Data science for lazy people, Automated Machine Learning
Diego Hueltes
Big Data Spain 2017

Original image from https://github.com/rhiever/tpot


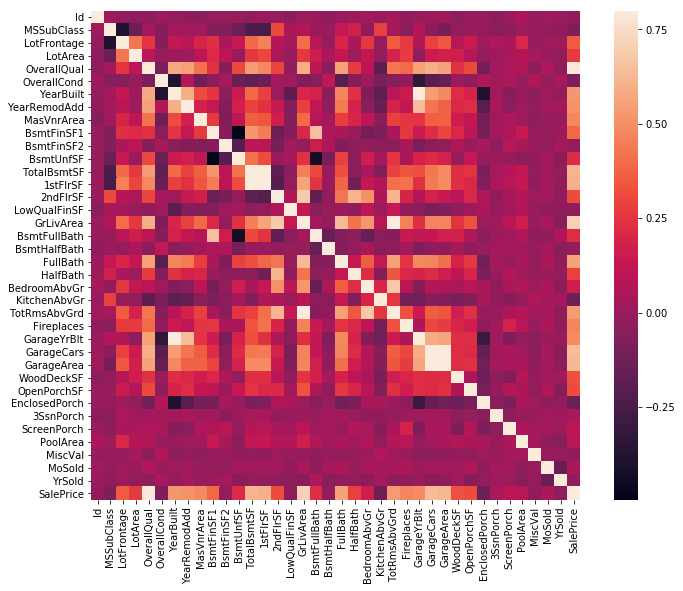
Data cleaning

Data cleaning
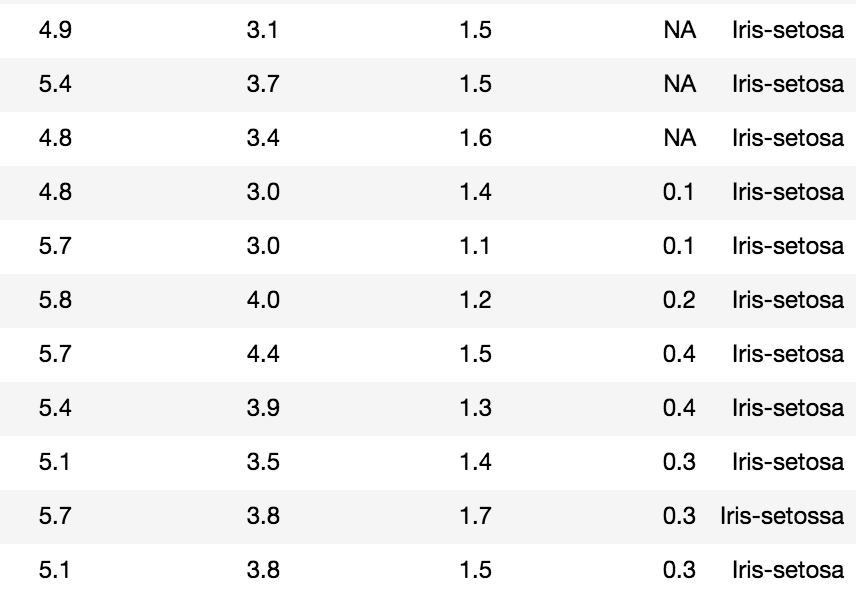
Data cleaning
Data cleaning

