Improving
web performance
Wed Feb 18 2015
Jhon Jairo roa
Full Stack Developer and Tech Lead
Co-Founder and VP of Engineering @ Trotter
What makes a web page slow?
Rendering Path
Rendering Path
<html>
<head>
<!-- loads external css file -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="small.css">
<!-- loads external javascript file -->
<script src="small.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="blue">
This page sucks
</div>
<!-- loads external image -->
<img src="grumpy.jpg" alt="Grumpy Cat" height="80%">
<div class="blue">
it's not optimized
</div>
</body>
</html>index.html
Rendering Path
.yellow {background-color: yellow;}
.blue {color: blue;}
.big { font-size: 8em; }
.bold { font-weight: bold; }small.js
/* contents of a small JavaScript file */small.css
Rendering Path
Summary
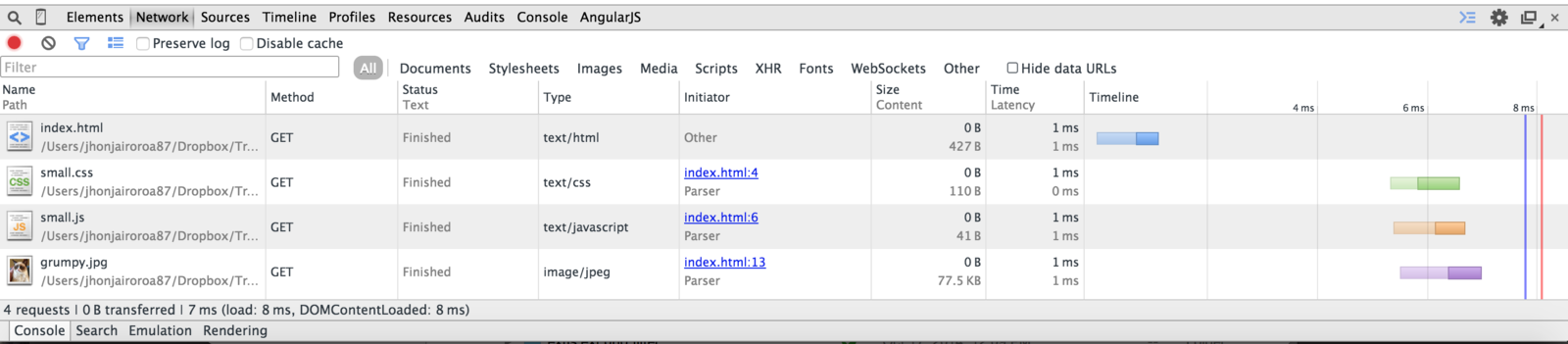
- Browser downloads the html file
- Browser reads the html and sees that there are one css file, one javascript file and one image
- Browser starts downloading the css file and reads it to make sure nothing else is being called
- Browser decides it can not display the webpage without first getting the javascript and the image
- Browser downloads the javascript file and reads it to make sure nothing else is being called
- Browser decides it still can not display the webpage yet until it has the image
- Browser downloads the image
- Browser now decides it can display the webpage
Rendering Path
What???
Rendering Path
Step 1
- Browser downloads the html file
Rendering Path
Step 2
2. Browser reads the html and sees that there are one css file, one javascript file and one image
Rendering Path
Step 3
3. Browser starts downloading the css file and reads it to make sure nothing else is being called
Rendering Path
Step 4
4. Browser decides it can not display the webpage without first getting the javascript and the image
Rendering Path
Step 5
5. Browser downloads the javascript file and reads it to make sure nothing else is being called
Rendering Path
Step 6
6. Browser decides it still can not display the webpage yet until it has the image
Rendering Path
Step 7
7. Browser downloads the image
Rendering Path
Step 8
8. Browser now decides it can display the webpage
:)
Let's start
optimizing !!!
Prioritize Visible Content
Prioritize Visible Content

Prioritize Visible Content
"Why should a user wait to see the page just so you can download the CSS, Javascript, images, etc. for your footer when you are not even sure if a user will ever see it?"
Optimization Check List
- Prioritize visible content
Optimize CSS Delivery
<html>
<head>
<!-- loads external css file -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="small.css">
<!-- loads external javascript file -->
<script src="small.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="blue">
This page sucks
</div>
<!-- loads external image -->
<img src="grumpy.jpg" alt="Grumpy Cat" height="80%">
<div class="blue">
it's not optimized
</div>
</body>
</html>.yellow {background-color: yellow;}
.blue {color: blue;}
.big { font-size: 8em; }
.bold { font-weight: bold; }small.css
index.html
Optimize CSS Delivery
<html>
<head>
<!-- inline css code -->
<style>
.blue{color:blue;}
</style>
<!-- loads external javascript file -->
<script src="small.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="blue">
This page is CSS optimized
</div>
<!-- loads external image -->
<img src="grumpy.jpg" alt="Grumpy Cat" height="80%">
<div class="blue">
but still sucks
</div>
<!-- loads asynchronously the rest of the css code -->
<script>
var cb = function() {
var l = document.createElement('link'); l.rel = 'stylesheet';
l.href = 'small.css';
var h = document.getElementsByTagName('head')[0]; h.parentNode.insertBefore(l, h);
};
var raf = requestAnimationFrame || mozRequestAnimationFrame ||
webkitRequestAnimationFrame || msRequestAnimationFrame;
if (raf) raf(cb);
else window.addEventListener('load', cb);
</script>
</body>
</html>index.html
Optimization Check List
- Prioritize visible content
- Optimize css delivery
Remove Render-Blocking JavaScript
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript" src="small.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
Hello, world!
