Open ocean systems
- ASV biogeography
- Model-data comparison
- Methods development
Jesse McNichol, St. Francis Xavier University (StFX)

Local model system
- "Extreme" redox chemistry with climate implications
- ASV-guided process studies



Postdoc: 2018 - 2023
2023 -


Large-scale diversity: "functional guilds" (e.g. SAR11, Roseobacters, SAR202, SUP05, etc.)
"Microdiverse subclusters":
What level approximates biogeochemical function?

functional trait axis x
functional trait axis x
functional trait axis y
functional trait axis x
functional trait axis x
functional trait axis y
(note: dots represent prokaryotic "microdiverse subclusters")
High functional diversity due to niche differentiation
genetic distance ≈ functional difference
Low functional diversity (neutral genetic processes)
genetic distance ≠
functional difference

Rii et al., 2021
Blue: Strength of environmental selection
Yellow: Strength of diversity-generating processes
Lower functional diversity
A marine ecosystem

Higher functional diversity
A soil ecosystem
functional trait axis x
functional trait axis x
functional trait axis y
functional trait axis x
functional trait axis x
functional trait axis y
Red arrows = stress
Soil ecosystem
Marine ecosystem
Community abundance before stress
Community abundance after stress
Circle size = abundance
functional resilience?
lack of functional resilience?



A soil ecosystem
A marine ecosystem
Rii et al., 2021
Full-length rRNA databases:
- Ecosystem-specific (non-redundant) database
- Allows design of specific fluorescent probes for "microdiverse subclusters"
- Can be combined with activity assays
Dueholm et al. (2020) mBio, e01557-20
Environmental DNA/RNA
Long-read sequencing (e.g. PacBio CCS)
Database of full-length 16S rRNA
Brüwer et al., 2023 doi.org/10.1128/msystems.01287-22




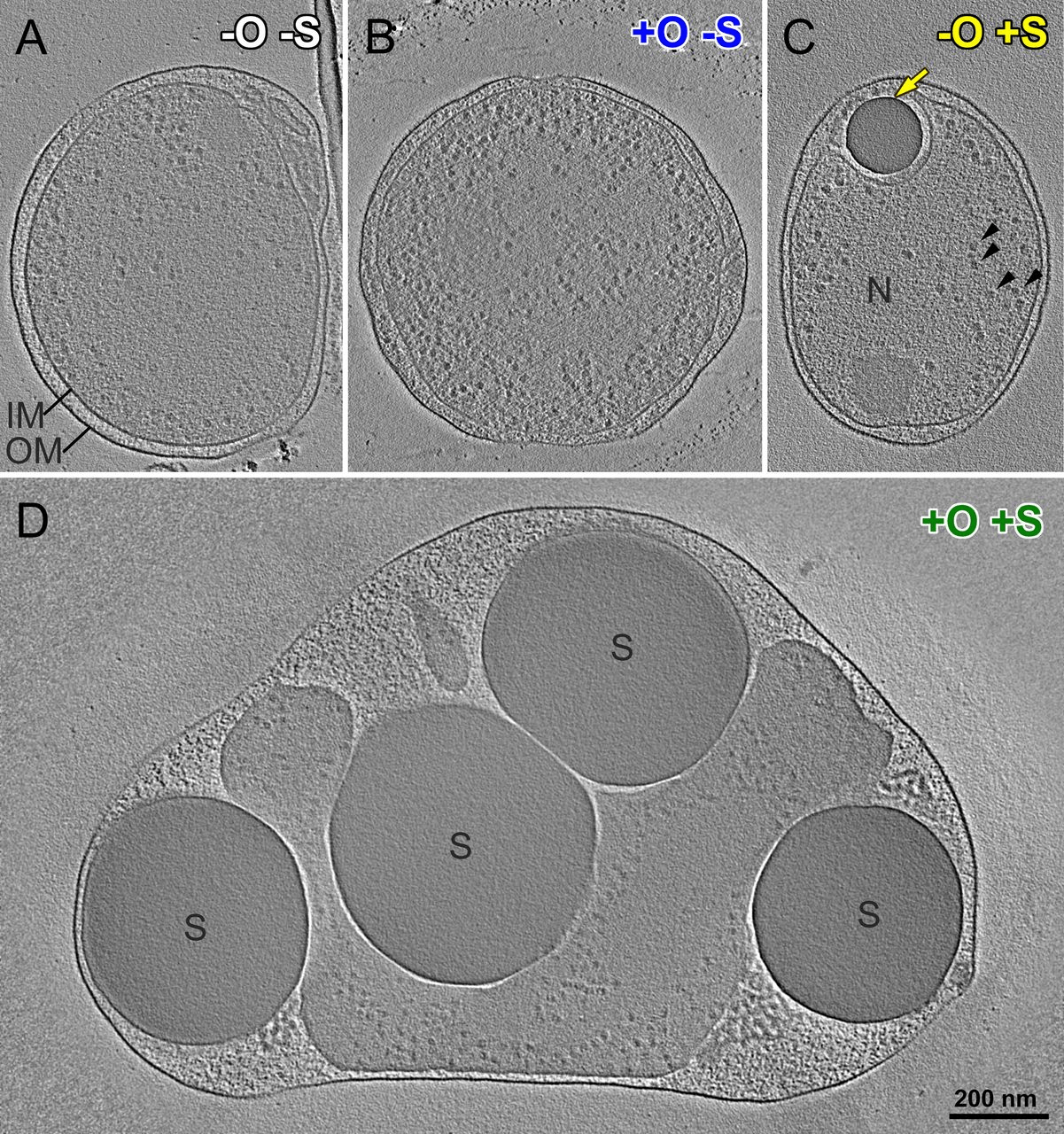
Shah et al., 2019 doi.org/10.1128/mbio.00216-19


