Human-in-the-loop
in Langgraph
Acme Design is a full service design agency.
Presenter:
Otis x Harold
- Components in LangGraph?
- Memory (in chat)
- Breakpoints & Human-in-the-loop (HITL)
-
Demo:
- Breakpoints & HITL
- Debugging Time Travel
Outline




Components in LangGraph?
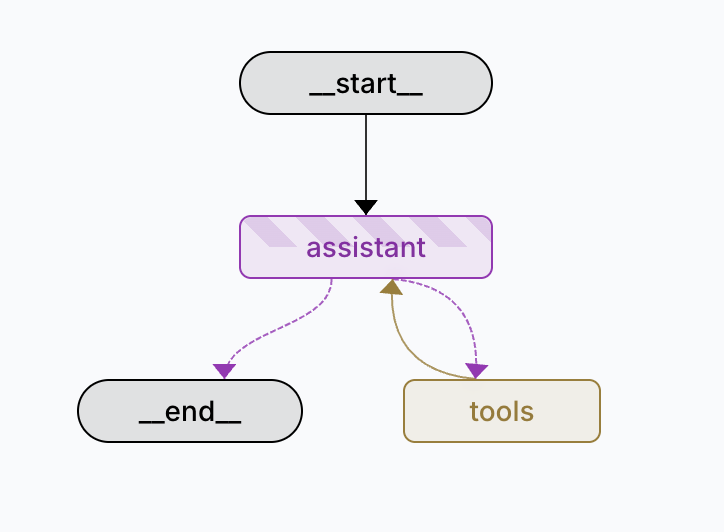
Node (step)
Edge
Edge
Conditional edge
State: a shared data structure that holds the current snapshot of your application's data, accessible to all nodes in the graph
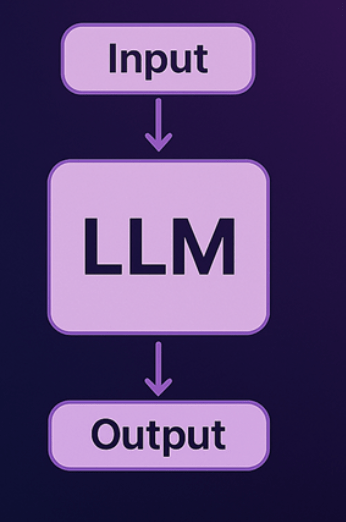
Stateless:
LLMs are designed to treat each input as a new, independent request, without retaining any memory of past interactions.
LLM memory
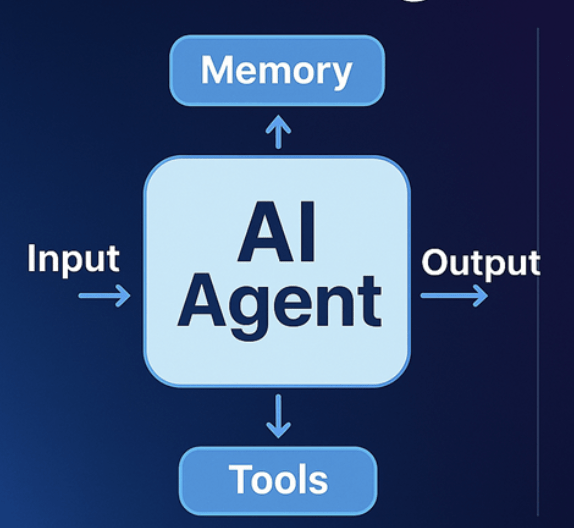
Stateful:
