Meeting II | 6/30/21
Regional Broadband American Rescue Plan Convening
POST IN THE CHAT!
Your Name and Affiliation
Favorite Summer Food Item

Agenda
Welcome and Communications Update
Community Exchange Waterfall
ARPA Funding Breakdown
Principles for ARPA Spending
Digital Access Issues Explained

Potential ARPA Funded Uses
Please post questions and comments in the chat!
Meeting Goals

Clarify ARPA guidance regarding use for digital access / broadband
Outline principles and potential vehicles for ARPA spending

Organize stakeholder priorities as related to digital access and broadband
MAPC'sGoals

Support municipalities in acheiving their goals related to Digital Access
Advocating for State resources that will support municipal and community efforts to close the digital divide.

Develop purchasing or other procurement vehicles for collective uses.
| ARPA Provision | Administering Agency | Mass Allocation (Approximates) |
Physical Network Build Out | Device Support | Broadband Subscription | Digital Literacy Training |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief Fund | DESE - School Districts | $1,83B | X | X | ||
| Emergency Connectivity Fund | FCC (Federal) | $148M | X | X | X | |
| Institute of Museum and Library Services | Board of Lib Commissioners - Local Libraries | $3,5M | X | X | X | X |
| Economic Adjustment Assistance | EDA (Federal) | $64,5M | X | |||
| Homeowner Assistance Fund | DHCD | $178M | X | |||
| Coronavirus State Fiscal Recovery | ANF | $5,28B | X | X | X | X |
| Coronavirus State Local Recovery | DoR - Local Municipalities | $3,38B | X | X | X | X |
| Coronavirus Capital Projects Fund | ANF | $174M | X | X |
ARP Guidance:
State and Local Allocations
Broadband Infrastructure Guidance
"Infrastructure investments in areas that lack wireline connection that reliably delivers 25/3 service"
"Prioritize middle mile and last mile connections"
"Prioritize projects that use modern technology delivering 100/100 service"
"Recipients are encouraged to pursue fiber optic investments"
Demonstate COVID Impact
Source: US Treasury Fact Sheet, 5/10/21
https://home.treasury.gov/system/files/136/SLFRP-Fact-Sheet-FINAL1-508A.pdf
ARP Guidance:
State and Local Allocations
Digital Divide
"In view of the wide disparities in broadband access, assistance to households to support internet access or digital literacy is an eligible use to respond to the public health and negative economic impacts of the pandemic, as detailed above."
"Recipients may use funds to provide assistance to households facing negative economic impacts due to Covid-19, including digital literacy training and other programs that promote access to the Internet."
ARP Guidance:
State and Local Allocations
Cybersecurity
"Recipients may also use funds for modernization of cybersecurity, including hardware, software, and protection of critical infrastructure, as part of provision of government services up to the amount of revenue lost due to the public health emergency."
ARP Summary

Infrastructure investments in areas that are underserved by reliable high speed internet.
Cybersecurity
Offset Tax Reduction
Pensions
Debt Service
Digital literacy and connectivity programs



Stabilization Funds


Other demonstrate disproportionate COVID impact

Guiding Principles for State and Local Government
DRAFT Principles for Local Government
Remove affordability and adoption barriers that prevent universal access to reliable and high speed internet.


Ensure all residents who desire to improve their digital / technology literacy have a pathway to educational opportunities at a range of skill levels, offered in community appropriate languages and settings.
Augment the capacity of key stakeholders such as IT Departments, School Districts, Libraries, Community based organizations, and municipal staff to address the digital divide
Promote competition among internet service providers offering broadband service.
Recognize the importance of proactively investing in cybersecurity measures.


DRAFT Principles for State Government
Augment ARPA funds made available to municipalities for those municipalities who have been hit hardest by COVID (health and unemployment) and likely have competing needs for funds in other areas that may outweigh digital divide issues.

