Gokulan R - CS15B033
Prof. Pratyush Kumar
30 May 2020
\({}^1\) Shakti Multiplier-Accumulate Accelerator Network
ShaktiMAAN\({}^1\)
An open-source DNN Accelerator
- Background
- Contributions
- ISA
- Microarchitecture
- Design Space Exploration
- Custom Compiler Flow
- Conclusion
Overview
$$x_1$$
$$x_2$$
$$x_3$$
$$w_1$$
$$w_2$$
$$w_3$$
b
\( y \) \(=\) \(\sigma\) \((\sum_{i} \) \(w_i\) \( \cdot\) \(x_i\) \( +\) \( b\) \() \)
- Inputs
- Weights
- Bias
- Activation Function
- Output
Building block - a neuron
$$x_1$$
$$x_2$$
$$x_3$$
$$h_1$$
$$h_2$$
$$h_3$$
$$h_4$$
$$h_5$$
$$y_1$$
$$y_2$$
$$w_{153}$$
$$w_{111}$$
$$w_{225}$$
$$w_{211}$$
Input Layer
Hidden Layer
Output Layer
Two Layered NN
| w11 | w1n | ||||||||
| wm1 | wmn | ||||||||
| b1 | b2 | bn |
| x1 |
| xm |
| 1 |
| y1 |
| yn |
Input of size m, output of size n
Output computed as vector-matrix multiplication
Fully Connected layer (FC)
Input vector, transposed
Weight Matrix
Output vector, transposed
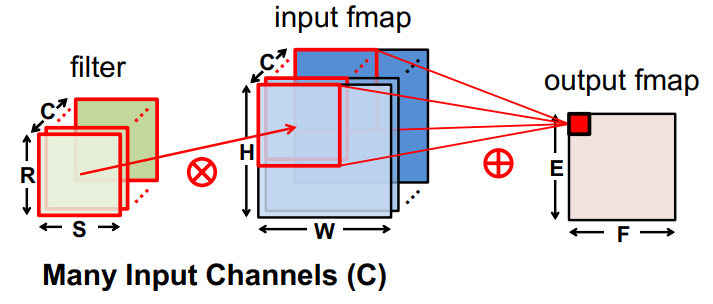
Source: ISCA 2019 Tutorial

