web Servics
Secure Web Application Development
Joshua Mcshannon
University of Nebraska at Omaha
CYBR 8470
Today: Web Services
Part 0: Stress Tests and Scaling Woes
- Discuss latest MATRIX stress test
- The importance of failure
- Postmortem Review
Part 1: Service-oriented Architectures (SOA)
- History and SOA introduction
- Service actors
- Modularization and Service orientedness (to microservices)
- Types of services
Part 2: Service Oriented Methods and Data formats
- WSDL, SOAP, and WS-* standards
- REST and JSONAPI standard
- GraphQL
- Web sockets
- Data Formats: XML, JSON
Part 3: Building Services in Django (lab)
Part 0: StresS Tests And Scaling Woes
What is a Stress Test
- Intentionally placing higher than average load on an entity. This helps to understand the performance of whatever is being stress tested under heavy load conditions.
What is Scaling
Scaling is a process for increasing the capacity of a system to address growing needs and resource constraints and generally has two flavors
- Horizontal Scaling - Add more servers
- Vertical Scaling - Add more resources
The importance Of Failure
- Experience
- Resiliency
- Improvement

PostMORTEM Review
- Blameless culture
- Purpose
- Structure
- Date
- RCA
- Trigger
- Resolution
- Detection
- AI (Action Items)
- LL
- What went well
- What went poorly
- Where we got lucky
- Timeline

Part1: Service-Oriented Architectures
History and SOA introduction
What Is a Service?
Real world 'service':
-
A piece of work performed by a service provider
-
Takes some input and produces some desired results
-
e.g. a restaurant: pay some money and get some food
-
e.g. a roofing company: pay some money, get a roof repair
-
-
Has quality characteristics (price, time, goodness of product, etc.)
Software world 'service':
- Takes some input, performs some work, produces some output
- Request-response model: client requests, server responds
- Has quality characteristics (price, execution time, availability, security, goodness of product, etc.)
Definition
A "web service" is a piece of software that performs processing and uses a web protocol to accept requests and issue responses.
earlier...
web service: a piece of software that serves up data through a web interface. Typically web services are object-oriented, provide access to a database, and encode data in XML or JSON.
Definition
SOA (Service-Oriented-Architecture) is an architectural paradigm that modularizes business functions into services by decoupling and encapsulating different portions of the business logic into different service components.
- Services in SOA:
- are autonomous and stateless
- accept requests and return responses
- use well-defined, standard interfaces (standard protocols) that define inputs and output structures
- platform independent
- discoverable
Autonomous -> Need not be aware of other services
stateless -> need not remember state from request to request
- Improves scalability through horizontal cloning
- Can store state in a database if it needs to be saved
standard interfaces -> Re-use web stack and define custom application endpoints
credit:
Torsten Braun, Universität Bern
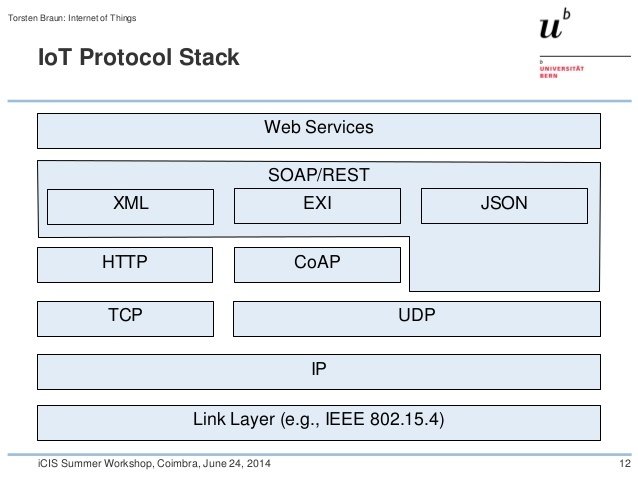
platform independent -> Write a service once, support many platforms

discoverability
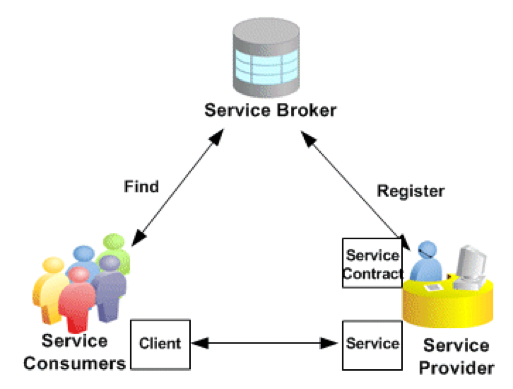
Service Actors
Services need consumers. Consumers use a client to make requests to the service's server. They expect to get a desired result or an error message.
