Building 3D Worlds in the Browser

James Milner
@JamesLMilner
jmilner@esriuk.com
loxodrome.io

The web was very different growing up...







The Web has Matured

-
Open GL ES 2.0 for the web
-
Allows us to create 2D & 3D graphics
-
Plugin free; JavaScript API
-
Integrates into HTML page via canvas
-
No file formats, markup etc.
Increasingly a common choice is WebGL



*NPAPI now disabled in Chrome 45
Why WebGL?

More Plugins == More Attack Vectors


Plugins are Frustrating
Credit: xkcd.com
Some are Platform Specific

... but many of them were very valuable and served their purpose
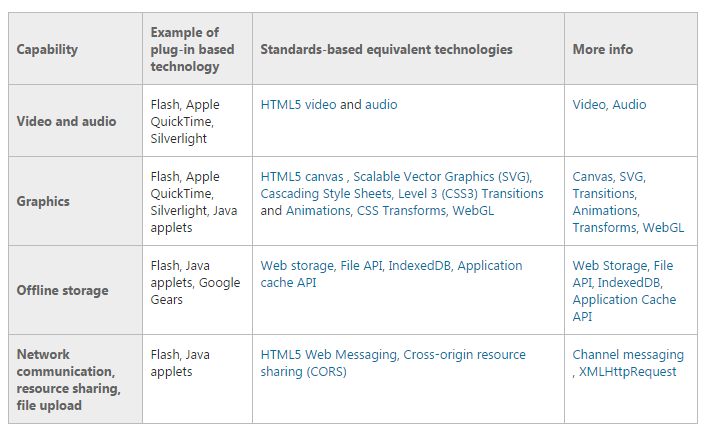
A Plugin Free World
Source: Microsoft
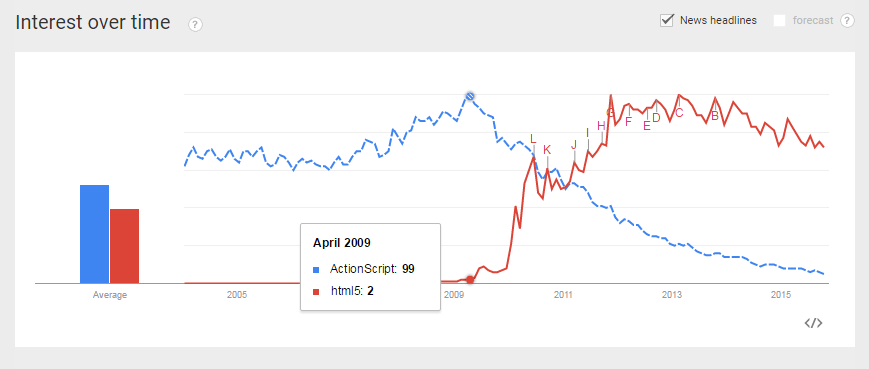
HTML5 vs ActionScript
- WebGL is a separate spec from HTML5 but requires canvas support
- WebGL also depends Typed Arrays (ECMAScript 2016) : an array-like view of an underlying binary data buffer
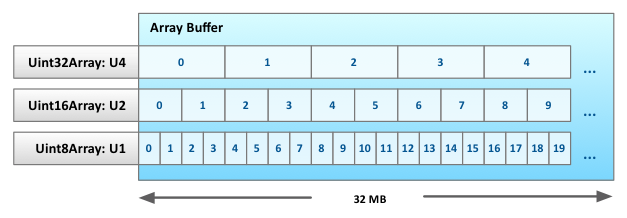

