Paper Review: Watch-It-Next: A contextual
Ingibjorg Osk Jonsdottir
Advanced Concepts in Machine Learning

TV RECOMMENDATION SYSTEM
Summary

- Recommendations on smart television sets shared by multiple users whose tastes may vary.
- Temporal and sequential context.
- Empirical evaluation of several recommendation methods.
- WatchItNext recommendation system. Verifies methods on top of two learning models.
limited DATa
| Total | Train | Test | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Month | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| Devices | 339.647 | 339.647 | 311.964 |
| Items | 19.546 | 17.232 | 11.640 |
<deviceID, itemID, timeStamp>
- itemID doesn't detect a specific episode
- no user identification
- length of TV program unknown
- Inventory unknown
Recommenders
| Recommender | Description |
|---|---|
| GeneralPop | General popularity of item i |
| TemporalPop | Popularity of i at time t |
| SequentialPop | Popularity of i watched after c |
| DevicePop | Popularity of i within device d |
| DevicePop+X | DevicePop combined with a recommender X |
| LFM | LFM with a stochastic gradient descent |
| LDM | LDA applied as and LFM recommender |
| SequentialLFM/LDA | LFM/LDA with sequential context |
| TemporalLFM/LDA | LFM/LDA with temporal context |
| TemporalSeqLFM/LDA | LFM/LDA with sequential & temporal contexts |
Collaborative filtering methods
- Output two matrices as their resulting models:
- |D| × n matrix M_D
- n × |I| matrix M_I
- where D and I are the sets of all devices and items respectively.
- Each row of M_D and each column of M_I are vectors corresponding to a device and an item respectively.
- n is the selected latent dimension that represents n latent factors or topics.
- Recommendation Score:
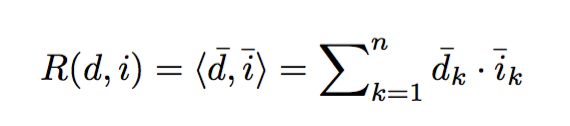
LFM with a stochastic gradient descent
- The cost function used for optimization is a log-sigmoid function that penalizes watched items with a low score and non-watched items with a high score:
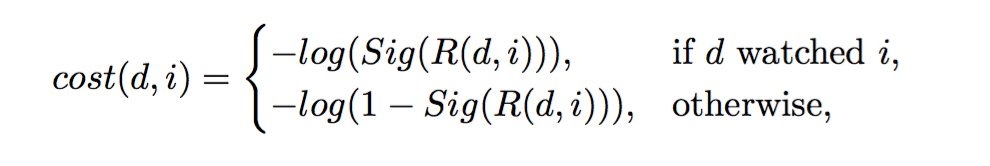
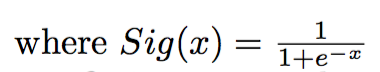
- Early-stop used to avoid overfitting and determine number of training iterations.
LDA as a Collaborative Filtering Recommender
- Every device considered to be an input document for LDA and every item watched by that device is a word in the document.
- Models each device as a mix of topics that relate to the combinations of entities that share the device.
- Used an existing LDA implementation to produce M_I matrix from which they inferred the M_D matrix.
- Probability that i will be watched on d:
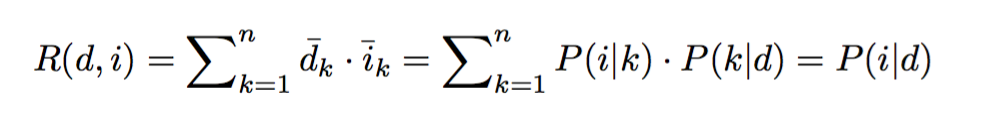
Contextual Personalization
Sequential Context
- Add the context of a currently watched item c
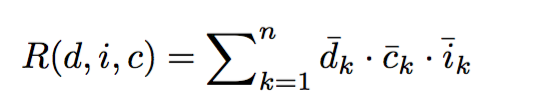
- LFM model values often negative so M_I was normalized by adding the absolute value of M_I minimal entry to all entries.