Service providers host and manage their service offerings - maintaining service quality and security.
Service brokers match service consumers and providers - sometimes composing multiple services to fulfill consumer needs.
Modularization and Service orientedness
Modularization Through Service-orientedNess
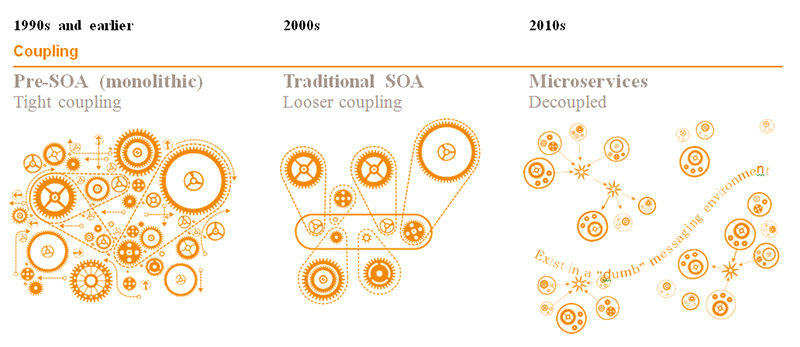
Will come back to this
img credit: http://usblogs.pwc.com/emerging-technology/agile-coding-in-enterprise-it-code-small-and-local/
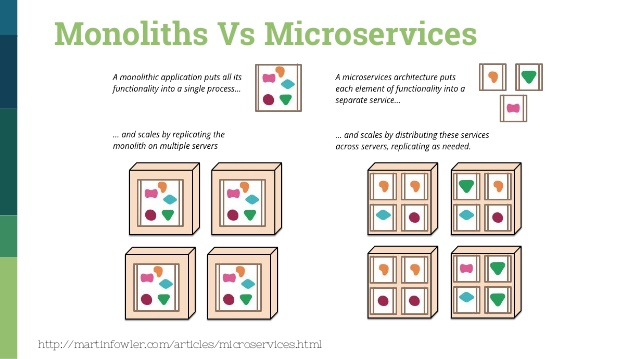
Service Types
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS)
- Platform as a service (PaaS)
- Software as a service (SaaS)
- Desktop as a service (DaaS)
- Service as a service (SaaS2)
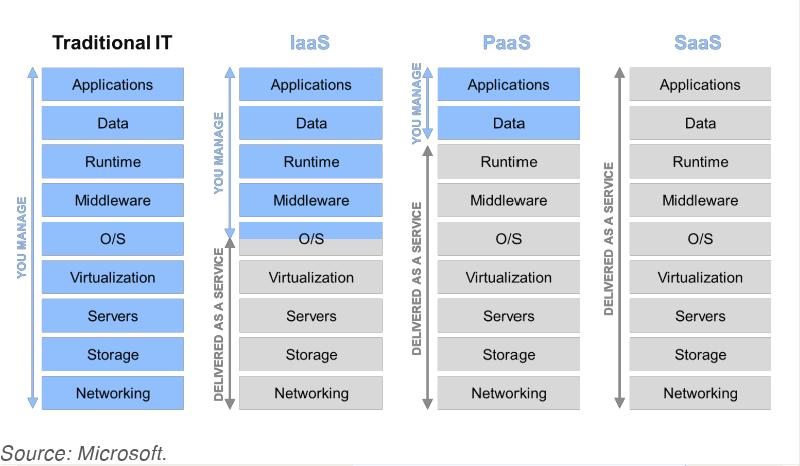
Example
