What is geo data and how to get the most from it

james.milner@geovation.uk
@JamesLMilner
loxodrome.io
James Milner



Enough about me






Positioning & location sharing has become an indispensable part of modern life
What do we mean by location?
That bar behind the coffee shop on Westferry Road?
An address?
A postcode?
A latitude and longitude?
Easting and Northing?
x and y?



Lets call this 'geo data'
Many providers build up lots of geo data into products or assets




-
460+ million geographic features in the database
- 29,105,155 residential addresses
- 2681 Roads named High Street
- 10,000 changes a day to the master map of Great Britain
- 16 full coverage UK level, maintained, open data sets
Data at the Ordnance Survey
How do we locate things precisely?
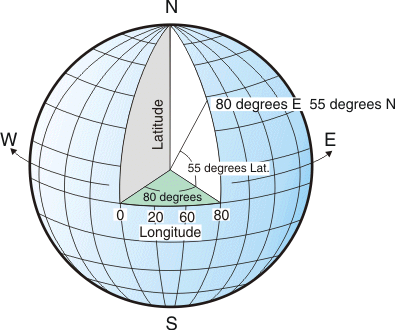
Coordinate Systems
Textual data may be useful in context, but it is not directly plottable on a map
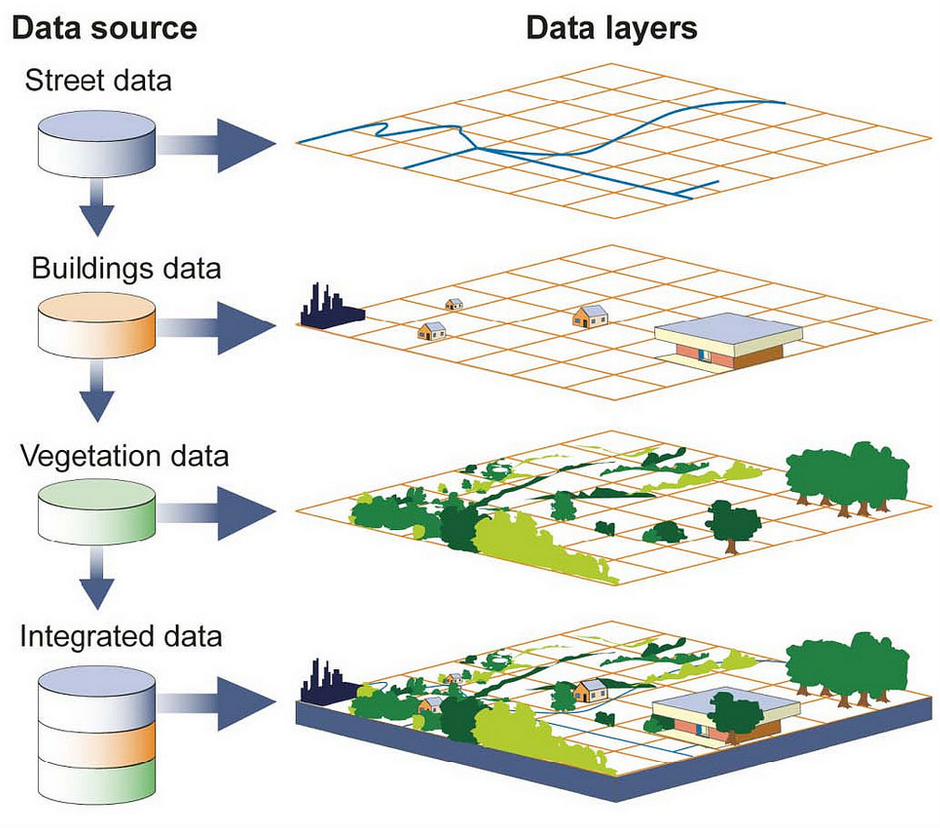
How do we model geographical data?

