3-domain Metabarcoding and its Application to Arctic Time-Series Data
2022-06-24 Meeting AWI-USC
- Provide overview of 3-domain metabarcoding approach, and the unique information it provides
- Describe how these types of data can inform global models, and the importance of Simons CMAP for this work
- Present our vision for a paper comparing 18S community profiles from specific and 3-domain approaches, using FRAM RAS data
- Propose that AWI could become involved in a "global paper"
- Describing patterns from globally-distributed, unfractionated (>0.2µm) microbiome profiles
- AWI would provide critical coverage in Arctic for a truly global perspective
Meeting plan

Microbe art: @claudia_traboni
p16S
e16S
18S
-
Comprehensive community data from single PCR assay:
- p(rokaryotic)16S
- e(ukaryotic)16S
- Eukaryotic 18S
(1) 3-domain Metabarcoding: A holistic picture

Microbe art: @claudia_traboni
18S
p16S
e16S
-
Comprehensive community data from single PCR assay:
- p(rokaryotic)16S
- e(ukaryotic)16S
- Eukaryotic 18S
(1) 3-domain Metabarcoding: A holistic picture
Craig Carlson, Elisa Halewood, UCSB
Fraction of 18S amplicon sequences

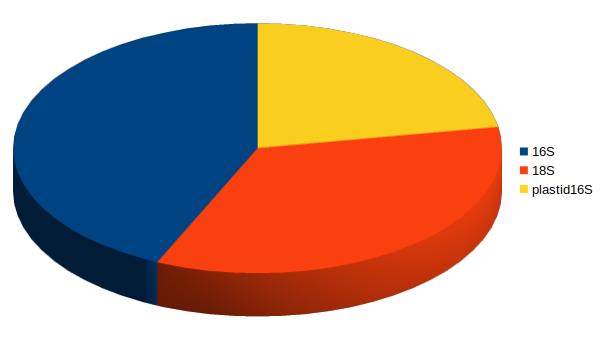
16S
plastid 16S
18S




Jan-Feb 2005
Feb-Mar 2006
With deep sequencing, good coverage for all 3 domains
(1) 3-domain Metabarcoding: A holistic picture
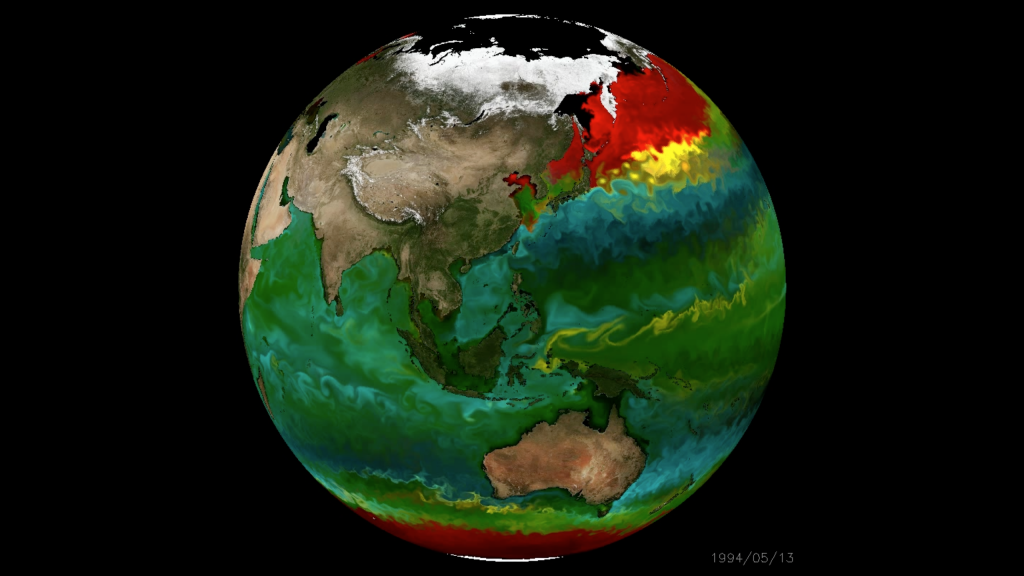
An in silico global phytoplankton model (DARWIN project, MIT)
- How robust are model predictions?
- What is the function of microbial "black box"?
- Can models and data help predict consequences of climate change?
