The Impact of Exchange Rates on Imports and Exports
CAO YING (Jesse), NO.41787
If the value of your national currency decreases rapidly, will you still choose to study in Australia?
What determinate imports and exports?
-
Factor endowments & Trade policies are fundamental influencing factors of imports and exports.
-
Exchange rates are the most direct influencing factor.
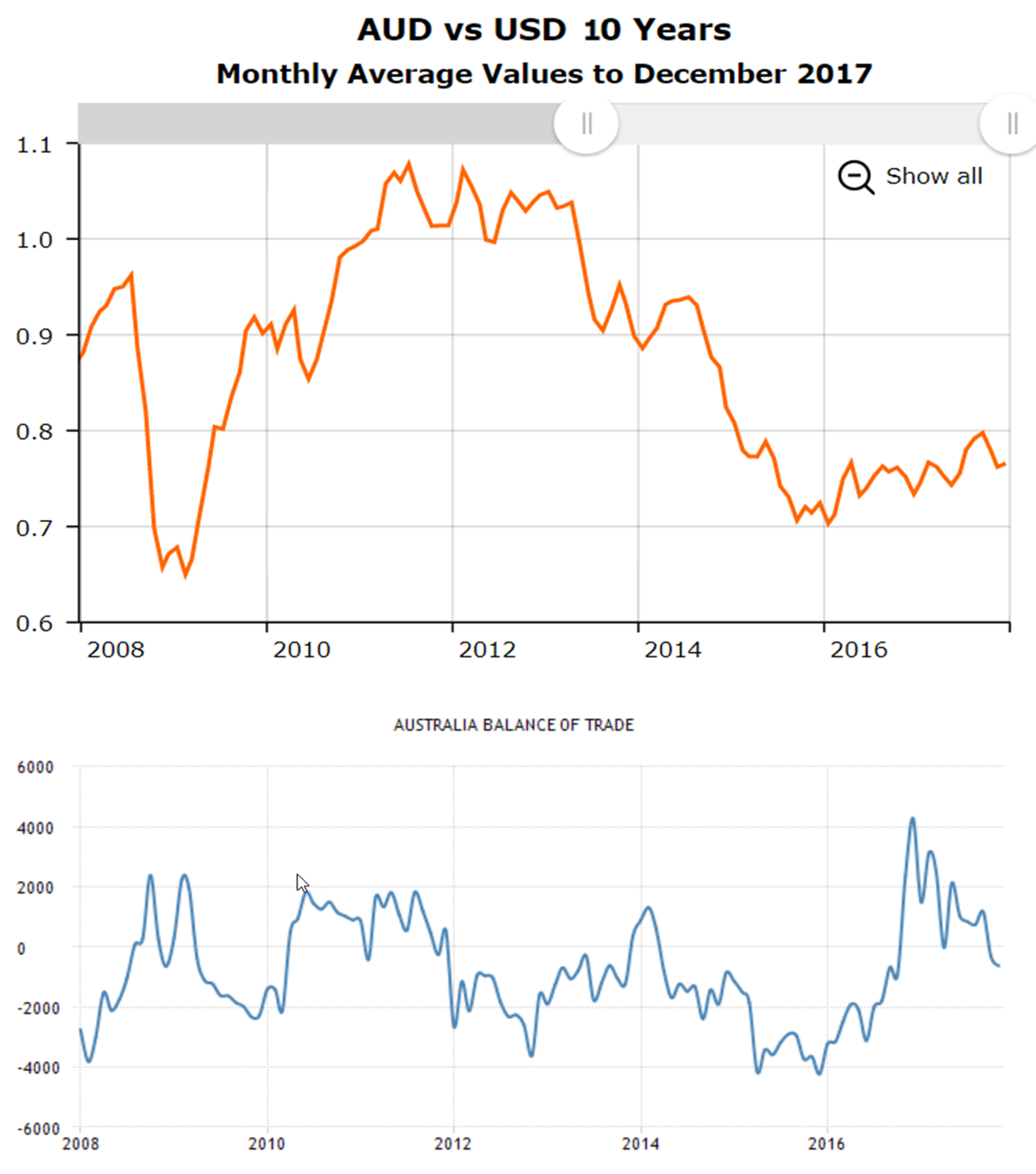
Australian Exchange Rates VS Net Exports
- Basically shows different tendencies.
- Low exchange rates bring high net export.
- Increasing exchange rates bring decreasing net exports.
Text
Sources: Forex Charts: AUD vs Major Currencies: 20 Years & TRADING ECONOMICS:
Australia Balance of Trade
-
Price Effect
-
Income Effect
-
Policy Effect
Outline
Exchange Rates
-
National Central Bank’s Paying Ability
-
The Value of Currencies in The International Market
-
Follow the Rule of Supply and Demand
-
Direct Term & Indirect Term
Price Effect
-
Prices of Imported Goods
-
Manufacturing Costs
-
National Aggregate Demand
-
Prices Competitiveness of Domestically Goods
-
The exchange rate goes up, the price of export goods will reduce.
-
Expansion of national exports
-
The exchange rate goes down, the price of export goods will increase.
-
Reduction of national exports
Price Effect
Income Effect
-
Nominal Income is Unchanged
-
Real National Income Increase
-
National Purchasing Power Increase
-
Foreign Goods Inflow
Policy Effect
-
To Achieve National Economic Targets
-
Demand Side: Fiscal Policies
-
Supply Side: Monetary Policies
Conclusion
- The exchange rate is the most direct determinant.
- There are three effects of exchange rates.
- For developing countries, high exchange rates can stimulate exports.
- For developed countries, low exchange rates can help them keep a high-level purchasing power.
References
-
Investopedia 2018, Oanda, USA, viewed 21 January 2018, <https://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/041615/which-factors-can-influence-countrys-balance-trade.asp>. -
Krugman, PR, Obstfeld, M & Melitz, MJ 2012, International economics: theory & policy, 9th edn, Addison-Wesley, Boston. -
Lu, XQ & Dai GQ 2004, The influence of fluctuation of real RMB exchange rate to Chinese import and export: 1994—2003, Economic Research Journal, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 31-9, viewed 21 January 2018, <http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-JJYJ200505003.htm>. -
Mankiw, NG 2012, Macroeconomics, 8th edn, Worth Publisher, New York. -
Mishkin, FS 2014, The economics of money, banking & financial markets, 11th edn, Person Education, London. -
Statista 2018, Top 20 export countries worldwide in 2016 (in billion U.S. dollars), Hamburg, viewed 21 January 2018, <https://www.statista.com/statistics/264623/leading-export-countries-worldwide/>. -
WING, TW 1984, Exchange rates and the prices of nonfood, nonfuel products, viewed 21 January 2018, <https://www.brookings.edu/bpea-articles/exchange-rates-and-the-prices-of-nonfood-nonfuel-products>.
Thank You
Q&A
Exchange rate
By jessejoker
Exchange rate
- 532