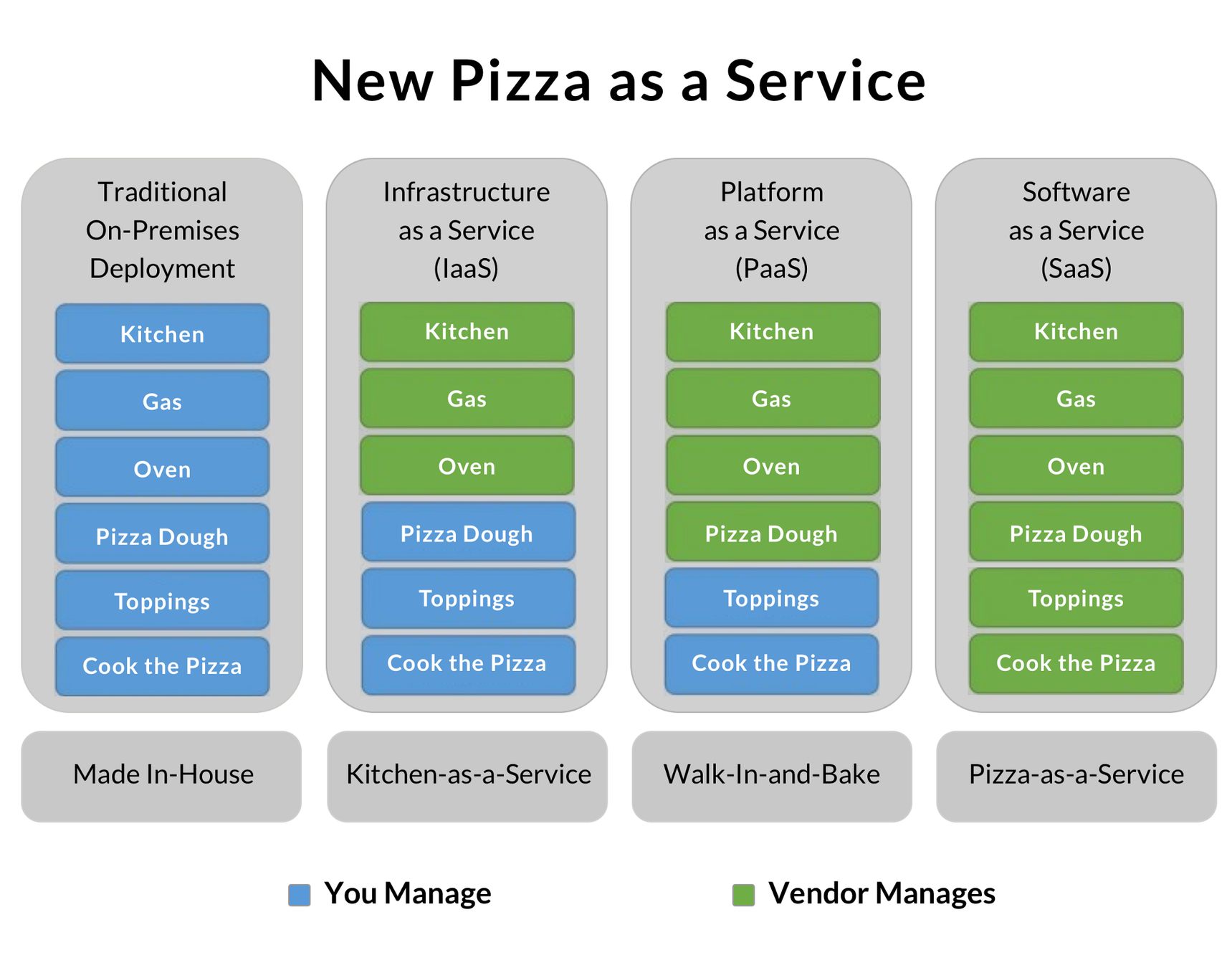
credit: https://m.oursky.com/saas-paas-and-iaas-explained-in-one-graphic-d56c3e6f4606
Part2: Service Oriented Methods/protocols
and Data formats
A Tale of Two Eras
Legacy Services:
-
Uses SOAP, WSDL, XML, WS-*, etc
-
Older, more formally specified service types
Modern Services:
-
RESTful API services:
- Uses HTTP, REST, JSON
- Most pervasive services circa 2020
-
"Streaming" services:
- Uses websockets
- real time applications with "server push"
usecases
- New age services:
- graphQL
- gRPC (google Remote procedure call)
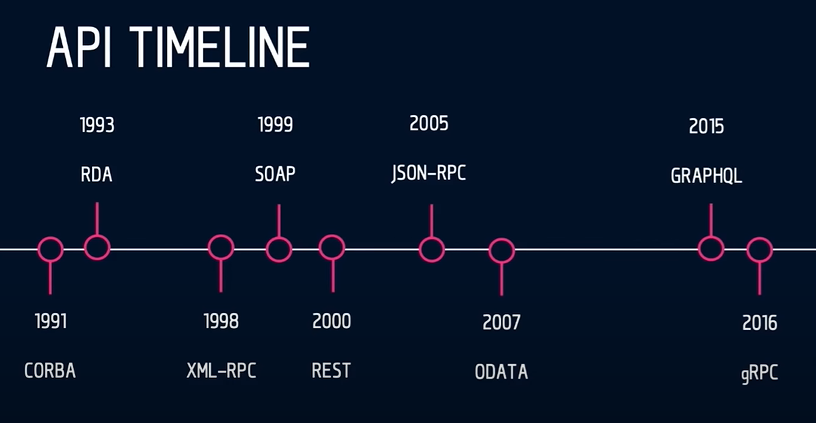
SOAP ERA
RESTful ERA
Elements of a "Legacy" Service
Description in terms of WSDL (Web Service Definition Language):
- Describes what a web service can do