Transitioning to a WebGL World
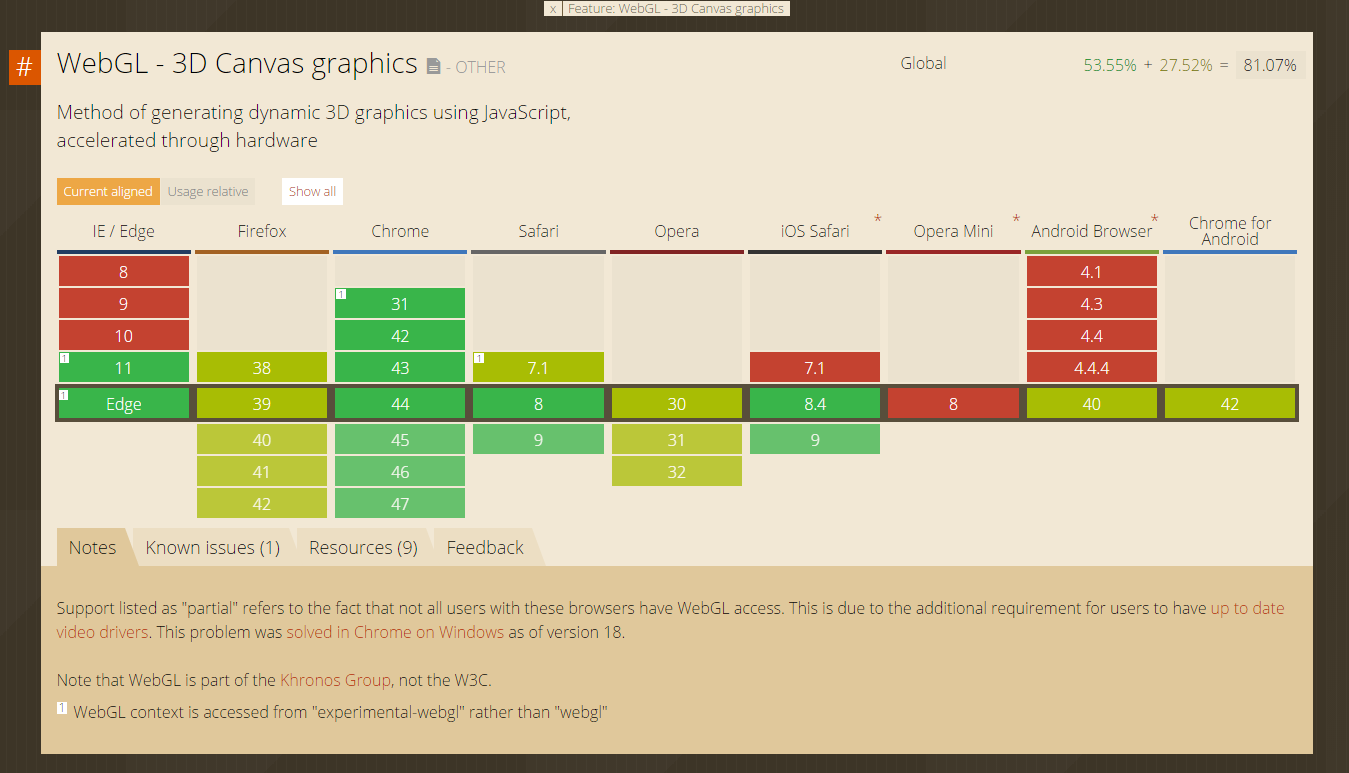
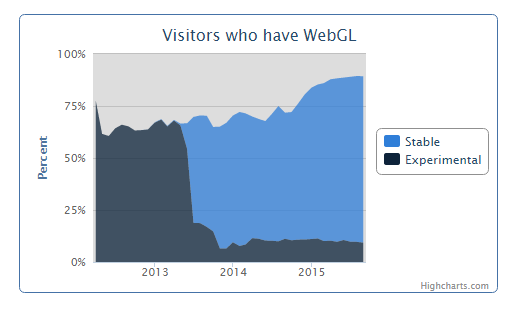
What About Support?
Sources: caniuse.com/webgl and webglstats.com
"WebGL is already a standard"
Ricardo Cabello (Three.js)
WebGL is a Low Level API

"low-level means that WebGL commands are expressed in terms that map relatively directly to how a GPU actually works" - Robert Nyman
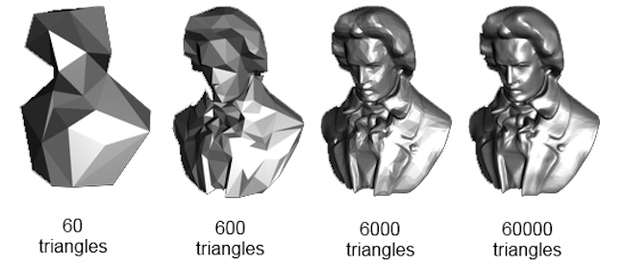
Constructing Things in WebGL
Source: University of New Mexico
Alongside our WebGL JavaScript API we require shaders

