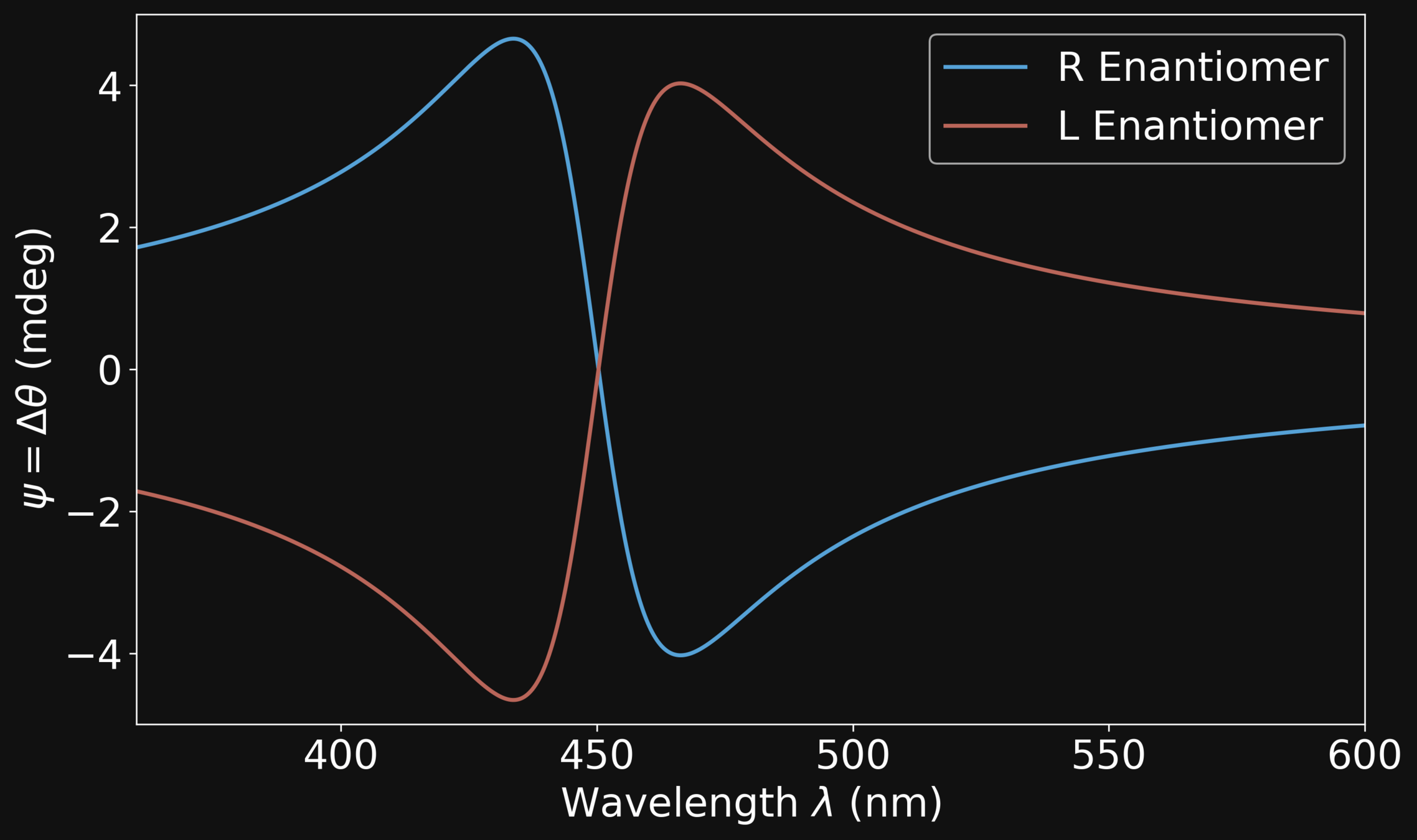
L Enantiomer
R Enantiomer

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
PROBING CHIRALITY WITH ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS
TE Polarization
TM Polarization
Left = TE + i*TM
Right = TE - i*TM
Circular Dichroism (CD)
Optical Rotation (\(\psi\))
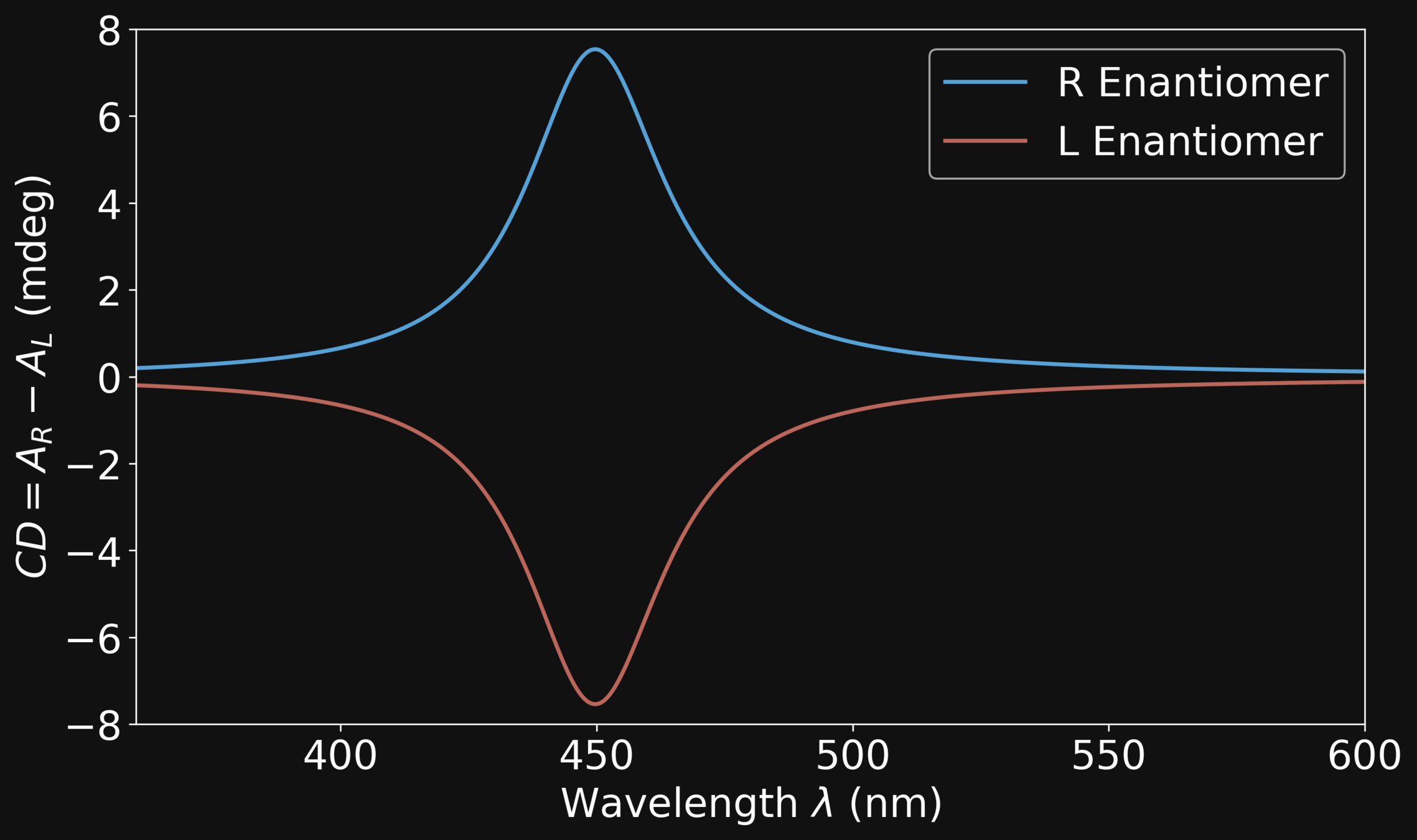
\[\mathrm{CD = A_{R}-A_{L}}\]
\[\mathrm{\psi = \Delta \theta} \]

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
SUPERCHIRAL LIGHT
Local optical chirality
Optical chirality enhancement
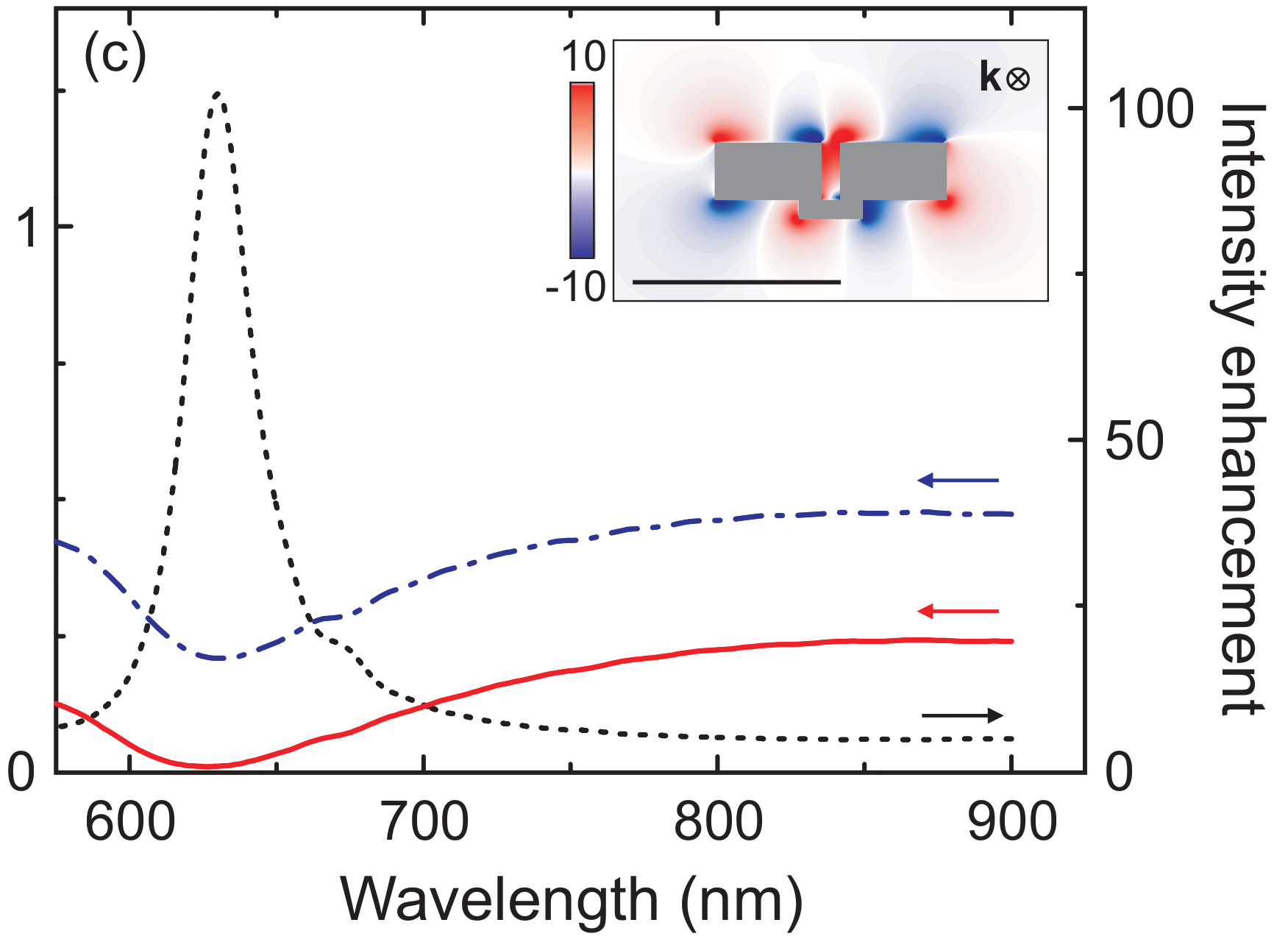
Finazzi, Marco, et al. "Quasistatic limit for plasmon-enhanced optical chirality." Physical Review B 91.19 (2015): 195427.
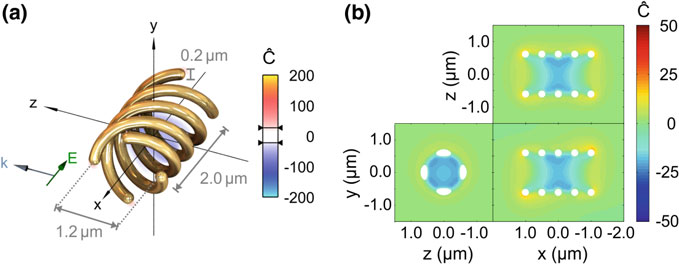
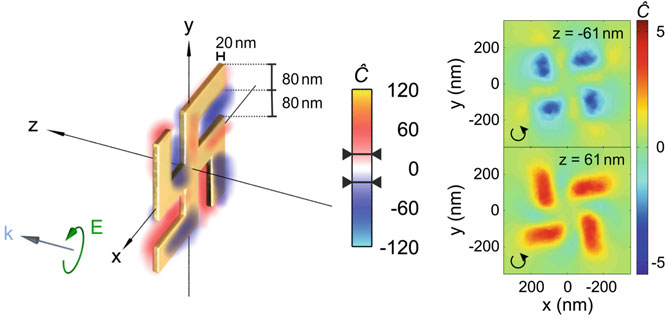
Schäferling, Martin. "Chiral nanophotonics." Springer Series in Optical Sciences 205 (2017): 159.
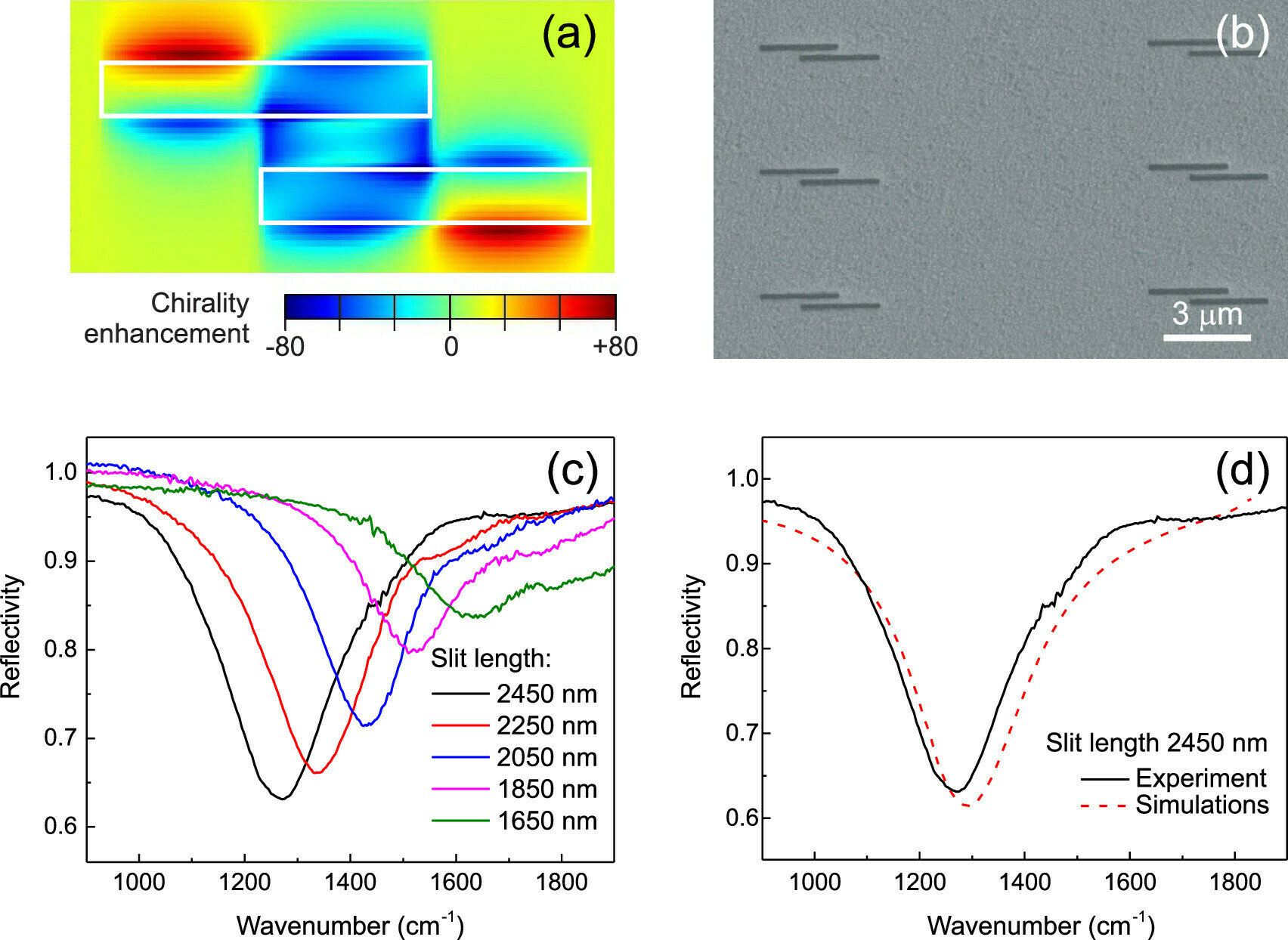
Mattioli, F. et al. Plasmonic Superchiral Lattice Resonances in the Mid-Infrared. ACS Photonics 7, 2676–2681 (2020)