- WSDL is an XML based, open standard from W3C
- Declares available methods (endpoints)
- Identifies Input and output parameters
Protocol uses SOAP to exchange XML, XSD on top of HTTP
-
SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol)
-
XML (Extensible Markup Language)
-
XSD (Extensible Schema Definition)





HTTP
Example WSDL
SOAP
Simple Object Access Protocol
- Encapsulated in an Envelope
- SOAP Header
- SOAP Body
- operates over HTTP or TCP
- Allows for requests and responses
- fill in parameters according to WSDL

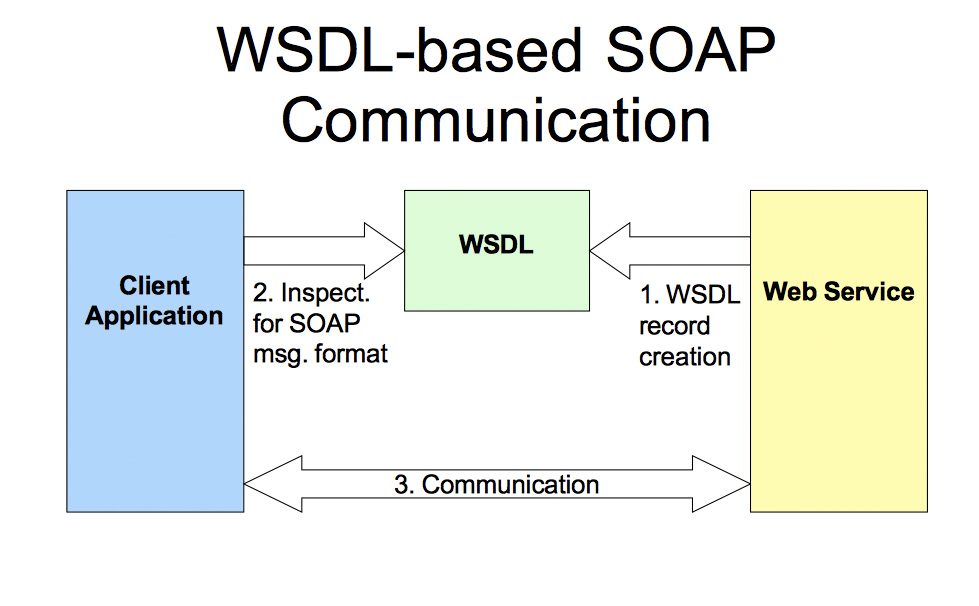
SOAP Request Example

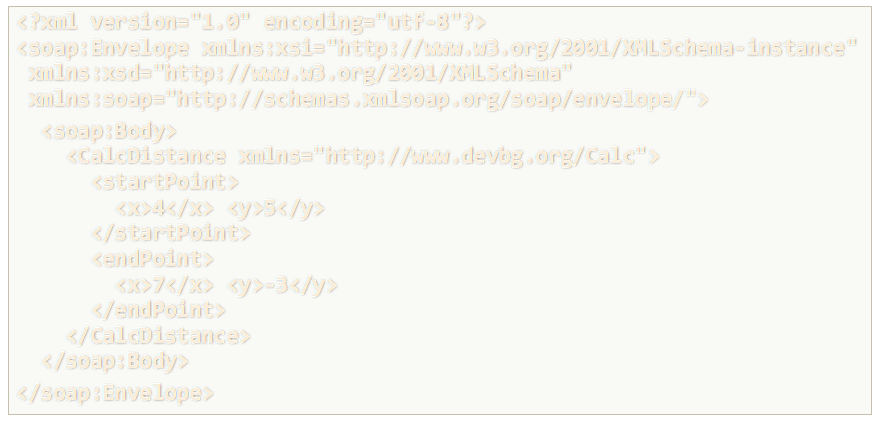
Note: Refers to some function called 'CalcDistance' that has two parameters 'startPoint' and 'endpoint'. Each point has an x and y field in the object.