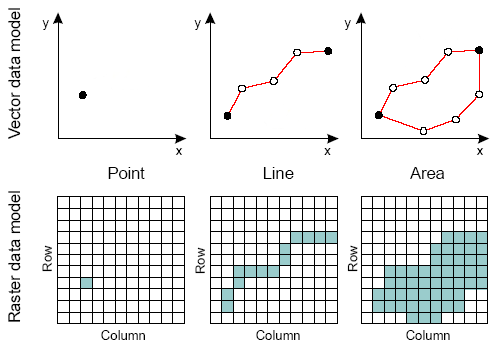
Points: a house, a shop, a postbox, etc
Lines : Roads, Rivers, Paths etc
Polygons: fields, parks, lakes etc
Raster to Vector
Storing and Retrieving Data
Flat Files
Shapefile
Tabfile
CSV
KML
GML
etc
Databases also play a key role




SELECT ST_Area(the_geog)/POWER(0.3048,2)
As sqft, ST_Area(the_geog) As sqm FROM somegeogtable;Spatial Querying
What about serving out data?
OGC Standard Services

Also increasingly we serve and query this data via de facto APIs







Alongside this ~30% have access to GPS. This ignores cellphone triangulation, WiFi etc
We can conservatively estimate 20% of the world will be able to consume and produce geo data by 2020
That's ignoring machine produced data
Cell phone networks can produce ~100'000 geo events per second
To put that into perspective, there are around ~6000 Tweets per second globally
Source: Open Signal 2015
OK, so you've got all this data, now what?
Processing
Actually processing data to a useful state can take up a lot of time





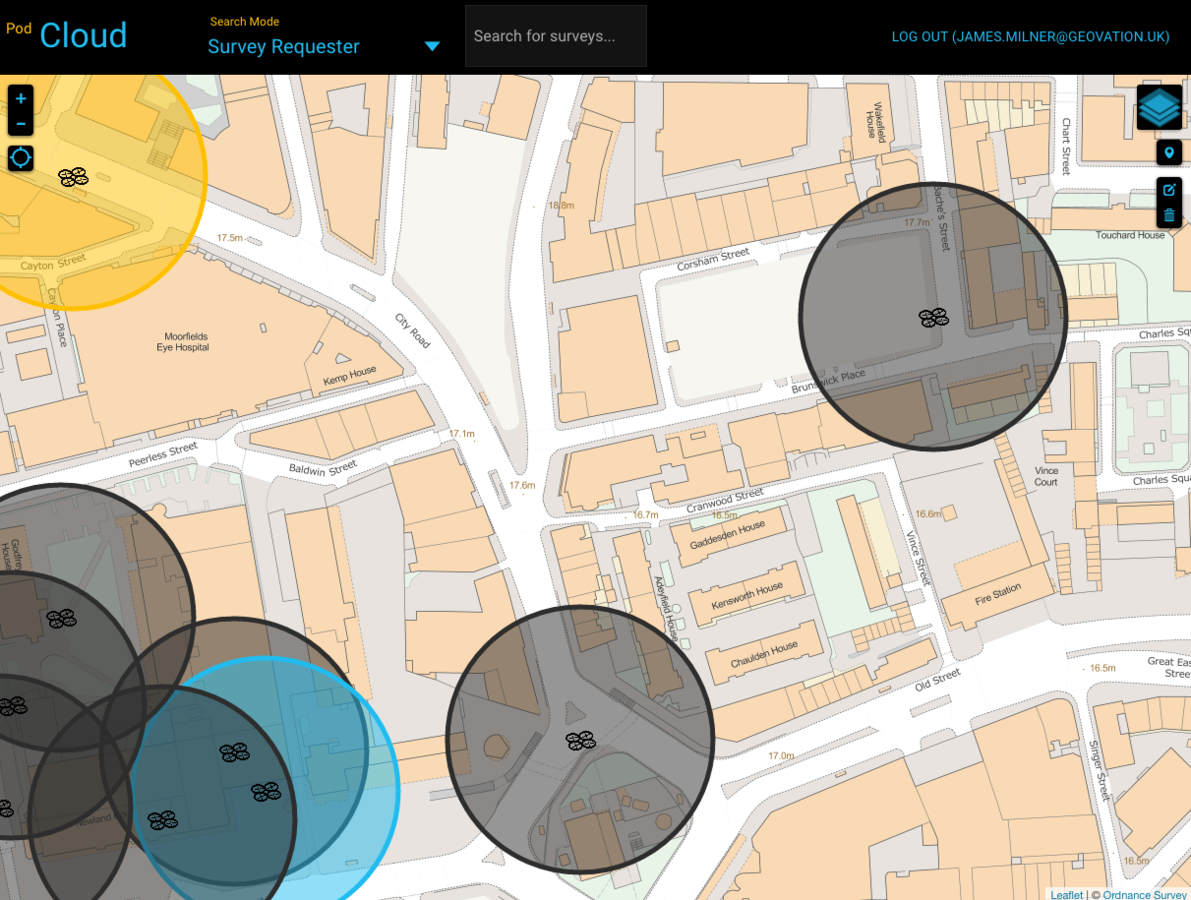
Mobile and Web Viewing
What are your mapping framework options?