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
SUPERCHIRAL LIGHT WITH A PLANAR GEOMETRY
-
Large optical chirality enhancement
-
Uniformity over large areas
-
Optical chirality switching
-
Broadband operation
-
Flat spectral response
Planar Geometries as an Ideal Candidate

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
A PLANAR GEOMETRY FOR SUPERCHIRAL LIGHT: TAKE 1
TE ± i*TM
TE ± i*TM
Surface Plasmon

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
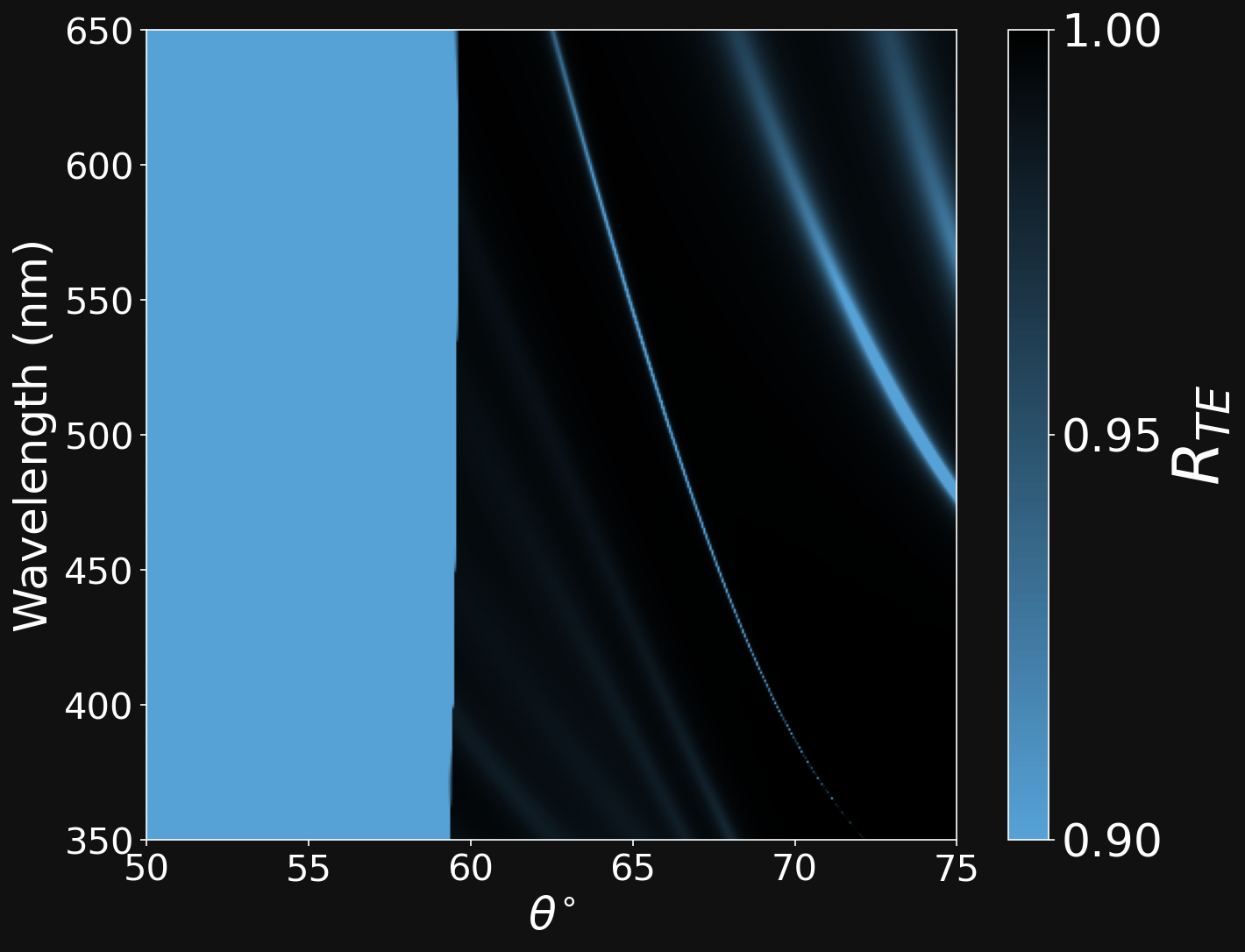
A PLANAR GEOMETRY FOR SUPERCHIRAL LIGHT: TAKE 2

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
\[ \mathrm{ (\lambda_{TM},\theta_{TM})} \]
\[ \mathrm{ (\lambda_{TE},\theta_{TE})} \]
\[ \mathrm{ (\lambda_{TM},\theta_{TM})} \neq \mathrm{ (\lambda_{TE},\theta_{TE})} \]
Bloch Surface Waves (BSW)
TE ± i*TM
TE ± i*TM

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
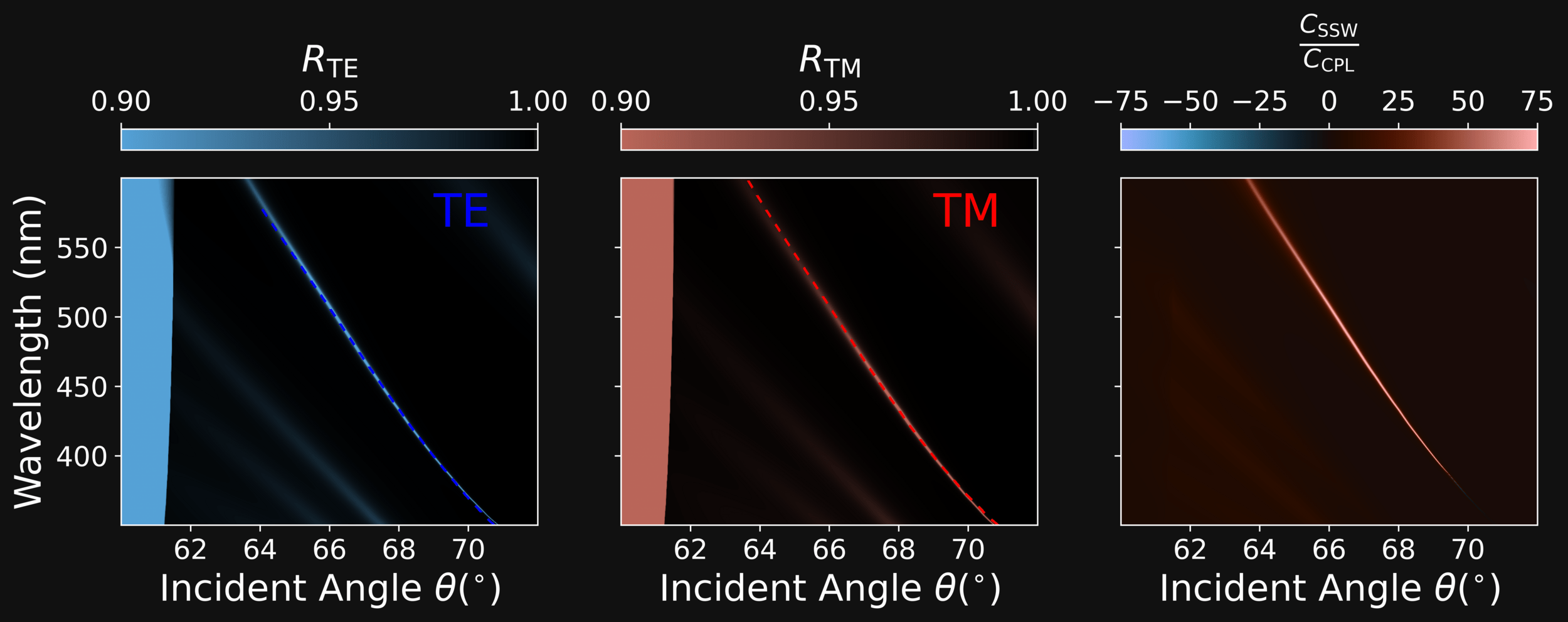
ALIGNING THE DISPERSION RELATIONS
\[ \mathrm{ (\lambda_{TM},\theta_{TM})} \neq \mathrm{ (\lambda_{TE},\theta_{TE})} \]
\[ \mathrm{ (\lambda_{TM},\theta_{TM})} = \mathrm{ (\lambda_{TE},\theta_{TE})} \]
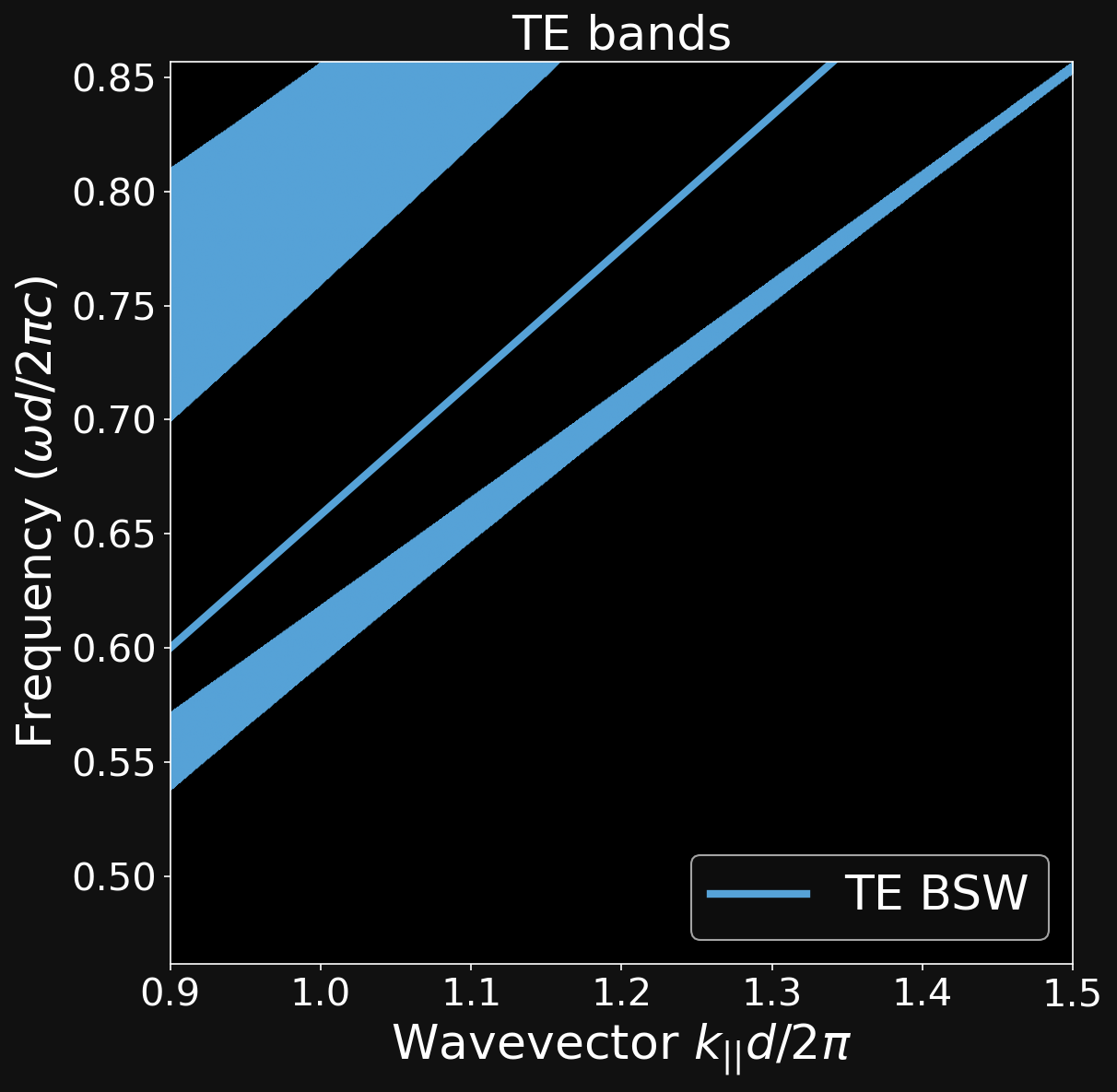
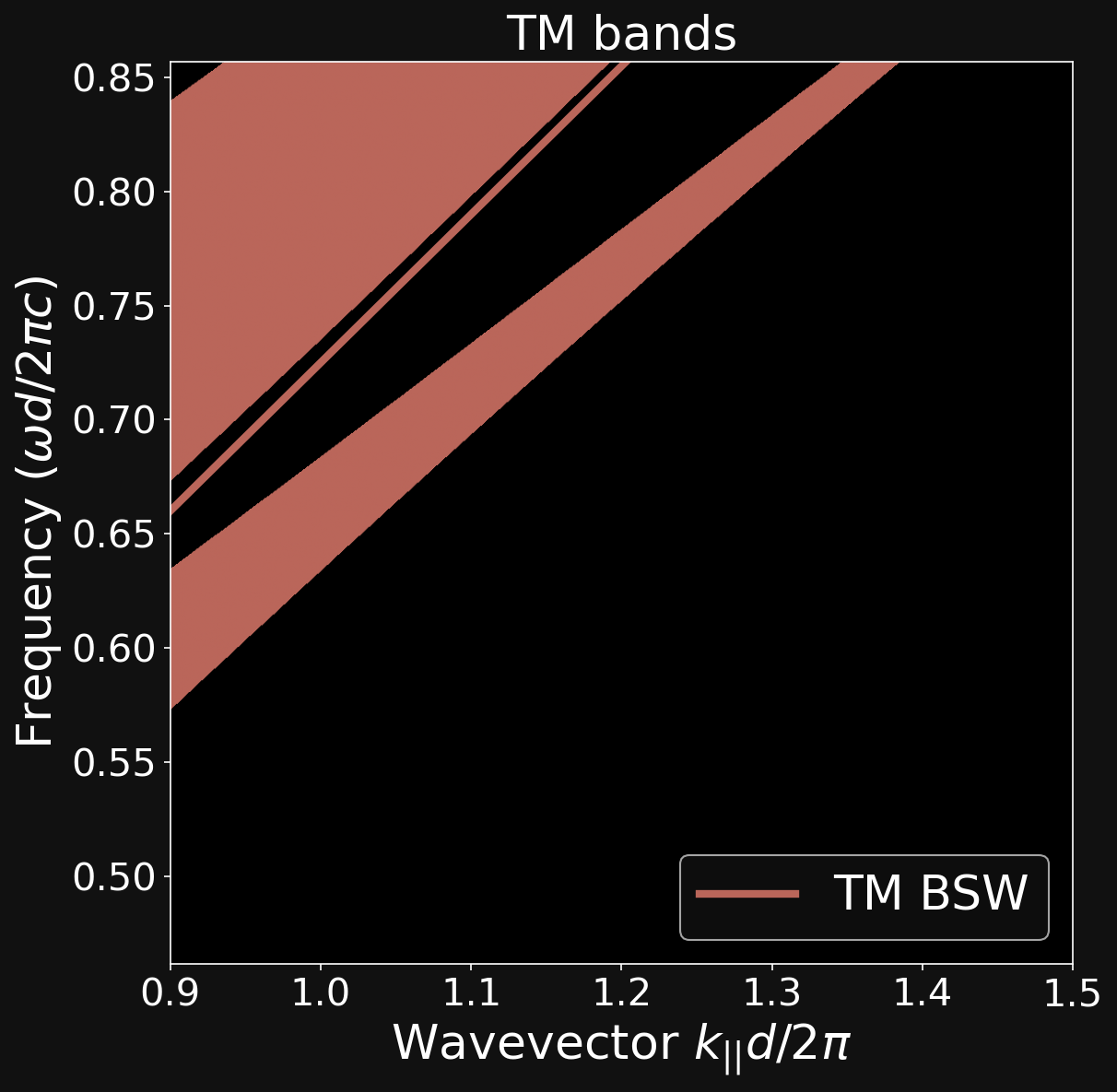
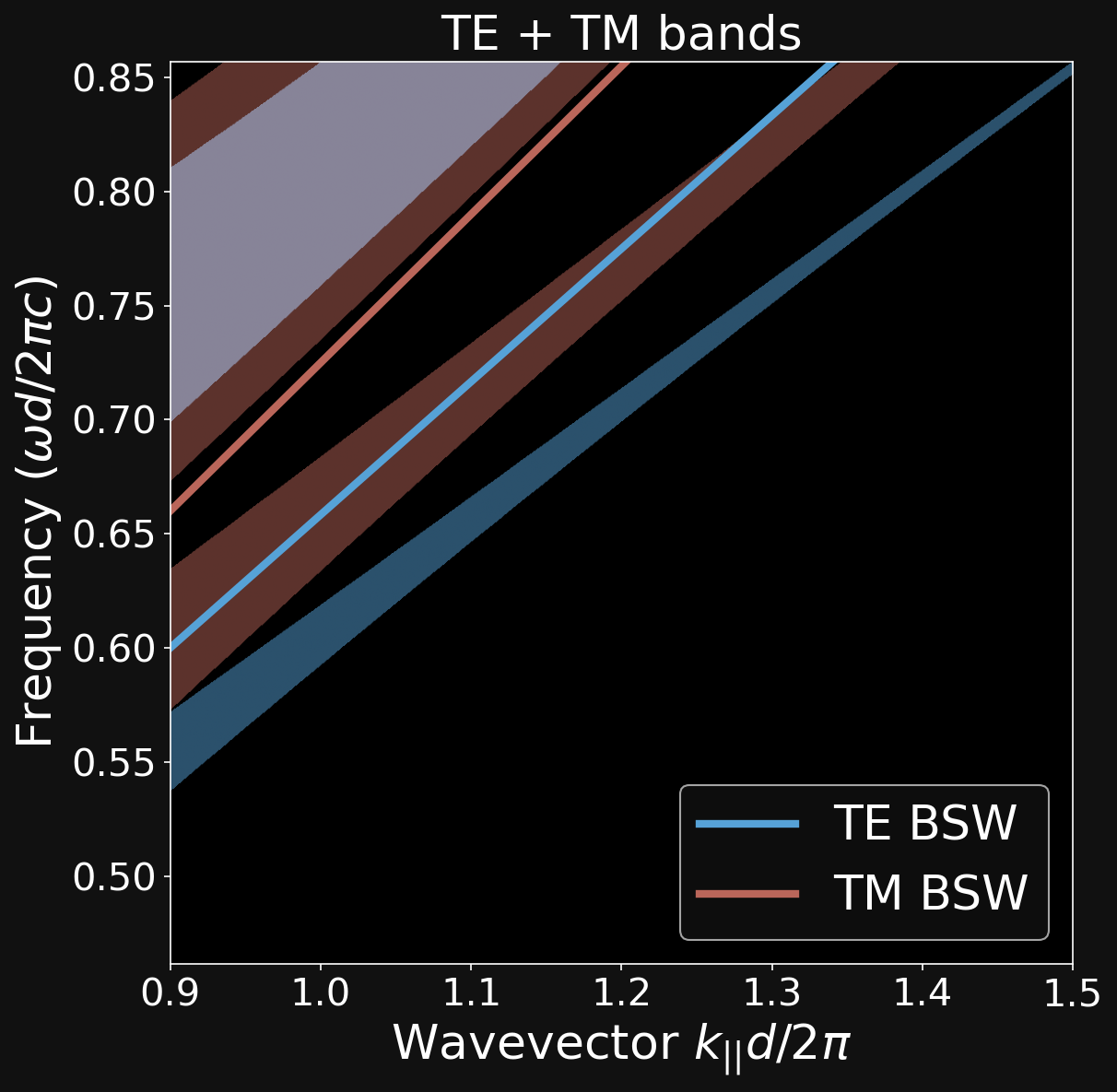
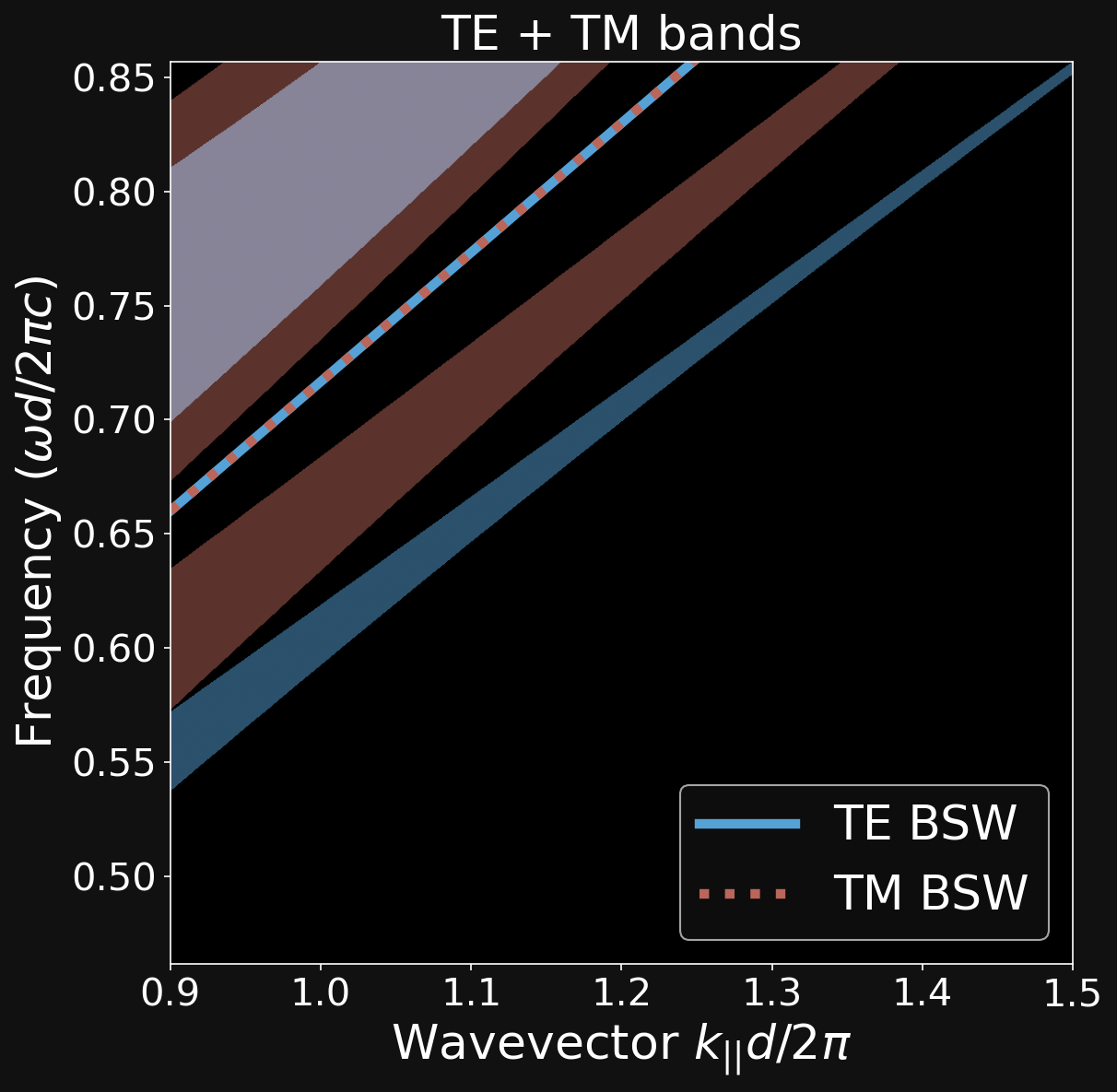