-
Shader - "a program that tells a computer how to draw something in a specific and unique way"
-
Vertex Shader - generates scene coordinates
-
Fragment Shader - provide colour for current pixel
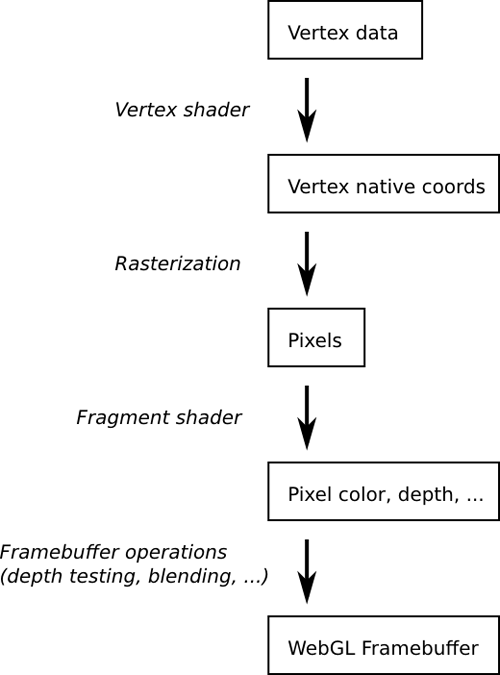
A Simplified Pipeline
Source: Mozilla
Introducing GLSL ES
Graphics Library Shader Language
<!-- Drawing a green square -->
<script id="2d-vertex-shader" type="x-shader/x-vertex">
attribute vec2 a_position;
// Storage qualifer - type - variable name
void main() {
gl_Position = vec4(a_position, 0, 1); // X, Y, Z, W
// gl_Position is a built in variable
}
</script>
<script id="2d-fragment-shader" type="x-shader/x-fragment">
void main() {
gl_FragColor = vec4(0, 1, 0, 1); // R, G, B, A (Green)
// gl_FragColor is a built in variable
}
</script>
-
Typed, C like language
-
Stored in a string, a script tag, or separate file
-
Has vectors and matrices as primitives
Hurry up and show me some JavaScript!
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>WebGL - Black and White Square</title>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<script type="text/javascript" src="glMatrix-0.9.5.min.js"></script>
<script id="shader-fs" type="x-shader/x-fragment">
precision mediump float;
void main(void) {
gl_FragColor = vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0);
}
</script>
<script id="shader-vs" type="x-shader/x-vertex">
attribute vec3 aVertexPosition;
uniform mat4 uMVMatrix;
uniform mat4 uPMatrix; // more info on these matrices at: http://www.opengl-tutorial.org/beginners-tutorials/tutorial-3-matrices/
void main(void) {
gl_Position = uPMatrix * uMVMatrix * vec4(aVertexPosition, 1.0);
}
</script>
<script type="text/javascript">
startWebGLScene = function() {
var gl;
function initGL(canvas) {
// Initialise the WebGL context on the canvas element
try {
gl = canvas.getContext("experimental-webgl");
if (!gl) {
gl = canvas.getContext("webgl");
}
gl.viewportWidth = canvas.width;
gl.viewportHeight = canvas.height;
} catch (e) {
}
if (!gl) {
alert("Could not initialise WebGL, sorry :-(");
}
}
function getShader(id) {
// Get the shader from the script tag
var shaderScript = document.getElementById(id);
if (!shaderScript) {
return null; // No shader script with that id
}
var shaderStr = ""; // Concatenate the whole shader together
var content = shaderScript.firstChild;
while (content) {
if (content.nodeType == 3) { // Text will have nodeType property will return 3.
str += content.textContent;
}
context = content.nextSibling;
}
var shader;
if (shaderScript.type == "x-shader/x-fragment") {
shader = gl.createShader(gl.FRAGMENT_SHADER); // if fragment
} else if (shaderScript.type == "x-shader/x-vertex") {
shader = gl.createShader(gl.VERTEX_SHADER); // if vertex
} else {
return null;
}
gl.shaderSource(shader, shaderStr); // Link type and source
gl.compileShader(shader); // Compile shader
if (!gl.getShaderParameter(shader, gl.COMPILE_STATUS)) {
alert(gl.getShaderInfoLog(shader)); // That went wrong
return null;
}
return shader;
}
function initShaders() {
var fragmentShader = getShader("shader-fs"); // Get fragmentshader
var vertexShader = getShader("shader-vs"); // Get vertex shader
var shaderProgram = gl.createProgram(); // create shader program
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader); // add vertex shader
gl.attachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader); // add vertex shader
gl.linkProgram(shaderProgram); // Link the two to program
if (!gl.getProgramParameter(shaderProgram, gl.LINK_STATUS)) {
alert("Could not initialise shaders");
}
gl.useProgram(shaderProgram); // Use the shader program
// Explicitly say which variable is the vertex position in vertex shader
shaderProgram.vertexPositionAttribute = gl.getAttribLocation(shaderProgram, "aVertexPosition");
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(shaderProgram.vertexPositionAttribute); // Enable it
// Set the uniform locations - uniforms stay the same per frame render
shaderProgram.pMatrixUniform = gl.getUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "uPMatrix");