(2) Metabarcoding data and global models
Model-data intercomparison (Yubin Raut, USC)



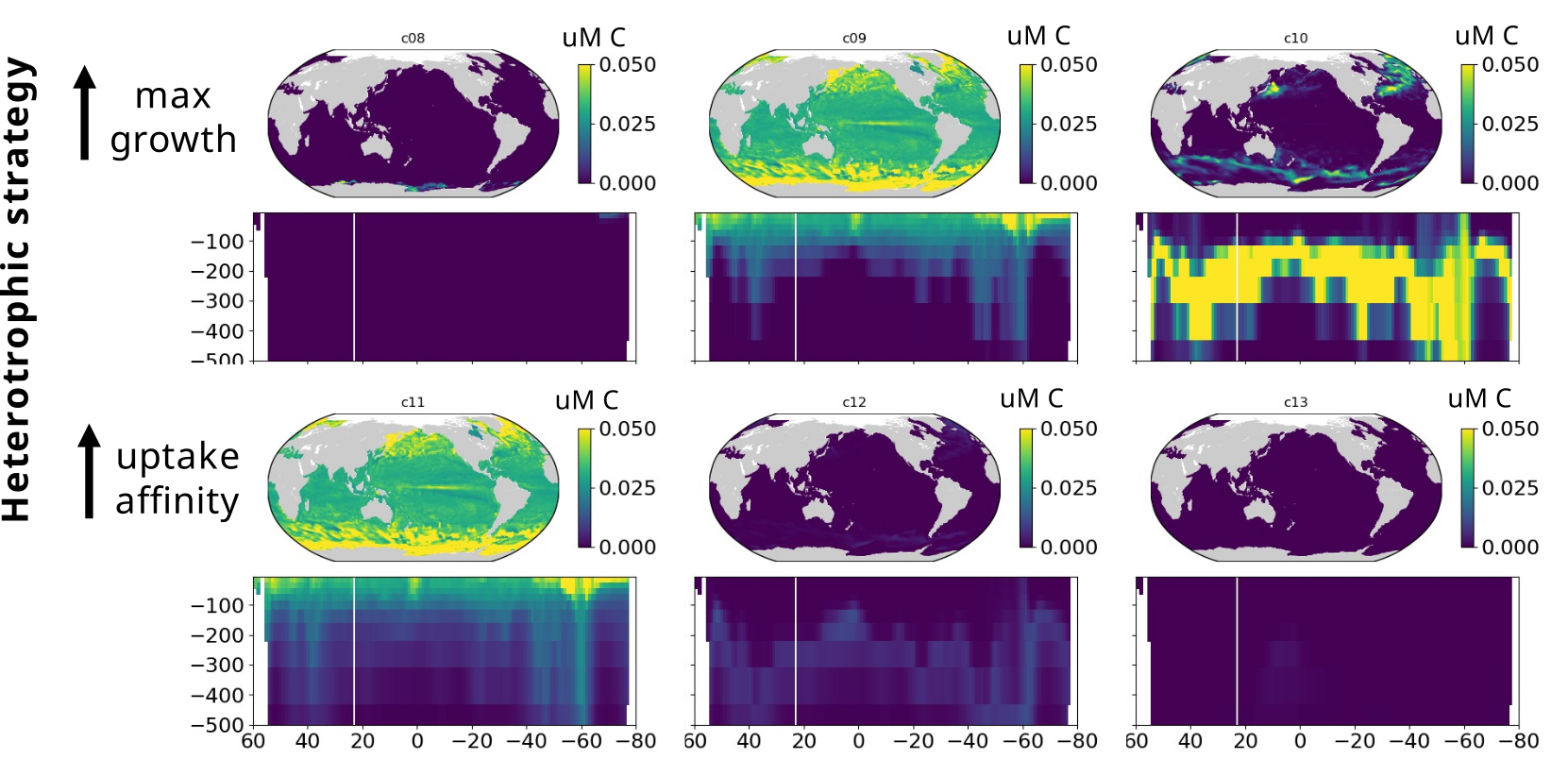
Modelling marine heterotrophs (Emily Zakem, Carnegie Inst.)

