vCache: Supporting Cost-Efficient Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Motivation
Agenda
- Adaptive bitrate (ABR) streaming
- vCache
- System Design
- Workflow
reference: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7999149
Adaptive bitrate (ABR) streaming
Reality
- limited bandwidth capacity
- unstable network conditions
- diverse viewing devices
Result
-
growing demand for video traffic
-
low quality of viewing experiences
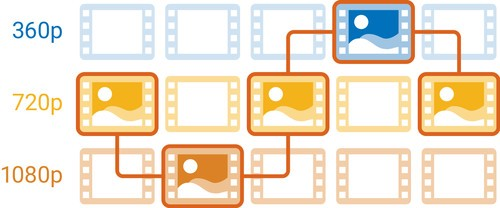
ABR
ABR Streaming
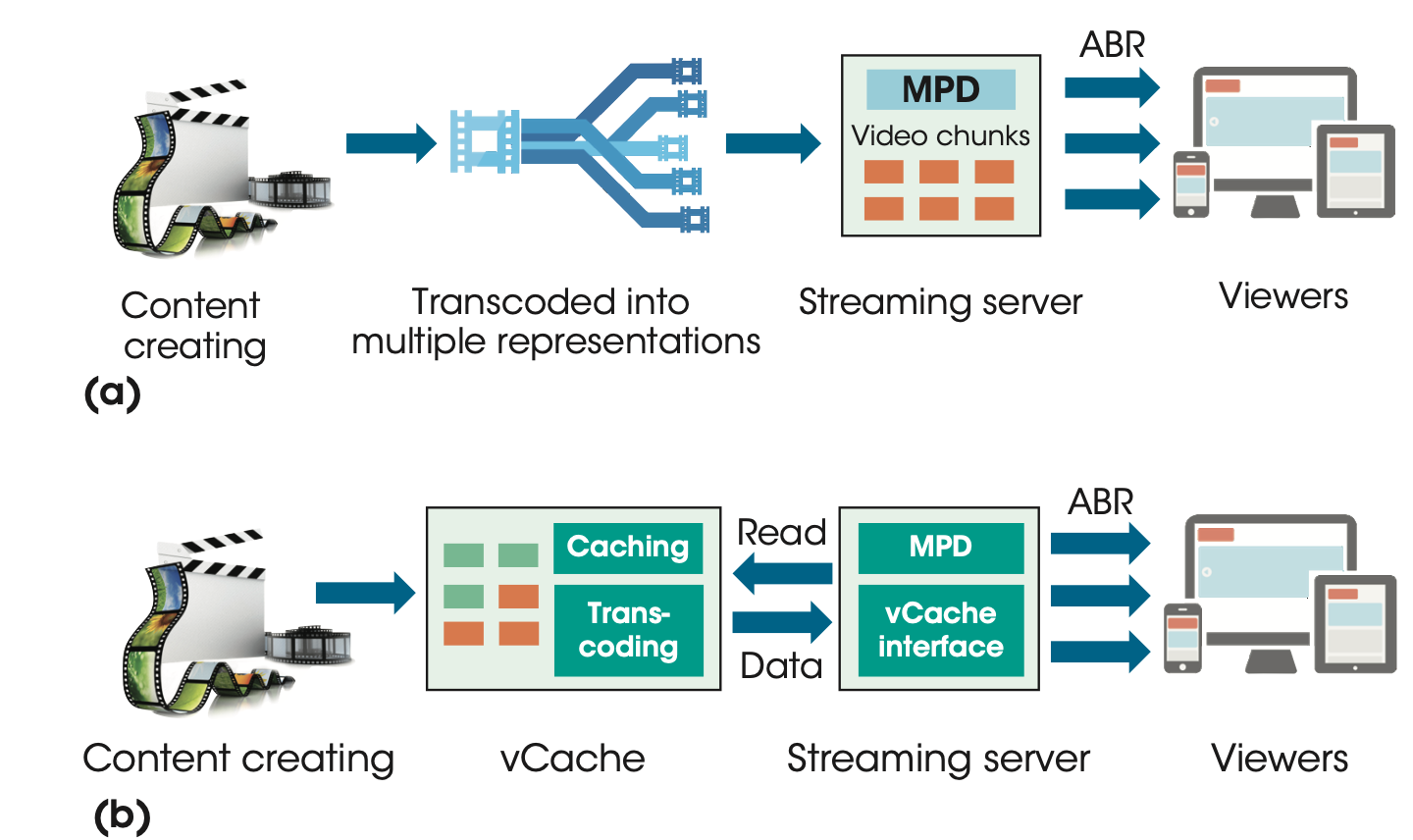
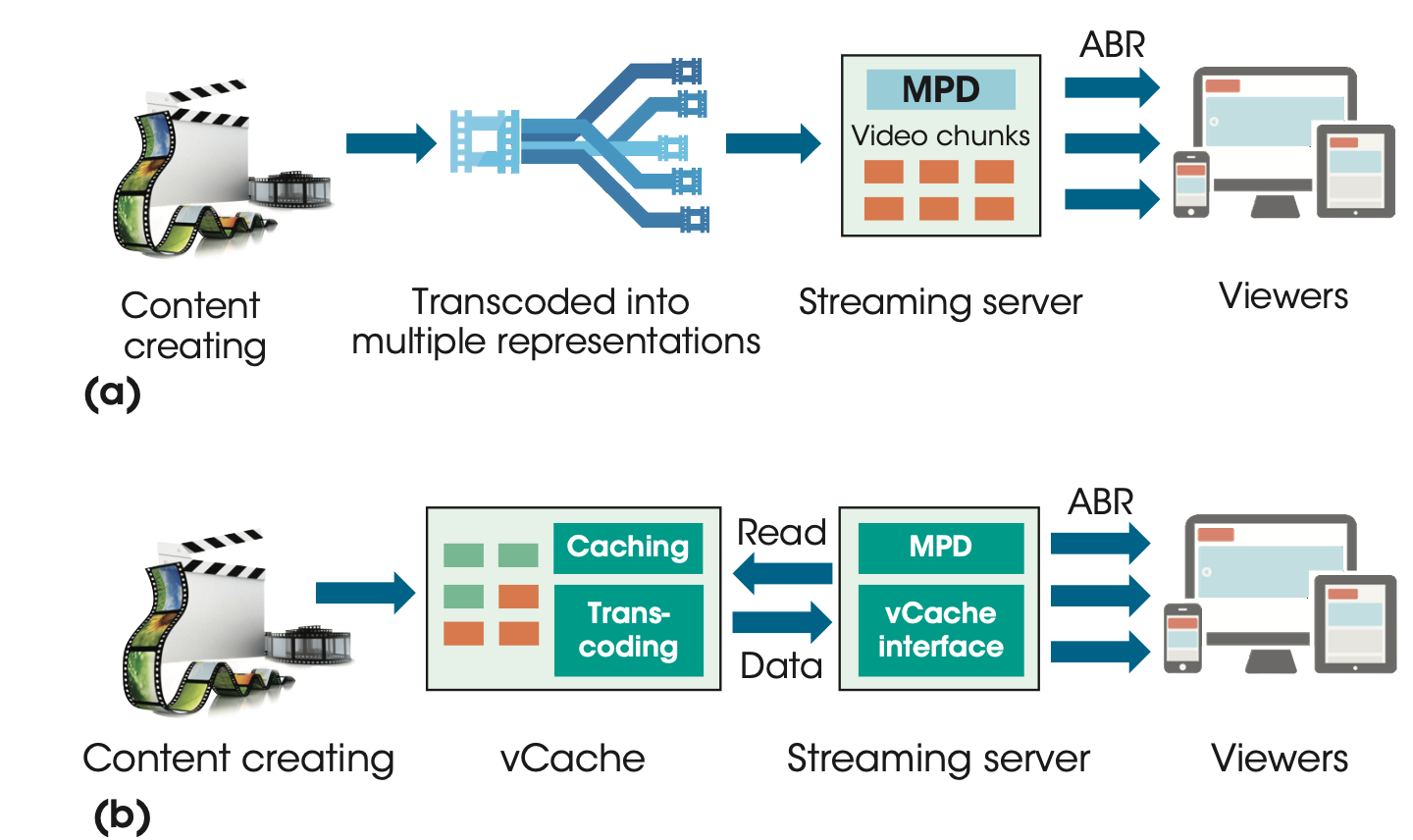
Each video is transcoded into multiple representations and then cached in streaming servers.
ABR Streaming
A media presentation description (MPD) file is required to manifest the available representations for a video.