shaderProgram.mvMatrixUniform = gl.getUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "uMVMatrix");
return shaderProgram;
}
function setMatrixUniforms(pMatrix, mvMatrix, shaderProgram) {
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(shaderProgram.pMatrixUniform, false, pMatrix);
gl.uniformMatrix4fv(shaderProgram.mvMatrixUniform, false, mvMatrix);
}
function initBuffers() {
var triangleVertexPositionBuffer;
var squareVertexPositionBuffer;
//Triangle
triangleVertexPositionBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, triangleVertexPositionBuffer);
var vertices = [
0.0, 1.0,
-1.0, -1.0,
1.0, -1.0
]; // X, Y, Z
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(vertices), gl.STATIC_DRAW); // Static_draw =Modified once used many times
triangleVertexPositionBuffer.itemSize = 2; // 2 Numbers (X, Y)
triangleVertexPositionBuffer.numItems = 3; // 3 Vertices
//Square
squareVertexPositionBuffer = gl.createBuffer();
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, squareVertexPositionBuffer);
vertices = [
1.0, 1.0,
-1.0, 1.0,
1.0, -1.0,
-1.0, -1.0
];
gl.bufferData(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array(vertices), gl.STATIC_DRAW);
squareVertexPositionBuffer.itemSize = 2; // 2 Numbers (X, Y)
squareVertexPositionBuffer.numItems = 4; // 4 Vertices
return {
"triangle" : triangleVertexPositionBuffer,
"square": squareVertexPositionBuffer
};
}
function drawScene(gl, shaderProgram, vertexPositionBuffers) {
var mvMatrix = mat4.create(); // glMatrix functions
var pMatrix = mat4.create();
var triangleVertexPositionBuffer = vertexPositionBuffers.triangle;
var squareVertexPositionBuffer = vertexPositionBuffers.square;
gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.viewportWidth, gl.viewportHeight); // Set viewport
gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | gl.DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
// Clears the color and depth buffers
mat4.perspective(45, gl.viewportWidth / gl.viewportHeight, 0.1, 100.0, pMatrix);
// Field of View = 45 , width-to-height ratio of canvas, min view distance, max view distance
mat4.identity(mvMatrix); // Set the identiy to be
// DRAW THE TRIANGLE
mat4.translate(mvMatrix, [-1.5, 0.0, -7.0]); // Translate modelview matrix
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, triangleVertexPositionBuffer);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(shaderProgram.vertexPositionAttribute, triangleVertexPositionBuffer.itemSize, gl.FLOAT, false, 0, 0);
setMatrixUniforms(pMatrix, mvMatrix, shaderProgram); // Provide the matrix with current mvMatrix and pMatrix
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLES, 0, triangleVertexPositionBuffer.numItems);
// Draw vertices as a triangle
// DRAW THE SQUARE
mat4.translate(mvMatrix, [3.0, 0.0, 0.0]); // Translate modelview matrix
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, squareVertexPositionBuffer);
gl.vertexAttribPointer(shaderProgram.vertexPositionAttribute, squareVertexPositionBuffer.itemSize, gl.FLOAT, false, 0, 0);
setMatrixUniforms(pMatrix, mvMatrix, shaderProgram); // Provide the matrix with current mvMatrix and pMatrix
gl.drawArrays(gl.TRIANGLE_STRIP, 0, squareVertexPositionBuffer.numItems);
// Draw vertices as a triangle strip (back to back triangles)
}
var canvas = document.getElementById("webgl-canvas"); //Get Canvas
initGL(canvas);
var shaderProgram = initShaders();
var vertexPositionBuffers = initBuffers();
gl.clearColor(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0); //Black
gl.enable(gl.DEPTH_TEST); //
drawScene(gl, shaderProgram, vertexPositionBuffers);
};
</script>
</head>
<body onload="startWebGLScene();">
<canvas id="webgl-canvas" style="border: none;" width="500" height="500"></canvas>
</body>
<!-- Adapted from: http://learningwebgl.com/blog/?p=28 -->
</html>
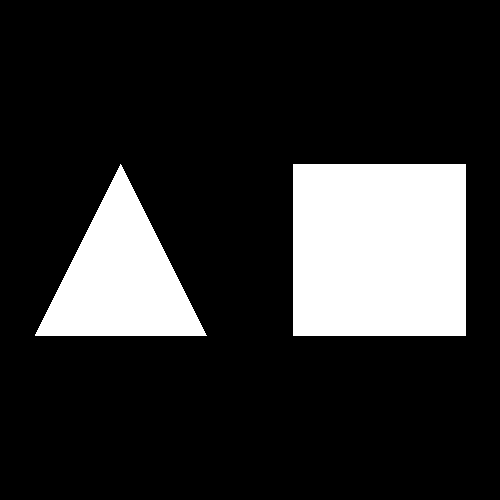
Raw WebGL
TWGL
PhiloGL
Three.js
Babylon.js
Scene.js
OSG.js
GLGE
CopperLicht
WebGL Studio
Increasing Abstraction
Frameworks Help us Move Faster