Feature selection
Feature selection
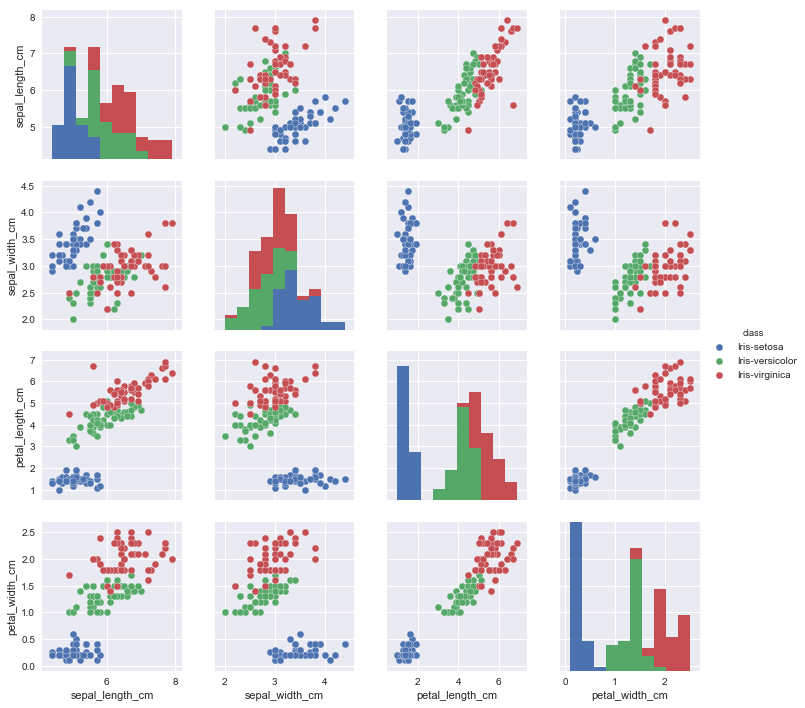

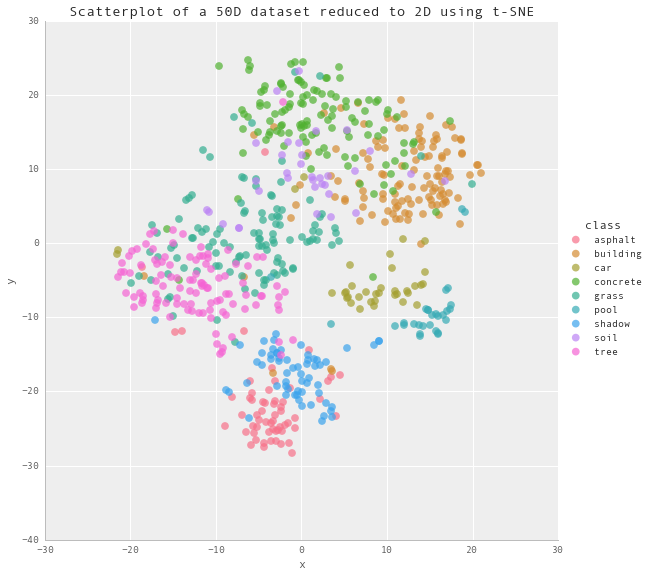
Feature preprocessing
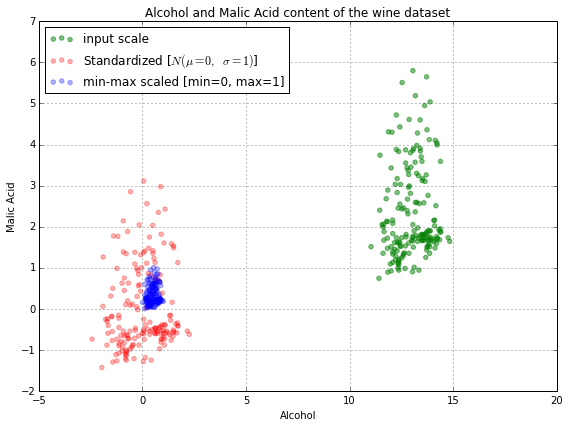