SOAP ReSponse Example


Modern Services
REST
- Representational State Transfer
- Associate every resource with a URI (Universal Resource identifier) - accessible from a URL
- Allow CRUD operations to retrieve and persist data -> works really well with SOA
- We've seen REST at work with services like Twitter
- REST has lots of advantages of most other approaches, but can result in overfetching or underfetching
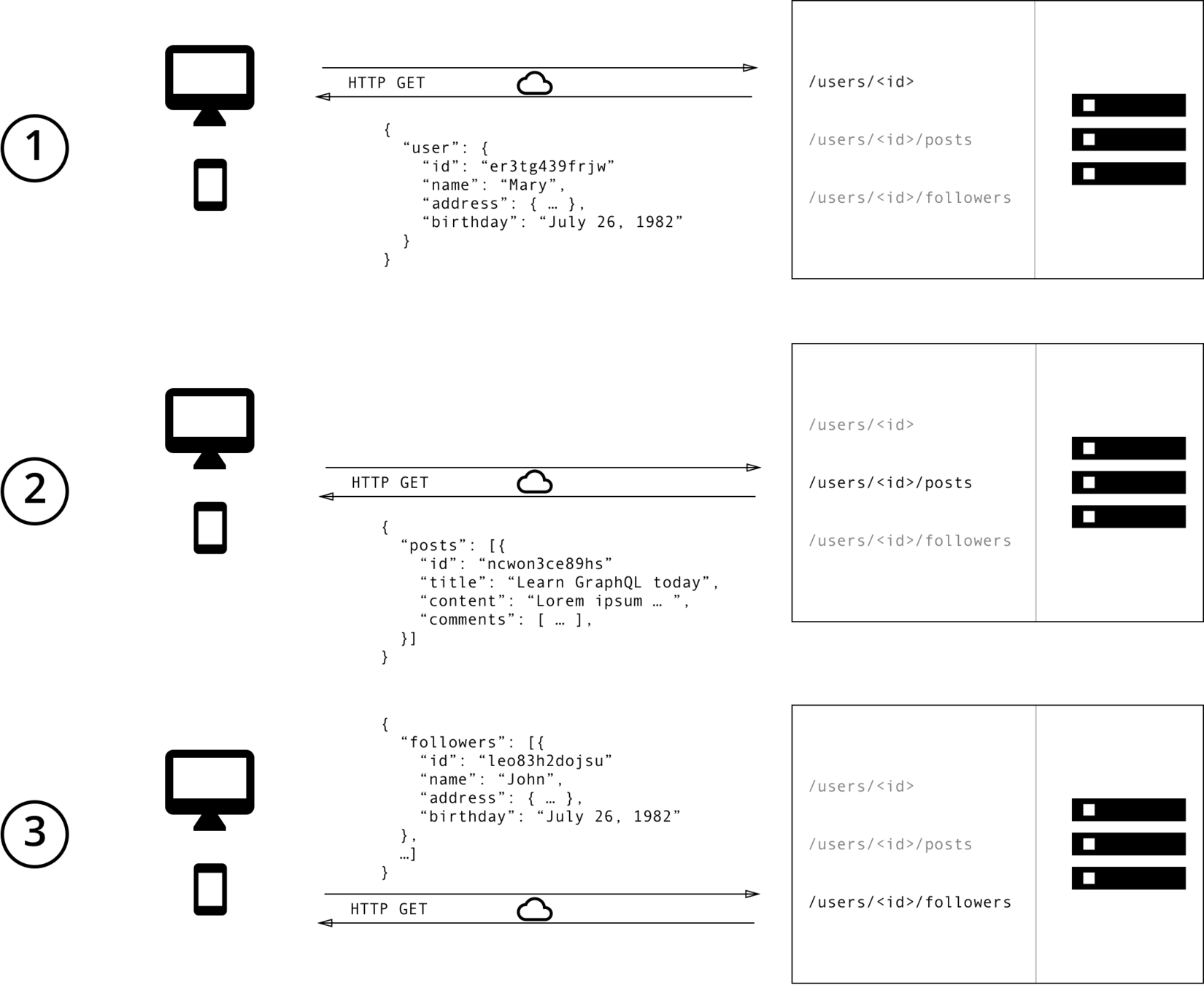
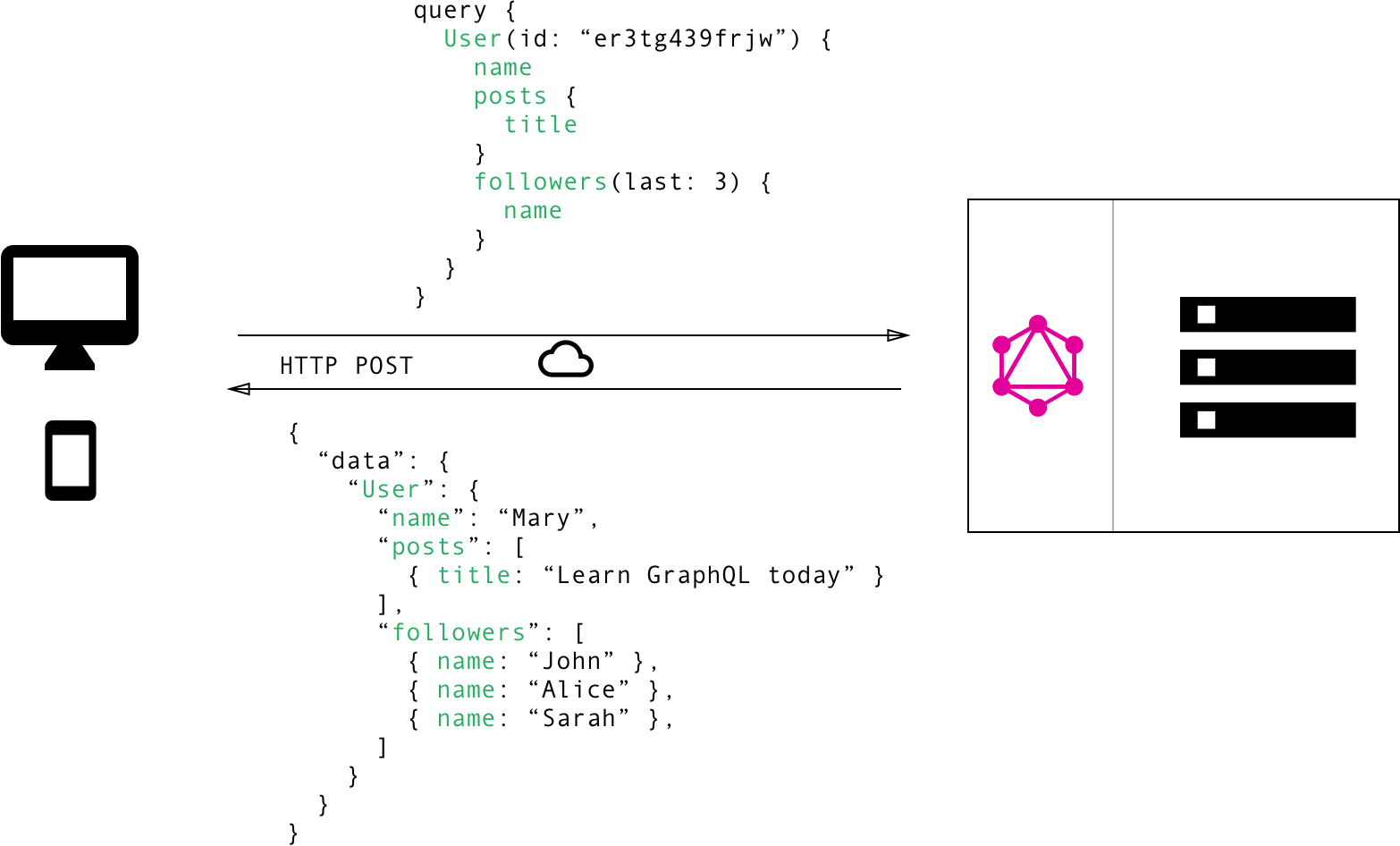
graphQL
- Basic idea: Traverse a graph to get only the data you need
- Solves the problem of underfetching or overfetching
- Invented by facebook
- downside:
- complicates architectural design (harder to use micro services)
- very difficult to cache, since all requests are unique
WebSockets
- Works directly on a single TCP connection
