19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Evaluation 6
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Aadharsh Aadhithya - CB.EN.U4AIE20001
Anirudh Edpuganti - CB.EN.U4AIE20005
Madhav Kishor - CB.EN.U4AIE20033
Onteddu Chaitanya Reddy - CB.EN.U4AIE20045
Pillalamarri Akshaya - CB.EN.U4AIE20049
Team-1
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Pieper's Solution for 6-axis robots
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Piper's Solution for 6-axis robots
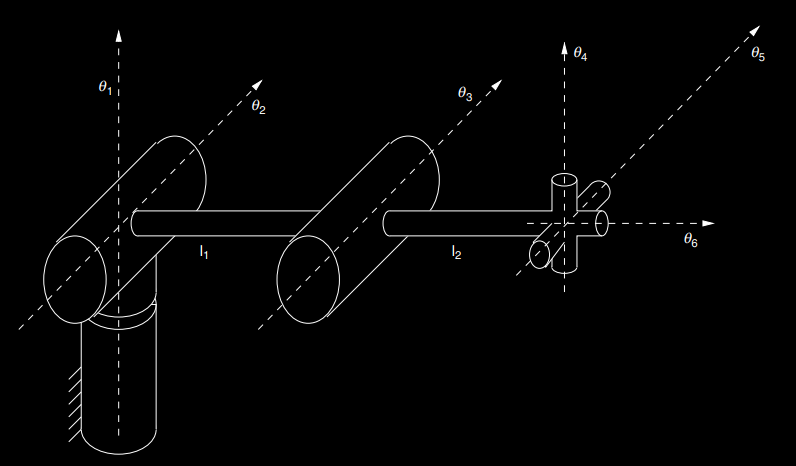
Conditions
- Last three axes of manipulator must be intersecting
- All the six joints must be revolute joints
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Piper's Solution for 6-axis robots
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Piper's Solution for 6-axis robots

- The distance between the axes 1,2,3 and axes 4,5,6 only depends on
- The height of end manipulator only depends on and
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Piper's Solution for 6-axis robots
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Piper's Solution for 6-axis robots
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Piper's Solution for 6-axis robots
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Piper's Solution for 6-axis robots
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Piper's Solution for 6-axis robots
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Piper's Solution for 6-axis robots
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Piper's Solution for 6-axis robots
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Newton-Raphson method
19AIE201
Introduction to Robotics
Newton-Raphson method
Newton-Raphson method
Newton-Raphson method
Newton-Raphson method
Newton-Raphson method
Jacobian Matrix
Robotics A5
By Incredeble us
Robotics A5
- 131