Feature construction


Model selection
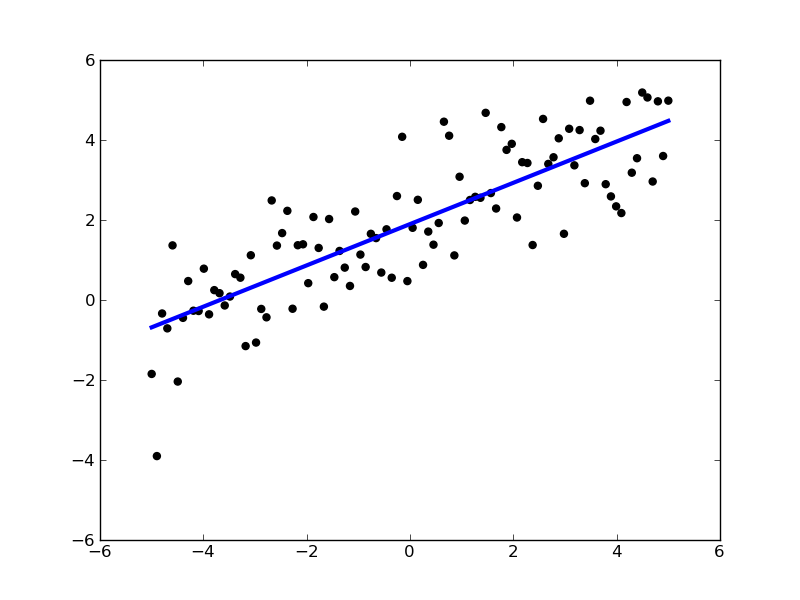
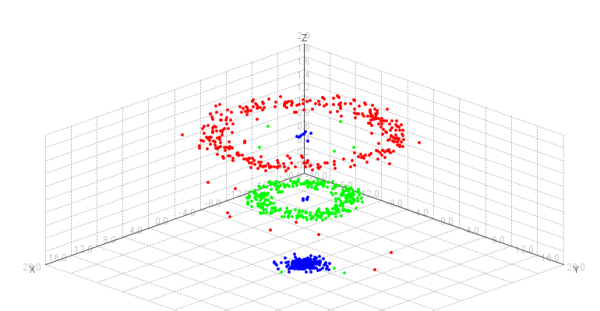
Model selection
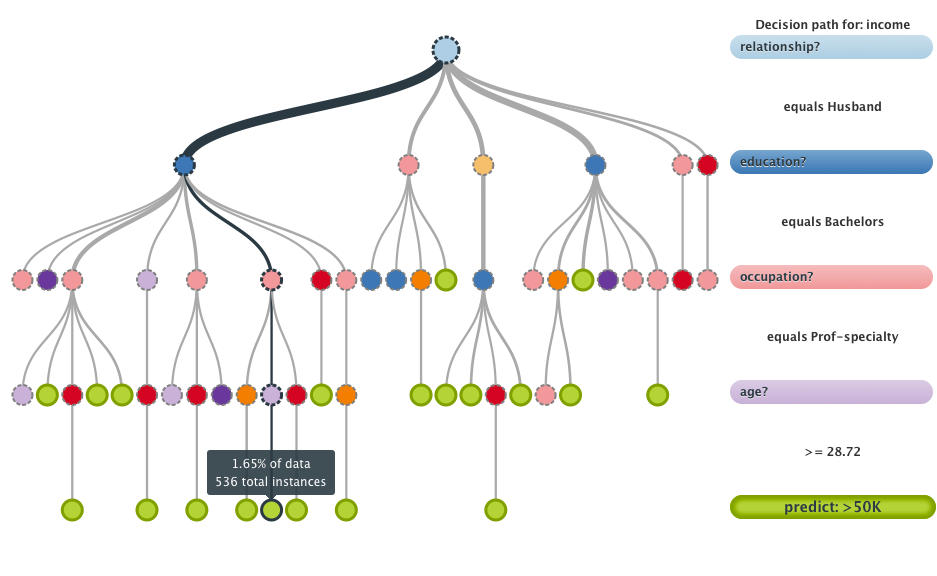

Parameter optimization
RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=2, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=10, n_jobs=1,
oob_score=False, random_state=0, verbose=0, warm_start=False)