Build the nascent capacity of local government and community groups in the area of the digital divide and digital infrastructure.
Catalyze additional investment by municipalities and private sector actors to improve affordability, reliability, and speed of the internet; as well as market competition for broadband service.
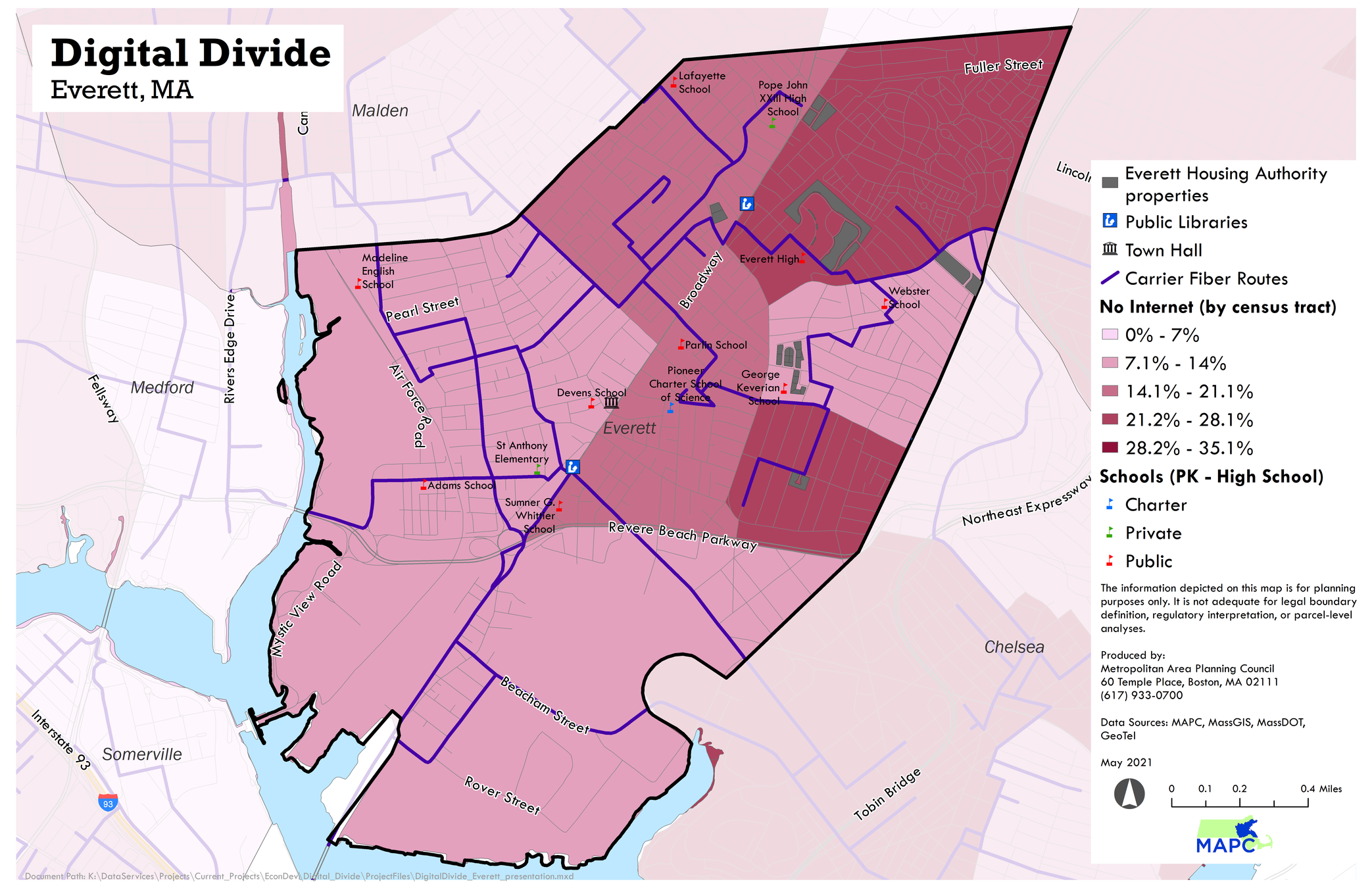
Diagnosing the Problem
Draft Research Findings from Chelsea, Everett, and Revere Digital Access Planning Process

Three Determining Factors of Digital Access



Connection
Adequate Device
Literacy
Fast
Affordable
Router
Personal Computer /Laptop
Use of Technology
Ensuring functioning equipment
Evaluating quality of information and privacy risks

Connection
Is it Fast?
40 – 50%
of households in Chelsea Everett, and Revere with internet access do not have "broadband" speeds

Speed Sources: MLab, Microsoft US Broadband Usage, Demographic Source: US Census ACS 5 Year, 2019
"I live in a 40 unit mid-rise and am told by the internet provider that most of the issues are because the wiring in the building is old. The provider says it's not their problem. We have interruptions all the time, no notice, residents just start calling each other to see if they have wi-fi. Could be down for hours. I work from home and it's a real issue for me."
Is it Reliable?

Connection
~19% of
Chelsea, Everett, and Revere households lack internet service.
~40%
of survey respondents do not believe their internet service is affordable.
72%
of survey respondents have had to cancel or change their internet subscription because it is too expensive

Is it Affordable?
Sources: US Census ACS 5 Year, 2019.
MAPC Community Digital Needs Assessment 2021
"Necesitamos que el costo del internet sea mas justo
-
We need the cost of the internet to be fairer"
Device Access
How accessible are devices?
12%
of Chelsea & Revere households have no computing device at all
23%
of survey respondents disagree with "People in my household always have access to a computer if needed."
About 60%
of Chelsea, Everett and Revere households with internet lease a router from their service provider

Are routers adequate?

