echo "Bash" > intro
Learning outcomes
- You will Learn basic and more advanced commands
- You will be able to Write basic scripts
- You will know how to Debug them
- You will be able to Improve your work productivity
Examples
- search for a sequence of characters inside several files
- start a webserver locally
- get information on your network
- ...
Plan
- Basic introduction: Set up your environment, few commands to warm up a bit. Users, authorization...
- Your first script
- More advanced commands (grep, awk, sed...) & Introduction to regular expression
- Process & system management
- Final Hands-on
YouR environment (MAC/Linux)
YouR environment (MAC only)
# issamhammi at issams-air.home in ~ [18:09:27]
→ bash --version
GNU bash, version 5.0.18(1)-release (x86_64-apple-darwin19.5.0)
Copyright (C) 2019 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>
YouR environment (Windows)
A bit of theory
Bourne Again SHell or commonly called Bash is a command language interpreter

A bit of theory
A Shell is a program taking commands from the keyboard ans passing them to the operating system to be executed. Today shells are accessible through terminals
A script allows a set of commands to be executed one after the other
A bit of theory

A bit of theory

A bit of theory

Enough with that SH*T, I want to Code !

Basic Commands
- cd - change directory
- pwd - print working directory
- ls - list content
- cat - concatenate files and print output
- touch - create a file
- echo - display a line of text
- mkdir - make a directory
- rm - remove a file or directory
- mv - move a file or directory
Basic Commands - practice
- make a directory called pokemon
- change directory to the pokemon folder
- create a file called pikachu.txt
- change the name of pikachu.txt to evee.txt
- make a copy of the evee.txt file and call it evee2.txt
- remove the evee2.txt file
- make a copy of the first folder and call it pokemon2
- remove the pokemon2 folder
Basic Commands - practice
- What does the man command do? Type in man rm. How do you scroll and get out?
- Look at the man page for ls. What does the -l flag do? What does the -a flag do?
- Type the following command to download and save the contents of google.com: curl https://www.google.com > google.html
- Use less to look at the contents of google.html.
- Look at the man page for less. Read the section on /pattern. Search for the text hplogo in the google.html file.
Basic Commands - practice
- How do you jump between words in the terminal?
- How do you get to the end of a line in terminal?
- How do you move your cursor to the beginning in terminal?
- How do you delete a word (without pressing backspace multiple times) in terminal?
- What is the difference between a terminal and shell?
- What is an absolute path?
- What is an relative path?
- What is a flag? Give three examples of flags you have used.
