So you want to be a Gopher
Hackference, 2016
James Milner

Software Engineer

@JamesLMilner
james@loxodrome.io
Why this talk?
What is Go?
Go is a compiled, statically typed programming language created at Google in 2007 by by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson
How did I get here?
Humble Beginnings
# Python
x = 10
x = "Hello World"
x = 1.1
print x
# JavaScript
var x = 10;
x = "Hello World";
x = 1.1;
console.log(x)
function dis() { return this }
// undefined
five = dis.call(5)
// [Number: 4]
five.wtf = 'potato'
// 'potato'
five.wtf
// 'potato'
five * 5
# 25
five.wtf
// 'potato'
five++
// 5
five.wtf
// undefinedThe Javas
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Prints "Hello, World" to the terminal window.
String hello = new String("Hello World");
System.out.println(hello);
}
}"The problem is you can be productive, or you can be safe, but you can't really be both" - Rob Pike, 2009
Reasons I like Go
- Typed language
- Fast
- Comprehensive standard library
- Clean syntax
- Memory managed
- API doesn't change much
- UTF-8 by default
and of course...
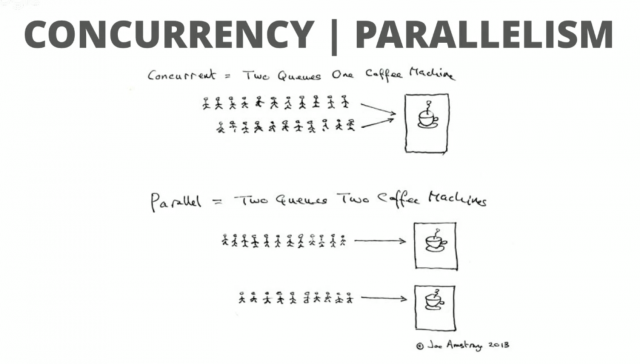
'That's super great James, but just give me the low down'
The Different Parts
Assignments
// JAVASCRIPT (ES5)
var a = "Hello";
var b; // b === undefined
// GO LANG
var string a = "Hello"
var b = "Hello"
c := "Hello"
var d string // Defaults to empty string
if/else
// JAVASCRIPT
if (someCondition) {
doSomething()
}
else {
doSomethingElse()
}// GO LANG
if someCondition {
doSomething()
} else {
doSomethingElse()
}For Loops
for {
doSomethingEndlessly()
}
for x < 10 {
x++
}
for i := 0; i <= 9; i++ {
fmt.Println(i)
}
for i, num := range nums {
if num == 3 {
fmt.Println("index:", i)
}
}
arrays
slices!
-
We do have arrays in Go
-
We use them far less frequently than slices
-
Arrays in Go have a fixed length
-
Slices can be of varying length
Errors
Errors are just values in Go
func f1(arg int) (int, error) {
if arg == 42 {
return -1, errors.New("can't work with 42")
}
return arg + 5, nil
}Pointers
Errors are just values in Go
package main
import "fmt"
func zeroval(ival int) {
ival = 0
}
func zeroptr(iptr *int) {
*iptr = 0
}
func main() {
i := 1
fmt.Println("initial:", i)
zeroval(i)
fmt.Println("zeroval:", i)
zeroptr(&i) //The &i syntax gives the memory address
fmt.Println("zeroptr:", i)
}
The Cool Parts
Multi Returns
// PYTHON 2
def vals:
return [3, 7]
// GO LANG
func vals() (int, int) {
return 3, 7
}Variadic Functions
func sum(nums ...int) {
fmt.Print(nums, " ")
total := 0
for _, num := range nums {
total += num
}
fmt.Println(total)
}Structs
type Person struct {
name string
job string
age int
phrase string
}
hugh := Person{
name: "Hugh",
job : "The Spotifys",
age : 23,
phrase : "That sound's sub optimal",
}
fmt.Println(hugh.phrase)Go Routines / Channels
The Tools
...


So you want to be a Gopher
By James Milner
So you want to be a Gopher
- 1,361