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
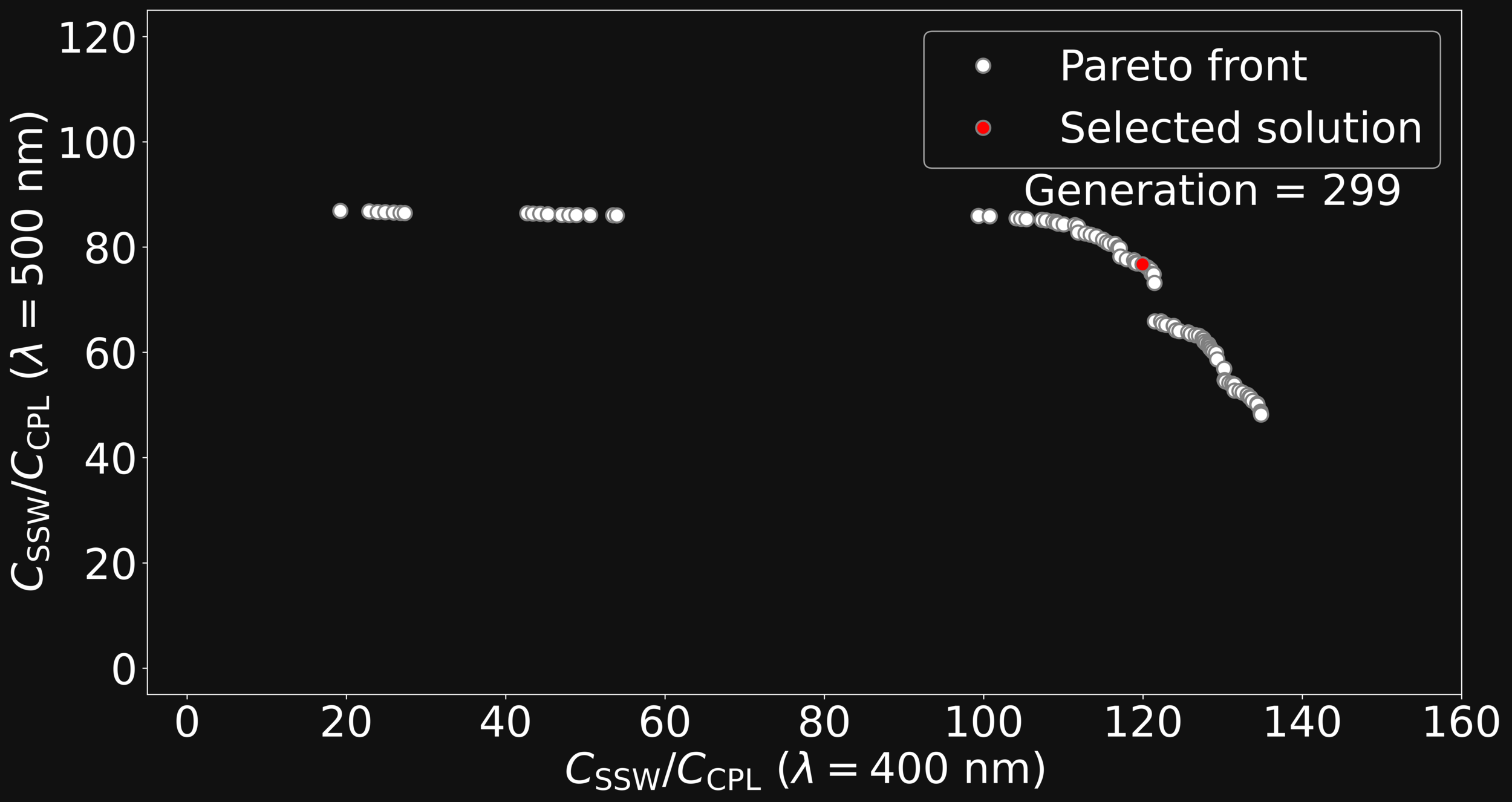
AN INVERSE DESIGN SOLUTION
GENETIC MULTI OBJECTIVE OPTIMIZATION

Maximize \(C \)
@ \(\omega_1\) and \(\omega_2\)
@ the 1DPC Surface
SIMULTANEOUSLY!!!
Band Alignement

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
GENETIC MULTI-OBJECTIVE OPTIMIZATION: NSGAII

Vilfredo Pareto
Mixing
Mutation
Selection
1st Gen.
2nd Gen.
n-th Gen.
Evolution

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
GENETICALLY EVOLVED (NSGAII) SiO₂-Ta₂O₅ 1PDC
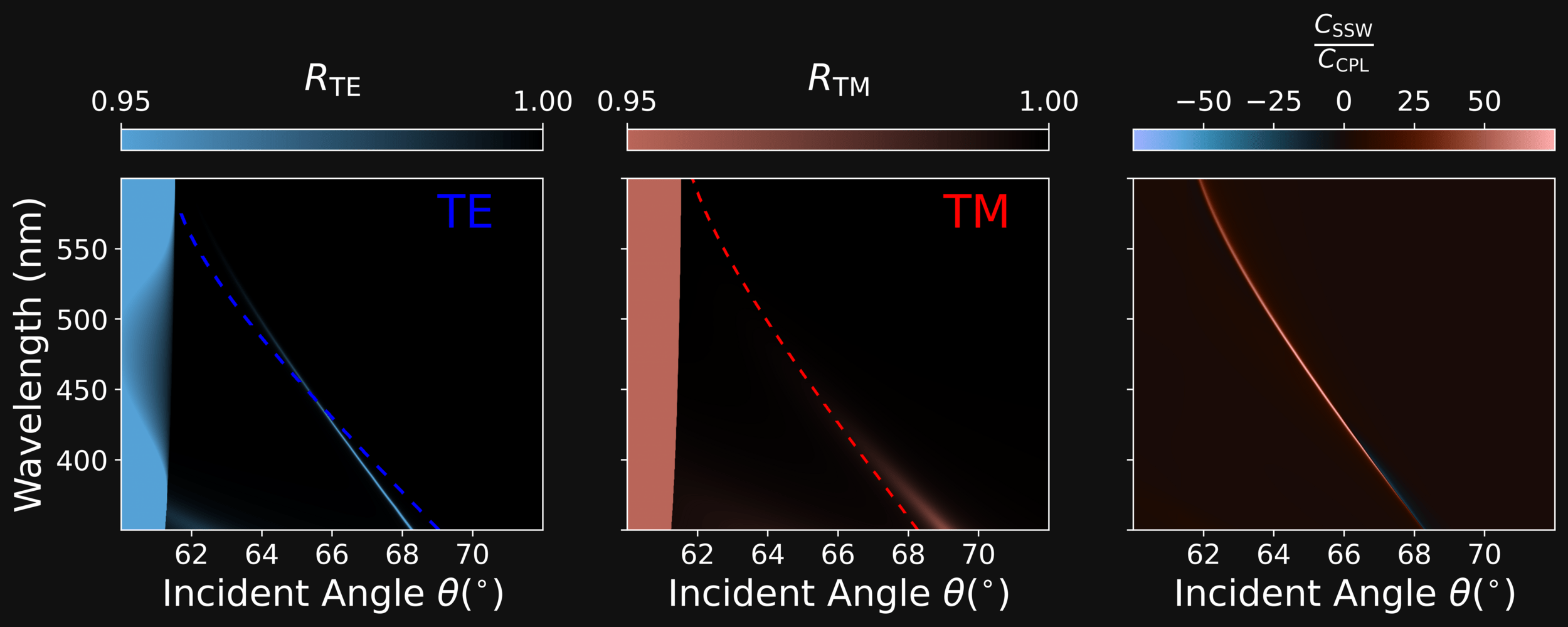
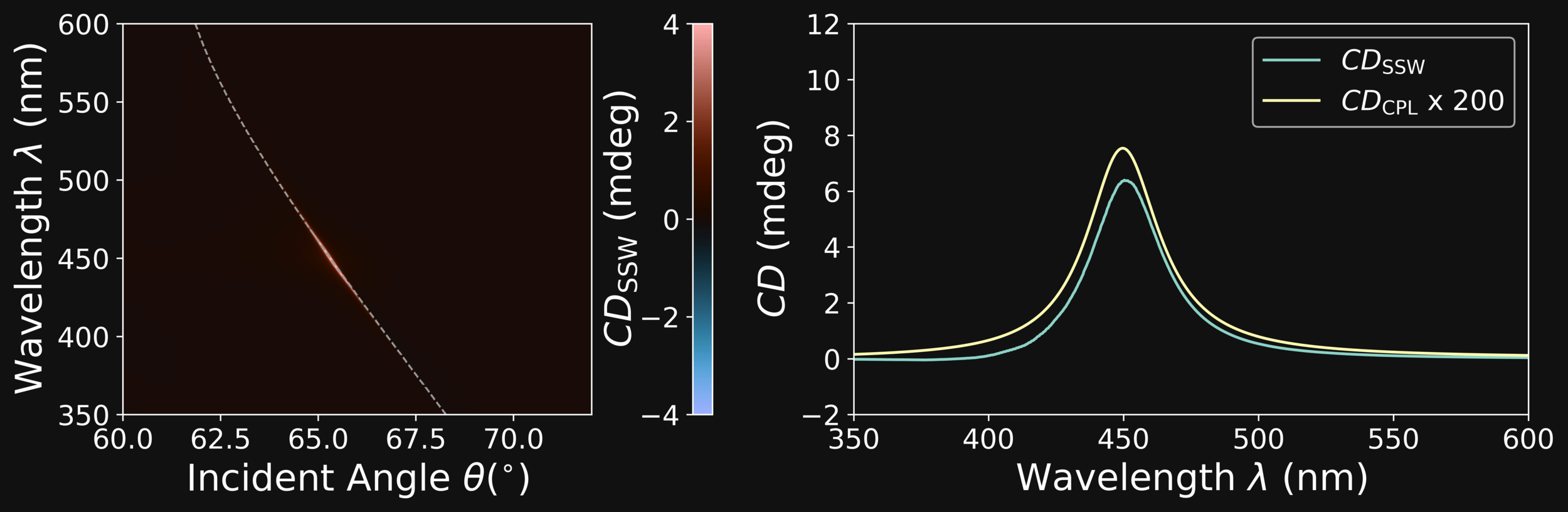
SiO\(_{2}\)
Ta\(_{2}\)O\(_{5}\)
SiO\(_{2}\)
Ta\(_{2}\)O\(_{5}\)