TempoRal Context
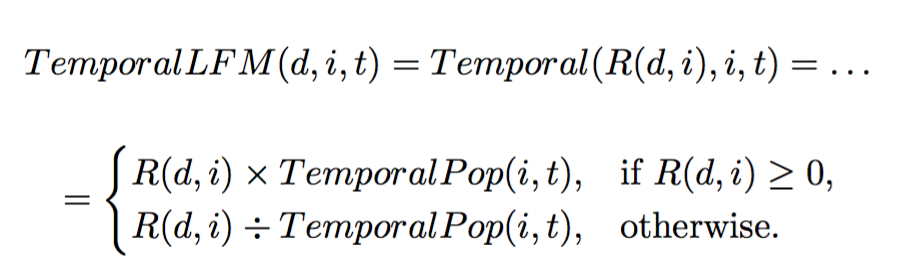
TEMPORAL and sequential CONTEXT
- Combine temporal context on top of a sequential context recommender
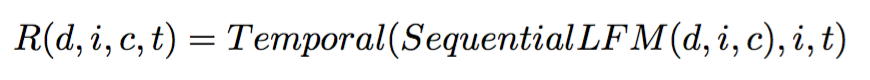
Experimental Setting
Emulate Inventories
- Go over pairs of items watched on a device d.
- Emulate inventory of items available after watching c at time t as the set of all shows j that were watched by some device while d watched i.
two scenarios
(1) exploratory setting
items which have yet to be consumed by a user
(2) habitual setting