Image: Bjarne Hansen
1. Water sampling
3. Compare metabolism between control (in situ) and disturbance
Image: CSIRO

2. Incubation under in situ and "disturbance" conditions (< 24 h)

Sebastián & Gasol (2019), 10.1098/rstb.2019.0083

Image: Bjarne Hansen
1. Water sampling
2. Water incubation (< 8 h)


in situ conditions (control)
"disturbance" condition
3. Compare metabolism between conditions
| Bulk rates | Single cells |
|---|---|
| -Dissolved oxygen with optodes | -RSG* for single cell respiration rates |
*Redox sensor green + rRNA-FISH = taxon-specific rates
Microbiology
Bioinformatics
Environmental science
Long term vision: A lab that links microbial diversity & biogeochemical function in the context of global ecosystem change with modern 'omics-enabled techniques
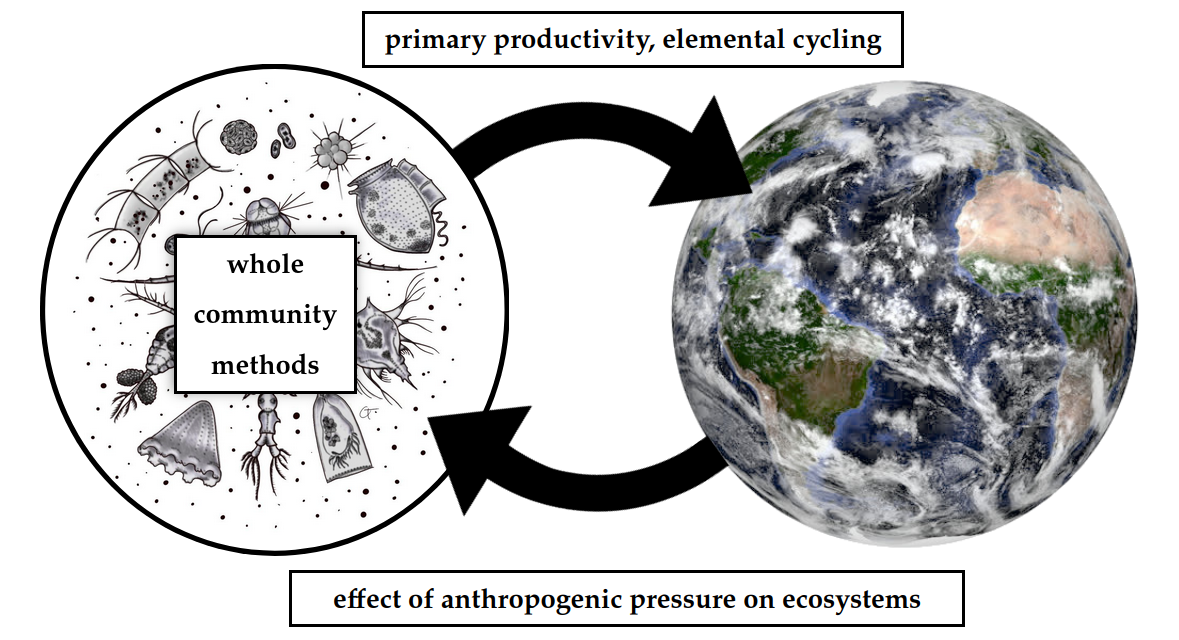
How do microbial communities influence the Earth System, and vice-versa?