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
GENETICALLY EVOLVED (NSGAII) SIO2-SIOX 1PDC
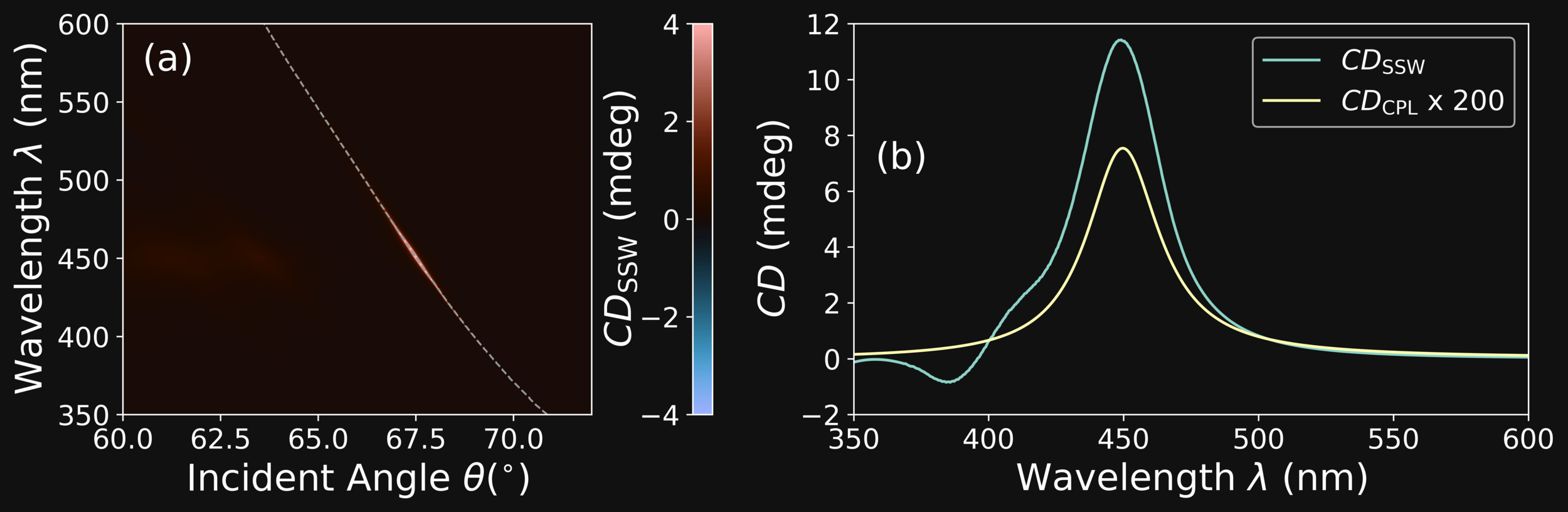
SiO\(_{2}\)
SiO\(_{x}\)
SiO\(_{2}\)
SiO\(_{x}\)

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
GENETICALLY EVOLVED (NSGAII) POLYMERIC 1PDC
Cellulose
Polystyrene
Cellulose
Polystyrene
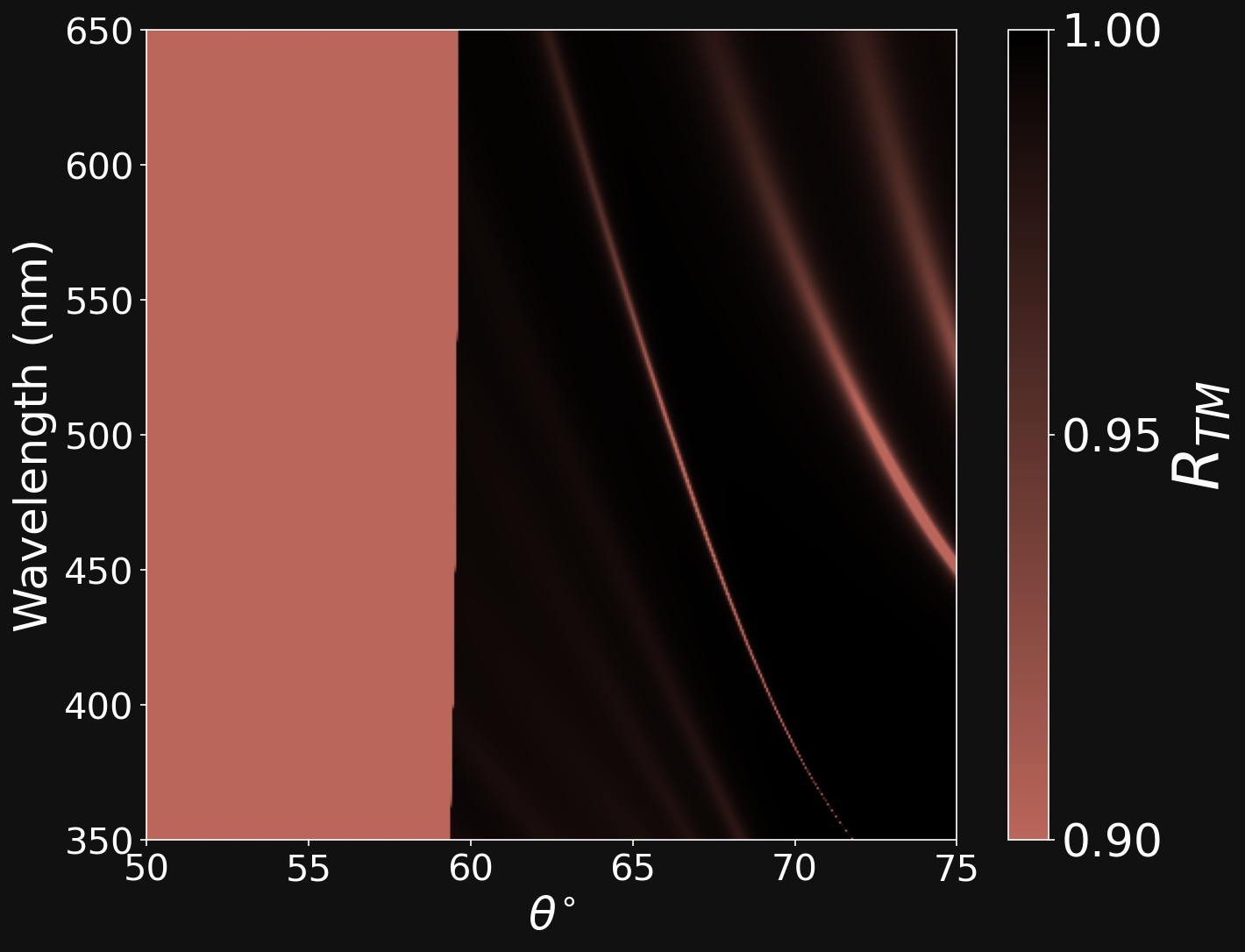
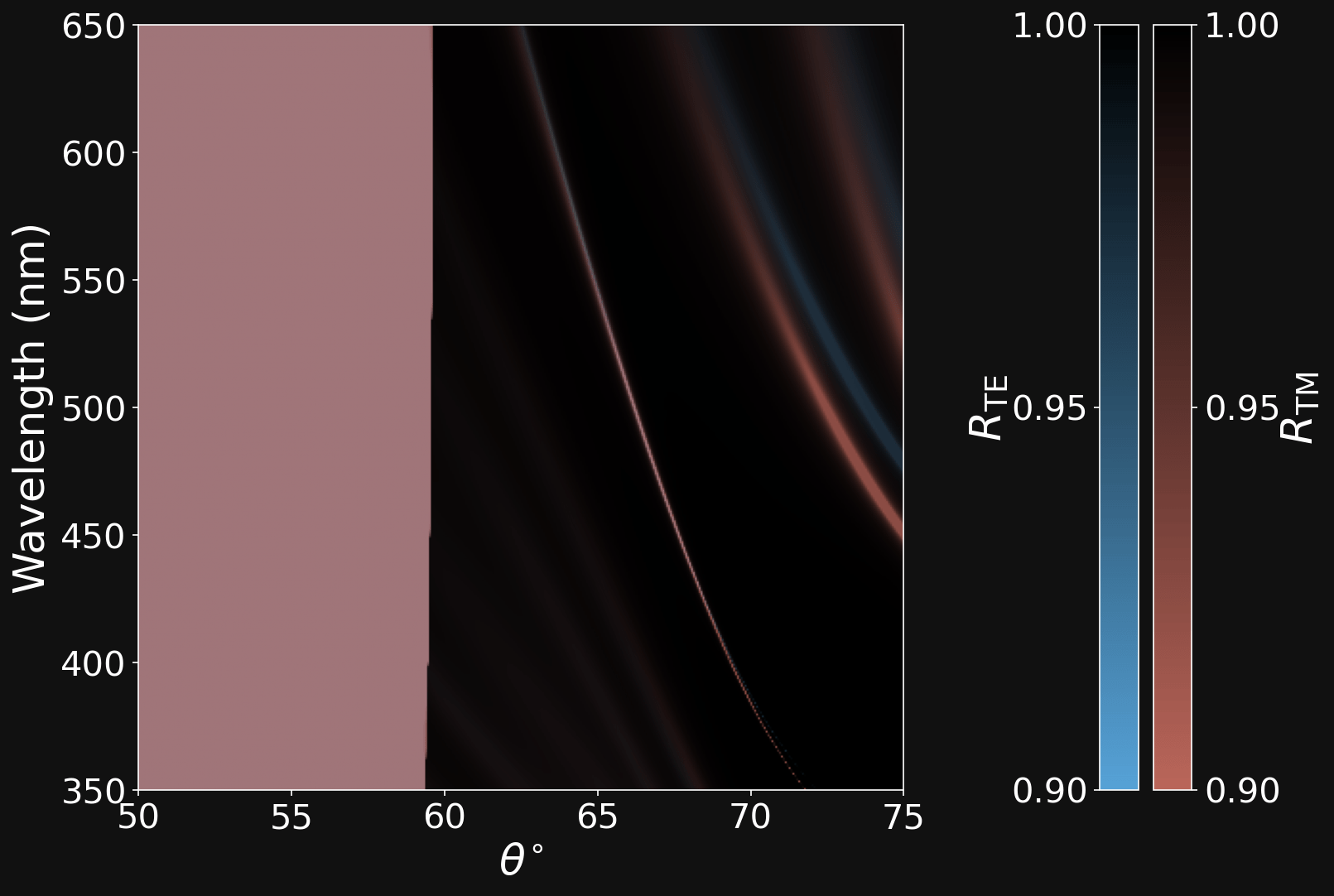
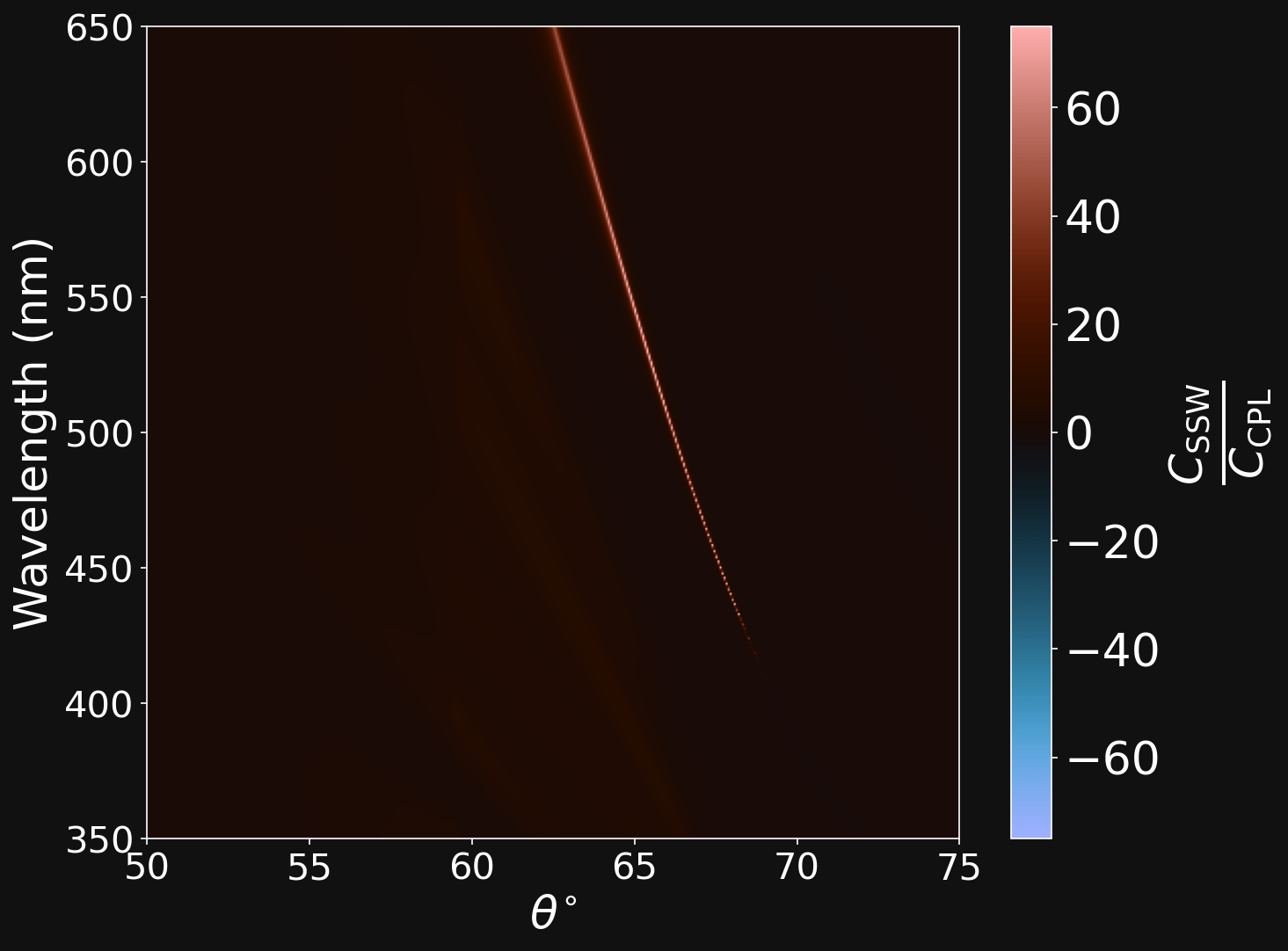

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
GENETIC MULTI-OBJECTIVE INVERSE DESIGN
FINAL CONSIDERATIONS
-
Multiple Objectives
-
Global
-
Robust
-
Flexible
-
Physical Insight


Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
SUPERVISED, PHYSICS INFORMED NEURAL NETWORKS FOR DIRECT AND INVERSE DESIGN OF NANOHOLE ARRAYS
| n.1 | n.2 | n.3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lattice | Hexagonal | Square | Square |
| Material | Ag | Au | SiOx |
| Thickness (nm) | 100 | 115 | 90 |
| Radius (nm) |
60 | 110 | 140 |
| Pitch (nm) |
450 | 550 | 515 |