Convolution layer (CONV)
Source: ISCA 2019 Tutorial
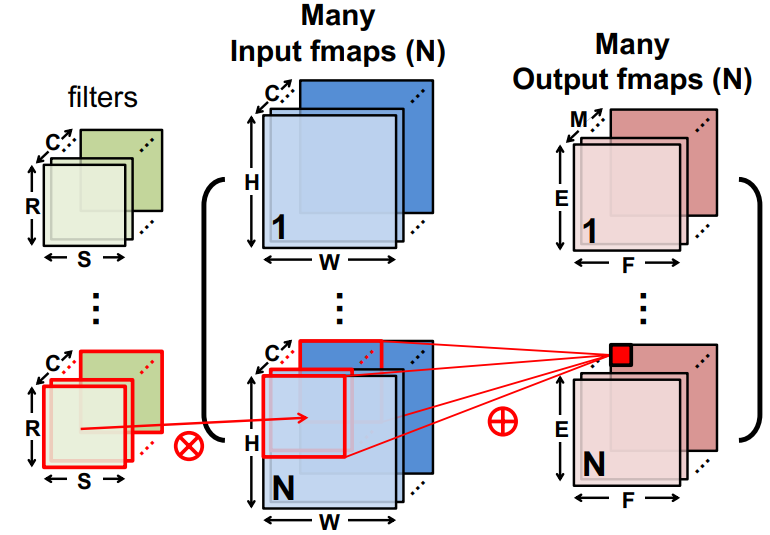
Convolution layer (CONV)
Simple way to subsample
Max Pooling
2 x 2
stride 2
Average Pooling
2 x 2
stride 2
| 1 | 4 |
| -2 | 7 |
| 2 | -20 |
| 31 | 11 |
| 41 | -8 |
| 0 | 3 |
| -6 | 0 |
| -11 | -1 |
7
31
41
0
2
6
9
-5
Pooling layers
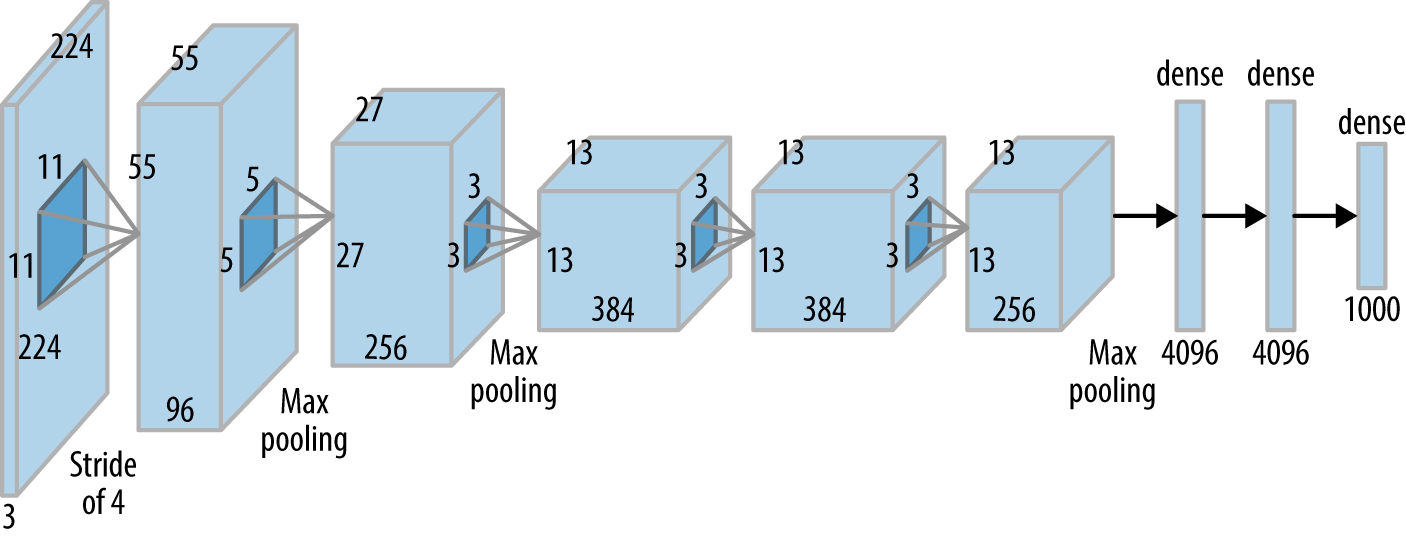
Deep Neural Networks
AlexNet (2012) - Breakthrough in ImageNet dataset
Alex et. al. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks
DNN Workload
- Workloads across domains - vision, NLP, statistical ML have a common operation - matrix multiplication
- Goal: Build a fast matrix-multiplier!
- General Matrix Multiplication (GEMM) algorithm
- Embarrassingly parallel
- Can reuse data significantly
- Highly ordered computation - across parallel units, the smallest unit of computation is the same
- Improves compute throughput without improving B/W
- Used in signal processing, polynomial operations
- Smallest unit: Processing Element
- Scalabity achieved by replicating PEs across different dimensions
- Reuse achieved by communication between adjacent PEs
H.T.Kung, Why systolic architectures?
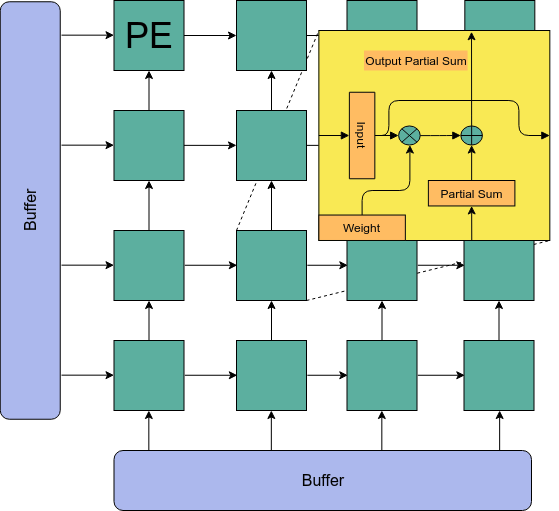
Systolic Array
$$ C = A \times B$$
- Columns of B are loaded into columns of systolic array
- Rows of \( A^T\) are sent into rows of systolic array
- Partial sums (rows of C) flow along the columns of systolic array
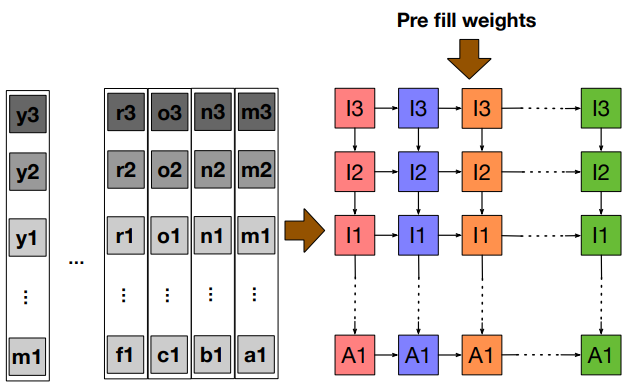
Image: Samajdar et. al. SCALE-Sim: Systolic CNN Accelerator Simulator
Systolic Array