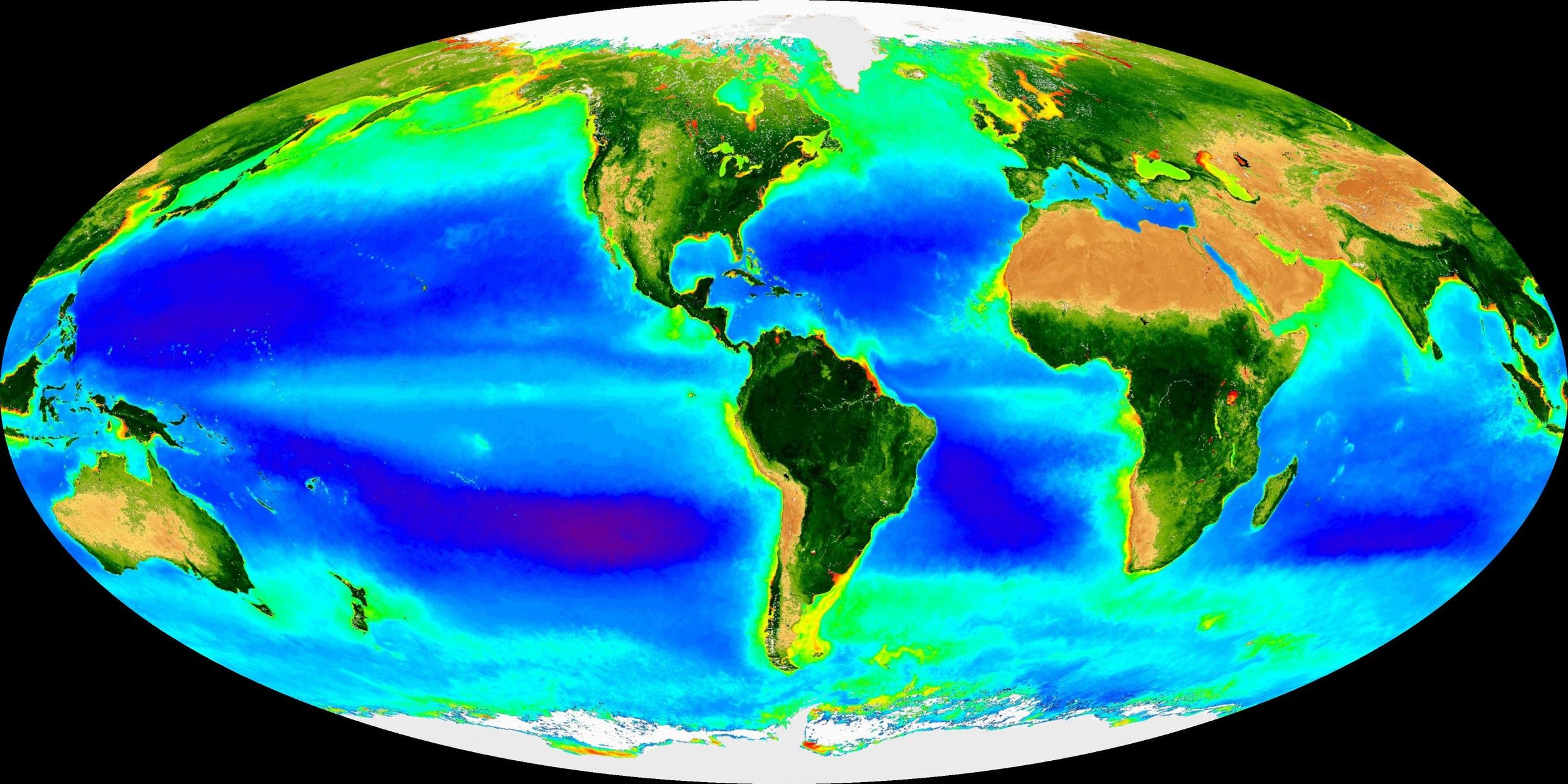


Sebastián & Gasol (2019), 10.1098/rstb.2019.0083 ; McNichol et al (2018) 10.1073/pnas.1804351115 ; Zehr (2015) 10.1126/science.aac9752; Bramucci et al (2021) 10.1038/s43705-021-00079-z

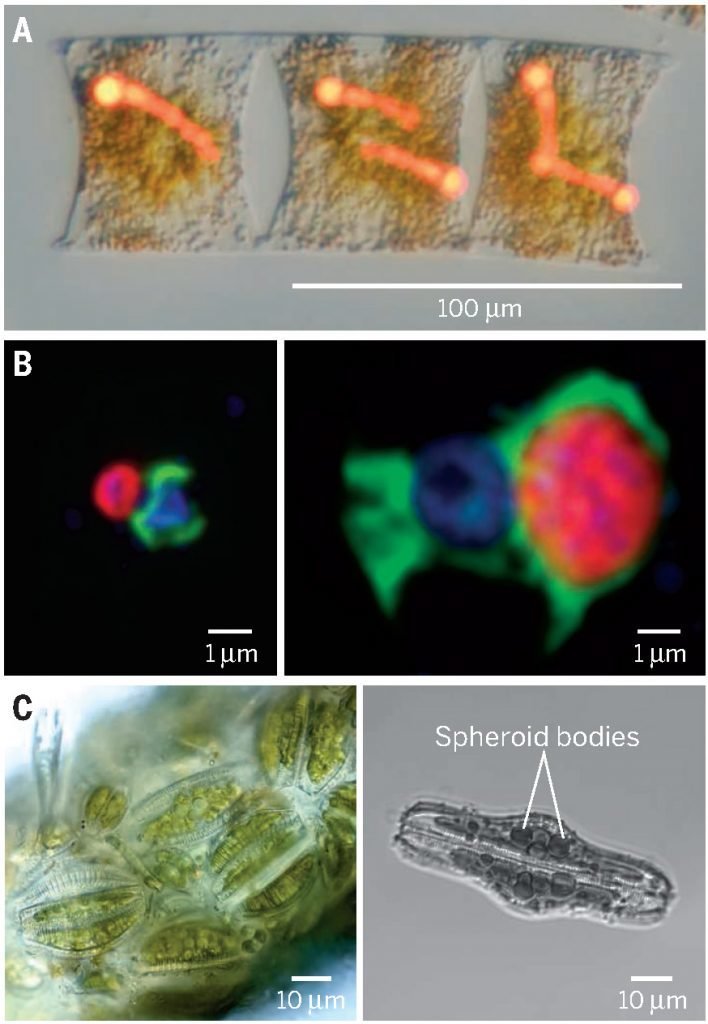

Microscale ecology & biogeochemistry

CBIOMES 2024 Poster Diagrams
By jcmcnch
CBIOMES 2024 Poster Diagrams
- 65