Device Source, Computers: US Census ACS 5 Year, 2019. Device Source, Routers: MAPC Survey - 6/29/21
"Our internet speed greatly improved after we bought our own router; the routers provided by our provider don't seem to be very good"
Literacy in Chelsea & Revere
Using Technology
~75%
of survey respondents agree with "I feel confident in my ability to use a computer/laptop/Chromebook
~50%
of survey respondents agree with "I feel confident that I am able to resolve issues related to my internet connection"

Ensuring Functioning Equipment

Evaluating Information and Privacy Risks
Anecdotal information gleaned from stakeholder conversations indicates that there are serious concerns related to privacy, particularly among the immigrant population
Source: MAPC Survey - 5/26/21
Internet Subsidies
~500,000
families in Massachusetts are eligible for Internet Essentials and the Emergency Broadband benefit fund
Comcast Internet Essentials Plan offers basic internet service for $10 / Month to income eligible households (SNAP, Free or Reduced Lunch, etc)
The Emergency Broadband Benefit program will subsidize $50 for all service plans - as of June 29th only 30,000 households in the program
Only 30,000
households have taken advantage of EBB since May 16 2021
Source: Universal Services Administrative Co, National Center for Education Statistics, MAPC Digital Access Survey 6/29/2021
"سمعت بأن شركة كومكاست توفر انترنت مجاني لأصحاب الدخل المحدود .هل هذا صحيح؟
-
I heard that internet service companies provide free internet to people with limited income. Is this true?"
Why is it this way?
The cable infrastructure at the household level is likely impacting service and reliability.
A lack of competition, shrinking cable service revenues, and a lower income service area are likely disincentives for investment from the private sector.
At the household level, individuals are likely using outdated or ineffective routers and devices.
Internet subscribers may not have the confidence or technical skills to trouble shoot internet speed or function issues.
Larger households who may need faster speed packages may be cost burdened and unable to afford those plans.
Individuals who are eligible for subsidized services may not be taking advantage of them due to a lack of information, trust, stable housing, documentation, or other structural and social factors.
Private Sector Activties
Cable Providers in Chelsea
Comcast
No Competitor
Incumbent Cable Franchise, Full Coverage in Chelsea and Revere
In 2011 Comcast had 8,266 Cable TV Subscribers.
In 2020 it had 6,718
Source: Mass DTC Form 500, 2011 - 2020
Cable Providers in Revere
Comcast
RCN
Incumbent Cable Franchise, Full Coverage in Revere
In 2011 Comcast had 14,532 Cable TV Subscribers.
In 2020 it had 10,555
Source: Mass DTC Form 500, 2011 - 2020
Competitive Cable Franchise, Partial Coverage in Revere
In 2018 RCN had 661 Cable TV Subscribers.
In 2020 it had 1,702
Cable Providers in Everett
Comcast
RCN
Incumbent Cable Franchise, Full Coverage in Everett
In 2011 Comcast had 10,603 Cable TV Subscribers.
In 2020 it had 7,000
Competitive Cable Franchise, Limited Coverage in Everett
In 2017 RCN had 2,171 Cable TV Subscribers.
In 2020 it had only 957
Source: Mass DTC Form 500, 2011 - 2020
Infrastructure Upgrades
Pull Fiber to Buildings and Retrofit Coaxial
Expand Municipal Fiber Infrastructure

ISP Fiber is typically limited to privately owned infrastructure. Bringing fiber closer to the end user by pulling it into buildings will improve speed and reliability of service (although may not impact price without other strategies).
Municipal fiber has traditionally been limited to a loop that connects public buildings like schools, town hall, and libraries. Expanding municipal fiber, or at least conduit can serve to open new options for public and commercial connectivity.
Fiber Retrofits
Examples
San Francisco Public Housing
Cambridge MA
Expanded Municipal Infrastructure
Santa Monica
Guiding Principles for Public Private Partnership
DRAFT Principles for PPP
Enhance existing service to standard 100/100




Enable competition
Create pathways to careers in the telco / networking industries
Promote competition among internet service providers offering broadband service.
Recognize the importance of proactively investing in cybersecurity measures.


Public Private Partnership Opportunities
FTTP Pilot
Partnerships with ISPs

Examples
Examples
- ID Multi Fam Props that are proximate to existing fiber lines to test FTTP install
- Partnering with Public or Private Equity to bringing fiber closer to the end-user by pulling it into buildings
- Retrofitting buildings with outdated wiring
- Leverage cable franchise agreement
- RFP for use of assets like rooftops
- Qualifying residents based on need, removing the administrative burden from resident and companies.
Coordinated ROW Fiber Expansion
- RFP optical fiber and conduit ROW
Help Us Help You!
MAPC <> Comcast
By jeichen
MAPC <> Comcast
Presentation for Comcast
- 747