(2) Metabarcoding data and global models
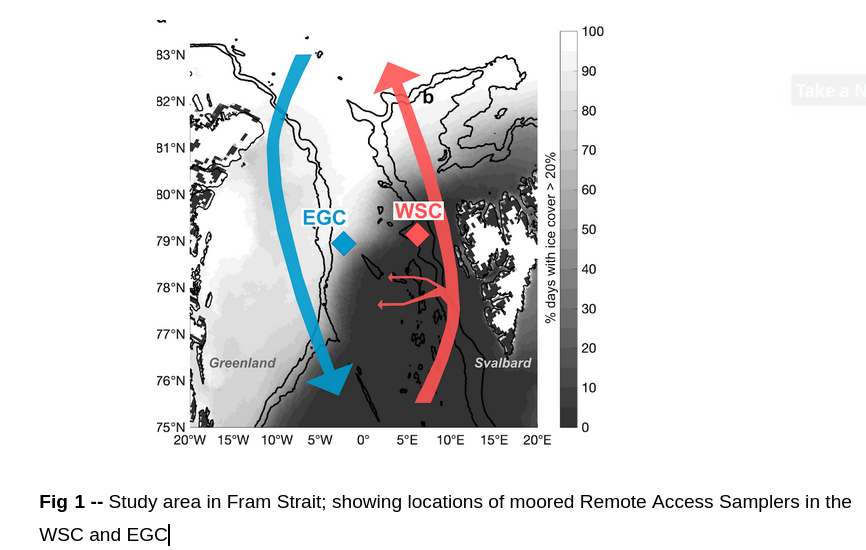
(3) Application to FRAM data
- July 2016 - July 2017 from remote access sampler (RAS); >0.2µm fraction
-
Scientific questions:
- How does the performance of 18S-specific primers compare with 3-domain primers?
- Which taxa may be under- or over-estimated by each primer set?
-
What new biological insights can we gain from a holistic dataset?
- "Cross-domain" interactions unique to Arctic ecosystems