Hello Map
// ArcGIS JavaScript API
require(["esri/map", "dojo/domReady!"], function(Map) {
var map = new Map("map", {
center: [-118, 34.5],
zoom: 8,
basemap: "topo"
});
});
// Google Maps JavaScript API
var map;
function initMap() {
map = new google.maps.Map(document.getElementById('map'), {
center: {lat: -34.397, lng: 150.644},
zoom: 8
});
}
// Leaflet JS
var map = L.map('map').setView([51.505, -0.09], 13);
var attr = '© <a href="http://osm.org/copyright">OpenStreetMap</a> contributors';
L.tileLayer('http://{s}.tile.osm.org/{z}/{x}/{y}.png', {
attribution: attr
}).addTo(map);Lets look at some fun examples
Some ideas about handling geo data in your apps
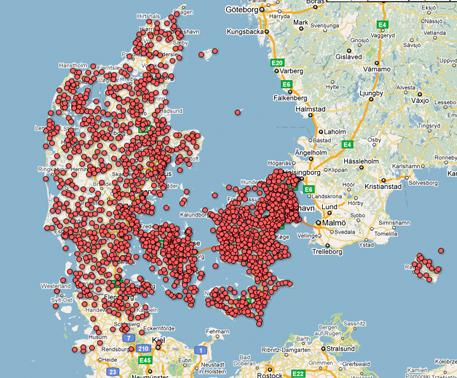
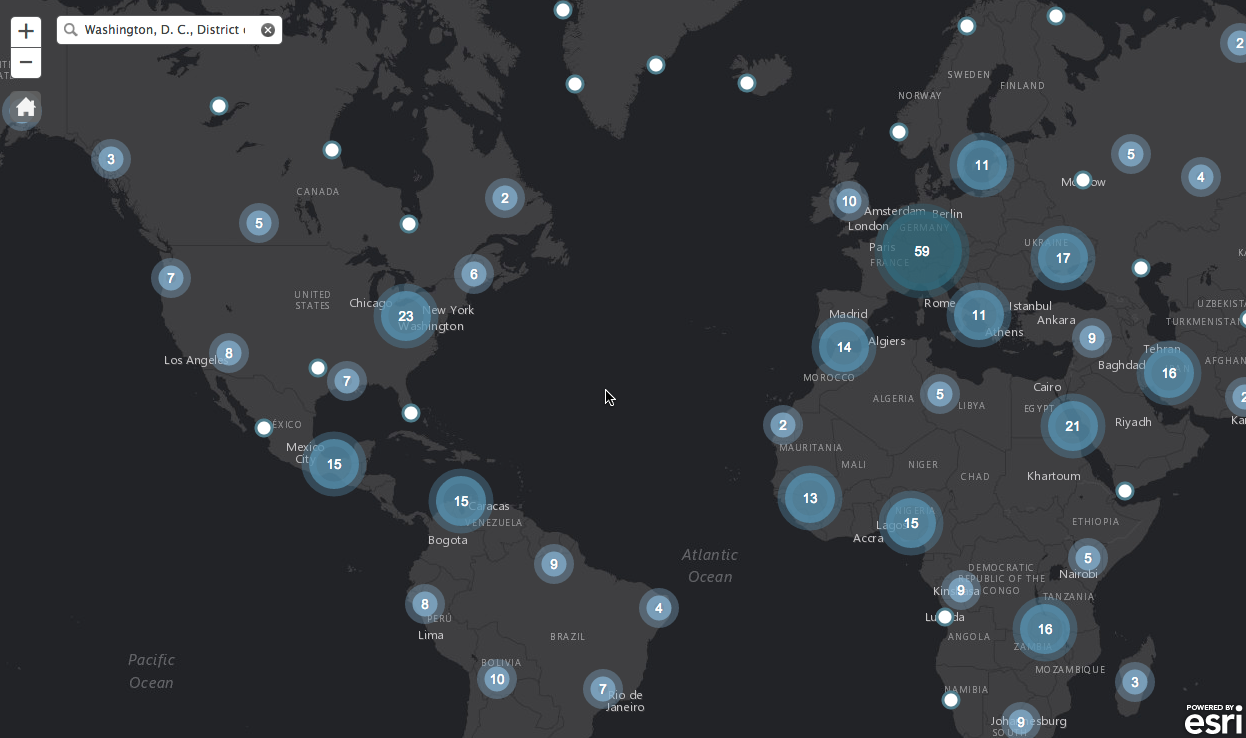
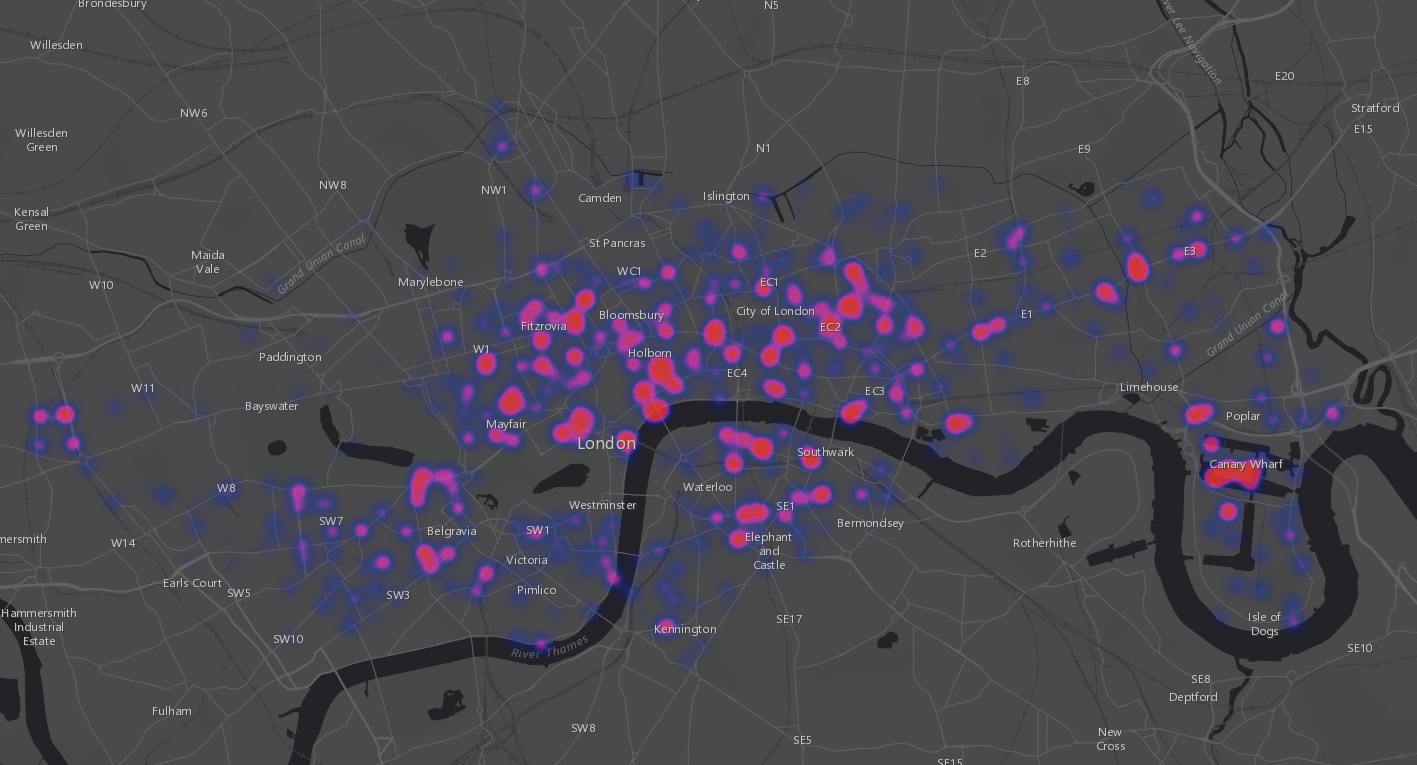
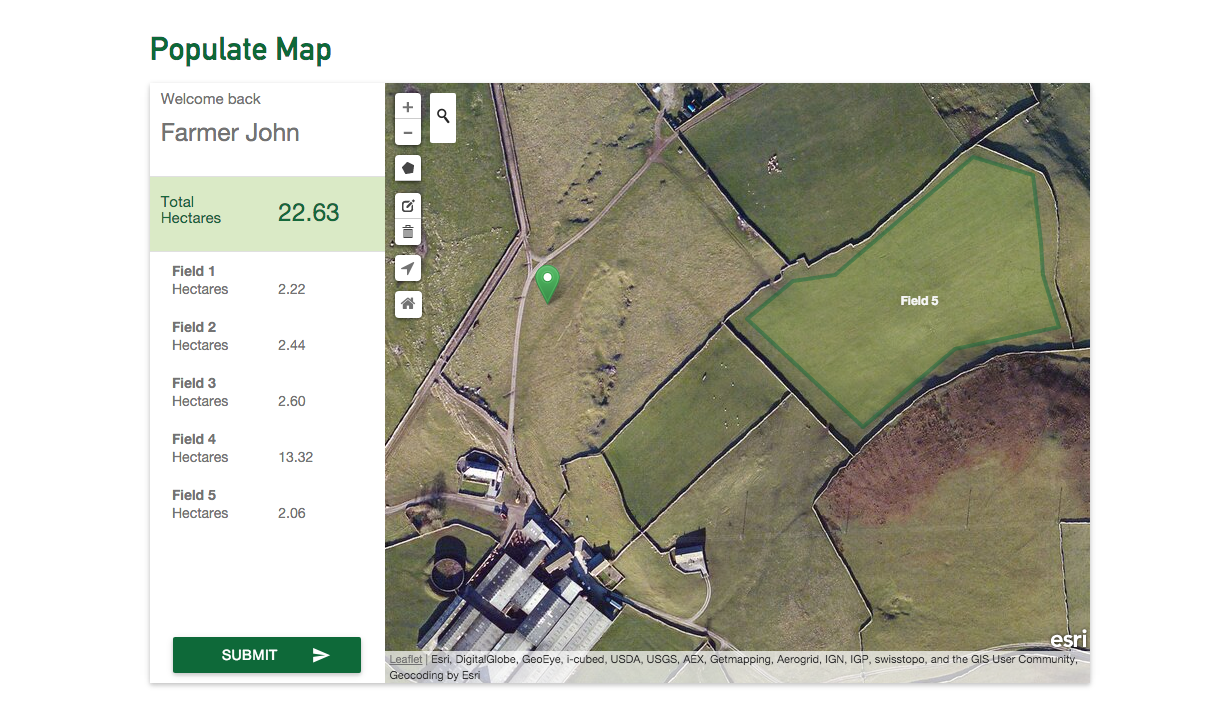
Visualising Points
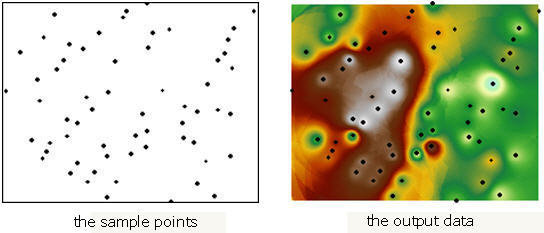
Interpolation
Leveraging Networks
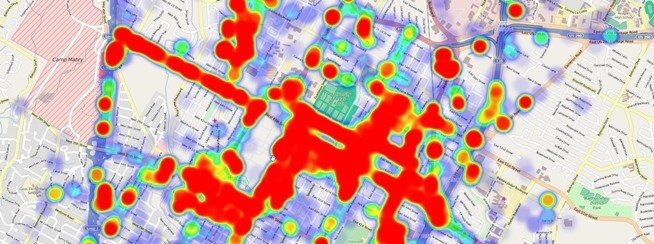
Determining Patterns
Handling Geometries