Model validation

lazy Oxford dictionary
Unwilling to work or use energy
lazy Oxford dictionary
Unwilling to work or use energy
in repetitive tasks
Diego dictionary

naive_bayes.GaussianNB
naive_bayes.BernoulliNB
naive_bayes.MultinomialNB
tree.DecisionTreeClassifier
ensemble.ExtraTreesClassifier
ensemble.RandomForestClassifier
ensemble.GradientBoostingClassifier
neighbors.KNeighborsClassifier
svm.LinearSVC
linear_model.LogisticRegression
xgboost.XGBClassifier
preprocessing.Binarizer
decomposition.FastICA
cluster.FeatureAgglomeration
cluster.FeatureAgglomeration
preprocessing.MaxAbsScaler
preprocessing.MinMaxScaler
preprocessing.Normalizer
kernel_approximation.Nystroem
decomposition.PCA
preprocessing.PolynomialFeatures
kernel_approximation.RBFSampler
preprocessing.RobustScaler
preprocessing.StandardScaler
tpot.builtins.ZeroCount
feature_selection.SelectFwe
feature_selection.SelectPercentile
feature_selection.VarianceThreshold
feature_selection.RFE
feature_selection.SelectFromModel
linear_model.ElasticNetCV
linear_model.ElasticNetCV
ensemble.ExtraTreesRegressor
ensemble.GradientBoostingRegressor
ensemble.AdaBoostRegressor
tree.DecisionTreeRegressor
neighbors.KNeighborsRegressor
linear_model.LassoLarsCV
svm.LinearSVR
ensemble.RandomForestRegressor
linear_model.RidgeCV
xgboost.XGBRegressor
Automated Machine Learning
TPOT is a Python tool that automatically creates and optimizes machine learning pipelines using genetic programming.

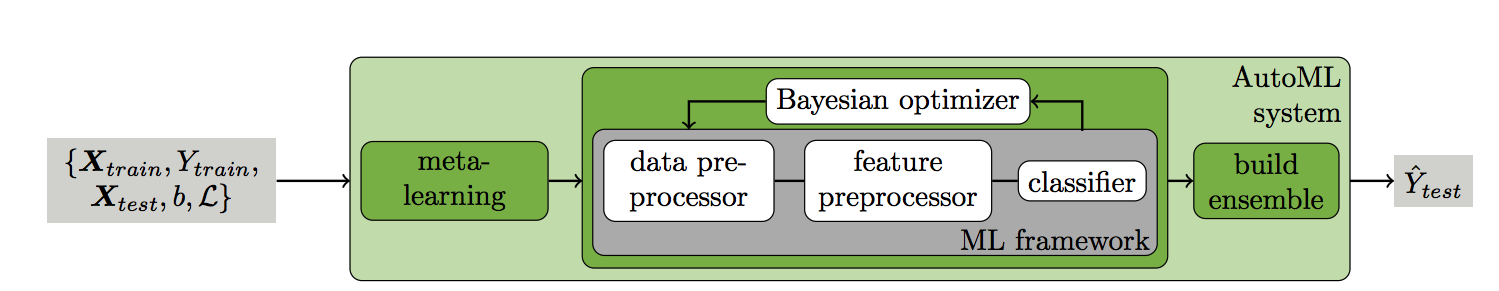
auto-sklearn frees a machine learning user from algorithm selection and hyperparameter tuning. It leverages recent advantages in Bayesian optimization, meta-learning and ensemble construction
auto-sklearn
Genetic programming

