NodeJS #6
Databases
$ whoami
Inna Ivashchuk
Senior Software Engineer
JS developer, music fan, movie-dependent and Star Wars fan 🤓
May the Force be with you!


Agenda
-
What is Database?
-
SQL vs NoSQL
-
ORMs
-
Sequelize
-
Mongo & Mongoose
What is Database?
Let's imagine situation

We have an online store and every product should be added and described in some list (can be Exel)

And every user should be able to buy a product


How to handle all this information in a correct way 🤔?
EXCEL file
Database
What is Database?
A database is a systematic collection of data. They support electronic storage and manipulation of data. Databases make data management easy.

Data in a Database
Product_ID
Name
Price
Type
Product
Customer_ID
Name
Adress
Phone
Customer
Order_ID
Customer_ID
Date
Shipping adress
Order
Product_ID
Every table in a database is an entity.
Column categories in a table (like Customer name, ID) - attributes of an entity
Data relationship: one-to-many
Customer_ID
Name
Adress
Phone
Customer
Order 01
Customer_ID
Order
Order 02
Customer_ID
Order
Order 02
Customer_ID
Order
Data relationship: many-to-many
Product_ID
Name
Price
Type
Product
Customer_ID
Name
Adress
Phone
Customer
Order_ID
Customer_ID
Date
Shipping adress
Order
Product_ID
Database transactions
A database transaction symbolizes a unit of work performed within a database management system (or similar system) against a database and treated in a coherent and reliable way independent of other transactions.
A transaction generally represents any change in a database.
Transaction
{ Query 1,
Query 2
......
Query N }
All queries executed successfully
Any of the Query failed
Initiate transaction
Transaction succeeded
Transaction failed
commit
rollback
Database transactions
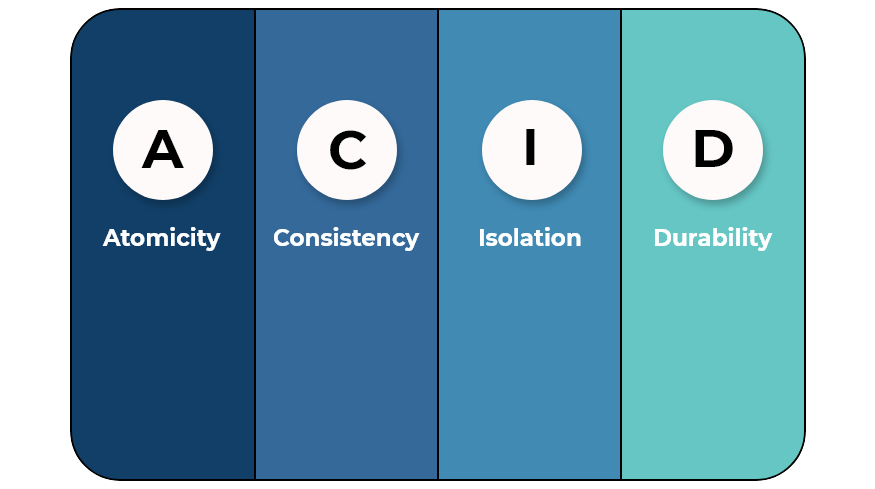
All database transactions must be ACID compliant or be Atomic, Consistent, Isolated and Durable to ensure data integrity.
Database transactions
Database types
Product
Customer
Databases can be classified according to content type: bibliographic, full text, numeric and images. In computing, databases are sometimes classified according to their organizational approach
SQL vs NoSQL
SQL
SQL (pronounced "ess-que-el") stands for Structured Query Language.
SQL is used to communicate with a database. According to ANSI (American National Standards Institute), it is the standard language for relational database management systems.
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderDate
FROM Orders
INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID=Customers.CustomerID;
SQL Databases
A relational database is a type of database that stores and provides access to data points that are related to one another.





NoSQL
A NoSQL (aka "not only SQL") database provides a mechanism for storage and retrieval of data that is modeled in means other than the tabular relations used in relational databases.