- Provides full duplexing (bi-directional) communication between server and client - remains open during the duration of the connection
- Great for streaming applications that rely upon a rapidly updating publish/subscribe model - particularly for server pushes
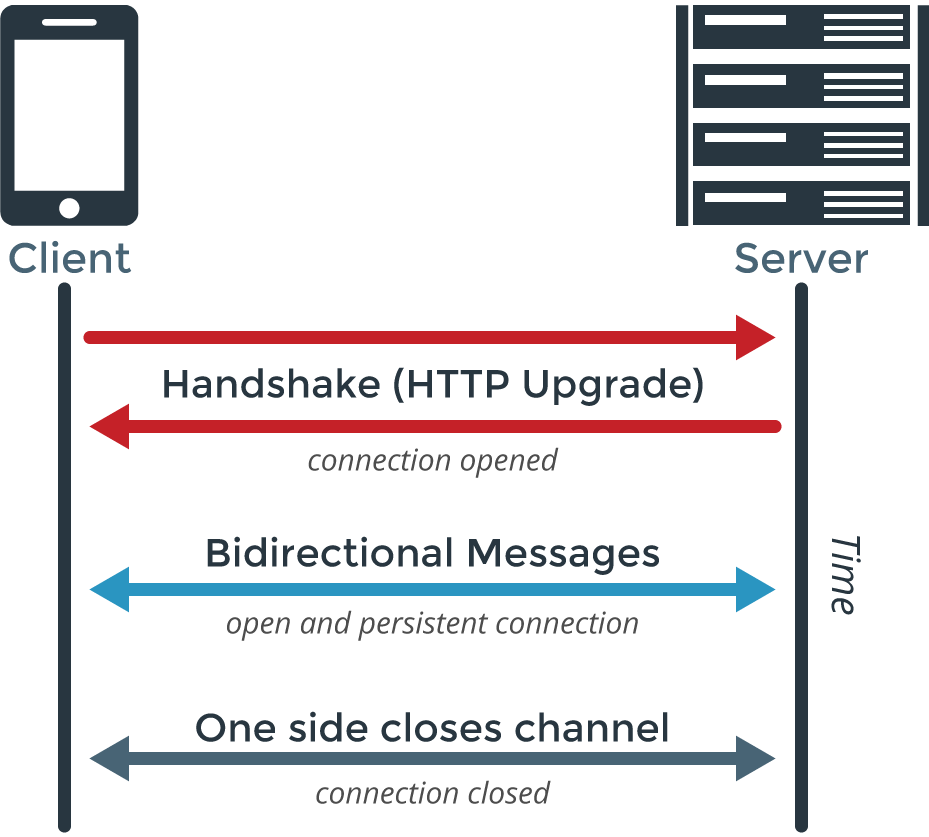
DATA Formats
XML

- XML is a markup-language for data representation
- Used for encoding documents in machine-readable form
- Text-based format, consists of tags, attributes and content
- Can be used for data, meta-data, and structural presentation
JSON
- JavaScript Object Notation
- Basically a set of key:value pairs that define data according to a dictionary structure.
- Typically much less verbose than XML
- e.g. <somedatatype>somedatavalue</somedatatype> becomes { "somedatatype": somedatavalue}.
- particularly true for nested structures
- Used for data structures not page or document structuring
- Can still include meta-data easily.
RPC/graphs/etc
- Remote procedure calls have been around for a long time. Depending on the RPC framework used, there are variant semantics.
- Graphs are data representations of actual networks of connected objects. Data is often serialized into a JSON format, but may be held in a variety of different formats.
Part3: Web Services (In Django) Lab
Questions?


Joshua Mcshannon
University of Nebraska at Omaha
Adjunct , Cybersecurity
MATRIX Engineer
jmcshannon@unomaha.edu
Attribution: Some slides are based on material from:
"Web services, SOA, and REST" course by the SoftUNI Foundation and are used under the CC-BY-NC-SA license
CYBR 8470 Web Services
By jmcshannon
CYBR 8470 Web Services
- 26