- Changing ratio of PROK:EUK across extreme seasonal cycle
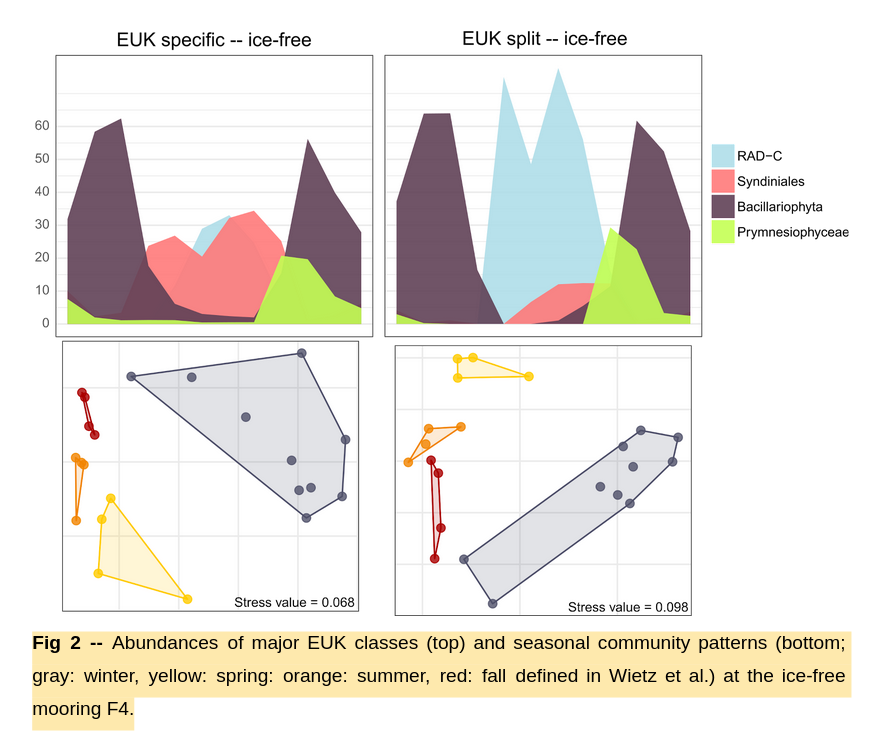
(3) Application to FRAM data: Comparison
Differences to be investigated with MGPrimerEval pipeline using TARA TOPC metagenomes as "ground truth"
- Not just saying "they're different", but which is more accurate
(3) Application to FRAM data: Holistic picture
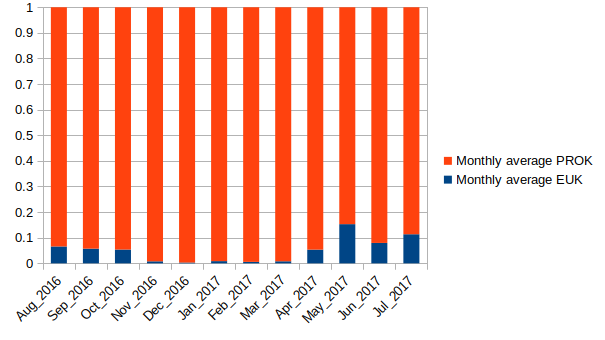
- Blue = all EUK-originating SSU rRNA
- Orange = all free-living PROK rRNA