DIRECT
INVERSE
Jahan, T. et al. Deep learning-driven forward and inverse design of nanophotonic nanohole arrays: streamlining design for tailored optical functionalities and enhancing accessibility. Nanoscale (2024) doi:10.1039/D4NR03081H.
Structural parameters
spectra

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
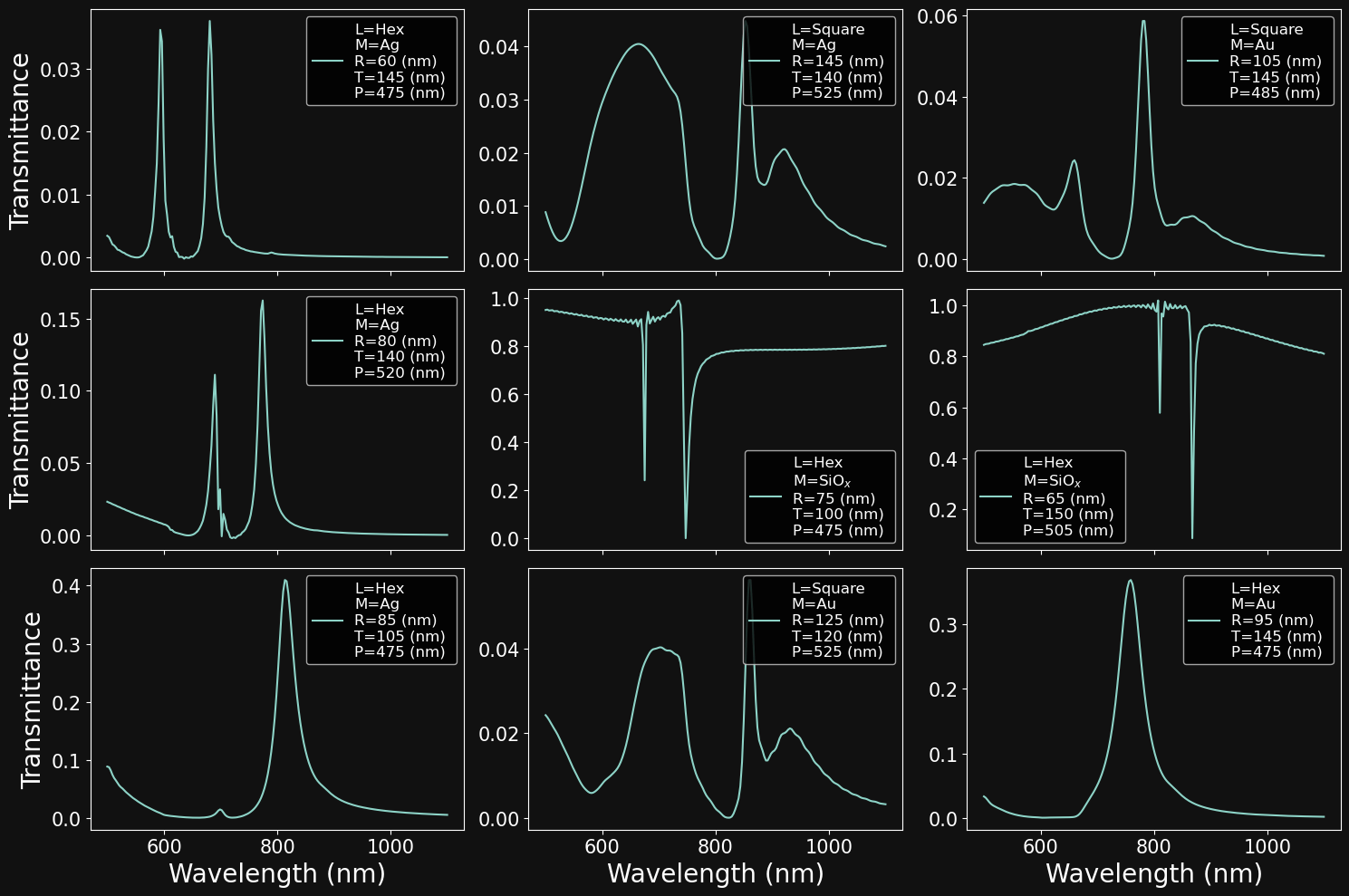
INVERSE DESIGN WITH NEURAL NETWORK: A TOY PROBLEM
OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF NANOHOLE ARRAYS
Jahan, T. et al. Deep learning-driven forward and inverse design of nanophotonic nanohole arrays: streamlining design for tailored optical functionalities and enhancing accessibility. Nanoscale (2024) doi:10.1039/D4NR03081H.

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
THE NOTEBOOKS AND THE TUTORIAL SLIDES



Data analysis
Direct model
Inverse model

Slides for the full tutorial

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
A "TOY" PROBLEM FOR OUR TUTORIAL

OPTICAL PROPERTIES OF NANOHOLE ARRAYS
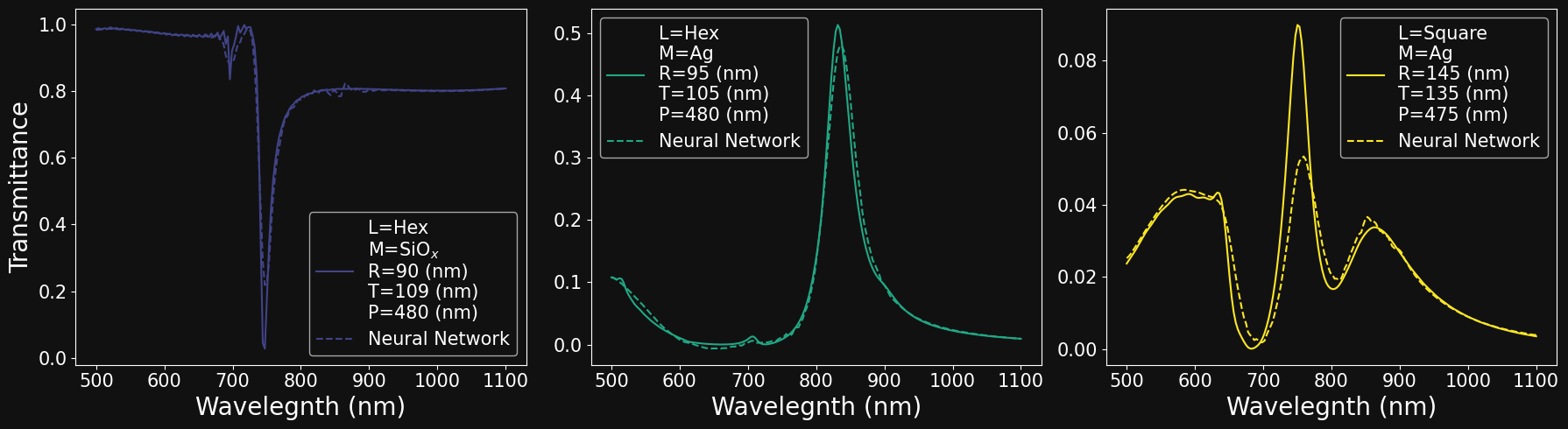
| n.1 | n.2 | n.3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lattice | Hexagonal | Square | Square |
| Material | Ag | Au | SiOx |
| Thickness (nm) | 100 | 115 | 90 |
| Radius (nm) |
60 | 110 | 140 |
| Pitch (nm) |
450 | 550 | 515 |

DIRECT
INVERSE
Jahan, T. et al. Deep learning-driven forward and inverse design of nanophotonic nanohole arrays: streamlining design for tailored optical functionalities and enhancing accessibility. Nanoscale (2024) doi:10.1039/D4NR03081H.
Structural parameters
spectra

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
IN PRACTICE

| Lattice | Hexagonal |
| Material | Ag |
| Thickness (nm) | 100 |
| Radius (nm) |
60 |
| Pitch (nm) |
450 |

Direct: \( g_{_{W}}:\mathbb{R}^{5} \to \mathbb{R}^{200} \)
Inverse: \( g_{_{W}}:\mathbb{R}^{200} \to \mathbb{R}^{5} \)

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
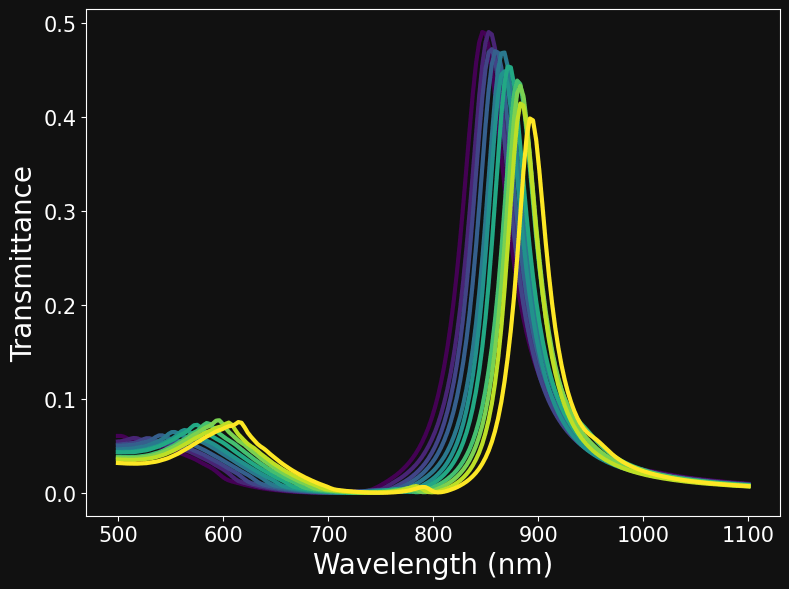
EXPLORING THE DATA: PLOT

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
THE IMPORTANCE OF THE DATA
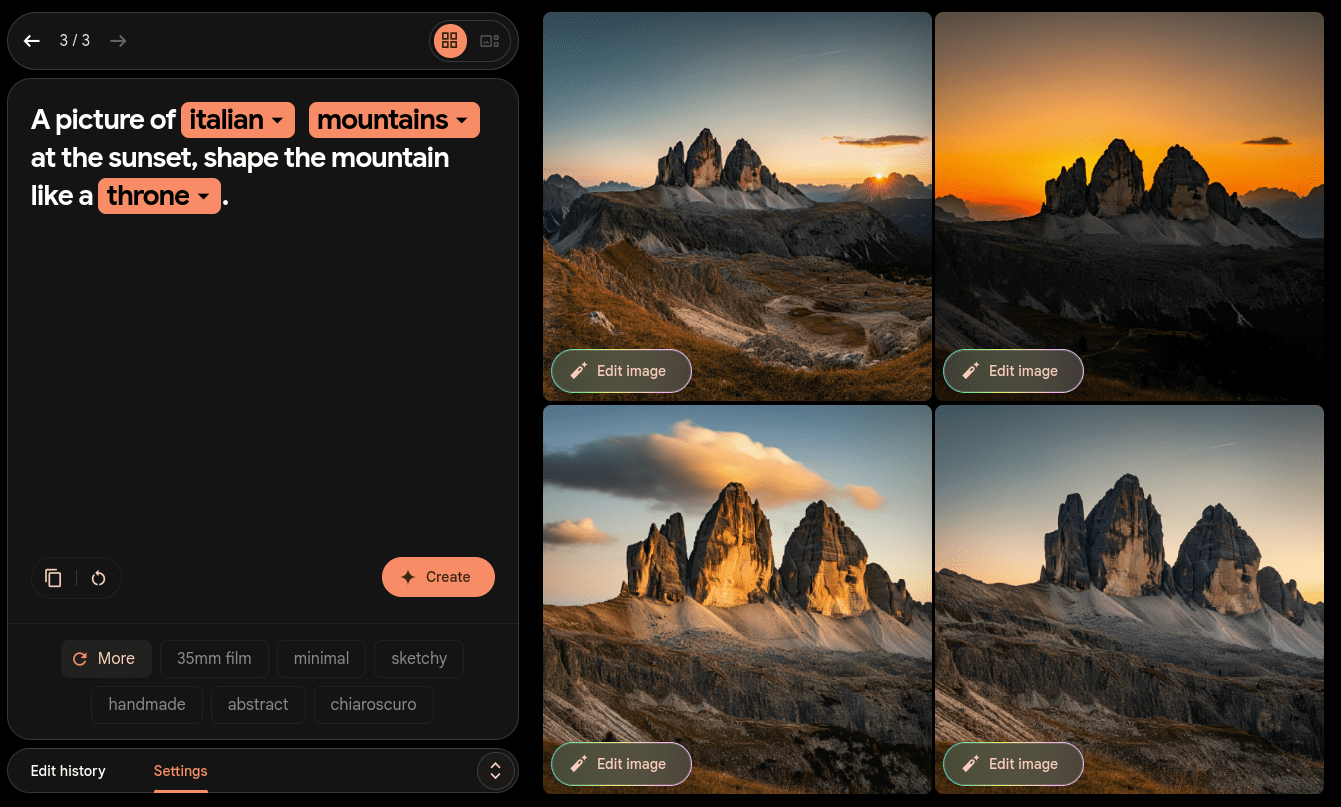

Credits: Alberto De Giuli
AI GENERATED
REAL PICTURE

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
MODEL PERFORMANCE: DIRECT PROBLEM


Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
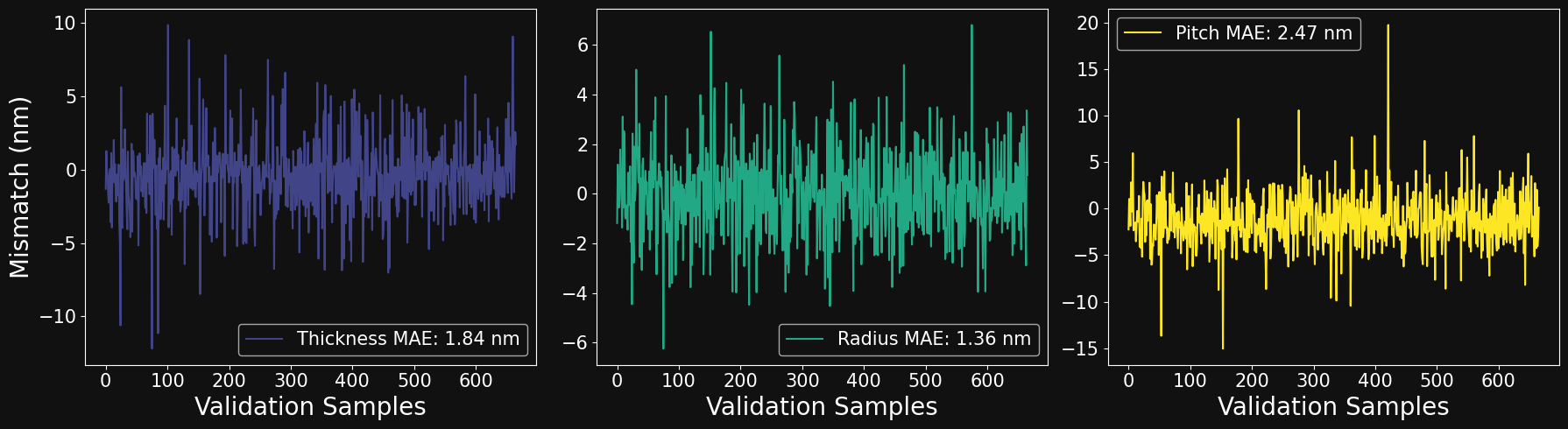
MODEL PERFORMANCE: INVERSE PROBLEM

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
SUPERVISED, PHYSICS INFORMED NEURAL NETWORKS FOR PHASE RETRIEVAL

Giovanni Pellegrini and Jacopo Bertolotti



Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
HOW THIS COLLABORATION WAS BORN

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
THE PROBLEM



Scattering
Autocorr
Autocorr

Inversion
Inversion

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
THE IDEA: NEURAL NETWORK VS ITERATIVE METHODS
ALSO: We want to erode the correlation information!!!



Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
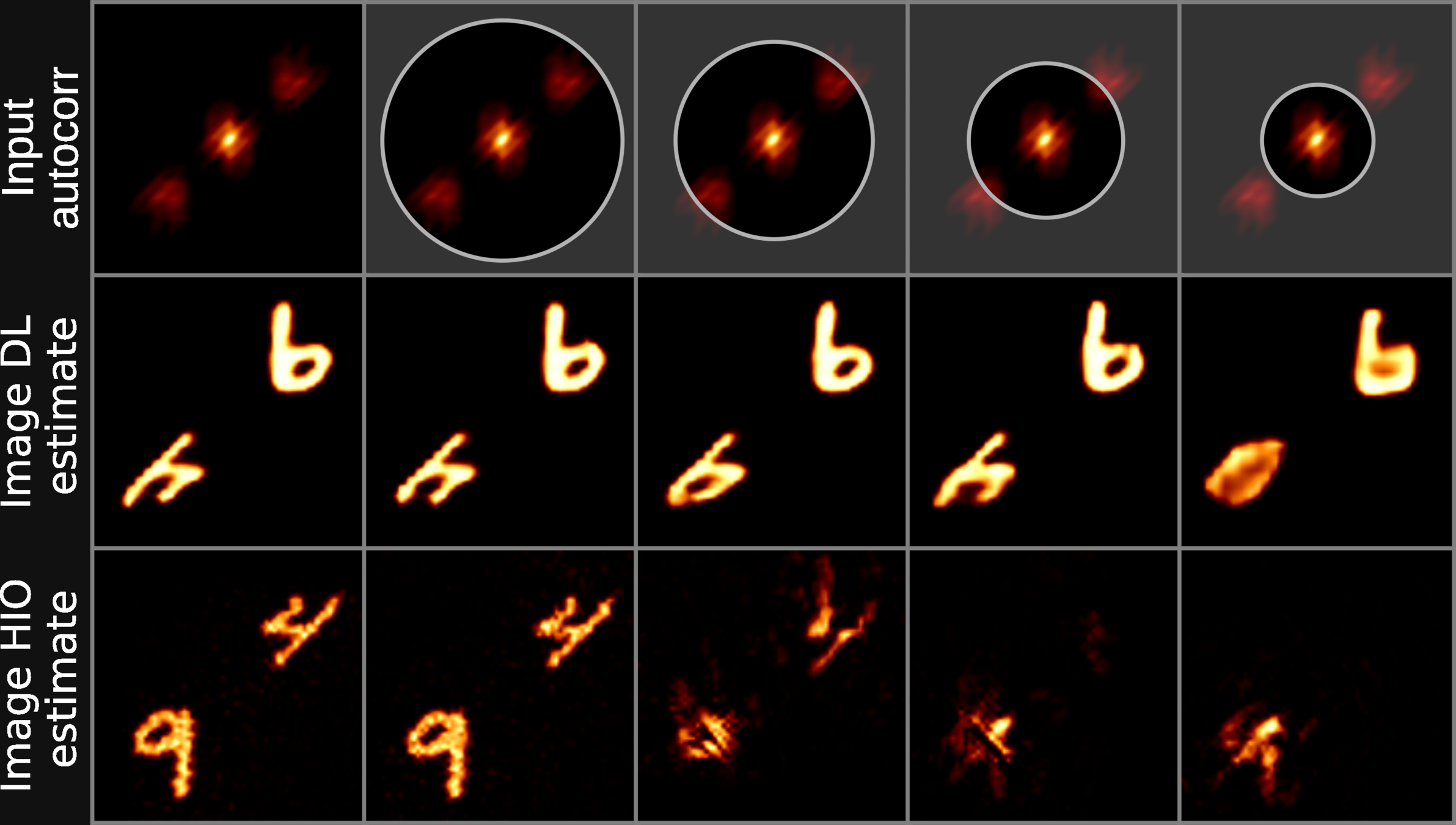
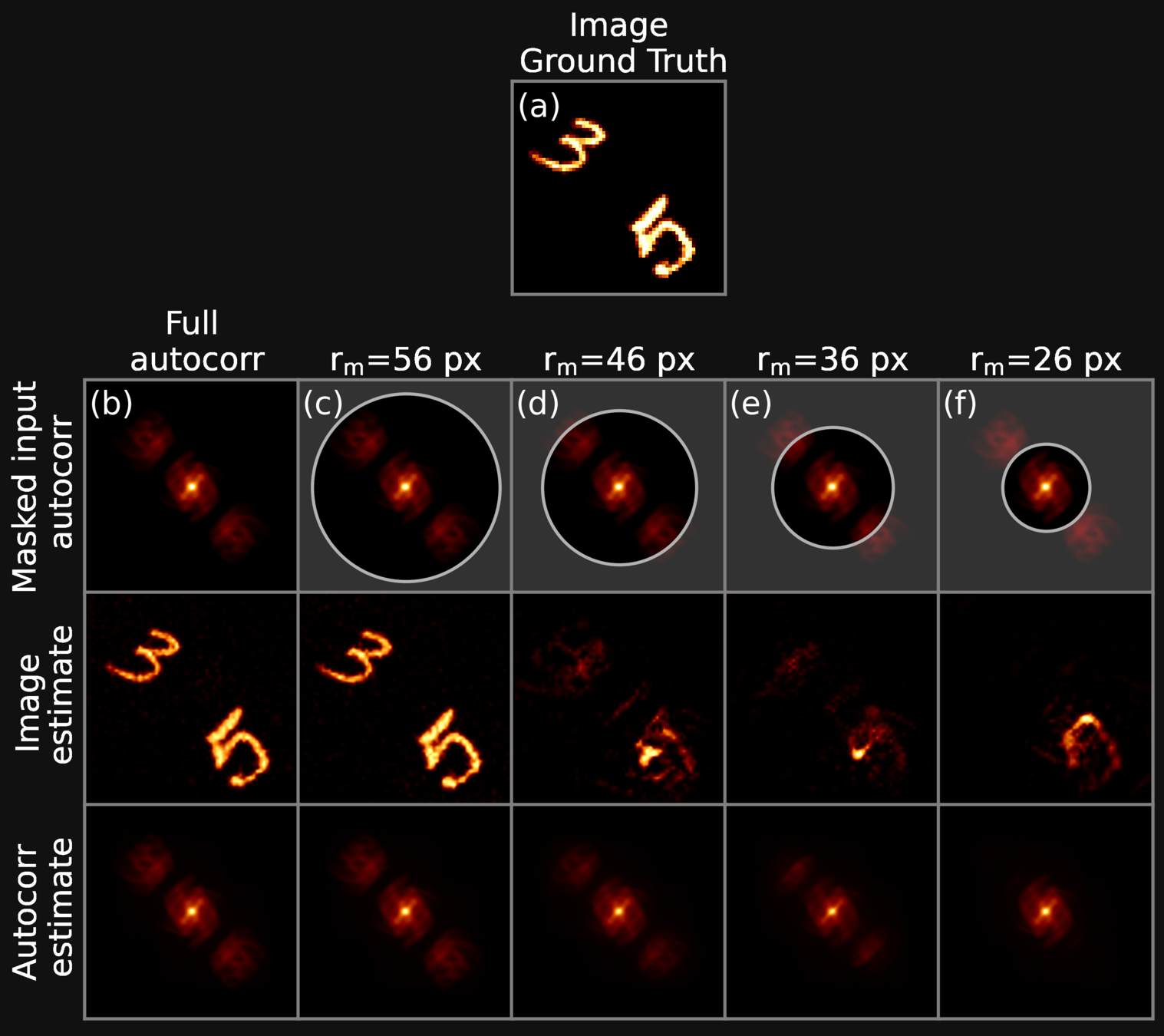
THE IDEA: RECONSTRUCTING INCOMPLETE INFORMATION

-
Current phase retrieval techniques adopt iterative approaches to recover phase information from the modulus of the Fourier transform
-
We apply a circular erosion mask to the Fourier autocorrelation, in order to assess the performance of traditional methods in presence of partial information
-
We observe that traditional approaches struggle in the presence of incomplete information. We employ a deep neural network to overcome these limitations, and show that such and approach vastly over-performs traditional methods in a large variety of scenarios

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
THE FUNDAMENTALS: DEFINING THE DATASET

-
We devise a synthetic dataset based on the MNIST handwritten digits as a benchmark for the reconstruction performance

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
DEFINING THE NEURAL NETWORK ARCHITECTURE
-
We adopt a deep convolutional autoencoder based on the DeepLabV3+ architecture with a L1 loss computed on the input and reconstructed autocorrelations


Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
TAILORING THE TRAINING PROCESS
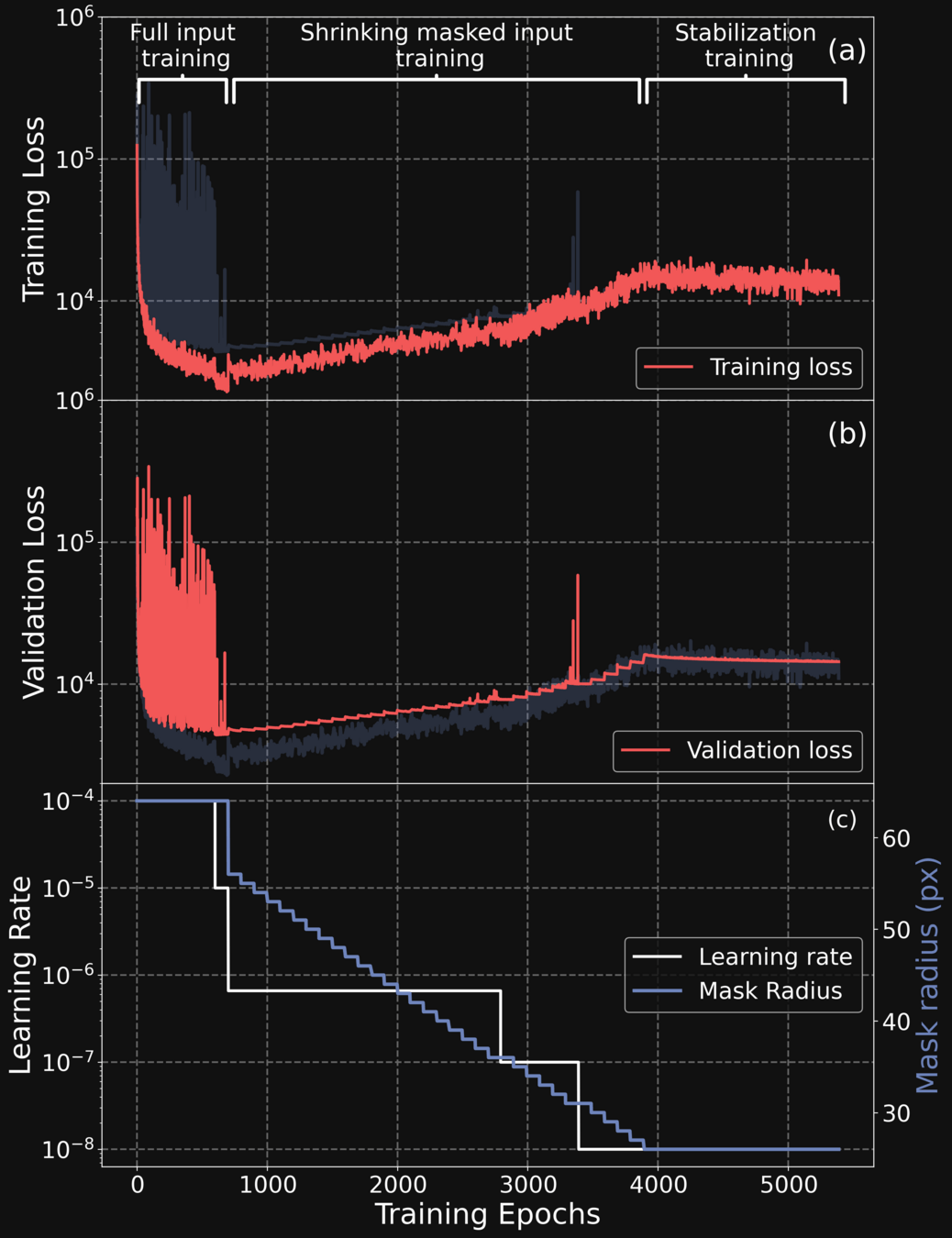
-
Phase 1: We train the network on full autocorrelation
-
Phase 2: We progressively erode the input autocorrelation, and train the network to reconstruct the missing information
-
Phase 3: We perform a final stabilization training

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
DEEP LEARNING: RESULTS
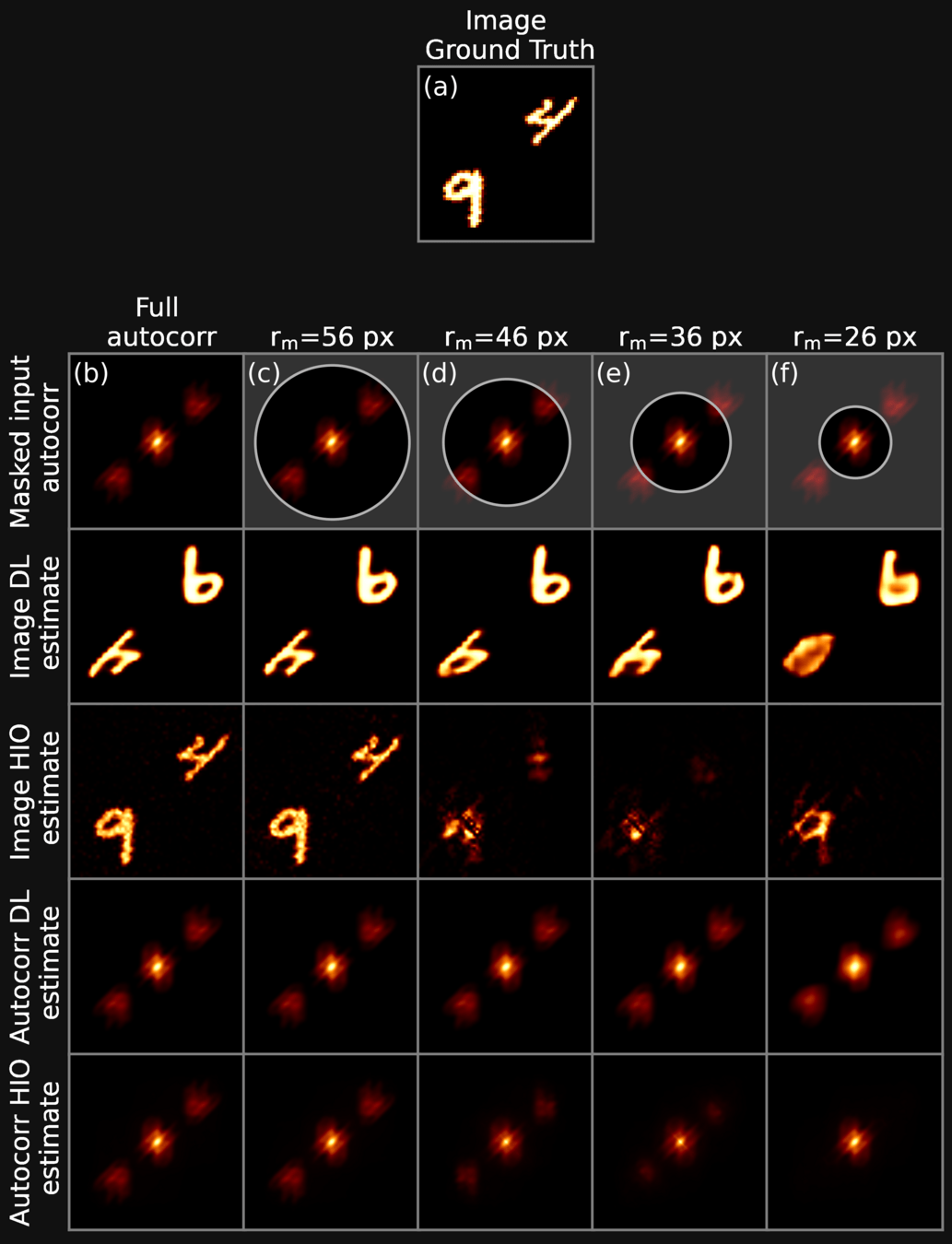
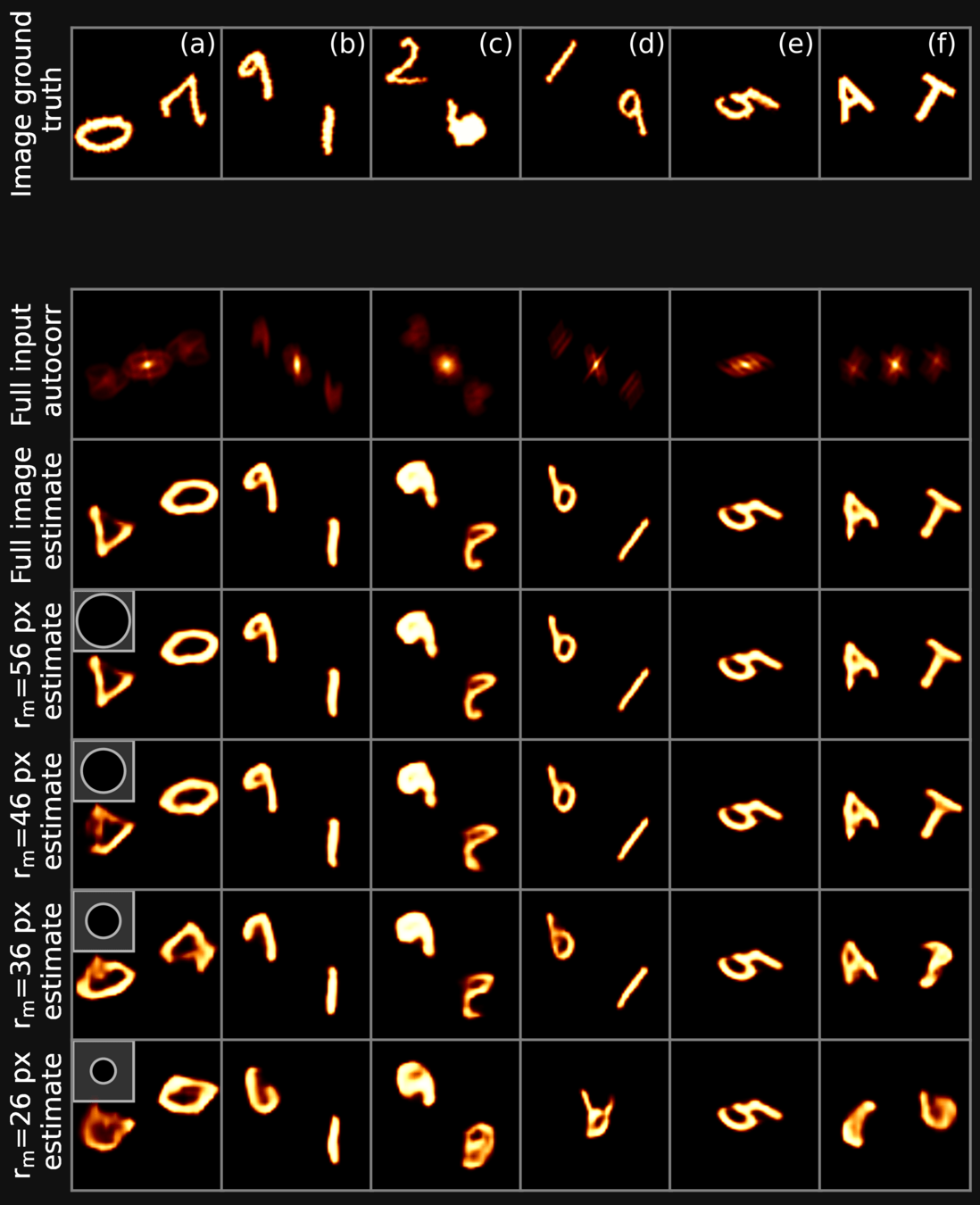
Deep Learning Vs Iterative
Deep Learning: exploration