- What do the r and f flags do with the rm command?
Linux filesystem
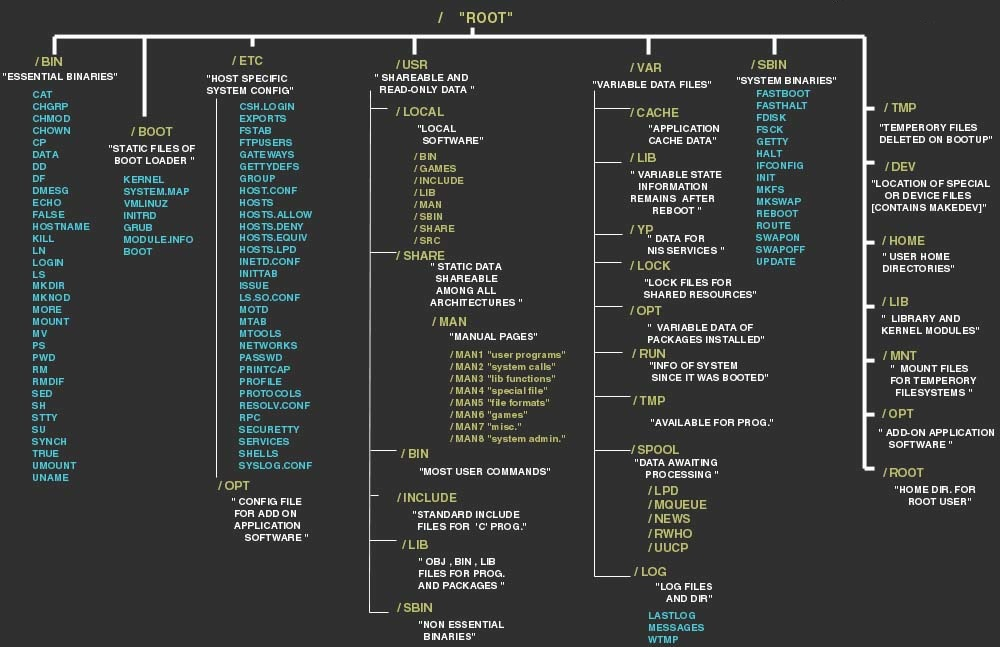
| path | |
|---|---|
| /bin | where I can find my binaries (ls, cat...) |
| /sbin | system administrator binaries (used by root) |
| /boot | where lives your OS (do not touch) |
| /etc | etcetera - system config files |
| /dev | special folder dedicated to hardware |
| /lib | libraries required by the binaries to run |
| /sys | kernel system files (do not touch) |
| /var | files expecting to grow in files (logs) |
| /root | root user dedicated folder |
| /usr | installed user applications |
| /home | user files |
Quiz
- Where are my personal programs located ?
- What does etc stands for ?
- Should I touch the files in /boot if I am new to Linux ?
- As a standard user, will I be able to see what is inside antother /home directory ?
- Is Linux a file system operating system ?
Environment Variables
Variables accessible outside of your program.
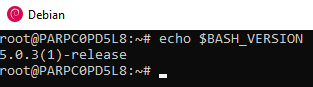
- printenv or set -> list your environment variables
- echo $BASH_VERSION -> print your bash version
- export POKEMON=pikachu -> set a new env variable
Environment Variables
$SHELL
$HOME
$PATH
...
.BASHRC file
When a login shell is started, it reads and execute commands from this file.
Users and groups
Users and groups
chmod u=rwx,g=rx,o=r myfilechmod 754 myfilechmod +x myfilePermissions
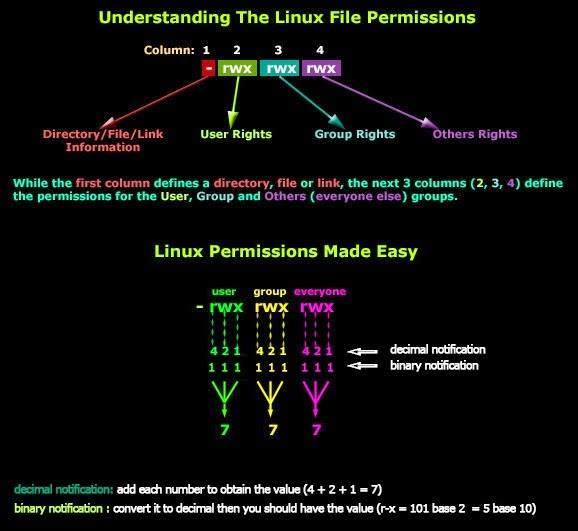
Permissions
| Number | Permission | rwx (display in terminal) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | none | --- |
| 1 | execute | --x |
| 2 | write only | -w- |
| 3 | write and execute | -wx |
| 4 | read only | r-- |
| 5 | read and execute | r-x |
| 6 | read and write | rw- |
| 7 | read, write and execute | rwx |
Permissions
- adduser -> add a new user
- addgroup -> create a new group
- chmod -> manage and change permissions
- su -> switch to user
- chown/chgrp -> manage and change owner and groups
- sudo -> gives the power of the root user

PRACTICE
- Create a file called restricted.txt.
- Change the permissions on the restricted.txt file to allow the owner to read and write to the restricted.txt file.
- Change the permissions on the restricted.txt file to only allow the owner, group and everyone to read and write and execute the restricted.txt file.
- Create a folder called secret_files. Inside the secret_files folder create a file called first_secret.txt and another folder called classified. Inside of the classified folder create a file called super_secret.txt.
- Change the permissions on the secret_files to only allow the owner and group to read, write and execute in all the files and folders inside of secret_files.
Bash - session 1
By Issam Hammi
Bash - session 1
First session about how to setup your environment and start playing with some commands
- 821