Source: http://www.genetic-programming.org/gpbook4toc.html
Photo: Diego Hueltes

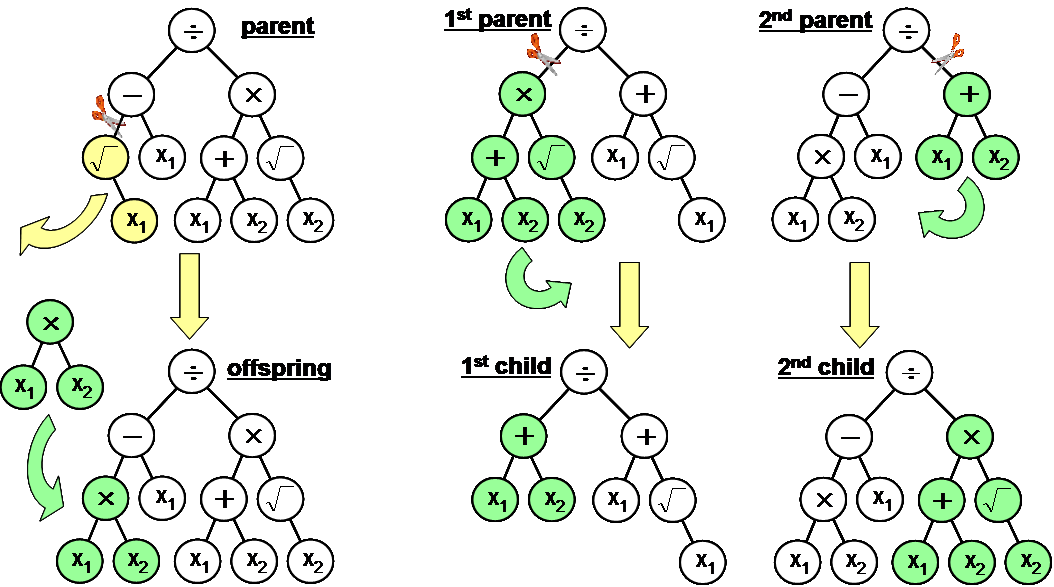
Crossover
Mutation
Source http://w3.onera.fr/smac/?q=tracker
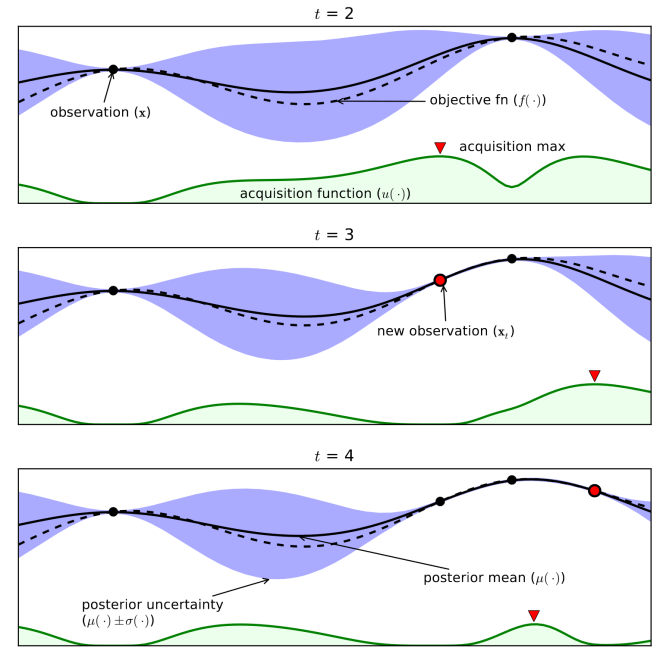
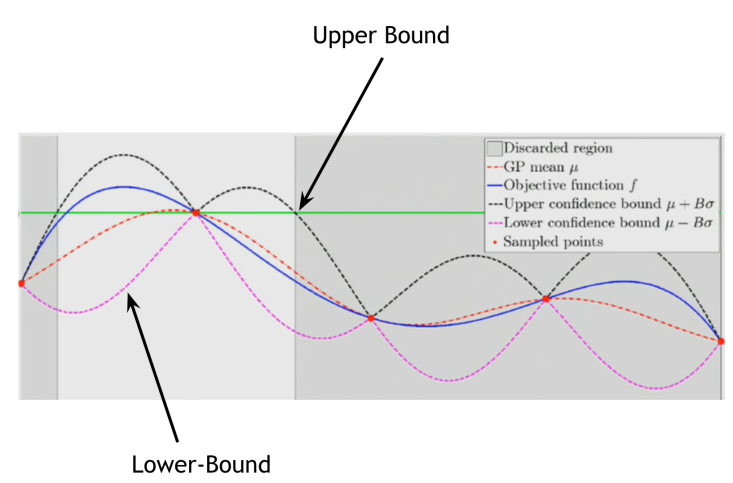
Bayesian optimization
Bayesian optimization
source: https://advancedoptimizationatharvard.wordpress.com/2014/04/28/bayesian-optimization-part-ii/
Bayesian optimization
source: https://advancedoptimizationatharvard.wordpress.com/2014/04/28/bayesian-optimization-part-ii/