NoSQL

SQL vs NoSQL
NoSQL (“non SQL” or “not only SQL”) databases were developed in the late 2000s with a focus on scaling, fast queries, allowing for frequent application changes, and making programming simpler for developers.
Relational databases accessed with SQL (Structured Query Language) were developed in the 1970s with a focus on reducing data duplication as storage was much more costly than developer time. SQL databases tend to have rigid, complex, tabular schemas and typically require expensive vertical scaling.
Differences between SQL and NoSQL
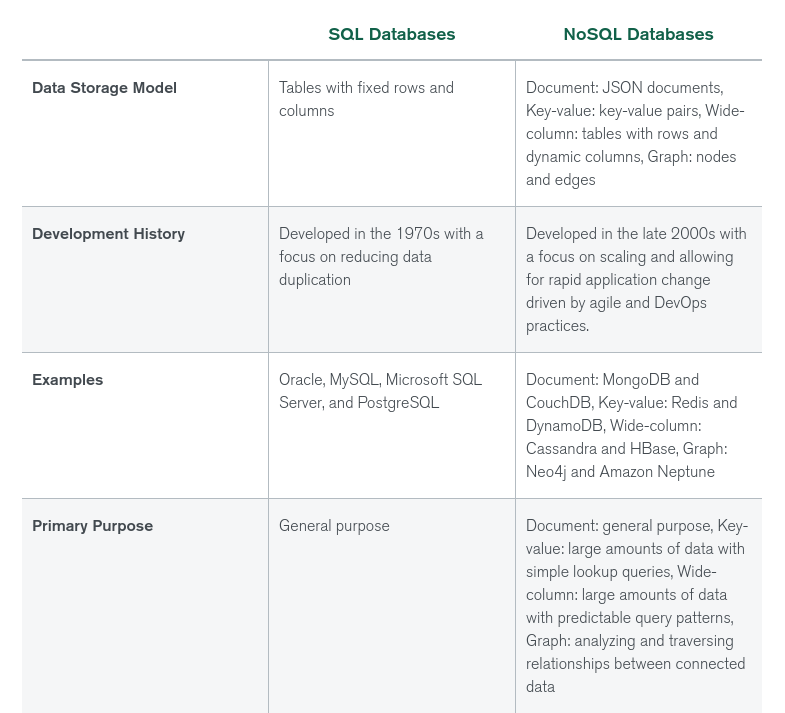
Differences between SQL and NoSQL

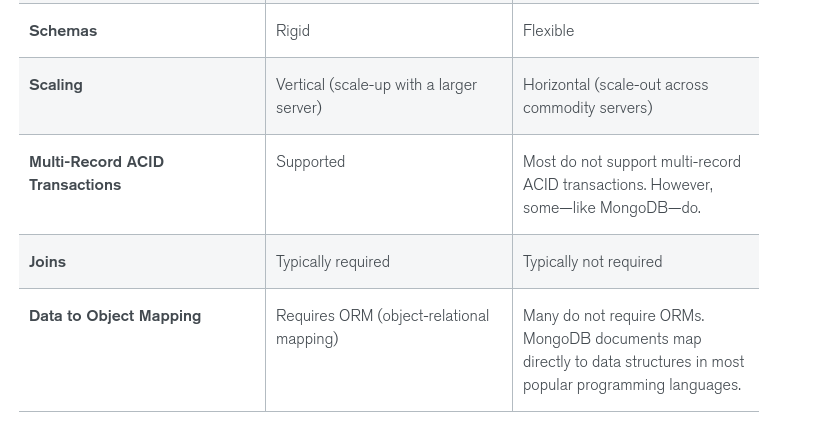
Benefits of NoSQL Databases
Flexible data models
Horizontal scaling
Easy for developers
Fast queries
Benefits of SQL Databases
High speed
No coding needed
Portability
Interactive language
Well defined standards
Interactive language
ORMs
What is ORM?
Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) is a technique that lets a query and manipulates data from a database using an object-oriented paradigm.
When talking about ORM, most people are referring to a library that implements the Object-Relational Mapping technique, hence the phrase "an ORM".