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
UNSUPERVISED, PHYSICS INFORMED NEURAL NETWORKS FOR PTYCHOGRAPHY

Giovanni Pellegrini, Jonathan J. Barolak, Carmelo Grova, Charles S. Bevis, Daniel E. Adams and Giulia F. Mancini



Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
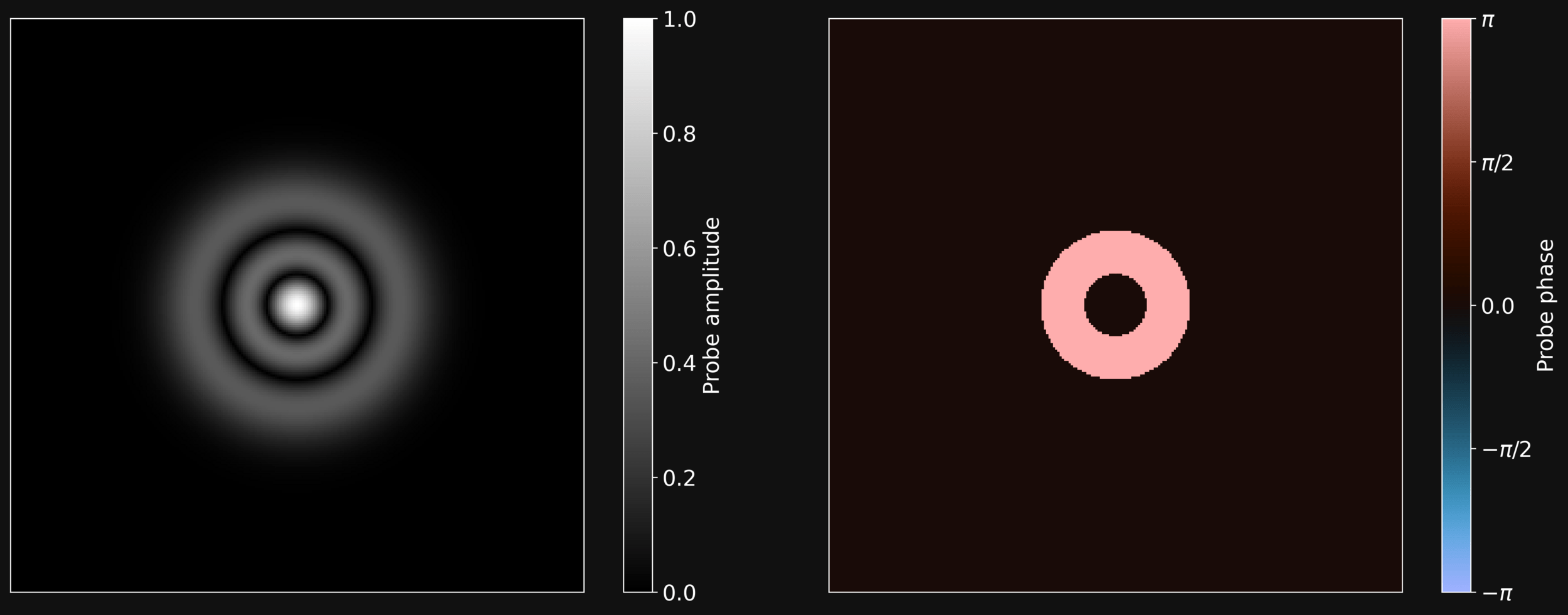
PTYCHOGRAPHY FOR DUMMIES
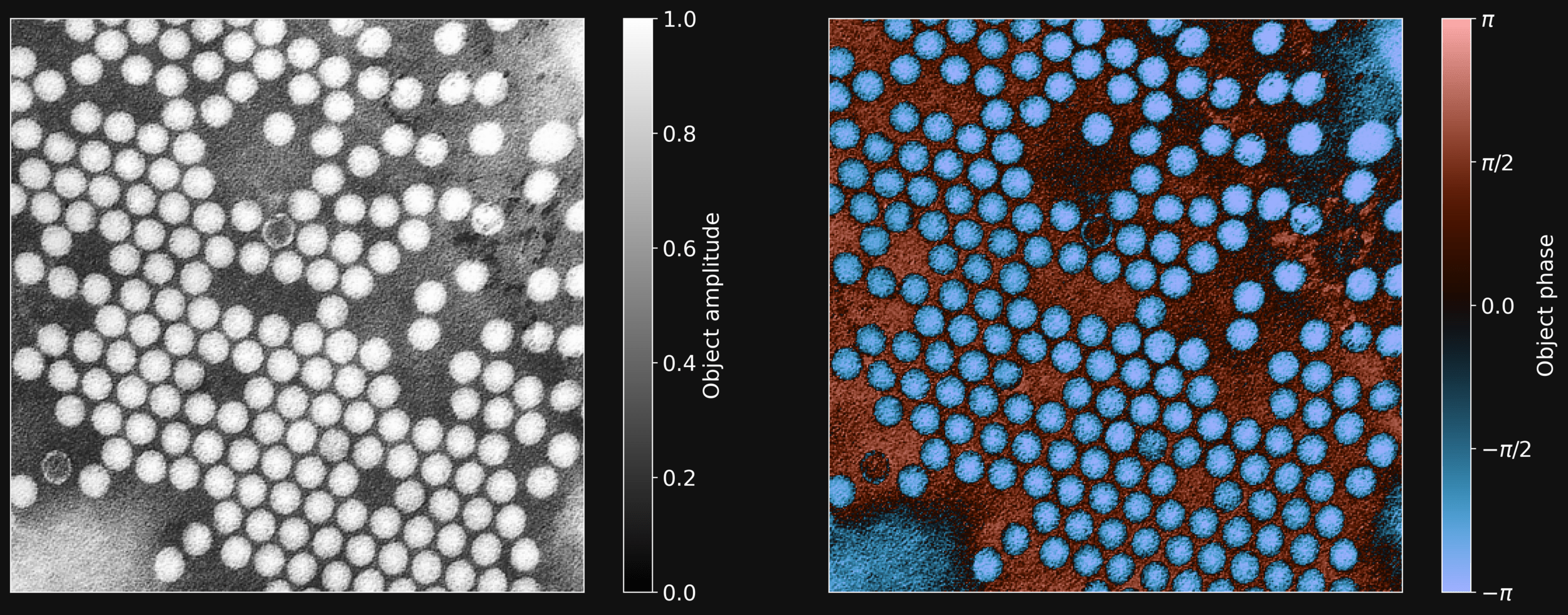
Complex Image
Complex Probe
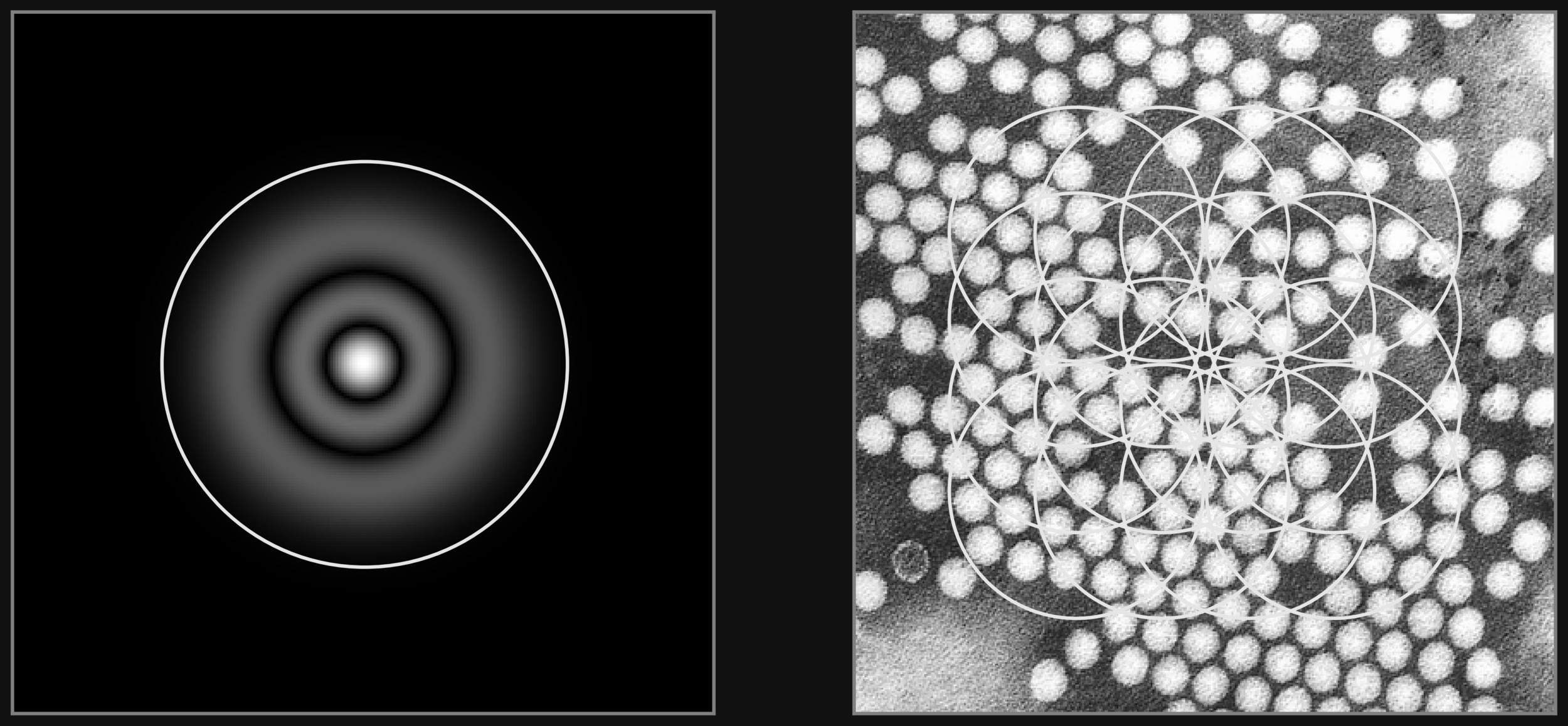
Probe Raster on a Grid

