Introducción a Java Enterprise Edition (JEE)

¿Para qué Java EE?
- Extiende Java SE para la creación de aplicaciones
sobre la red con las siguientes características:- Larga escala
- Multi-capas
- Escalables
- Confiables
- Seguras
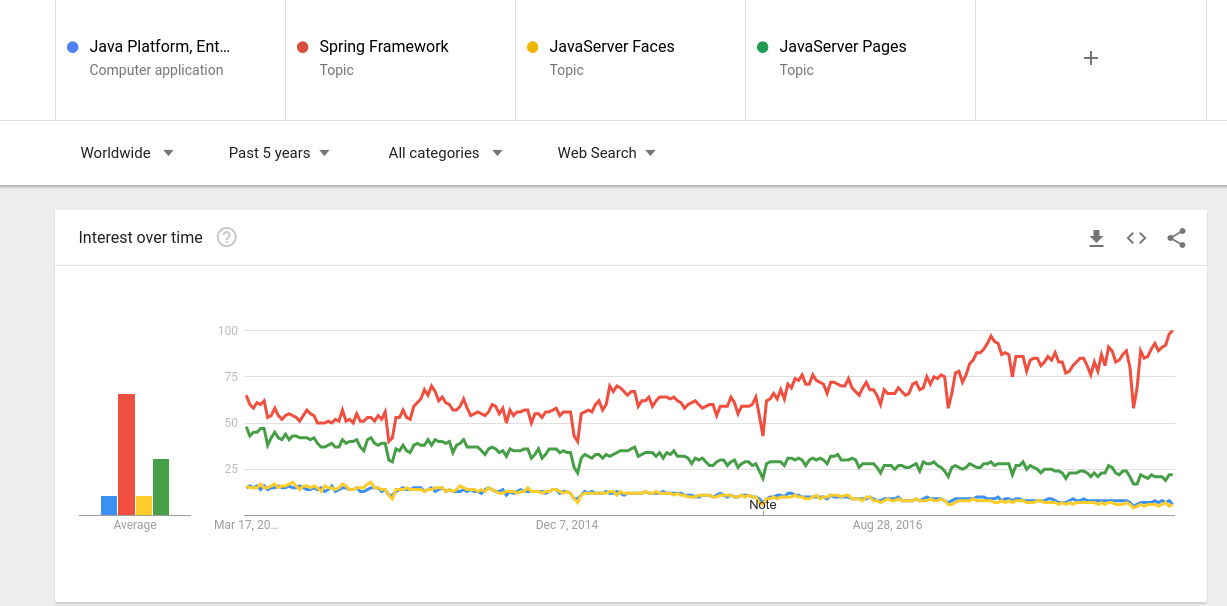
¿Para qué Java EE?
Fuente: Google Trends
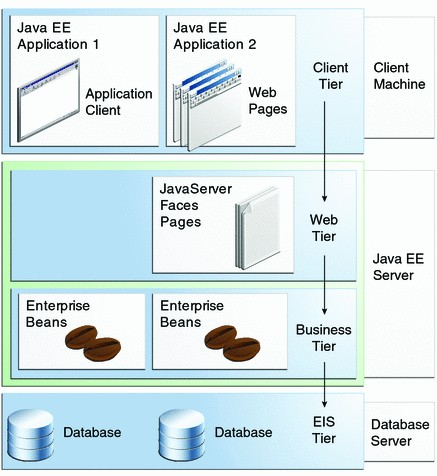
Multicapas
- La funcionalidad de la aplicación se separa en areas
funcionalmente aisladas llamadas capas. - Cada capa ofrece servicios a sus capas superiores
- Capas típicas:
- Capa cliente
- Capa media (Java EE)
- Capa web
- Capa de negocio
- Capa de datos
Multicapas
Capa Web
- Funciones
– Generar dinamicamente contenido en varios formatos
para el cliente
– Obtener entradas de los usuarios y retornar resultados
de los componentes de negocio
– Controlar el flujo de pantallas o páginas en el cliente
– Mantener el estado de los datos para la sesión del
usuario
– Realizar algúna lógica básica y mantener datos
temporales
Capa Web
Capa Web - Servlet
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class ServletExample extends HttpServlet {
private int count;
@Override
public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException {
super.init(config);
getServletContext().log("init() called");
count = 0;
}
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
getServletContext().log("service() called");
count++;
response.getWriter().write("Incrementing the count: count = "
+ count);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
getServletContext().log("destroy() called");
}
}Ejemplo 1 - Servlet
- Instalar Spring Tool Suite
- Crear nuevo "Dynamic Web Project"
- Incluir creación del web.xml
- En la carpeta WebContent crear una nueva página index.html
- En la carpeta src crear un nuevo servlet con los métodos init, doGet, doPost
- Desplegarlo en el servidor
Nota: Observar la respuesta usando el Advanced REST Client
Ejemplo 2 Servlet
(link)
Capa Web - JSP
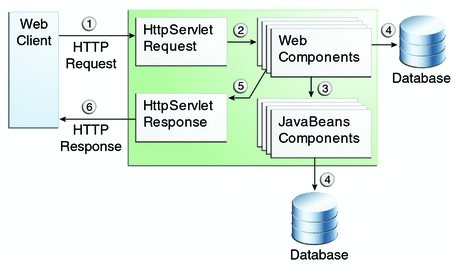
Capa Web - Expression Language
<%@ page import="java.io.*,java.util.*" %>
<%
String title = "User Agent Example";
%>
<html>
<head>
<title><% out.print(title); %></title>
</head>
<body>
<center>
<h1><% out.print(title); %></h1>
</center>
<div align="center">
<p>${header["user-agent"]}</p>
</div>
</body>
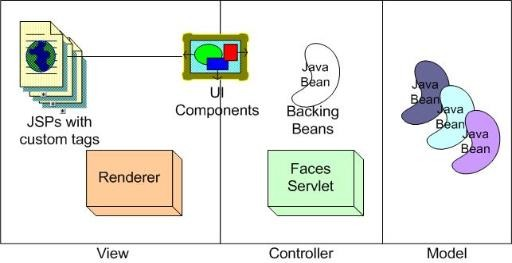
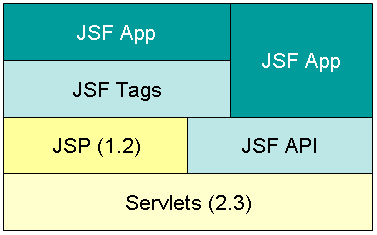
</html>Capa Web - Java Server Faces
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.RequestScoped;
@ManagedBean(name = "helloWorld", eager = true)
@RequestScoped
public class HelloWorld {
public HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("Hello World a comenzado!");
}
public String getMessage() {
return "Hello World!";
}
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>Welcome JSF!!</title>
</head>
<body>
#{helloWorld.getMessage()}
</body>
</html>Ejemplo - JSF
- Crear nuevo "Dynamic Web Project"
- Incluir creación del web.xml
- Convertir a proyecto Maven (click derecho -configure... - Convert to maven project)
- En el archivo pom.xml incluir después de la etiqueta <name>:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.faces</groupId>
<artifactId>jsf-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.sun.faces</groupId>
<artifactId>jsf-impl</artifactId>
<version>2.1.7</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies> Ejemplo - JSF
- Modificar el archivo WebContent/WEB-INF/web.xml de la siguiente manera:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:web = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"
id = "WebApp_ID" version="2.5">
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>home.xhtml</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<!--
FacesServlet is main servlet responsible to handle all request.
It acts as central controller.
This servlet initializes the JSF components before the JSP is displayed.
-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>javax.faces.webapp.FacesServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/faces/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.jsf</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.faces</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>*.xhtml</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>Ejemplo - JSF
- Crear la Clase HelloWorld de la diapositiva 4.8, en el paquete co.edu.unicauca.
- Crear el archivo WebContent/home.xhtml con el código de la diapositiva 4.8.
- Correr el proyecto. Maven Install - Run on Server.