- Background
-
Contributions
- ISA
- Microarchitecture
- Design Space Exploration
- Custom Compiler Flow
- Conclusion
Overview
Paradigm
- ISA level choices
- Mapping GEMM to systolic array
- Double buffering
- Instruction fetch
- Array dimension
- Buffer sizes
- Queue sizes
- Buffer organisation
- Tiling config
- loop ordering
- instruction scheduling
Synthesis
Dynamic
Human-made choices
Exploration performed using task-level simulator
Compile-time exploration by compiler
Design Space Exploration
LOAD/STORE
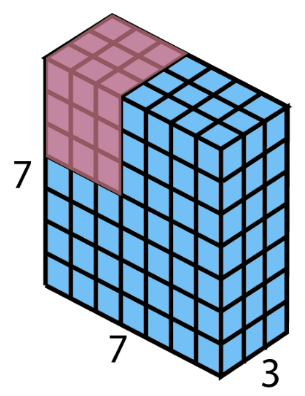
- Load/Store a 3D slice of an n-D matrix
- Read from DRAM and write it to on-chip SRAM
- The slice can be discontinuous in DRAM, but continuous in SRAM.
- LOAD \(4 \times 8 \times 8 \times 512\)
- 1 \(\times \) LOAD(4, 8, 8, 512)
- 4 \(\times\) LOAD(8, 8, 512)
- 4 * 8 \(\times\) LOAD(8, 512)
LOAD/STORE

- DRAM base address, SRAM base address
- Z_SIZE, Y_SIZE, X_SIZE
- Z_STRIDE, Y_STRIDE
- RESET
GEMM



- Weight load phase: Load weights onto PEs
- Compute phase
- Read input and send it along rows
- Read output and send it along columns from top
- Read output and store it back in buffer
Image: Samajdar et. al. SCALE-Sim: Systolic CNN Accelerator Simulator
GEMM



- input \(1 \times 8 \times 8 \times 512\)
- weight \(256 \times 3 \times 3 \times 512 \)
- output \(1 \times 8 \times 8 \times 256 \)
- systolic array: \(64 \times 64\)
- 64 different filters across different columns
- 64 different channels across different rows
- \( \frac{256}{64} \times \frac{512}{64} \times 3 \times 3 \) GEMM instructions
Image: Samajdar et. al. SCALE-Sim: Systolic CNN Accelerator Simulator
GEMM

- {input, weight, output} base address
- output {height, width}
- Stride {X, Y}, Padding {Top, Left, Right, Bottom}
Tensor ALU
- Performed a windowed reduction over output feature maps
- Similar to convolution, but without weights
- Operation is vectorised across channels
- ReLU can be mapped using R=S=1
- \( k \times m\) maxpool can be mapped using R = k and S = m

Tensor ALU

- {input, output} base address
- ALU opcode
- {height, width} of {output, window}
- stride {R, S, OW}
Microarchitecture
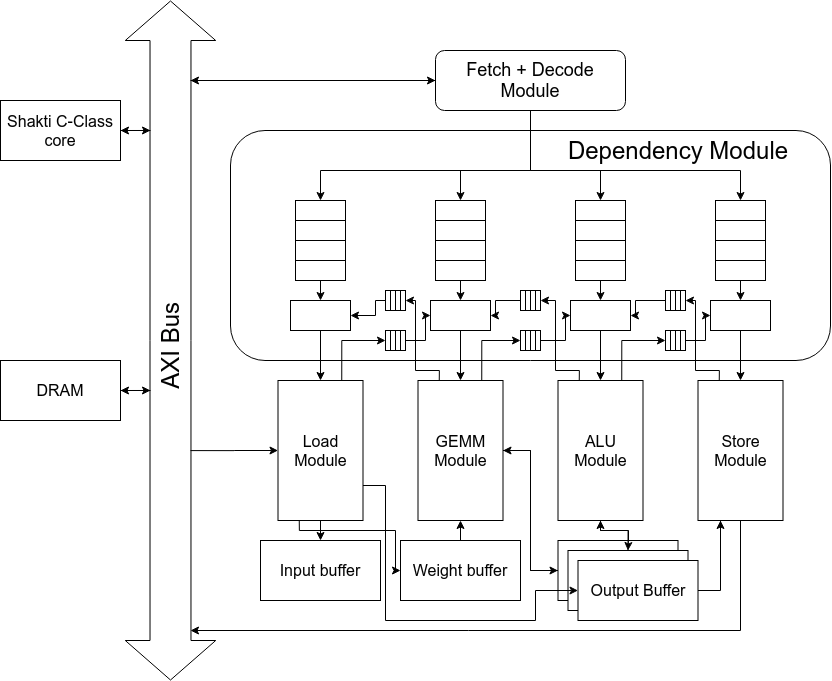
Dependency Resolution
$$ C = A \times B $$
LOAD A
LOAD B
GEMM: C = A*B
STORE C
push next
pop prev
push next
pop prev
- Dependency module ensures that instructions are dispatched to execute only after dependencies are met
- Dependency flags are inserted by compiler at compile time
1
2
3
4
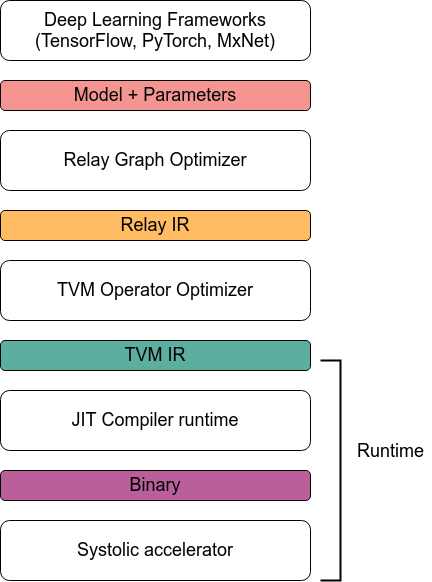
Compiling model to accelerator