Agent memory allows AI systems to maintain context and learn from past interactions, becoming more effective over time
MemorySaver in Langgraph save the context
Agent memory

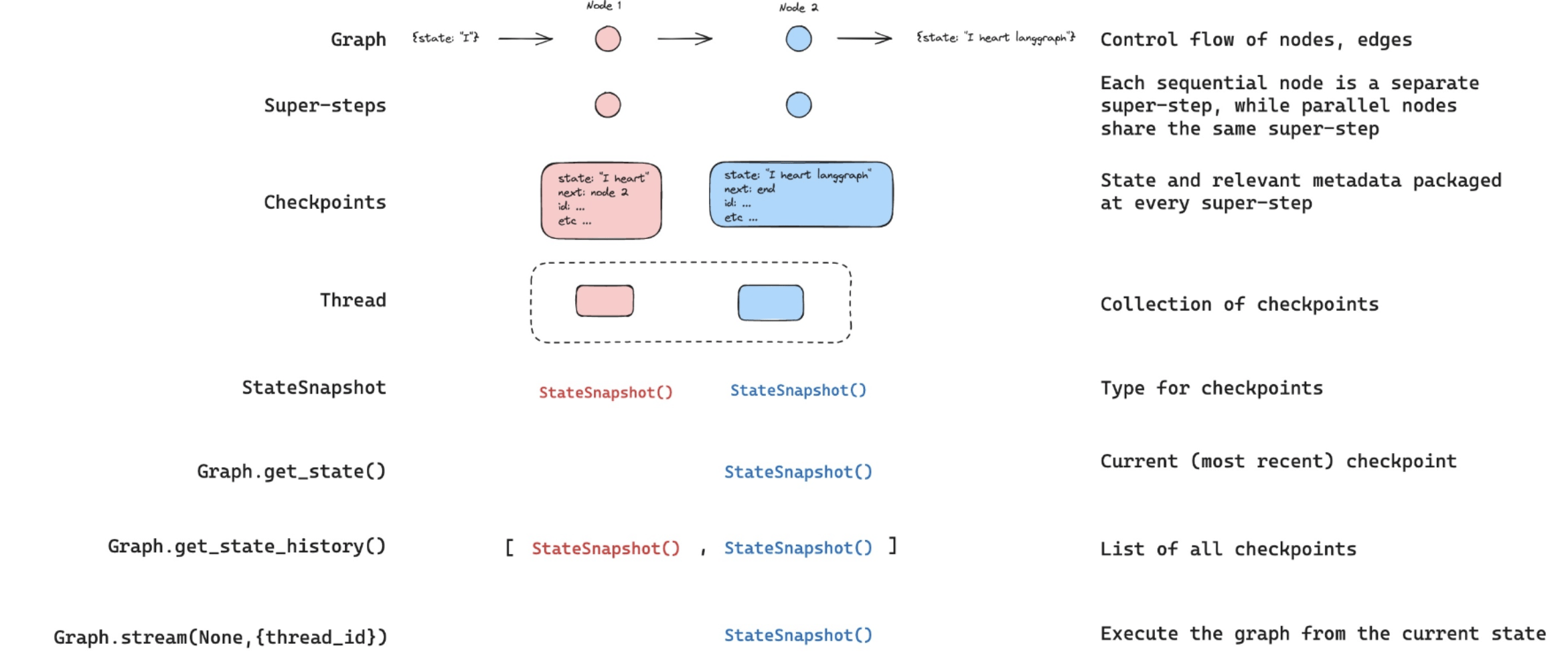
Breakpoints
&
Human-in-the-loop (HITL)
A feature that pauses the execution of a graph to:
Approval- We can interrupt our agent, surface state to a user, and allow the user to accept an actionDebugging- We can rewind the graph to reproduce or avoid issuesEditing- You can modify the state
Breakpoints
There are 2 ways to create a breakpoint:
- Use the
interruptfunction - Use the config
interrupt_before,interrupt_afterwhen compiling a graph - Use the middleware
HumanInTheLoopMiddleware
After creating a breakpoint, we need to resume it by Approve/Edit/Reject (Ref)