"It shouldn't be underestimated how much WebGL adoption has been driven by Three.js."
Let's see some examples
Obviously these are fairly trivial...
It's not just fantasy worlds benefiting from WebGL...
WebGL Powered Map Tiles
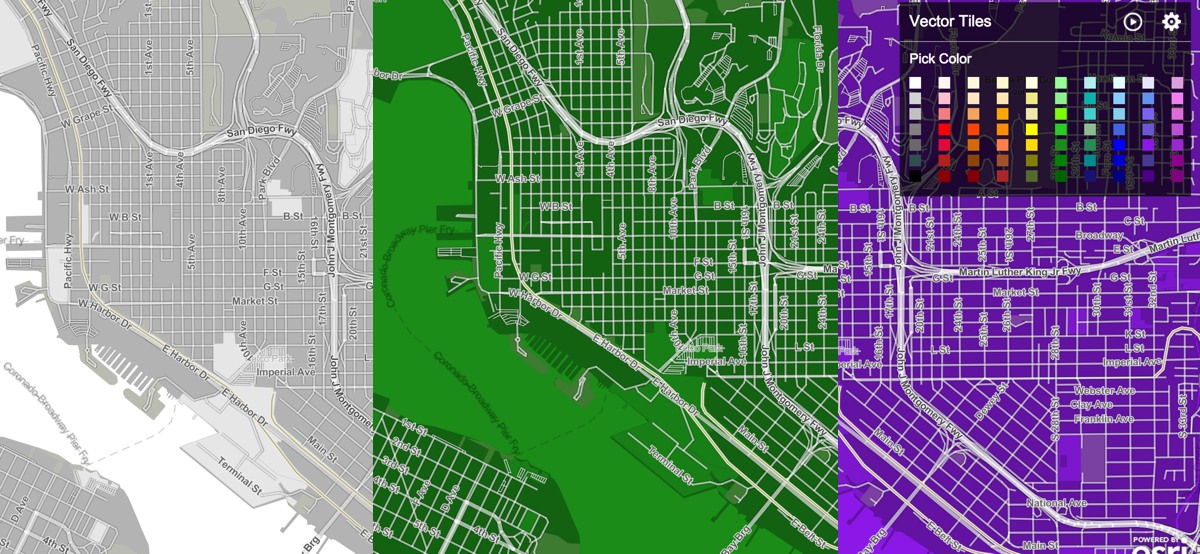