include items previously watched on the device
Experimental Setting
Evaluation metric
- Average Rank Percentile (ARP) : how high was the show that was actually watched next ranked by the recommender.
- Rank percentile:
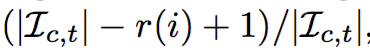
where I_c,t is the generated inventory and r(i) is i's rank on the output of the model
Results
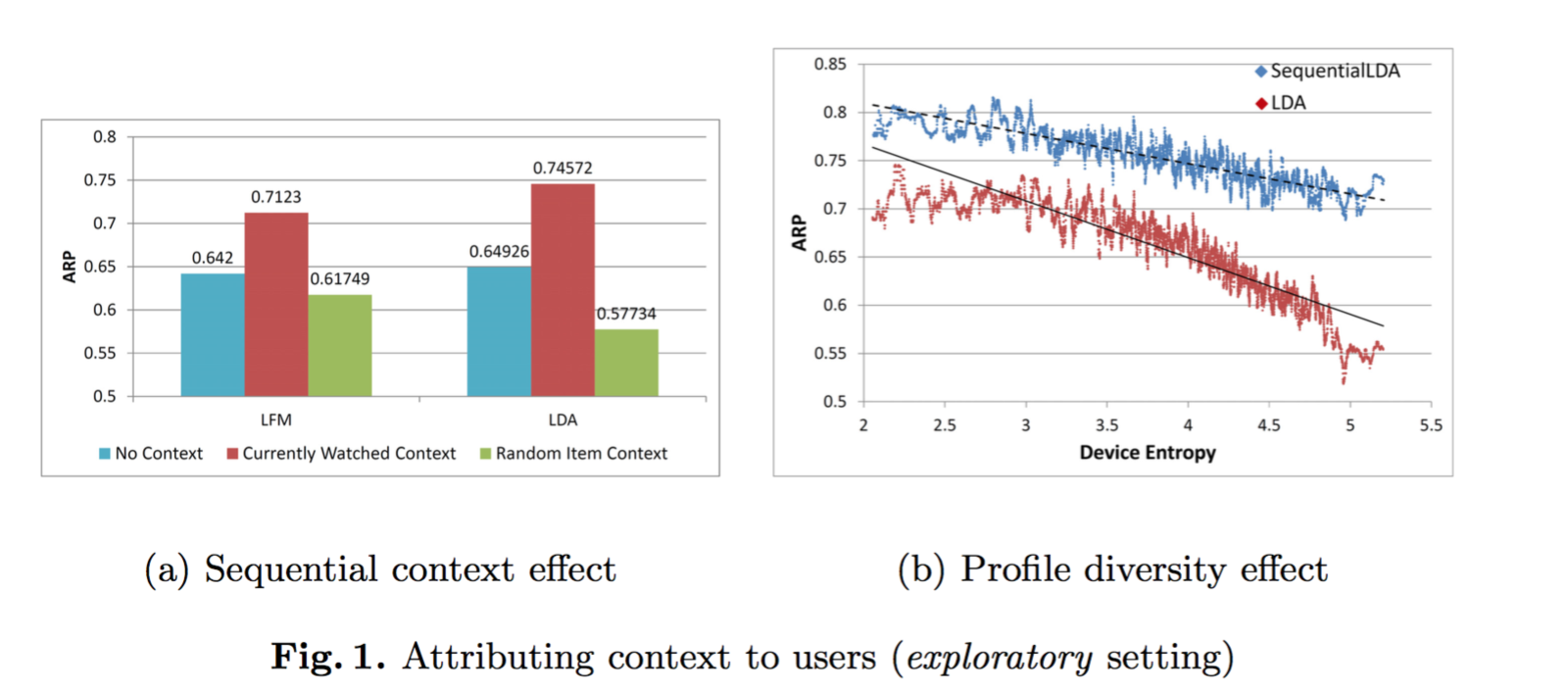
Assume a correlation between the taste diversity and the number of users sharing a device.
Results
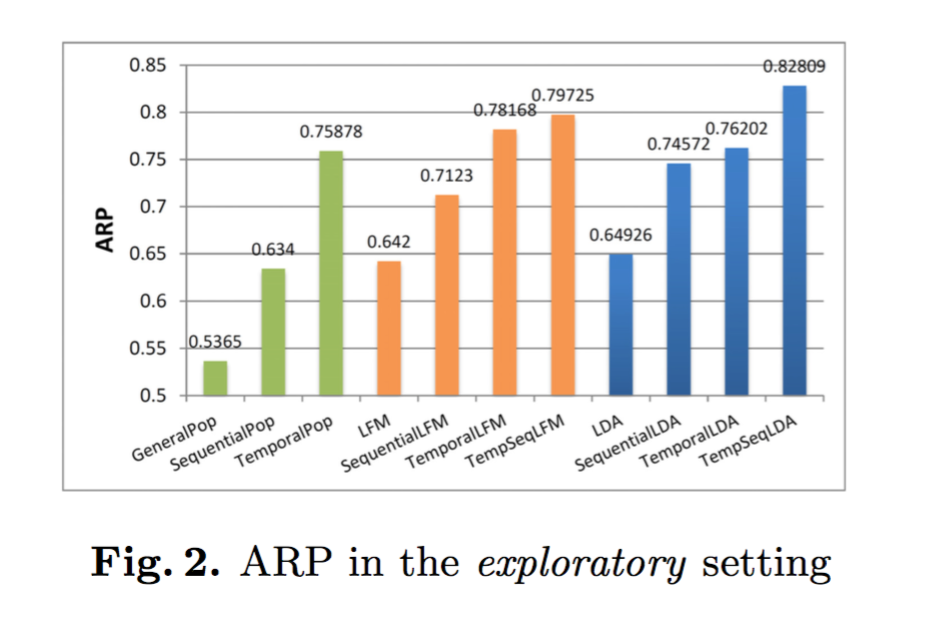