Breakpoints
- Do not wrap interrupt calls in try/except
- Do not reorder interrupt calls within a node
- Do not return complex values in interrupt calls
- Side effects called before interrupt must be idempotent
Interrupt rules
What
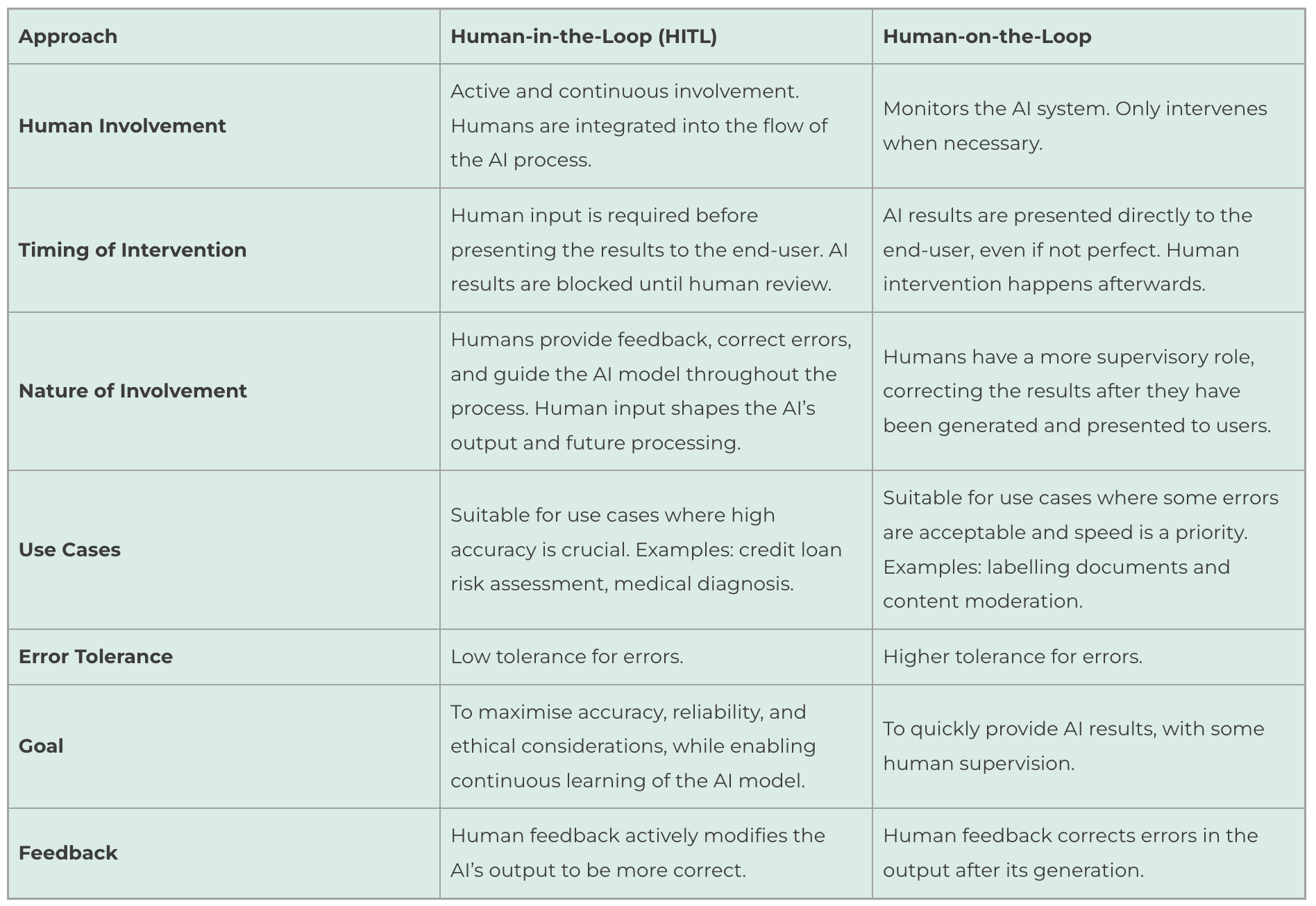
- Combines human intelligence with machine learning capabilities
- It involves active and continuous human participation, integrating humans into the AI process flow
Human-in-the-loop (HITL)
Why
To maximise accuracy, reliability, and ethical considerations, while enabling continuous learning of the AI model.
Human-in-the-loop (HITL)
Demo
Thank You!
Questions?
Human-in-the-loop in Langgraph
By Hiếu Lê Minh
Human-in-the-loop in Langgraph
- 15