Transition from PROK-dominated system to a higher contribution of EUKs
in silico method optimization
3-domain metabarcoding primers work almost* perfectly across global oceans (including for Arctic based on TOPC)
Data for global paper from many collaborators
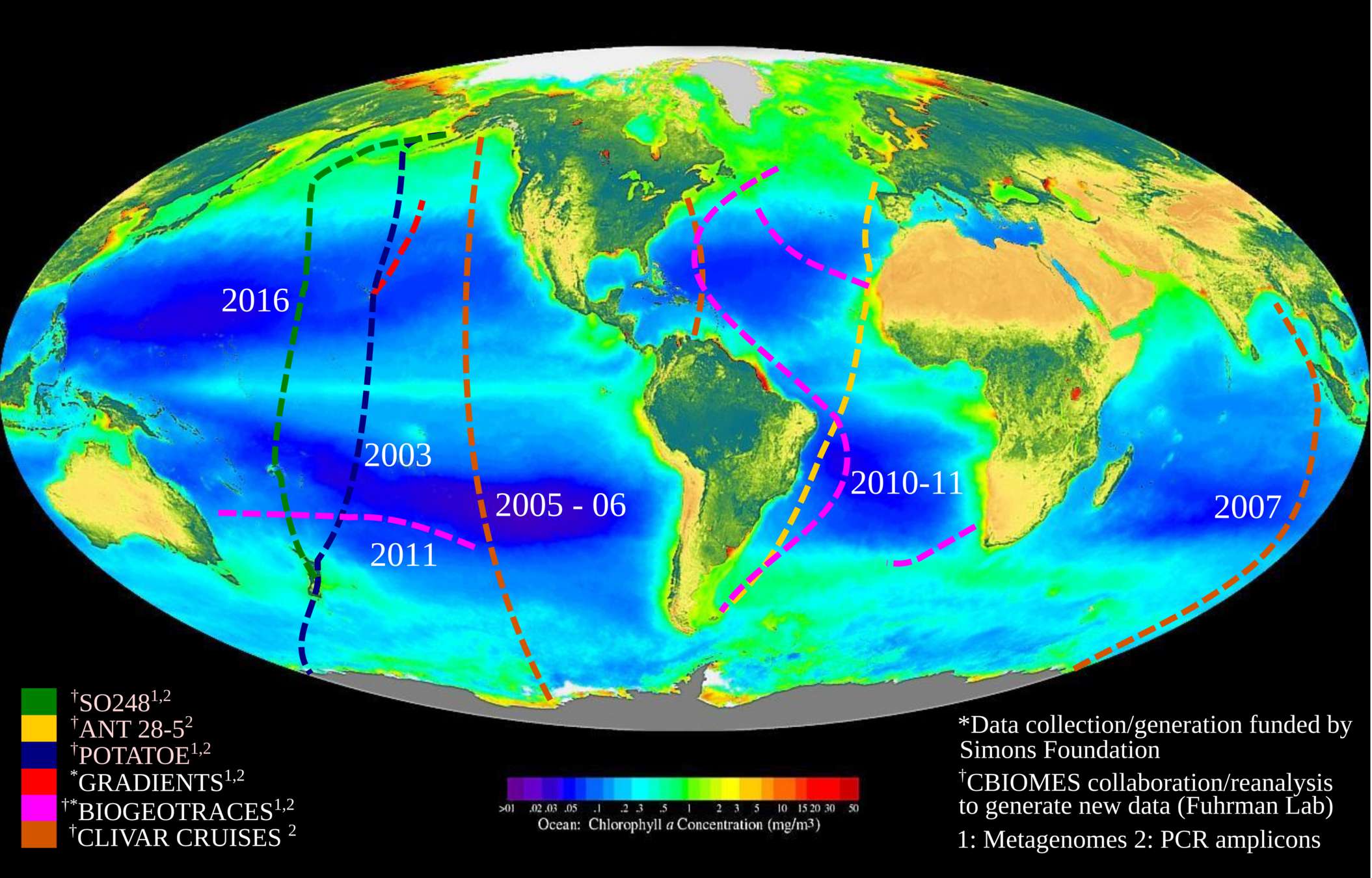



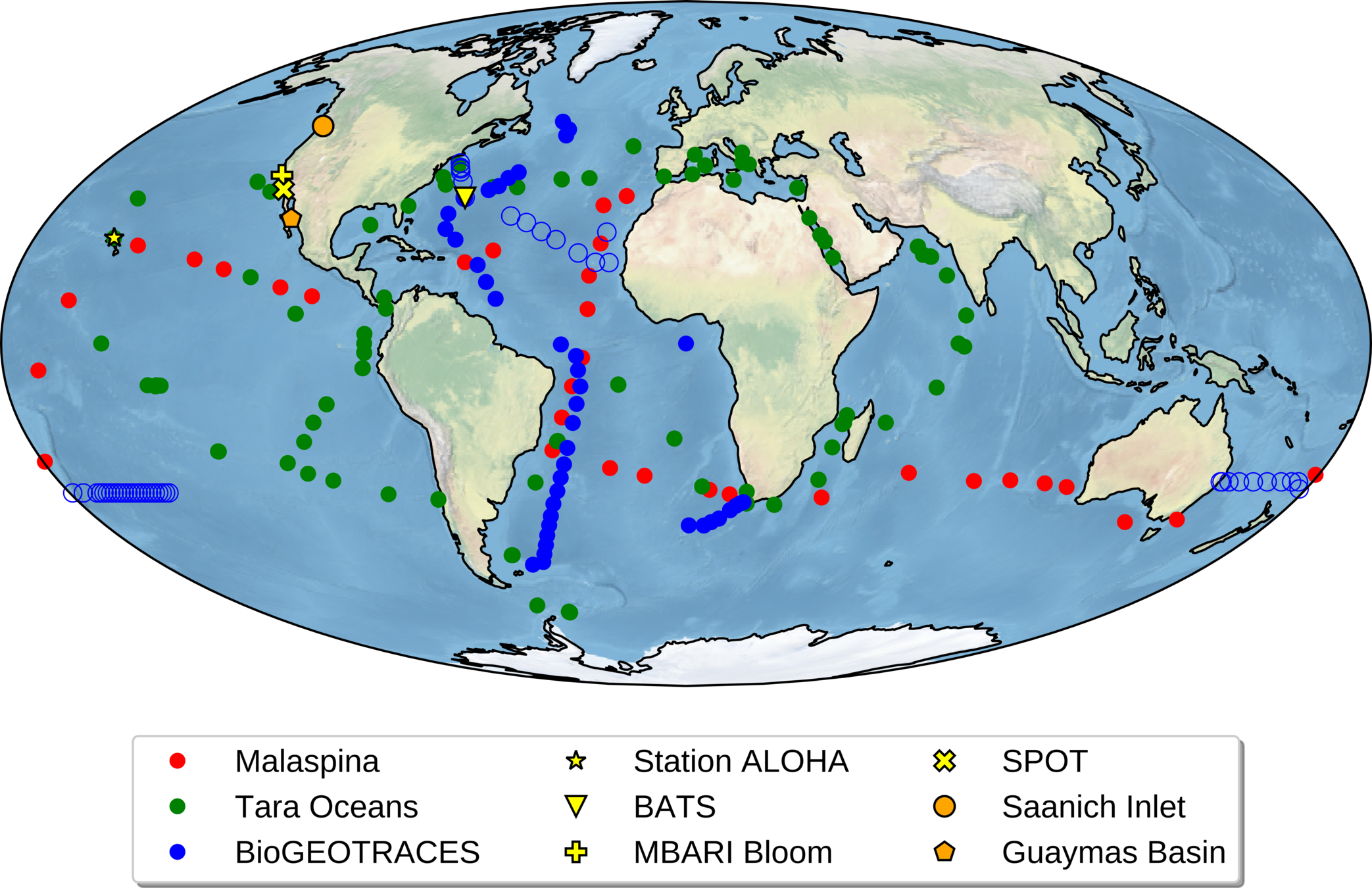
Global metagenomes
Over 800 globally-distributed barcode samples allow model-data intercomparison but we lack coverage in Arctic!