- Relay IR: Map models from multiple frameworks to a single IR
- TVM IR: Perform optimizations, schedule exploration, portable across hardware
- JIT Compiler Runtime: Generate accelerator-specific binary from TVM IR
Chen et. al. TVM: An Automated End-to-End Optimizing Compiler for Deep Learning
Custom Compiler - inspired by TVM
Model to Accelerator ISA
- input \(1 \times 8 \times 8 \times 512\)
- weight \(256 \times 3 \times 3 \times 512 \)
- output \(1 \times 8 \times 8 \times 256 \)
- systolic array: \(64 \times 64\)
for i=1 to 256/64
for j=1 to 512/64
LOAD(input, j)
for l=1 to 3, for m=1 to 3
LOAD(weight, i, j, l, m)
GEMM(input', weight', output')
ALU(output, i)
STORE(output, i)- 64 filters across different columns
- 64 channels across different rows
- \( \frac{256}{64} \times \frac{512}{64} \times 3 \times 3 \) GEMM instructions
Task-level Simulator
- Functional simulator, not cycle accurate
- Provides an estimate of execution time for a given instruction trace on a given accelerator configuration
- Input - instruction trace, Output: Execution summary
- Execution time of entire trace, instruction level logs
- Utilisation of components, module-level logs
- Uses
- Interface with TVM compiler to schedule exploration
- Analyse bottlenecks and refine configuration of accelerator
Status and Future Work
| Module | Status |
|---|---|
| fetch-decode | Completed |
| dependency resolver | Completed |
| load | Final stages |
| store | Final Stages |
| GEMM (16x16) | Completed |
| ALU (vec_size=16) | Completed |
| Custom compiler | Work-in-progress |
| Task level simulator | Work-in-progress |
- Future directions
- cycle-accurate simulator
- explore big.LITTLE systolic arrays
FPGA Synthesis Results
| Module | LUTs | FIFOs |
|---|---|---|
| fetch-decode | 823 | 1317 |
| dependency resolver | 1427 | 858 |
| load | * | * |
| store | * | * |
| GEMM (16x16) | 90464 | 0 |
| ALU (vec_size=16) | 1280 | 0 |
*Work-in-progress
- RTL in Bluespec System Verilog (BSV)
- Synthesis using Xilinx Vivado v2018
- Target FPGA: Xilinx Artix 7
Summary
- ShaktiMAAN: open-source accelerator for DNNs
- Matrix multiplication is performed by systolic array
- Vector ALU to perform activation and pooling functions
- TVM compiler to execute model across frameworks on the accelerator
- Design space exploration of various hardware choices
- Task level simulator for
- Interfacing with TVM compiler
- optimizing accelerator configuration
Acknowledgements - The Team
Vinod Ganesan
Neel Gala
Arjun Menon
Mohan Prasath
Rohan Kaulgekar
Sadhana
Sujay Pandit
Surya Selvam
Anand Uday Gokhale
Nidesh
Sundar Raman
Shilpa
Selvaraj
Rishabh Jain
Thank You!
ddp_final
By Gokulan Ravi
ddp_final
- 433