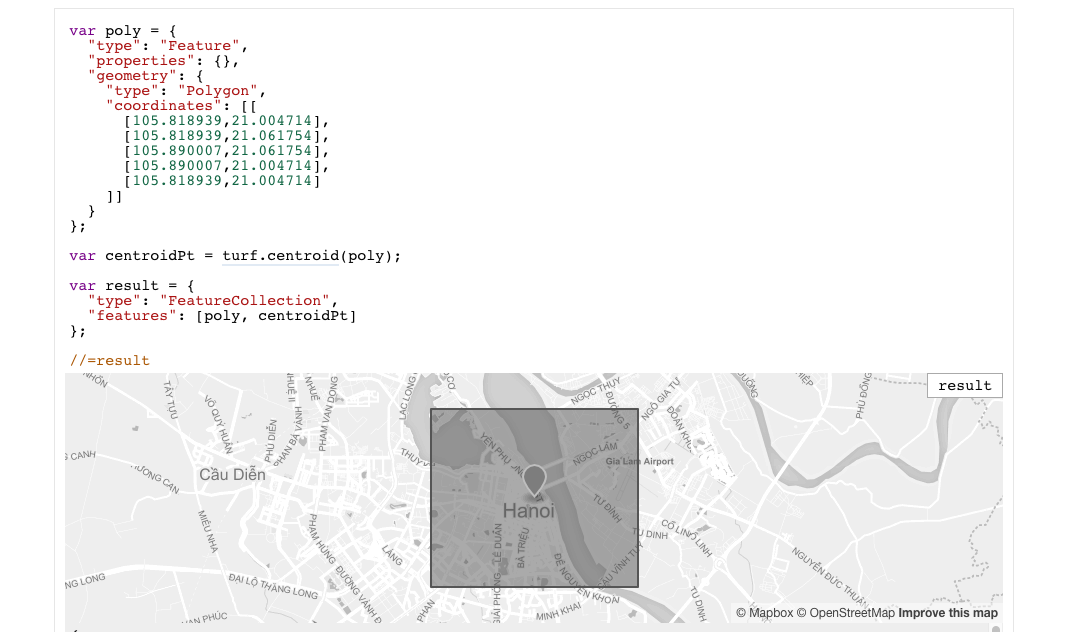
Editing Data
3D?

Pros
- Realism
- No distortions (geodesic)
- Opens up new analysis options
- Looks cool
Cons
- Expensive to collect data
- GPU intensive
- Less advanced tech
Plugs
-
I do freelancing
-
Also working on a startup; GeoPrint
-
Geo Startup Weekend
@JamesLMilner

Questions?
What is geo data and how to get the most from it (UKGovHack 2016)
By James Milner
What is geo data and how to get the most from it (UKGovHack 2016)
- 1,698