</div>
</body>
</html>index.html
Remove Render-Blocking JavaScript
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
/* contents of a small JavaScript file */
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div>
Hello, world!
</div>
</body>
</html>index.html
Inline Javascript
Optimization Check List
- Prioritize visible content
- Optimize css delivery
- Inline javascript
Remove Render-Blocking JavaScript
<html>
<head>
<!-- loads external javascript file -->
<script src="small.js"></script>
<!-- loads external javascript file -->
<script src="medium.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
Hello
</body>
</html>index.html
Defer loading of Javascript
Remove Render-Blocking JavaScript
<html>
<head>
<!-- loads external javascript file -->
<script src="small.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
Hello
</body>
<!-- defered loading of external javascript file -->
<script defer src="medium.js"></script>
</html>index.html
Defer loading of Javascript
Remove Render-Blocking JavaScript
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
/* contents of a small JavaScript file */
</script>
</head>
<body>
Hello
</body>
<!-- defered loading of external javascript file -->
<script defer src="medium.js"></script>
</html>index.html
Combined
Optimization Check List
- Prioritize visible content
- Optimize css delivery
- Inline javascript
- Defer javascript loading
Combine CSS files
Combine CSS files
visibleContent.css
team.css
testimonials.css
footer.css
social.css
Inline code
notSoPrior.css
(async loading)
Combine CSS files
How
merge-css: css merger toolkit for node js
https://www.npmjs.com/package/merge-css
shrinker: online app to merge and compress your CSS- and JavaScript-files.
Optimization Check List
- Prioritize visible content
- Optimize css delivery
- Inline javascript
- Defer javascript loading
- Combine css files
Combine JS files
Combine JS files
visibleContent.js
team.js
testimonials.js
footer.js
social.js
Inline code
notSoPrior.js
(defered loading)
Combine JS files
How
Grunt - concat: Javascript task runner
https://github.com/gruntjs/grunt-contrib-concat
compressJs.sh: Build several javascript files into the one build file
https://github.com/dfsq/compressJS.sh
shrinker: online app to merge and compress your CSS- and JavaScript-files.
Optimization Check List
- Prioritize visible content
- Optimize css delivery
- Inline javascript
- Defer javascript loading
- Combine css files
- Combine JS files
Minify CSS, JS and HTML files
Minify CSS, JS and HTML files
/* sets to yellow the background color*/
.yellow {background-color: yellow;}
/* sets to blue the color property*/
.blue {color: blue;}
/* sets to font size to 8em*/
.big { font-size: 8em; }
/* sets to font weight to bold */
.bold { font-weight: bold; }.yellow{background-color:#ff0}.blue{color:#00f}.big{font-size:8em}.bold{font-weight:700}To
Minify CSS, JS and HTML files
$(document).ready(function(){
// Initiate the router
var appRouter = new AppRouter;
// load initial views
appRouter.loadViews();
// Start Backbone history a necessary step for bookmarkable URL's
Backbone.history.start();
});
$(document).ready(function(){var e=new AppRouter;e.loadViews(),Backbone.history.start()});To
Minify CSS, JS and HTML files
<html>
<head>
</head>
<body>
<!-- form for sending new message to admin -->
<form action="/my-handling-form-page" method="post">
<div>
<!-- name label and input -->
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="user_name" />
</div>
<div>
<!-- mail label and input -->
<label for="mail">E-mail:</label>
<input type="email" id="mail" name="user_email" />
</div>
<div>
<!-- message label and input -->
<label for="msg">Message:</label>
<textarea id="msg" name="user_message"></textarea>
</div>
<div class="button">
<!-- submit button -->
<button type="submit">Send your message</button>
</div>
</form>
</body>
</html>Minify CSS, JS and HTML files
<html> <head> </head> <body> <form action="/my-handling-form-page" method="post"> <div>
<label for="name">Name:</label> <input type="text" id="name" name="user_name" /> </div>
<div> <label for="mail">E-mail:</label> <input type="email" id="mail" name="user_email" />
</div> <div> <label for="msg">Message:</label> <textarea id="msg" name="user_message">
</textarea> </div> <div class="button"> <button type="submit">Send your message</button>
</div> </form> </body> </html>RESULTS OF MINIFICATION:
Original size: 988 chars
Minified size: 472 chars
Useless chars: 516 chars
Optimization: 52.23%
Minify CSS, JS and HTML files
How
Grunt: task runner (uglifyjs)
https://github.com/gruntjs/grunt-contrib-uglify
html-minifier: HTML minifier with lint-like capabilities.
https://www.npmjs.com/package/html-minifier
HighTools: Online minimizer
Optimization Check List
- Prioritize visible content
- Optimize css delivery
- Inline javascript
- Defer javascript loading
- Combine css files
- Combine JS files
- Minify CSS, JS and HTML files
This is just the beginning...
This is just the beginning
- Enable keep alive
This is just the beginning
- Enable keep alive
- Browser caching
This is just the beginning
- Enable keep alive
- Browser caching
- Content delivery network
This is just the beginning
- Enable keep alive
- Browser caching
- Content delivery network
- Enable content compression
This is just the beginning
- Enable keep alive
- Browser caching
- Content delivery network
- Enable content compression
- Reduce server response time
This is just the beginning
- Enable keep alive
- Browser caching
- Content delivery network
- Enable content compression
- Reduce server response time
- Image optimization
- And much more...
References
Jhon Jairo Roa
Social
Thanks!
Improving web performance
By Jhon Jairo Roa
Improving web performance
Quick and straightforward tips to improve the performance of your web site or web application.
- 2,109