WebGL is also super useful for 3D web mapping
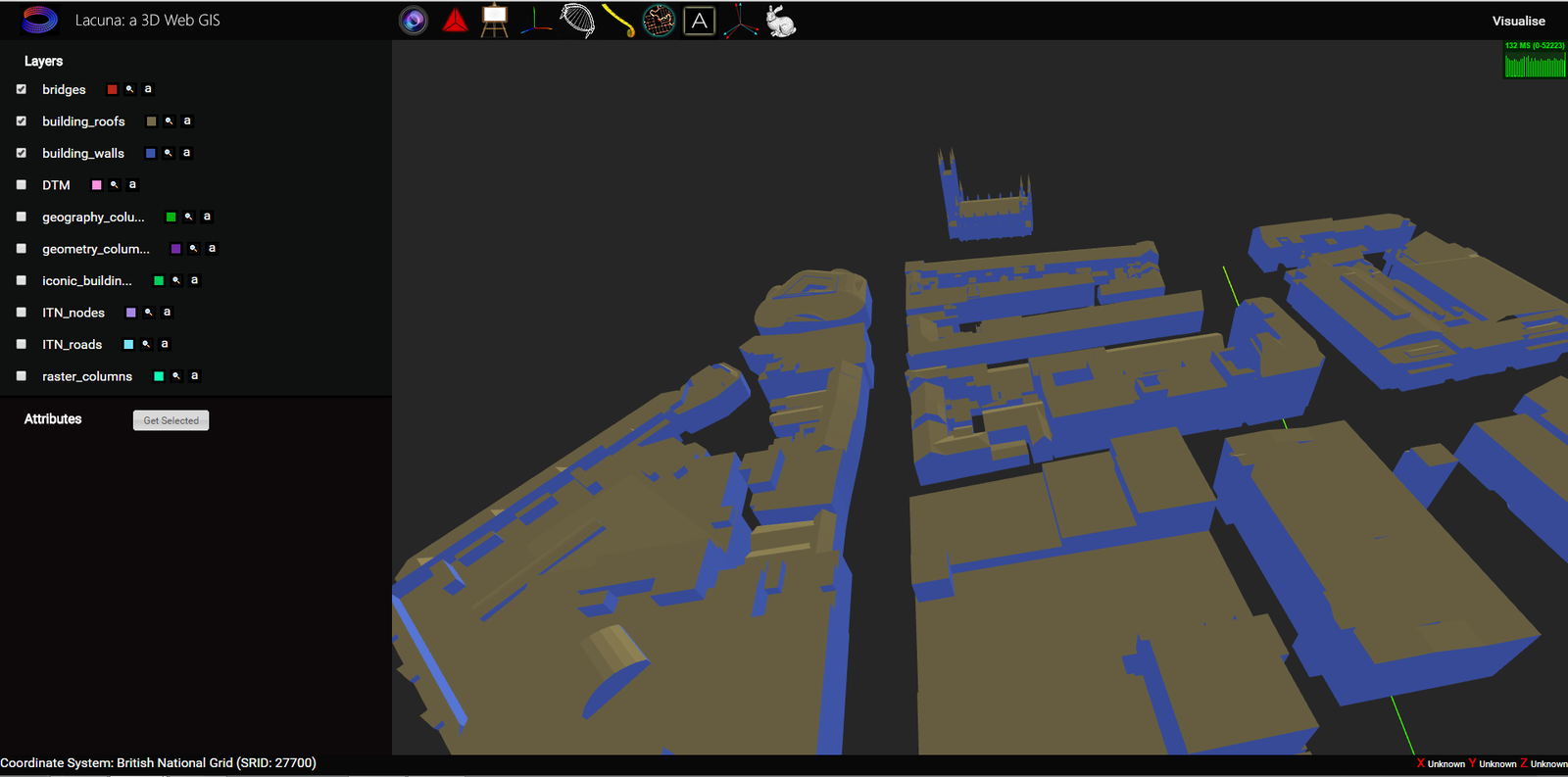
Why 3D?
Queen Flight Visualisation
3D Edition!
Let's have some fun...
Get ready to text, but hold fire!
+441254790245
Favourite City, Country
i.e. Paris, France
- Plugins are dying WebGL + HTML5 are powerful replacements
- ... but WebGL is low level and verbose
- Frameworks can help (Three.js, Babylon.js)
- We can now build immersive 3D apps
- They are not just limited to video games
- WebGL 2 is in the works...

Thanks!
@JamesLMilner
jmilner@esriuk.com

WebGL Links
Content Links
Building 3D Worlds in the Browser - HalfStack Edition
By James Milner
Building 3D Worlds in the Browser - HalfStack Edition
A talk on building 3D worlds in the browser with WebGL (or more specifically abstraction libraries for WebGL!)
- 2,166