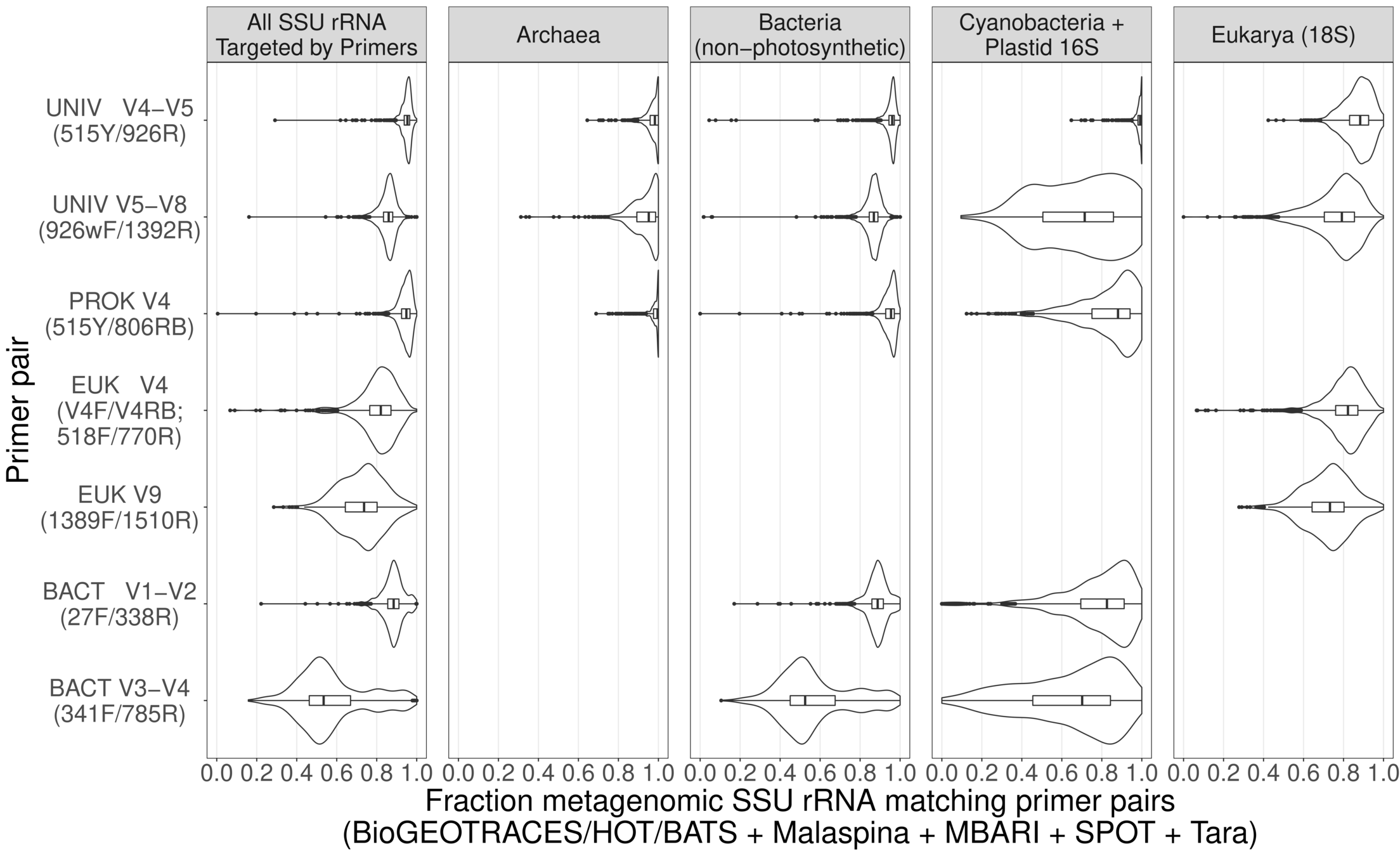
(4) Where does FRAM data fit in to global picture?
-
FRAM data have already been processed through our standard pipeline, making them ready for Simons CMAP database
-
Sets stage for AWI to be involved with "global paper"
- Aiming for high impact, including collaborators from USA, UK
-
Having datasets accessible on CMAP allows for broader collaborations (e.g. network analysis)
- Will be stored as a unique dataset with its own landing page, e.g.:
- cmap.readthedocs.io/en/latest/catalog/datasets/ESV.html
- Re-use and citation of FRAM study by non-molecular ecologists more likely
-
Sets stage for AWI to be involved with "global paper"
(4) Where does FRAM data fit in to global picture?
plastid
16S
mito 16S
nuclear 18S
Space / time
Abundance
A eukaryotic phytoplankter
Broader collaborations: network analysis
MOSAiC metagenomes, phyloFlash profiles
220624_Katja_Jed_Matthias
By jcmcnch
220624_Katja_Jed_Matthias
- 52



