字元&字串(C-style)
Sprout 2021/03/20

字元
什麼是字元?就...字啊🤷
字元
- 數字
- 0123456789
- 大寫英文字母
- ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
- 小寫英文字母
- abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
- 符號
- !@#$%^&*()_+{}|:”;?/><.,~
但不只這些!
特殊字元
- 換行
- \n
- tab
- \t
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "March" << '\t' << "20" << '\n';
cout << "Hello" << '\t' << "world" << '\n';
}宣告
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char c1; // 宣告
c1 = 'a'; // 給值
char c2 = 'b'; // 初始化
}輸入輸出
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char c;
cin >> c;
cout << c;
}輸入輸出
cout << '\'; //?
cout << '''; //?字元有包含引號(')跟反斜線(\)
但為什麼我輸不出來
error 顯示 missing terminating ' character 是什麼意思
跳脫字元
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << '\\' << endl;
cout << '\'' << endl;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
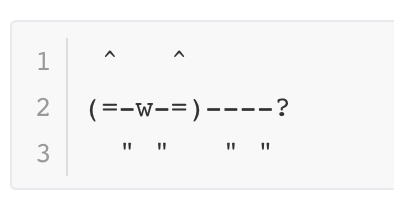
cout << " ^ ^ " << endl;
cout << "(=-w-=)----?" << endl;
cout << " \" \" \" \" " << endl;
return 0;
}
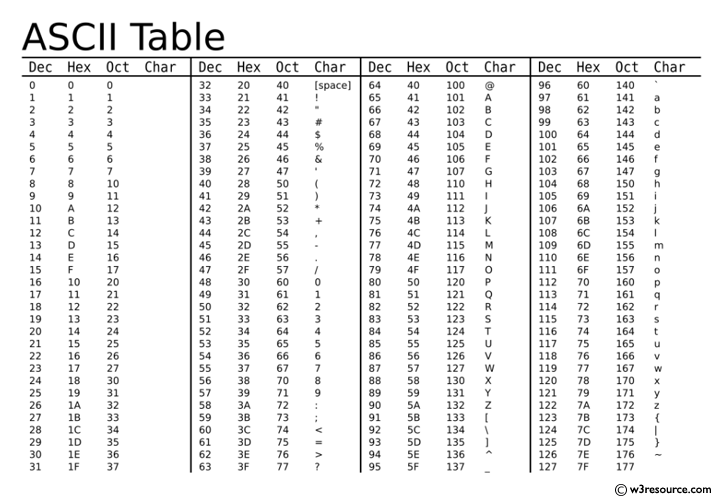
ASCII Code
電腦如何表達字元呢
電腦只有0跟1欸
ASCII編碼
Example 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int c1 = 'a';
cout << c1 << endl; // output: 97
int c2 = 97;
cout << char(c2) << endl; // output: a
return 0;
}
Example 2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char c1 = 97;
cout << c1 << endl; // output: a
char c2 = 'a';
cout << int(c2) << endl; // output: 97
return 0;
}小練習
用迴圈印出a~z (ascii code 97~122)
cout << “abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz”提示
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int i;
i = 97;
cout << char(i);
i = 98;
cout << char(i);
i = 99;
cout << char(i);
return 0;
}下面的程式會輸出什麼
Solution 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for(int i = 97; i <= 122; i++)
cout << char(i);
return 0;
}因為 a~z 對應到的 ASCII code 是 97~122,所以...
Solution 2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for(char c = 'a'; c <= 'z'; c++)
cout << c;
return 0;
}因為字元本質上就是數字,所以...
字元運算
字元與數字
可以
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char c = 'a';
cout << c << endl;
c += 2;
cout << c << endl;
c -= 1;
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
字元與數字
可以
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
if('b' == 'a'+1)
cout << "b is equal to a+1" << endl;
if(98 == 'a'+1)
cout << "98 is equal to a+1" << endl;
return 0;
}
字元與字元
也可以
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char c = 'z';
cout << c - 'a' <<endl;
cout << 'c'+'A'-'b'-'B' << endl;
}
字元比大小
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
if ('a' < 'b')
cout << "a < b" << endl;
if ('A' < 'a')
cout << "A < a" << endl;
else
cout << "A > a" << endl;
return 0;
}
小練習
如果輸入大寫,就輸出小寫
如果輸入小寫,就輸出大寫
if(c=='A') cout << 'a';
else if(c=='B') cout << 'b';
else if(c=='C') cout << 'c';
...