Free Space
Propagation
Sample Plane
Image Plane

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
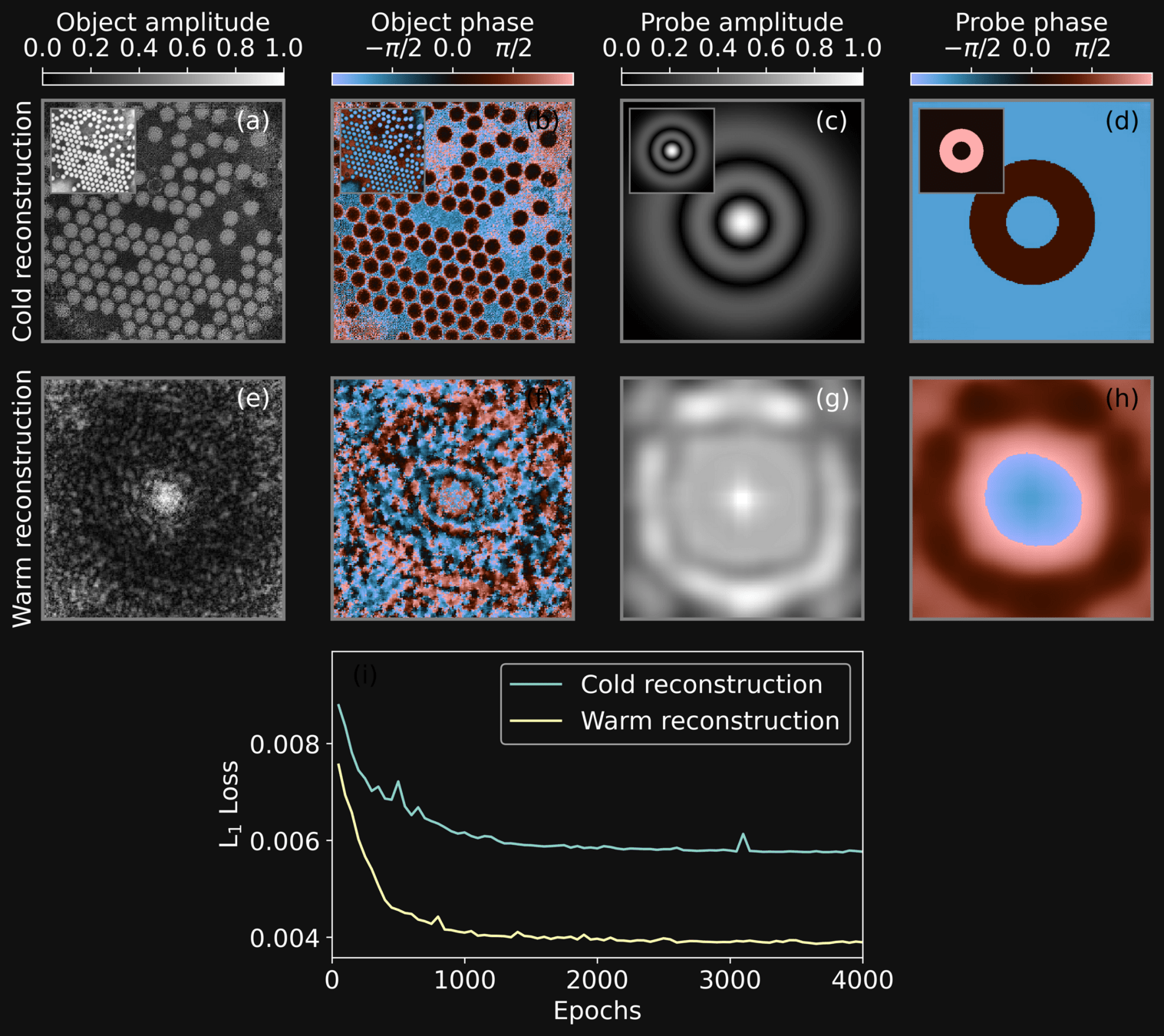
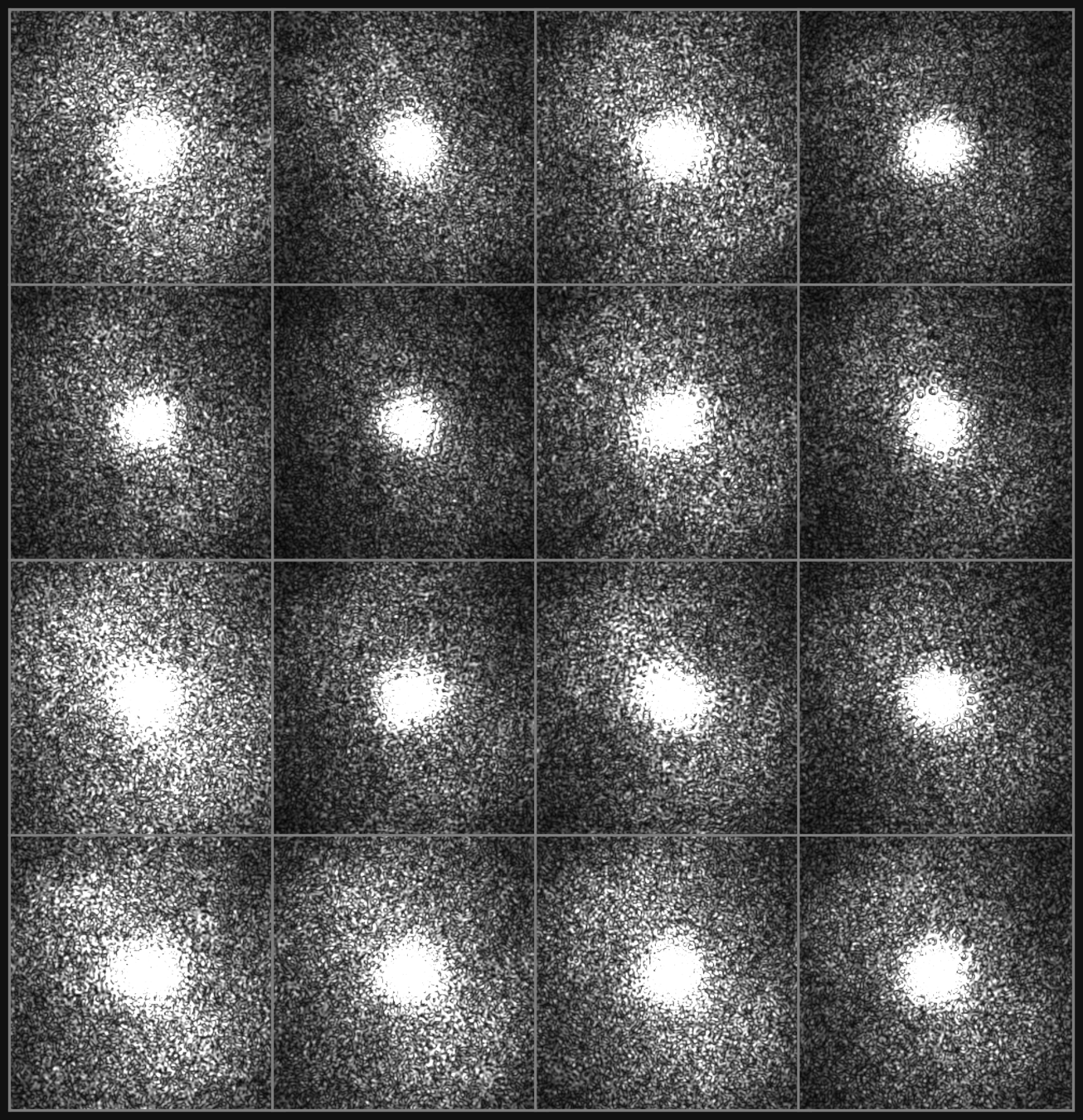
AN UNTRAINED, PHYSICS INFORMED NETWORK APPROACH

-
The reconstruction process happens with an untrained network on a physics-informed closed loop. The Neural Network substitutes entirely the iterative deterministic algorithm.

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
AN UNTRAINED, PHYSICS INFORMED NETWORK APPROACH
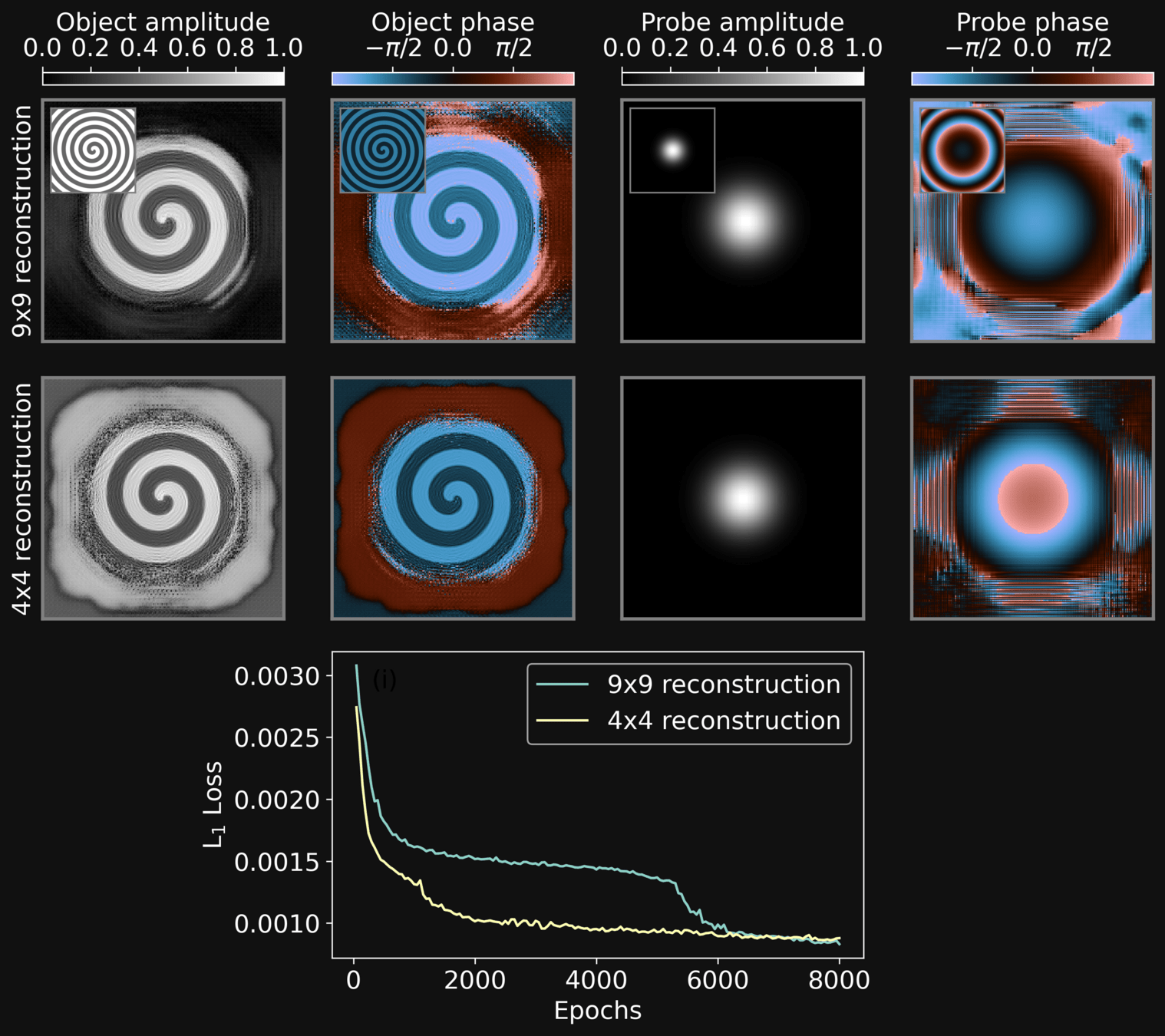
-
We tested the reconstruction performance against different probe grids
-
The physics informed neural network approach apparently allows for reconstructions with very sparse gridding
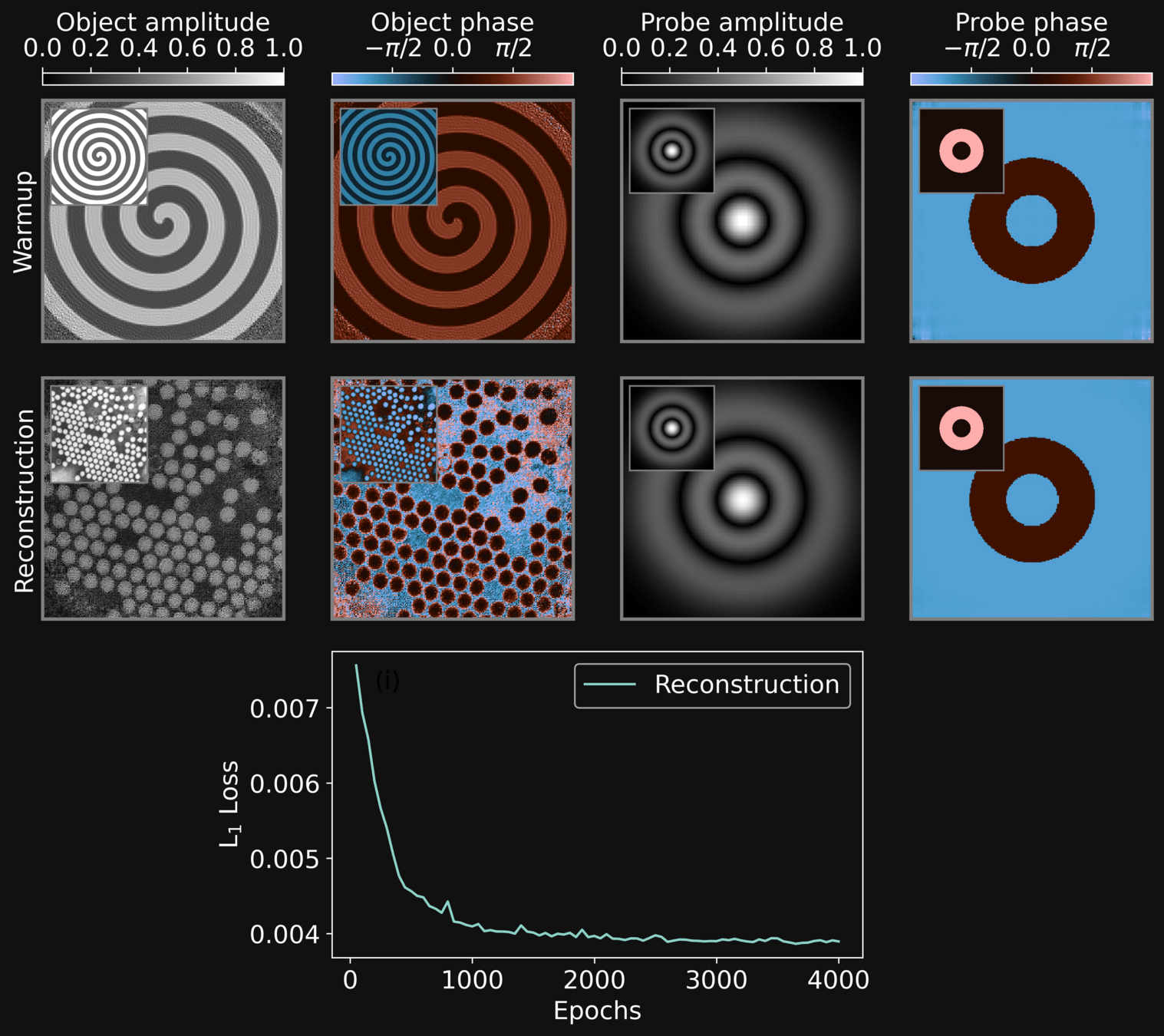
-
We devise a strategy to speedup the reconstruction
-
We adopt a warmup strategy reconstructing an unrelated dummy image with a similar probe
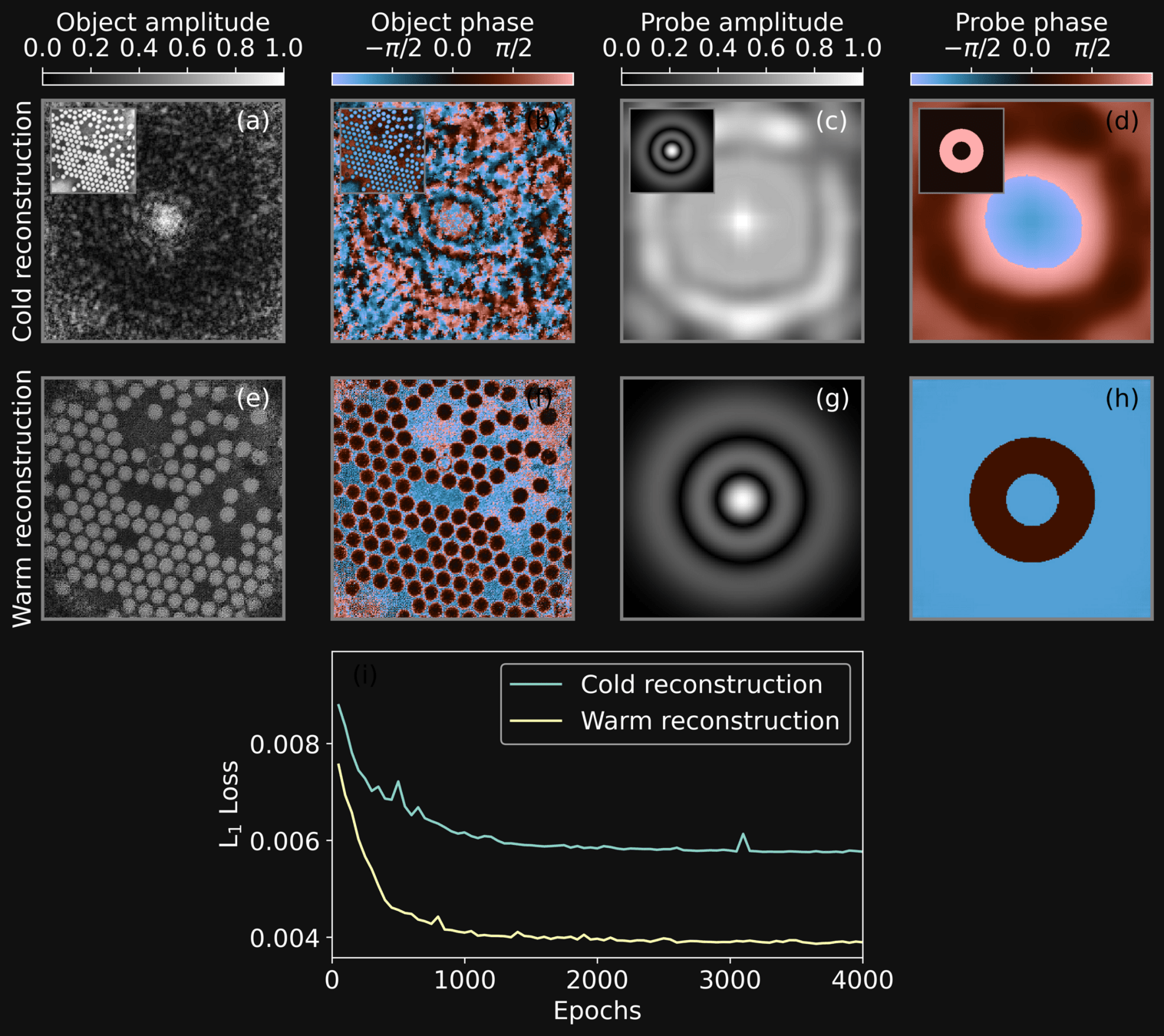
-
Without warmup the reconstruction does not reach convergence
-
With warmup the reconstruction quickly reaches convergence

Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
HAPPY INVERSE DESIGNING!


Dipartimento di Fisica - Università di Pavia
UniPD 28 March 2025, Padova, Italy
UniPd2025Optimization
By Giovanni Pellegrini
UniPd2025Optimization
- 74