ABR Streaming
When starting a video session, the video player
- obtains the MPD file
- selects the best possible quality representations according to the current network conditions and device capacity

Problem -- Operational Costs↑
Transcoding
- compute-intensive
- consumes tremendous resources
Caching multiple representations
- requires more storage space
- a few of video chunks are frequently requested
Is it necessary to pre-transcode each video and cache all video chunks?
vCache
Physically Cached
the video chunk is cached ➜ can be directly read from storage
Virtually Cached
only the metadata of the video chunk is cached
metadata contains
- location of the source version
- corresponding transcoding parameters (used to transcode a virtually cached video chunk on the fly)
ABR streaming with vCache
The MPD files are cached in streaming servers to manifest the available representations of each video.

ABR streaming with vCache
When starting a new session, the video player
- obtains the MPD file
- requests video chunks of the appropriate representations

ABR streaming with vCache
The streaming server will
read the requested video chunks in vCache
(dynamically cached / transcoded on the fly).

Difference
- not be pre-transcoded
-
vCache manages video chunks dynamically
What can vCache do
1. dynamically provision resources
transcoding delays <= acceptable range
2. strike a tradeoff between storage and computing costs
➜ reduce the operational costs of ABR streaming
System Design
Framework
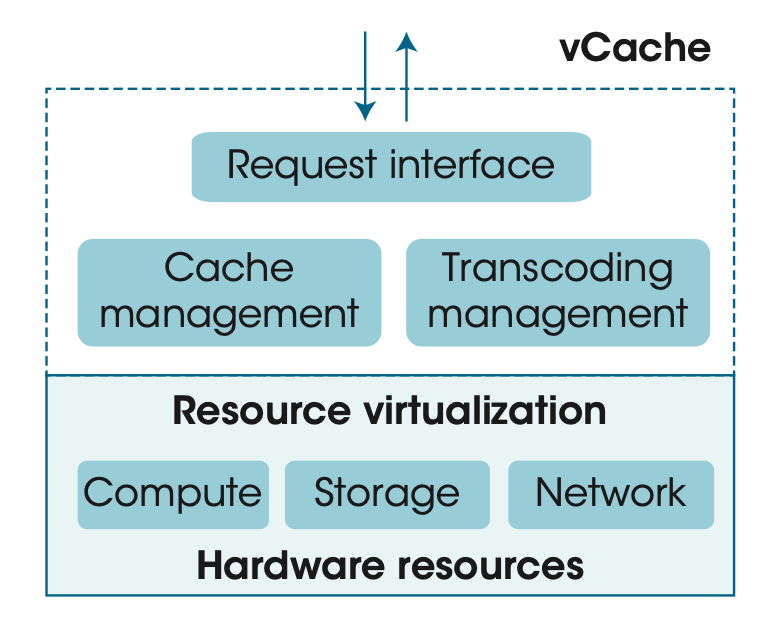
Resource
virtualization

- vCache is based on network function virtualization (NFV)
- provides the capacity of underlying hardware
- virtual computing
- storage
- network resources
Request interface

receives a request ➜ locates the video chunk
- physically cached
- directly read and delivered
- Otherwise
- initiate a transcoding request
- transcode the video chunk of the source version into the user-requested representation
- the transcoded video chunk will be rendered to the streaming server
- initiate a transcoding request
Cache management

-
analyzes the request information
-
dynamically determines whether a video chunk should be physically or virtually cached
-
Goal: reduce the overall cost
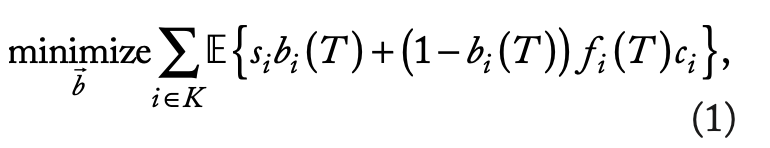
Transcoding
management

-
A virtually cached video chunk will be transcoded on the fly when being requested ➜ delays
-
dynamically provisions resources
-
transcoding workload is time varying
-
-
ensure that transcoding delays <= an acceptable range
Workflow
vCache receives a request for a video chunk
➜ looks up the requested video chunk
➜ reads and delivered / sends a transcoding request
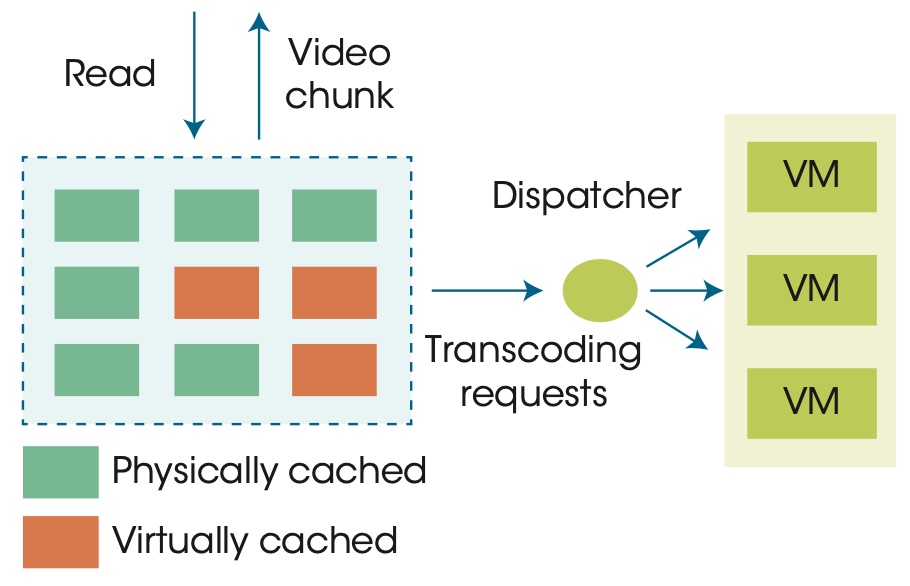
The dispatcher equally dispatches transcoding requests among the active virtual machines (VMs) for load balancing.

A transcoding server will transcode the requested video chunk on the fly when receiving a request.

vCache: Supporting Cost-Efficient Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
By hsutzu
vCache: Supporting Cost-Efficient Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Untitled TechShare 2021/04/01
- 316