Capa Web - Etiquetas JSF
<html xmlns = "http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:f = "http://java.sun.com/jsf/core"
xmlns:h = "http://java.sun.com/jsf/html">
<head>
<title>Ejemplo de etiquetas</title>
</head>
<h:body>
<h2>h:selectManyListbox example</h2>
<hr />
<h:form>
<h3>List Box</h3>
<h:selectManyListbox value = "#{userData.data}">
<f:selectItem itemValue = "1" itemLabel = "Item 1" />
<f:selectItem itemValue = "2" itemLabel = "Item 2" />
<f:selectItem itemValue = "3" itemLabel = "Item 3" />
<f:selectItem itemValue = "4" itemLabel = "Item 4" />
<f:selectItem itemValue = "5" itemLabel = "Item 5" />
</h:selectManyListbox>
<h:commandButton value = "Submit" action = "result" />
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html> Capa de Negocio
- Tecnologías
- Enterprise JavaBeans componentes
- Java API for RESTful Web Services (JAX-RS)
- Context Dependency Injection (CDI)
- Contexto: Definición de contexto que permite ligar las interacciones y los ciclos de vida de los componentes
- Inyección de dependencias: la habilidad de inyectar componentes en una aplicación. Se puede escoger en tiemplo de despliegue cual implementación de un componente inyectar.
Capa de Datos
- Tecnologías
- Java Database Connectivity API (JDBC)
- Java Persistence API
- Java EE Connector Architecture
- Java Transaction API (JTA)
Servidores o Contendores



JEE
By Gustavo Andrés Uribe Gómez
JEE
- 691