提示
char c;
cin >> c;
if( c是大寫 ) {
把c變小寫
cout << c;
} else if( c是小寫 ) {
把c變大寫
cout << c;
}| 大寫字元 | ASCII | 小寫字元 | ASCII |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 65 | a | 97 |
| B | 66 | b | 98 |
| C | 67 | c | 99 |
| ... | ... | ||
| Z | 90 | z | 122 |
Solution 1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char c;
cin >> c;
if(65 <= c && c <= 90) {
c += 32;
cout << c;
} else if(97 <= c && c <= 122) {
c -= 32;
cout << c;
}
return 0;
}
| 大寫字元 | ASCII | 小寫字元 | ASCII |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 65 | a | 97 |
| B | 66 | b | 98 |
| C | 67 | c | 99 |
| ... | ... | ||
| Z | 90 | z | 122 |
Solution 2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char c;
cin >> c;
if('A' <= c && c <= 'Z') {
c += 'a'-'A';
cout << c;
} else if('a' <= c && c <= 'z') {
c -= 'a'-'A';
cout << c;
}
return 0;
}65 ➜ 'A'
90 ➜ 'Z'
97 ➜ 'a'
122 ➜ 'z'
32 ➜ 'a' - 'A'
字串(C-style)
char s = 's', p = 'p', r = 'r', o = 'o', u = 'u', t = 't';
cout << s << p << r << o << u << t;一個字元一個字元的說話很累耶
把多個字元串在一起 => 字串

字元陣列
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 's' | 'p' | 'r' | 'o' | 'u' | 't' | '\0' |
\0
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 's' | 'p' | 'r' | 'o' | 'u' | 't' | '\0' |
- '\0’就像是字串的句點
- 在輸出字元陣列時,會輸出到’\0’為止
- 也就是說,’\0’後的字元不會被輸出
想想看會輸出什麼
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char str[100] = "Goodbye";
str[4] = '\0';
cout << str;
return 0;
}
\0
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 'G' | 'o' | 'o' | 'd' | 'b' | 'y' | 'e' | '\0' |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 'G' | 'o' | 'o' | 'd' | '\0' | 'y' | 'e' | '\0' |
宣告
char str1[100] = "Hello";
char str2[] = "World";
char str3[100] = {'c', 'p', 'p', '\0'};int arr1[100] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int arr2[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};想一下上堂課學的
換成字元陣列
輸入輸出
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char str[10];
cin >> str; // 至多輸入?個字元
cout << str;
return 0;
}課堂練習
卡住的話可以舉手問講師&助教哦

題目說明
輸入都是小寫
| 輸入 | 輸出 |
|---|---|
| a | d |
| b | e |
| c | g |
| ... | ... |
| x | a |
| y | b |
| z | c |
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 宣告字元陣列
// 輸入字元陣列
// for loop 改變字元陣列裡面的 char
/// 終止條件是遇到「句點」
/// 位移3可能跟字元運算有關?
// 輸出字元陣列
return 0;
}提示
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char str[505];
cin >> str;
for(int i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
str[i] += 3; // x, y, z +3 會超出範圍
}
cout << str << "\n";
return 0;
}Step by Step - 1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char str[505];
cin >> str;
for(int i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
if(str[i] + 3 > 'z') // 做是否超出範圍的判斷
str[i] = str[i] + 3 - 26;
else
str[i] += 3;
}
cout << str << "\n";
return 0;
}Step by Step - 2
| 97 | 98 | 99 | ... | 120 | 121 | 122 | 123 | 124 | 125 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | ... | x | y | z | ? | ? | ? |
Step by Step - 3
| a | b | c | ... | x | y | z |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 97 | 98 | 99 | ... | 120 | 121 | 122 |
| 0 | 1 | 2 | ... | 23 | 24 | 25 |
|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 | ... | 26 | 27 | 28 |
|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 | ... | 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|
| 100 | 101 | 102 | ... | 97 | 98 | 99 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| d | e | f | ... | a | b | c |
Solution
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char str[505];
cin >> str;
for(int i = 0; str[i]!='\0'; ++i)
str[i] = (str[i] - 'a' + 3) % 26 + 'a';
cout << str << "\n";
return 0;
}常見錯誤
為什麼無法編譯
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char a[6] = "abcde";
char b[6];
b = a;
cout << b << "\n";
return 0;
}
//error: invalid array assignment如何把陣列A的值複製到B?
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[6] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
int b[6];
// 選項一
b = a;
// 選項二
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
b[i] = a[i];
return 0;
}選項一 or 選項二
Solution
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
char a[6] = "abcde";
char b[6];
for(int i = 0; i<6; ++i)
b[i] = a[i];
cout << b << "\n";
return 0;
}Homework
Deadline: 3/26 Fri. 23:59
HW 提問方式
❌ 翻拍螢幕、螢幕截圖
字元、字串(C-style)
By hsutzu
字元、字串(C-style)
sprout 2021/03/20
- 992