Results
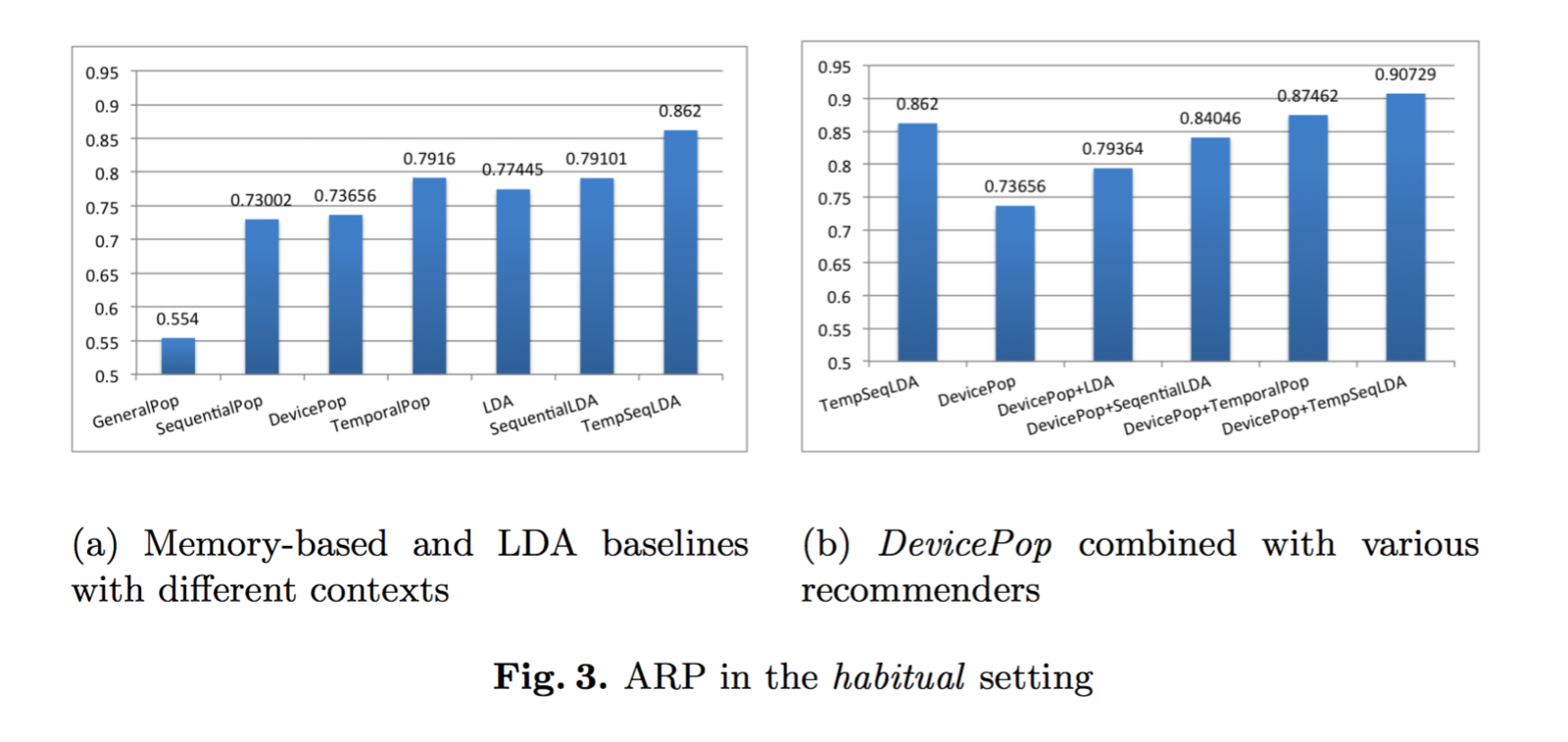
Conclusion
- Context significantly improves recommendation accuracy.
- Collaborative filtering schemes outperform the corresponding memory-based counterparts.
- Temporal context alone performs well but adding sequential context performs even better.
- Contribution? Useful? What about just identifying the user and tracking more data.
Watch-It-Next: A Contextual TV Recommendation System
By Ingibjörg Ósk Jónsdóttir
Watch-It-Next: A Contextual TV Recommendation System
Paper Review
- 304