An example
We have a book class and want to retrieve all the books, where the author is "Linus".
Manually, we would do something like that:
book_list = new List();
sql = "SELECT book FROM library WHERE author = 'Linus'";
data = query(sql); // I over simplify ...
while (row = data.next())
{
book = new Book();
book.setAuthor(row.get('author');
book_list.add(book);
}With an ORM library, it would look like this:
book_list = BookTable.query(author="Linus");The mechanical part is taken care of automatically via the ORM library.
Using ORM: Pros and Cons

Using ORM saves a lot of time
- DRY: You write your data model in only one place, and it's easier to update, maintain, and reuse the code.
- A lot of stuff is done automatically, from database handling to I18N.
- It forces you to write MVC code, which, in the end, makes your code a little cleaner.
- You don't have to write poorly-formed SQL (most Web programmers really suck at it, because SQL is treated like a "sub" language, when in reality it's a very powerful and complex one).
- Sanitizing; using prepared statements or transactions are as easy as calling a method.
Using an ORM library is more flexible
- It fits in your natural way of coding (it's your language!).
- It abstracts the DB system, so you can change it whenever you want.
- The model is weakly bound to the rest of the application, so you can change it or use it anywhere else.
- It lets you use OOP goodness like data inheritance without a headache.
But ORM can be a pain:
- You have to learn it, and ORM libraries are not lightweight tools;
- You have to set it up. Same problem.
- Performance is OK for usual queries, but a SQL master will always do better with his own SQL for big projects.
- It abstracts the DB. While it's OK if you know what's happening behind the scene, it's a trap for new programmers that can write very greedy statements, like a heavy hit in a for loop.

ORM libraries
- Java: Hibernate.
- PHP: Propel or Doctrine
- Python: the Django ORM or SQLAlchemy
- C#: NHibernate or Entity Framework
- Node.js: Sequelize

Sequelize
What is Sequelize?
Sequelize is a promise-based Node.js ORM for Postgres, MySQL, MariaDB, SQLite, and Microsoft SQL Server. It features solid transaction support, relations, eager and lazy loading, read replication, and more.
To start using it:

$ npm install --save sequelizeSequelize usages
Sequelize follows Semantic Versioning and supports Node v10 and above.
You are currently looking at the Tutorials and Guides for Sequelize. You might also be interested in the API Reference.
And an example:
const { Sequelize, Model, DataTypes } = require('sequelize');
const sequelize = new Sequelize('sqlite::memory:');
class User extends Model {}
User.init({
username: DataTypes.STRING,
birthday: DataTypes.DATE
}, { sequelize, modelName: 'user' });
(async () => {
await sequelize.sync();
const jane = await User.create({
username: 'janedoe',
birthday: new Date(1980, 6, 20)
});
console.log(jane.toJSON());
})();Sequelize: Core Concepts
Mongo & Mongoose
What is MongoDB?
MongoDB is a document database that provides high performance, high availability, and easy scalability.

Getting started: installation
Getting started: starting on Ubuntu
$ sudo systemctl start mongod
# Verify that MongoDB has started successfully
$ sudo systemctl enable mongod
$ mongo
> use brewCoffeeNow I can create a DB, that will be in use in our app
Getting started: structure
Getting started: connection
CRUD operations

CRUD: Create (insert)
CRUD: Read
CRUD: Update
CRUD: Delete
Mongo DB plugin in the VS Code
Mongoose


Mongoose provides a straight-forward, schema-based solution to model your application data. It includes built-in type casting, validation, query building, business logic hooks and more, out of the box.
It's ODM (Object Document Mapping)
Getting started
Q & A

Homework
-
Create a new directory tutorial6
-
Find an idea for your app (can be an online store, cafe website and etc.)
-
Create your app with the next technologies: Express, Mongo DB, Mongoose
-
Run Mongo DB locally and create a corresponding DB and collection (based on app usages)
-
API should follow REST API rules and accept CRUD operations
-
Use cURL to check your endpoints (you can commit them as an MD file)
-
Try to use VS Code plugin for MongoDB to interact with data in your local DB
Helpful souces

- My repository with NodeJS tutorials
- official Express documentation
- and of course Stackoverflow
NodeJS Core #6
By Inna Ivashchuk
NodeJS Core #6
- 691