TPOT is a Python tool that automatically creates and optimizes machine learning pipelines using genetic programming.

Scikit-learn pipelines

Warning
Code is coming
from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
count_vectorizer = CountVectorizer(ngram_range=(1, 4), analyzer='char')
X_train = count_vectorizer.fit_transform(train)
X_test = count_vectorizer.transform(test)
linear_svc = LinearSVC()
model = linear_svc.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_test = model.predict(X_test)from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import CountVectorizer
from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
pipeline = Pipeline([
('count_vectorizer', CountVectorizer(ngram_range=(1, 4), analyzer='char')),
('linear_svc', LinearSVC())
])
model = pipeline.fit(train)
y_test = model.predict(test)
TPOT

from tpot import TPOTClassifier, TPOTRegressor
tpot = TPOTClassifier()
tpot.fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = tpot.predict(X_test)
tpot = TPOTRegressor()
tpot.fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = tpot.predict(X_test)
Basic usage

Config dict
TPOTClassifier(config_dict = {
'sklearn.ensemble.RandomForestClassifier': {
'n_estimators': [100],
'criterion': ["gini", "entropy"],
'max_features': np.arange(0.05, 1.01, 0.05),
'min_samples_split': range(2, 21),
'min_samples_leaf': range(1, 21),
'bootstrap': [True, False]
},
'sklearn.feature_selection.RFE': {
'step': np.arange(0.05, 1.01, 0.05),
'estimator': {
'sklearn.ensemble.ExtraTreesClassifier': {
'n_estimators': [100],
'criterion': ['gini', 'entropy'],
'max_features': np.arange(0.05, 1.01, 0.05)
}
}
}
})
auto-sklearn frees a machine learning user from algorithm selection and hyperparameter tuning. It leverages recent advantages in Bayesian optimization, meta-learning and ensemble construction
auto-sklearn
auto-sklearn
Source: http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5872-efficient-and-robust-automated-machine-learning.pdf
import autosklearn.classification
import autosklearn.regression
automl = autosklearn.classification.AutoSklearnClassifier()
automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = automl.predict(X_test)
automl = autosklearn.regression.AutoSklearnRegressor()
automl.fit(X_train, y_train)
predictions = automl.predict(X_test)Basic usage
auto-sklearn
Custom configuration
auto-sklearn
- include_estimators
- exclude_estimators
- include_preprocessors
- exclude_preprocessors
Automated Machine Learning — A Paradigm Shift That Accelerates Data Scientist Productivity @ Airbnb
Automated Machine Learning
- Exploratory analysis
- Selective discovering
- New ideas for your model
- Model optimization
Thank you!




Data science for lazy people, Automated Machine Learning
By J. Diego Hueltes Vega
Data science for lazy people, Automated Machine Learning
Data science is fun… right? Data cleaning, feature selection, feature preprocessing, feature construction, model selection, parameter optimization, model validation… oh wait… are you sure? What about automating 80% of the work even doing better choices than you? Automated Machine Learning has arrived to be your personal assistant in Data Science
- 3,120
